All about gable roofs
A gable roof occupies a middle position between a single-pitched and multi-pitched roof in terms of complexity and ease of use. Reliable protection of the house from rain, wind and snow, a wide variety of shapes and easy installation - these factors have made the gable roof the most popular in our country. Its assembly can be carried out by both professional craftsmen and novice builders. The design is used in the construction of capital structures and for small architectural forms - gazebos, baths and tourist houses in campsites.
The device and the main elements of a gable roof
A gable roof is considered to be a roof consisting of two rectangular planes located above the walls of the building and connected at an angle from above.
The popularity of the gable roof is due to the simplicity of its manufacture.
The supporting structure of the roof is a truss system, the purpose of which is to:
- retention of the outer and inner roof covering;
- uniform load distribution on load-bearing walls;
- the formation of the roof frame, necessary for leveling the plane of the slopes.
To understand and successfully put into practice the principles of a gable roof, let's take a closer look at the main elements of its design. In any case, knowledge of the accepted professional terminology will help in the selection and calculation of materials.
- Mauerlat. Support beam mounted on the wall. It is made of a bar and logs of coniferous breeds of a tree. The purpose of the Mauerlat is to evenly distribute the weight of the roof onto the load-bearing wall. The dimensions of the beam section are determined in accordance with the overall dimensions of the roof, as a rule, it is from 10 to 25 cm in cross section. Fastening is carried out with anchor bolts, metal threaded rods, brackets or wire. A waterproofing material is laid between the Mauerlat and the wall surface to prevent contact between the hygroscopic stone and wood. Mauerlat can be made from solid wood, sewn boards or glued beams.
To fix the Mauerlat to the wall, you can use anchors, threaded studs, brackets or wire
- Rafter farms. The assembly of rafters can be carried out both on the ground and directly on the roof. The farm is a triangle with given dimensions. It is assembled from boards or timber with a thickness of 50 mm and a width of 150 mm. It is important to observe technological tolerances during the installation of trusses, since the final configuration of the slope plane depends on them. An error of 1 cm at a distance of 0.6 m is considered unacceptable: the roof will be wavy, and the fit of the roofing material is uneven. The installation step of the rafters varies from 0.6 to 1.2 m.
Assembly of roof trusses can be carried out both on the ground and directly on the roof
- Sill. This detail is used in layered structures. Like the mauerlat, it is installed on the supporting (inner) wall and serves to distribute the load from the racks under the ridge run. The dimensions of the bed usually do not differ from the dimensions of the Mauerlat, but there are exceptions (depending on the thickness of the wall).
In the construction of a gable roof, the bed is located on the middle support of the house
- Racks. An element used to compensate for vertical loads. Racks connect ridge and horizontal runs with a bed and load-bearing beams. The thickness of the timber is selected depending on the overall design of the roof. Fasten it with nails, screws and metal brackets.
Racks prevent deflection of rafters under load
- Crossbars (puffs). Reinforce the rigidity of the triangular structure of the rafters and connect the rafter logs together into a single frame.
The crossbar connects the rafters and enhances the strength of the truss structure
- Skate (or ridge run) - the upper horizontal part of the roof, located at the intersection of two slope planes. The run is a solid massive beam that connects the slopes along the entire length.
All upper points of the truss trusses are connected by a ridge beam
- Overhang. Part of the roof protruding 40-50 cm beyond the Mauerlat. Designed to protect the walls from getting wet. Gutters are installed under the overhangs.
The overhang performs protective functions, closing the walls from moisture
- Lathing. The outer part of the structure, which is laid over the rafter legs. It is made of wooden slats or (in the case of a soft roof) plywood, chipboard or OSB boards. The function of the crate is not only to fix the roofing material, but also to increase the rigidity of the frame as a whole. Edged or unedged barked boards impregnated with antibacterial compounds are used. The thickness of the crate varies from 22 to 30 mm.
Before installing the roofing on the rafters, a crate is installed
- Filly. An additional element that is used in cases where the rafter logs are not long enough to organize a full-fledged overhang. To build up the rafters, boards or timber of the same or slightly smaller size are used. Fix them with nails and screws.
Filly can be attached to the rafters with bolts or nailed
- Rafter legs (struts). Spacers that act as a link between the supporting beams and the rafter legs. They are made locally from boards and timber. In suburban construction, poles of small diameter (up to 14 mm) with turned flat ends are used.
