Installing rafters: step by step instructions
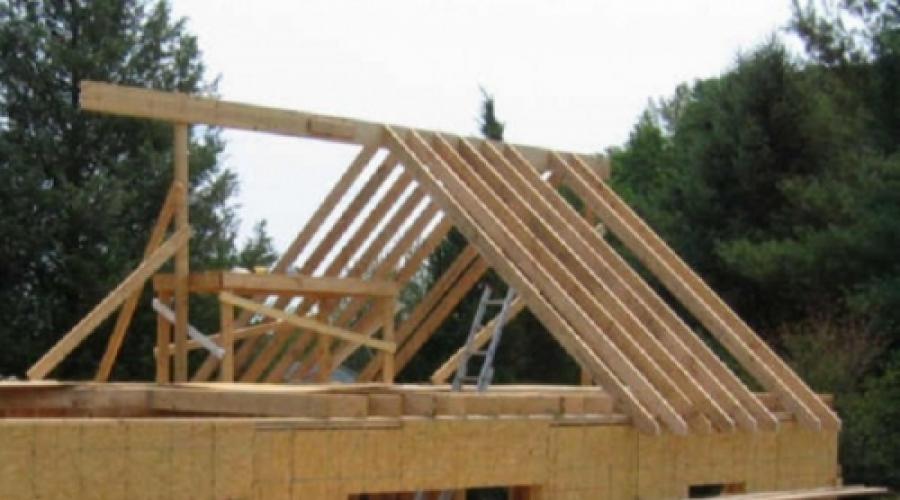

Rafters serve as the basis of the entire roof structure, and their installation is one of the most important tasks in building a house. The frame of the future roof can be made and installed independently, observing the technological features of roofs of different configurations. We will give the basic rules for the development, calculation and selection of the truss system, and also describe in stages the process of installing the "skeleton" of the roof.
Rafter system: rules for calculation and development
The rafter system is a supporting structure that can resist gusts of wind, take on all external loads and evenly distribute them to the internal supports of the house.

When calculating the rafter structure, the following factors are taken into account:
- Roof pitch:
- 2.5-10% - flat roof;
- more than 10% - pitched roof.
- Roof loads:
- constants - the total weight of all elements of the "roofing pie";
- temporary - wind pressure, snow weight, weight of people who carry out repair work on the roof;
- force majeure, for example, seismic.

The magnitude of snow loads is calculated based on the characteristics of the climate of the region according to the formula: S=Sg*m, where Sg- snow weight per 1 m2, m- calculation coefficient (depends on the slope of the roof). The determination of the wind load is based on the following indicators: type of terrain, wind load standards of the region, building height.
Coefficients, necessary standards and calculation formulas are contained in engineering and construction reference books
When developing a truss system, it is necessary to calculate the parameters of all components of the structure.
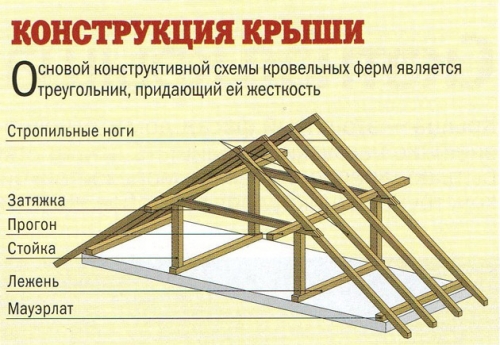
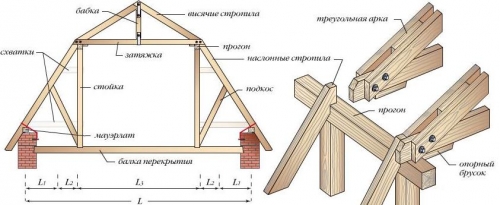
Roof structure elements
The truss system includes many components that perform a specific function:

Materials for the manufacture of rafters
Rafters are most often made from coniferous trees (spruce, larch or pine). For the arrangement of the roof, well-dried wood with a moisture level of up to 25% is used.

The wooden structure has one significant drawback - over time, the rafters can be deformed, so metal elements are added to the supporting system.
On the one hand, the metal adds rigidity to the truss structure, but on the other hand, it reduces the life of the wooden parts. Condensation settles on metal platforms and supports, which leads to decay and damage to the wood.

