Types of plaster and their purpose

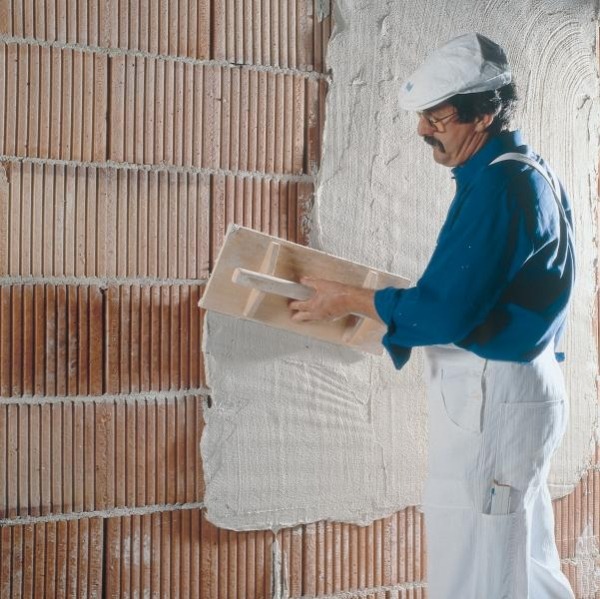
At first glance, plaster is a simple and familiar material for wall decoration. It is usually not visible to anyone, except when it becomes the final element of decoration. Its direct purpose is to level the walls, creating a perfectly flat surface for decorative wall coverings such as wallpaper and paint. However, there is quite a large variety of types of plaster, which are not limited to performing an exclusively leveling function. They can protect walls, decorate them, save money, and create coziness and comfort in your home. Let's talk more about these unusual and special types of building plasters.
Heat-insulating types of plaster
Heating bills are constantly rising and are forcing many residents to think more and more often about the need to somehow reduce the cost of heating their apartments and houses. After all, no one has the desire to spend their own money just heating the street. In this case, people come to the aid of energy-saving technologies: the installation of insulated entrance doors, and even the use of high-tech materials during the design of the building.
Among the illustrative examples of such materials, it is worth noting heat-insulating plasters. Usually, they include dry building mixtures, which have among their components, in addition to the usual binder (as a rule, gypsum or cement are taken as the basis), also various heat-insulating fillers (polymer additives), which are characterized by reduced thermal conductivity, which gives them the necessary properties.
|
|
|
|
|
|
In the role of heat insulators, granulated polystyrene foam is usually used, which is processed with a special additive, expanded perlite, glass or vermiculite. In addition to thermal insulation properties, this class of fillers characterizes the level of combustibility of the mixture. Plasters with polystyrene foam additives are classified as low-flammable and hardly flammable mixtures. Compositions containing mineral fillers (for example, perlite, vermiculite or foamed glass) are not combustible at all (NG group).
Mixtures of heat-insulating plasters can sometimes contain special substances that form a complex structure of tiny pores filled with ordinary air in the thickness of the product. Any student knows that air is a good and simple heat insulator! After all, thanks to the layers of air between the individual villi and fibers, down jackets and fur coats warm us in winter. In addition, air is an excellent sound insulator. Of course, in modern architecture, sound insulation is provided by the supporting structures themselves, but sometimes it is not enough for complete acoustic comfort.
So, in order to “feel complete silence”, the airborne sound insulation index of load-bearing structures, walls and ceilings in a standard apartment building should be at least 62 dB, but in fact its value usually ranges from 45 to 55 dB. We have a similar picture for impact sound insulation. The obvious solution is to take action yourself and provide additional noise protection for your own home!
Fillers for plaster
Perlite It is sand of volcanic origin. By heating the mineral at a high temperature up to 1000 ° C, expanded perlite is obtained, which is distinguished by porosity and friability. This is a fairly durable material with low weight. The water that was poured in the composition was in a bound state, quickly evaporating, leading to the appearance of many tiny bubbles. At the same time, the material itself increases in volume by 4-20 times! Such expanded perlite has good fire-resistant properties, so it can be used at temperatures from -200 to +900 °C. This material is biologically stable and chemically inert, but has a fantastic hygroscopicity, which limits its use for construction. Perlite can absorb a lot of liquid, which is 4 times heavier than it!
Vermiculite is a natural mineral belonging to the class of hydromicas. With the help of accelerated firing, an excellent free-flowing and porous material in the form of flakes is obtained from it. In its main characteristics, this material is quite similar to perlite.
Foam glass- multifunctional porous material with glass cells. This is a mixture of foaming agent and fine glass chips. It does not conduct heat and sound well. It practically does not absorb moisture and does not give significant shrinkage. The structure of foam glass is similar to frozen foam.
Styrofoam- this is a very light material, which is obtained by foaming granular polystyrene or its derivatives. It absorbs sound quite well and retains heat, but it belongs to combustible materials, and when heated enough, it can release harmful toxic substances into the air.
Unfortunately, most manufacturers can hide the type and characteristics of the filler they use, sometimes referring this information to trade secrets.