The main function of the rafter legs (struts) is to increase the rigidity of the truss system
Video: stages of construction of a truss structure
Rafter system options
Depending on the location of the load-bearing walls of the building, one of the possible types of truss system is chosen:
- layered;
- hanging.
Rafters
The layered mounting system assumes the presence of an additional supporting wall of the house, on which the weight of the roof is transferred. For this, a ridge run and a bed are used, interconnected by vertical posts. This type of structural reinforcement is simple and effective, but it interferes with the arrangement of the attic space for a living area. The useful area is reduced and there are additional costs for finishing. A good solution to the problem in this case is the male (which is a continuation of the wall and erected before the formation of the roofing system) pediment, which takes on the weight of the roof structure. In addition, the disadvantages of layered technology include the need for long elements. It is extremely problematic to transport and install runs, the length of which is more than 6 m, without lifting equipment. There are four types of layered structures.
- Strutless rafters. There are three types of assembly of this design:
- with a rigid attachment to the Mauerlat (the ridge run is connected to the top of the rafters by a sliding attachment with additional fixation with metal strips);
The rigidity of fixing the rafters to the Mauerlat is provided by metal brackets
- with slide fastening to the Mauerlat (the floating connection is duplicated by a flexible plate, the upper parts of the rafters are attached to the purlin or between themselves in pairs);
Slider fastening is provided by a flexible plate installed at the top of the roof trusses
- with rigid fastening of the rafter legs and the roof ridge into a single whole (using additional boards).
In this option, all elements of the truss truss are connected into a rigid triangle
- with a rigid attachment to the Mauerlat (the ridge run is connected to the top of the rafters by a sliding attachment with additional fixation with metal strips);
- Expanding rafters. The fastening of the rafter legs to the Mauerlat is rigid, but a horizontal run is added between the rafter legs. This design is intermediate between a layered structure and a hanging one. It is used in cases where the load-bearing wall is strong enough and able to withstand the bursting pressure from the roof. Sometimes for this, a reinforced concrete belt is installed around the entire perimeter of the roof.
Spacer rafters transfer bursting loads from the roof to the mauerlat, so they are used only in cases where sufficient wall strength can be ensured
- Rafters with struts. The strut performs the function of an additional support, it is often called the third rafter leg or rafter leg. It is installed at an angle of 45–50 ° and does not allow the main rafters to sag. With the help of struts, it is possible to cover spans with large distances (up to 15 m). The main thing during assembly is the accuracy in cutting the corners of the struts in accordance with the slope of the rafter leg. No other calculations are required. The brace is nailed to the bearing elements on both sides.
Rafters with struts allow you to cover spans of great length
- Rafters on rafter beams. An additional beam is laid along the length of the roof, on which the racks rest, supporting the rafters. The bed and other walls of the house perform the same function. If there are no runs, a separate rack is installed under each rafter leg. The puff is set below the run, thus eliminating the thrust. With the help of contractions installed in the lower part, they compensate for the load from the weight of the upper part of the rafters. Additional stitching, connected crosswise, fix the position of the fight.
To strengthen the structure of the rafters in the scheme with a rafter beam, additional elements are used: puffs, crossbars, contractions and jointing
hanging rafters
The hanging scheme is used in the absence of an average support. The rigidity of the roof is enhanced by the installation of ligaments and crossbars between adjacent roof trusses. Often this is the only way to equip the roof, especially in cases with small ceiling sizes.
One of the significant advantages of this type of construction is the high strength and rigidity of the frame. When installing a hanging truss system, there is no need to fix the Mauerlat.
Hanging systems, as well as layered ones, are divided into 5 types, each of which is three-hinged.
- Triangular three-hinged arch. The least expensive option for a roof device. It is a triangle with a limited degree of load. There are two options for attaching the rafters to the puff - an orthogonal frontal cut and a bunch using plate fasteners.
Rafters and puffs are fastened by cutting or using rigid plates made of wood or metal
- Three-hinged arch with a raised puff. It is used in the construction of attic spaces, which are planned under the attic. The transverse tightening is installed in the upper part of the truss truss. Fastening to the Mauerlat - sliding. For the system to work properly, a long extension of the rafters beyond the boundaries of the walls is recommended. To compensate for the possible sagging of the puff, suspensions are used (one or more - according to the circumstances). If the tightening length is large, it is possible to splice two beams using clamps.