Advice. When installing a truss system made of metal and wood, care must be taken that the materials do not come into contact with each other. You can use moisture barriers or apply film insulation
In industrial construction, metal rafters made of rolled steel (I-beam, brand, corners, channel, etc.) are used. This design is more compact than wood, but retains heat worse, and therefore requires additional thermal insulation.

The choice of truss system: hanging and hinged structures
There are two types of roof structures: hanging (spacer) and layered. The choice of system is determined by the type of roof, floor material and natural conditions of the region.
hanging rafters rely solely on the outer walls of the house, intermediate supports are not involved. Hanging type rafter legs perform work on compression and bending. The design creates a horizontal bursting force that is transmitted to the walls. With the help of wooden and metal puffs, this load can be reduced. Puffs are mounted at the base of the rafters.
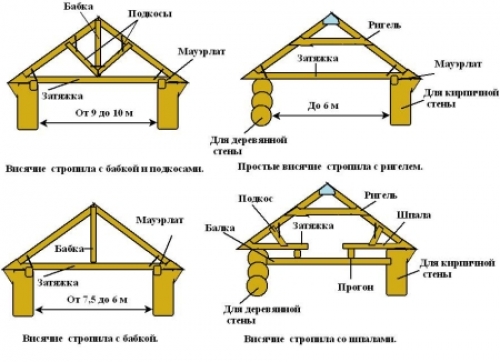
A hanging truss system is often used to create an attic or in situations where roof spans are 8-12 m, and additional supports are not provided.
Rafters mounted in houses with an intermediate column support or an additional load-bearing wall. The lower edges of the rafters are fixed on the outer walls, and their middle parts are fixed on the inner wall or bearing pillar.
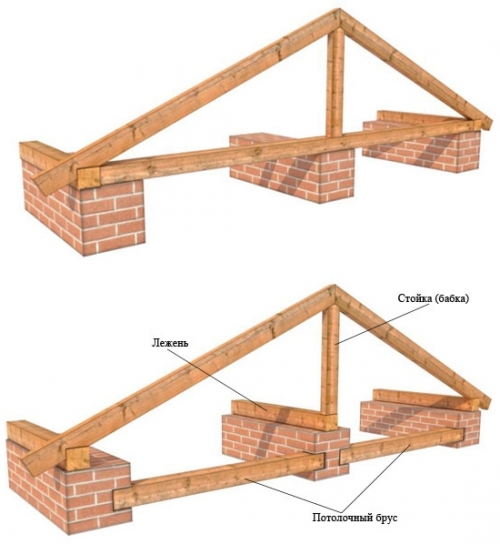
Installation of a single roofing system over several spans should include expansion and layered roof trusses. In places with intermediate supports, layered rafters are mounted, and where they are not, hanging ones.
Features of the arrangement of rafters on different roofs
Gable roof
The gable roof, according to building codes, has an angle of inclination up to 90 °. The choice of slope is largely determined by the weather conditions of the area. In areas where heavy rainfall prevails, it is better to install steep slopes, and where strong winds prevail - gentle roofs in order to minimize pressure on the structure.
![]()
A common version of a gable roof is a design with an angle of inclination of 35-45 °. Experts call such parameters the "golden mean" of the consumption of building materials and the distribution of the load along the perimeter of the building. However, in this case, the attic will be cold and it will not be possible to equip the living room here.
For a gable roof, a layered and hanging truss system is used.
hipped roof
All roof slopes have the same area and the same angle of inclination. There is no ridge run here, and the rafters are connected at one point, so the installation of such a structure is quite complicated.
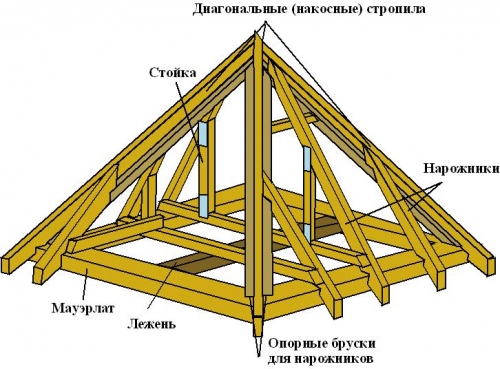
It is advisable to install a hipped roof when two conditions are met:
- the base of the building is square;
- in the center of the structure there is a bearing support or wall on which it will be possible to fix a rack supporting the junction of the rafter legs.
It is possible to create a hipped roof without a rack, but at the same time, the structure must be strengthened with additional modules - rack puffs.
hip roof
The traditional design of the hip roof assumes the presence of slanting rafters (diagonal) directed to the corners of the building. The angle of inclination of the slope of such a roof does not exceed 40 °. Diagonal runs are usually done with reinforcement, since they account for a significant part of the load. Such elements are made from a double board and a durable beam.