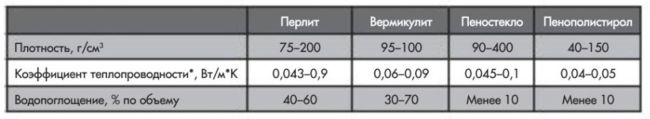
Comparative table of properties of some porous aggregates. *For comparison: the coefficient of thermal conductivity of mineral wool - the most popular thermal insulation material - 0.04-0.09 W/m*K.
Plaster with heat-insulating fillers can be used on almost any substrate: brick walls, light and heavy concrete coatings, even on old plaster. One condition: the base must certainly be strong enough, dry and not repellent to water. It must first be cleaned of dust and other exfoliating fragments. The concrete surface of the walls must be well cleaned of formwork oil before starting work.
All these fillers do not affect the complexity of working with such plasters, you can use the same tools and techniques.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Protective plasters
No less significant and interesting types of plasters are mixtures that can protect a person from the harmful effects of an electromagnetic field on the body. The technical regulation on the safety of buildings and structures establishes requirements for electromagnetic safety. According to this document, the level of electromagnetic fields in the walls of public and residential buildings must be strictly controlled.
But nowadays the level of man-made electromagnetic background has increased greatly, and antennas, high-voltage power lines, etc. have made a great contribution to this. In addition, the number of ordinary electrical appliances in apartments is growing every day. A person almost does not notice electromagnetic radiation, and therefore underestimates the danger that comes from them. Chronic diseases, increased fatigue have become companions of urban residents. Part of the reason for this is the invisible fields that permeate the space of metropolitan areas.
|
|
|
The main component of protective plasters that are present on the Russian market is shungite. This black rock contains a special form of carbon called fullerenes. Such protective plasters have all the advantages of standard ones: good adhesion to the base, crack resistance, strength. But among other things, they can smooth out electromagnetic radiation, thereby reducing its harmful effects on the human body.
Especially recommend use protective plasters in medical and treatment-and-prophylactic institutions, that is, where there are people with poor health. In shielded wards, doctors note a significant improvement in patients' sleep and their general condition. In an ordinary apartment, at least such rooms as a bedroom and a nursery should be made qualitatively shielded. The use of protective plasters does not require special qualifications, as they are similar to conventional mixtures.
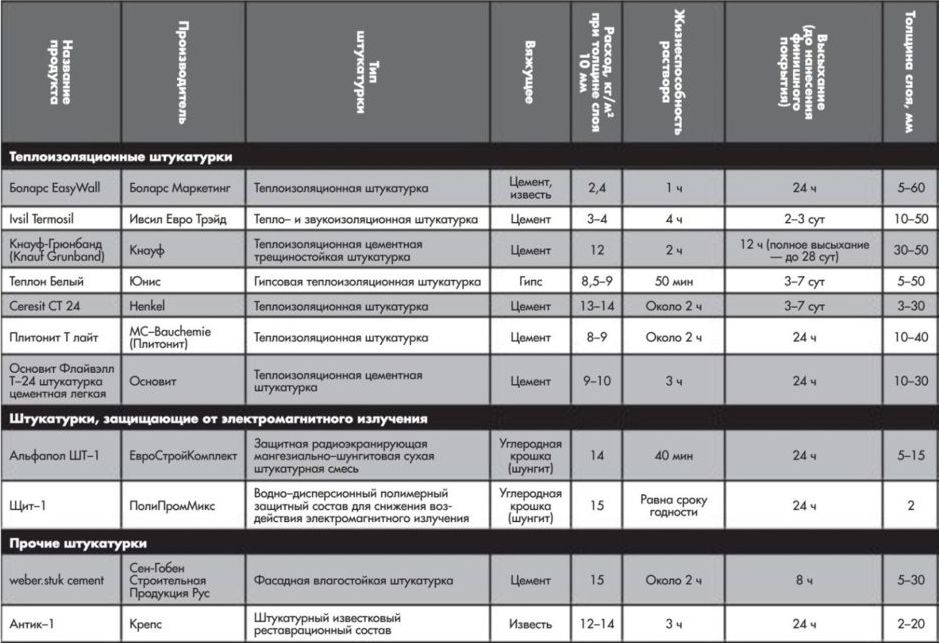
Other useful types of plaster
In unheated and damp rooms, as well as for external work in places with a rainy climate, special tools are also used during work - these are waterproof and frost-resistant plasters.
When restoring old houses, where it is necessary to preserve the historical appearance of the building, they are well suited lime-based plasters, since it was with these materials that the walls of buildings were finished several centuries ago.
Another option is modern ready-made pastes, as well as those that mimic the roughness of antiquity. Using such materials, one speaks more about styling than about the restoration itself.
A full-fledged article is worthy of a variety of decorative plasters. The surface treated with such plaster has an interesting relief, which in itself decorates the walls, therefore these plasters can be used as topcoats. The most popular textures are lamb and bark beetle.