Floating attachment to the Mauerlat relieves stress from the rafters, and the location of the puff determines the height of the attic
- Triangular arch with headstock and struts. In the case when the rafters are very long, additional struts are used to strengthen them. They reduce the likelihood of deflection under the influence of external loads and transfer the weight of the roof to the lower puff. In addition, a headstock is hung on clamps to the ridge run, which supports the ridge, and therefore helps to increase the rigidity of the entire structure.
A triangular arch with a headstock and struts is used for very long rafters, when it is necessary to unload the ridge knot and increase the rigidity of the entire system
- Three-hinged arch, reinforced with a suspension or headstock. This type of roof structure is used for roofs with large (more than 6 m) spans. Its essence lies in the fact that the weight of the puff is transferred to the ridge run. They are interconnected by pendants, the ends of which are clamped into clamps. A pendant made of a wooden bar is called a headstock, and an iron one is called a strand. Using the clamp bolts, you can adjust the degree of tension, which is especially important in case of slack in the tightening.
Hangers and headstocks prevent deflection of the tightening, and the degree of tension of the fastener assembly can be adjusted
- Triangular arch with crossbar. At high expansion loads, a crossbar is added in the upper part of the triangle. It, unlike tightening, compensates for compressive stress. The fastening of the crossbar does not allow articulated connection with the rafters. The puff is installed at the base of the structure.
To compensate for spacer loads, a horizontal crossbar is installed in the upper part of the roof truss
Video: installation of rafters for a garage and a bath
What determines the height of the ridge of a gable roof
As noted above, the ridge is the upper horizontal part of the roof, formed by the intersection of the slopes. Determining the height of the ridge is one of the key tasks in roof design. The wrong decision entails a number of problems associated with further operation.
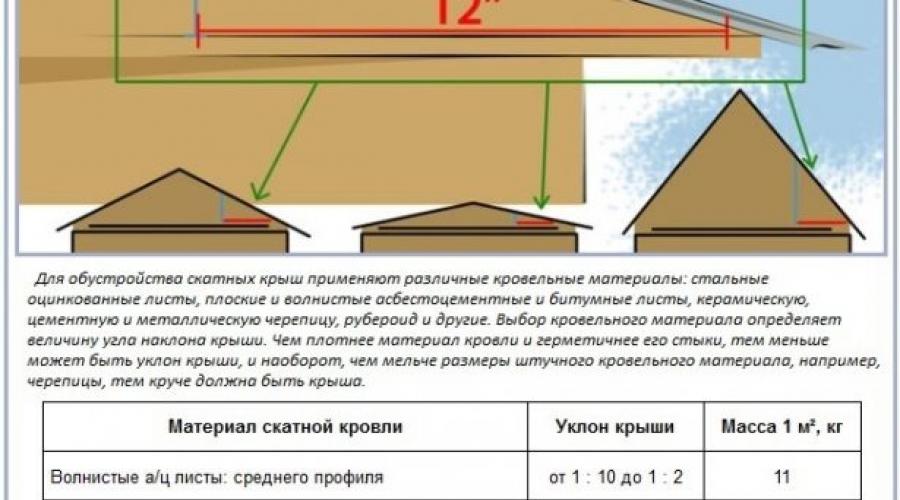
- Climatic conditions of the region. These include average annual precipitation, wind load and snow depth. Each factor makes its own adjustments when choosing the height of the roof. So, prolonged snow drifts and heavy rains suggest slopes steeper than 45 o, while precipitation leaves the roof rather quickly, without having time to cause damage. In the steppe zones, where stable winds prevail, it is customary to build sloping roofs, with slopes of no more than 10–12 degrees. Here, a roof with a low-pitched design will last longer and will be more efficient in retaining heat in the house.
- The presence or absence of an attic in the design of the house. Since gable roofs are of two types - with or without an attic, when choosing the angle of inclination, further stages of operation must be taken into account. One of the most common options for arranging an attic space is an attic. To do this, use a special design of a gable roof, which is called a broken line and expands the usable area of the attic. The option without an attic is more often used in the construction of garages, warehouse hangars and similar structures.