The joints of the elements are necessarily supported by a rack, which increases the reliability of the structure. The support is located at a distance of ¼ of the length of the large rafters from the ridge. In place of the gable roof gables, shortened rafters are installed.
The truss structure of a hipped roof may include very long diagonal elements (more than 7 m). In this case, a vertical rack must be mounted under the rafters, which will rest on the floor beam. Sprengel can be used as a support - the beam is located in the corner of the roof and is fixed on adjacent walls. The sprengel farm is reinforced with struts.
broken roof
Sloping roofs are usually created to equip a larger attic. The installation of rafters with this version of the roof can be divided into three stages:
- Installation of a U-shaped structure - supports for purlins that hold the rafter legs. The base of the structure is floor beams.
- At least 3 runs are installed: two elements pass through the corners of the U-shaped frame, and one (ridge run) is mounted in the center of the attic floor.
- Installation of rafter legs.
Gable roof: do-it-yourself installation of rafters
Calculation of the angle of inclination and loads
The calculation of a gable roof, of course, can be done independently, but it is still better to entrust it to professionals in order to eliminate errors and be sure of the reliability of the structure.
When choosing the angle of inclination, it is necessary to take into account that:
- an angle of 5-15 ° is not suitable for all roofing materials, so first choose the type of coating, and then make the calculation of the truss system;
- at an angle of inclination over 45 ° - material costs for the purchase of the components of the "roofing pie" increase.
Snow load limits range from 80 to 320 kg/m2. The design coefficient for roofs with a slope of less than 25° is 1, for a roof with a slope of 25° to 60° - 0.7. This means that if 140 kg of snow cover falls on 1 m2, then the load on the roof with a slope at an angle of 40 ° will be: 140 * 0.7 = 98 kg / m2.
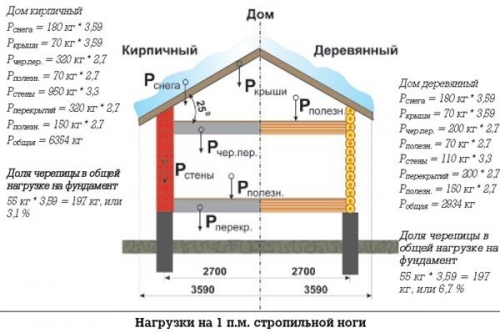
To calculate the wind load, the coefficient of aerodynamic influence and wind pressure fluctuations are taken. The value of the constant load is determined by summing the weight of all components of the "roofing cake" per m2 (on average - 40-50 kg/m2).
Based on the results obtained, we find out the total load on the roof and determine the number of rafter legs, their size and cross section.
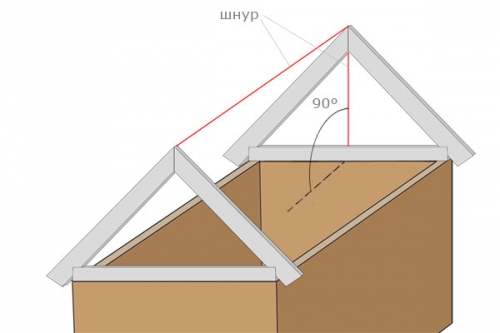
Installation of Mauerlat and rafters
Do-it-yourself installation of rafters begins with the installation of a Mauerlat, which is fixed with anchor bolts to the longitudinal walls.

Further construction of the structure is carried out in the following sequence:
Installation of rafters: video

Ways to connect the elements of the truss structure: video