A roof without an attic floor increases the volume of the room, but has large heat losses.
- Type of roofing material. Knowledge of the properties of the outer coating affects the optimal choice of the slope of the slopes and the height of the ridge. Here are some basic rules:

It should be taken into account the fact that raising the skate is accompanied by additional financial costs. For example, a structure with a slope of 40-45 degrees will cost 1.5-2 times more than a roof with slopes of 10-12 degrees. With a further increase in the angle of inclination, the cost increases exponentially.
The importance of correctly determining the height of the roof ridge in each specific situation cannot be overestimated. She did not remain without attention to regulatory building documents.
The collection of rules and tables of SNiP 23.01.99 and SP 20.13330.2011 reflect in detail the requirements for the construction of roofs in various climatic zones.
The minimum dimensions of operated attics (residential attics) are also regulated there. Not only the convenience of the premises for human life, but also fire safety standards are taken into account. The dimensions of the attic should not be less than the minimum required for the prevention and maintenance of the roof - 1.5 m in height and 1.2 m in length. It is allowed to narrow the passages in complex composite structures by 35–40 cm.
There are two ways to determine the height of the ridge:
- Graphical, which uses an exact drawing at a given scale.
- Mathematical - using geometric formulas expressing the dependence of the height of the ridge on the length of the roof base and the angle of inclination.
The third can be called an automatic method of calculation using online calculators, which the Internet abounds today. But with all due respect to modern computer technology, one must be aware that in the event of an error or inaccuracy of calculations, no one will be held responsible for wasted money.
Therefore, it is better to do the calculations yourself. Geometric calculations are made according to the formula H \u003d L ∙ tg A, where H is the height of the ridge, L is half the span, and tg A is the tangent of the slope angle, the value of which can be taken from the reference tables.
To determine the height of the ridge, you need to know the size of the base and the tangent of the slope angle
Table: tangent values of different angles for calculating a gable roof
Types of gable roofs
Above, we examined the options for gable roofs from the point of view of the internal structure of the structure. Now let's analyze their external structure.
Roof with different slope angles
Roofs with different slopes of slopes are also called asymmetric. More often they are used in small architectural forms, but there are cases of capital buildings with such roofs. The bottom line is that the building is covered with a roof with different lengths of slopes. The number of slopes does not change - there are also two of them, but the perception of the building as a whole changes significantly. The construction becomes unusual, stylish in its own way, acquires uniqueness and attracts the eyes of people.
An elongated roof slope can be used to organize an additional functional extension, for example, a garage
Despite the additional difficulties in the construction of such a roof, the popularity of the design does not decrease. On the contrary, developers strive to give houses unusual, original forms. To do this, they use various architectural techniques, including roofs with different lengths of slopes.
roof with skylight
Dormer windows bring a unique color to the exterior of the building and are very useful in a practical sense. With their help, the problem of lighting the attic, as well as natural ventilation, is solved without the involvement of additional technical means. Installing dormer windows is not an easy task, requiring knowledge and skills. Initially, a glazed opening in the gable of the roof was considered a dormer window, but today the range has expanded, and windows mounted in slopes also belong to this category. In appearance, dormers are divided into:
- attic;
- lean-to;
- gable;
- arched;
- hip;
- french flat;
- with side walls in the plane of the house;
- without side walls in the plane of the house;
- with side walls not in the plane of the house.
Each type of dormer window is installed according to its technology
Of all the listed categories, only skylights can be installed both at the time of the construction of the roof, and after construction is completed. The rest are built simultaneously with the assembly of the truss structure. This is due to the need to organically integrate a window into the support system, which must withstand climatic loads and not cause leaks or distortions of the roof.
The dormer window must fit into the general support system of the rafters and withstand all the loads acting on the roof
Dormer windows are installed in accordance with the normative documents SNiP 11-26 and SNiP 21-01.
They stipulate the conditions under which it is possible to install a dormer window:
- permissible slope slope - not less than 35 o;
- the maximum allowable size of a window with opening sashes is 1.2x0.8 m;
- a dormer window on the roof with a hip structure and a rectangular facade cannot be in the same plane with the walls of the building;
- tiles, copper, sheet steel can be used for the outer cladding of the window.
You can install the dormer window yourself or by contacting professionals for help. But in any case, it is necessary to comply with general construction rules developed by specialized organizations.
Cuckoo roofs
"Cuckoo" is a construction built into the main truss system in the form of a protruding window or balcony. The appearance of such a structure compares favorably with the houses surrounding it, and the interior space of the attic is transformed and becomes more interesting. In addition to the aesthetic advantages, the "cuckoo" increases the usable volume and area of the residential floor, increases the level of natural light. The window, located on the south side of the roof, contributes to the penetration of direct sunlight into the attic. Improves room ventilation.
The cuckoo design creates an original appearance and increases the attic lighting area, but requires careful calculation to maintain the bearing capacity of the roof
But the “cuckoo” also has disadvantages, mainly of a financial nature:
- the labor intensity of installation work increases;
- the total estimate for the construction of the roof is increased;
- there is a need to use the services of qualified designers and builders.
Illiterate installation of a remote window (or balcony) on a gable roof can cause damage to the roof and the formation of leaks.
Roof with large overhangs
A roof that extends far beyond the house is called a chalet roof. The technology is borrowed from Europe - from the mountainous Alpine regions of France and Switzerland.
One of the features of the "chalet" type roof is the increased size of the roof overhangs.
Distinctive features are the first floor, built of stone, and the second floor, completely made of wood with a voluminous flat gable roof and large extensions. The originality of the exterior is combined with practicality, due to the formation of a large area around the house, protected from snow and rain. This solution reliably protects the walls of the house from getting wet, increases the sound insulation inside the room. The front side is often equipped with full-length windows and balconies. Despite the impressive dimensions, the roof practically does not weigh down the building. If the roof extension exceeds 3 m, its edge is additionally supported by columns or walls. There are numerous projects in which the rafters smoothly descend to the ground. An additional isolated area is formed next to the building, which is used for auxiliary purposes, as a car parking, etc.
Traditionally, chalet roofs are covered with shingles, but for our latitudes this is a very expensive material (oak split into tile plates). Therefore, today modern natural and synthetic materials are used for such roofs, including:
- straw or reeds;
- flexible or ceramic tiles;
- composite stylized roof;
- larch shingles or shingles.
Off-center roofs
Roofs designed according to the principle of asymmetry belong to the avant-garde direction in architecture. The ridge is shifted from the central axis of the building, due to which the roof sometimes acquires the most fantastic outlines.
Despite the bizarre shape, roofs with a displaced center regularly perform their functions.
Formally, such a refinement can be considered one of the varieties of roofs with different slope angles. In practice, this technique is used in cases where the internal supporting walls are not in the middle of the building. The displacement is due to the designer's desire to support the truss structure in the most reliable way and reduce the cost of reinforcing the hanging span.
The choice of roofing materials
Of all the possible options for roofing, the most common today are materials of artificial origin. The table below shows the comparative characteristics of the main coatings on the construction market.
Table: properties of roofing materials
| Material name | Slope angle | Fire resistance level | Noise isolation properties | Specific gravity, kg / m 2 | Service life, years | Price | Assembly difficulty level | Difficulty of repair and replacement | Material disadvantages |
| Decking | 12–90 about | Tall | 5,7–9,4 | 30–35 | Low | Noisy, susceptibility to corrosion, large waste on roofs of complex shape | |||
| Asbestos-cement slate | 12–60 about | Tall | Medium (but higher than metal types of roofing) | 10–15 | 25–30 | Low | Average | Lightweight, replacement of the damaged area | The presence of asbestos in the composition, harmful to humans. Fragility, covered with moss. |
| Ondulin | 15–90 about | Short | High | 6–6,5 | 35–50 | Low | Easy installation that does not require high qualifications | Lightweight, replacement of the damaged area | Color is guaranteed for 5 years, low decorative properties. |
| Ceramic tiles | 15–60 about | Tall | Good ones | 40–100 | up to 100 | Very high | Lightweight, replacement of the damaged area | The only drawback is the fragility of the material to fracture | |
| Cement-sand tiles | 15–60 about | Tall | Good ones | 18–30 | up to 100 | High | Difficult, requires skill | Lightweight, replacement of the damaged area | Not |
| metal tile | from 14 o | Tall | Low (especially with illiterate assembly) | 3,5–5 | 40–50 | Low | Easy installation that does not require high qualifications | Lightweight, replacement of the damaged area | Large waste of material when installing a complex roof. Subject to corrosion. |
| Soft (bituminous) tiles | from 15 about | Tall | Good ones | 3–4 | 30–40 | Medium | Easy installation that does not require high qualifications | Lightweight, replacement of the damaged area | The composition contains bitumen, a carcinogen. |
In addition, non-standard types of coatings such as straw, reeds or turf are sometimes used in the construction of roofs. But this phenomenon can rather be called an exception to the rule and a tribute to ancient traditions; these materials do not have mass application.
Laying reed roofing requires a lot of hard work and is more of an exotic option.
Projects of houses with a gable roof
Most developers, when choosing a ready-made house or cottage project, pay attention to the functional features of the structure and the shape of the roof. And it is no coincidence. The cost of the roof can be up to 30% of the total estimate. But the budget can be significantly reduced if you change the shape and choose inexpensive roofing materials. In this respect, the gable roof has a clear advantage over the others. And so today it is the most sought after. Here is a far from complete list of the advantages of a gable roofing at home:
- any building, including complex multi-level buildings, can be covered with a roof with two slopes (without compromising the appearance and internal comfort);
- roof installation work will be much cheaper due to the ease of installation and the availability of materials (without compromising strength and reliability);
- when covered with metal tiles, the amount of waste will be minimal (for example, in a hip roof, waste can be up to 30%).
Architectural and construction organizations have a huge number of ready-made projects, and for little money they modify them to the conditions of customers.
Photo gallery: ready-made projects for houses with a gable roof
 A one-story economy class house covered with a gable roof is one of the most inexpensive and popular options for suburban housing.
A one-story economy class house covered with a gable roof is one of the most inexpensive and popular options for suburban housing.  Skylights partially replace artificial lighting in the attic
Skylights partially replace artificial lighting in the attic  In a two-story house, you can make a low ridge and a small attic room
In a two-story house, you can make a low ridge and a small attic room  A high gable roof allows you to organize full-fledged living quarters on the attic floor
A high gable roof allows you to organize full-fledged living quarters on the attic floor
Individual design (including independent) is mainly carried out for the construction of houses with gable roofs and an improved layout, such as:
- one-story residential buildings with increased dimensions of the under-roof space;
- mansard houses with and without lucarnes;
- two-story houses with attic and attic rooms.
Having decided on the necessary parameters of housing and financial opportunities, you can independently or with the help of specialists create your own project of your dream home.
Gable roof for gazebo
A wonderful invention of our ancestors is the gazebo. Holidays outside the city, family celebrations, meeting guests at their summer cottage and picnics - this is just a short list of those functions that are associated with the gazebo. Perhaps that is why such a structure is present in almost every suburban area. One of the main components of the gazebo is the roof.
The gable roof reliably protects the gazebo from rain, dust and falling leaves and gives it the look of a fabulous house
Pergolas are built with various types of roofs, but the most popular are gable roofs.
Photo gallery: gazebos with gable roofs
 The gable roof of the summer gazebo will reliably cover camping visitors from rain or direct sunlight.
The gable roof of the summer gazebo will reliably cover camping visitors from rain or direct sunlight.  The offset of the ridge is used so that you can install additional supports under the rafters that will not interfere with the entrance and exit
The offset of the ridge is used so that you can install additional supports under the rafters that will not interfere with the entrance and exit  The stove built into the gazebo turns it into a small summer cafe
The stove built into the gazebo turns it into a small summer cafe  Pergolas can be used in parks and recreation areas to shelter visitors from snow, rain or heat.
Pergolas can be used in parks and recreation areas to shelter visitors from snow, rain or heat.
The principles of erecting a roof over a gazebo are largely identical to those used in the construction of residential buildings. The difference lies only in the structure of the supports: the roof is not on the walls, but on columns or vertically installed bars.
Types of gable roofs for gazebos are identical in design with the roofs of ordinary houses
Building a pergola can be a good experience before building a large gable roof on your own.
Assembling a shed roof is, of course, faster and easier. But giving preference to the classic gable roof, the owner of the building at the same time acquires a more durable coating and an attic space, which over time can be turned into a residential attic. The initial costs will more than pay off, and the house will acquire a distinctive and at the same time attractive appearance.