What roof rafters should be used? Types and calculation of roof rafters
The construction of a roof is not an easy process, requiring certain knowledge and skills. Today in our article we will try to answer most of the questions that undoubtedly interest novice developers. And let's start, perhaps, with the most important thing - with the types of existing roofs and truss systems that are used in their construction.
Rafters (rafter legs) are the main load-bearing elements of any pitched roof. It is they who take on the main loads and environmental influences, such as snow and wind loads, and also carry the entire roofing pie. Rafters are components of the truss system, which includes many more elements, such as racks, struts, girders, mauelat, etc.
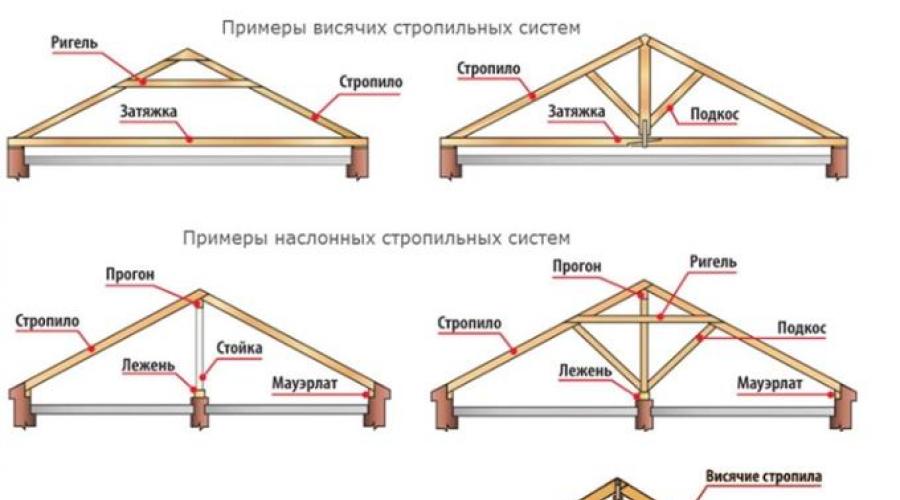
There are three types of rafters - layered, hanging and sliding.
Sliding rafters are mainly used only in wooden log houses. Their attachment method will allow them to move (slide) back and forth for a certain distance. This is due to the peculiarity of wooden houses.
Hanging rafters are used only in those houses where the distance between the walls does not exceed 6.5 m, as the ends rest on the opposite walls of the building.
Slanted rafters rest not only on the walls of the building, but also have an intermediate support, while the span between the supports should be 4.5 or more. Thanks to additional supports, it is possible to cover a span of up to 15 meters.
The support for the rafters is:
- the upper crown in chopped and cobbled houses;
- top trim in frame houses;
- mauetlat (bar 100-150 mm thick) in stone houses. Mauerlat can be laid around the entire perimeter of the building or only along the wall where the rafters rest.
Rafters, if necessary, can be reinforced with additional elements, such as puffs (crossbars) and struts. This will prevent them from sagging during operation.
Rafters for different types of roofs
Depending on the type of roof, different load-bearing elements of the roof are used, which ones we will now consider.

Shed roof - the most common type of roof. It is used mainly in the construction of relatively small buildings, for example, country houses, garages, bathhouses and other buildings.
The truss system of a shed roof consists of separate elements, the fulcrum of which is the opposite walls of the building. Most often, in this case, roof rafters with a length of about 4.5 meters are used. If a relatively large area is covered, it is necessary to use rafter legs and racks.

Rafters designed for a gable roof are a structure folded in the form of a house. The process of its arrangement is more complicated than in a pitched roof. Most often, this type of rafter is used in the construction of small buildings. They are divided into two main types - layered and hanging.
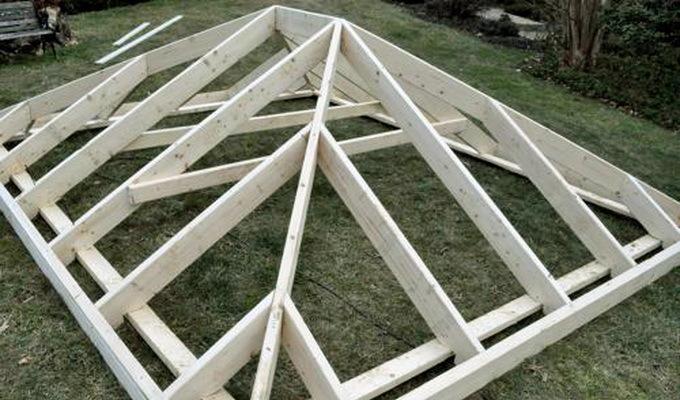

The hip roof is distinguished by the presence of additional slopes, which are created using the hip roof truss system. The design of this roof consists of a gable roof, which does not completely cover the side of the building along its length, as well as a hip covering the side, not closed part of the roof.
An example of this type of roofing can serve as the well-known "Khrushchev", where hip rafters have found their application.
Features of hipped roof rafters

Hip and hip roofs can also be attributed to hipped roofs. Their obvious advantage is the absence of gables, which implies a fair saving of building materials, and hence money. In addition, these houses are distinguished by a wonderful appearance, they look extremely impressive.
The hipped roof consists of Mauerlat, struts and braces, ridge and side runs.

The use of a sloping roof contributes to a significant increase in the attic area, which, in some cases, is used as an attic. When erecting such a rafter system, two short rafters are used, at the point of inflection of which a rack is used. As a result, the slope of the lower part of the roof will be 80 degrees, and the slope of the upper part will be only 25-30 degrees.
Varieties of rafters for the roof
In the construction of any roof, only two types of rafters find their application - layered and hanging. Hanging rafters have two points of support, which are located at the base, for example, support on the bearing walls of the building, in addition to this, layered rafters can rely on columnar supports, or internal walls.
Material for the manufacture of rafters
Wood and metal are the main materials from which rafters are most often made.

When erecting roofing of residential buildings, outbuildings, wooden rafters are used, less often metal ones. Metal (reinforced concrete) rafters are mainly used in the construction of roofs with large spans and roof loads, mainly for covering industrial buildings. The price of these truss structures is quite high, since all its elements are made of metal, mainly a channel is used.
Wooden rafters
In turn, wooden rafters are divided into three types:
- The most popular and widely used type of rafters are structures made of edged boards, usually a board with a section of 150x50 mm or 200x50 mm. This type of rafters gained popularity due to its low cost and ease of manufacture.
- Roof rafters made of logs. As a starting material, tree trunks with a diameter of 10-20 cm, cleaned and processed, are used.
- Rafters made of glued beams. Glued rafters are made from timber bars and boards glued together with a special compound. Such rafters are more convenient to use, the beam has a square or rectangle in cross section. As a result, it easily fits on the crate, besides, their attachment to the Mauerlat is simplified, as well as the process of building up. This type of rafters is much stronger than ordinary wooden rafters.
Before you start calculating the roof rafters, you need to clearly understand what types of loads and with what force they will act throughout the year on the roof of our house.
Factors that affect the roof, it is customary to classify depending on the intensity:
- Constant loads. This category combines the loads that constantly affect the structure of the building. These include both the weight of the roof itself, and waterproofing, heat and vapor barrier, lathing, as well as other structural elements of gable or, creating a constant weight value.
- Loads of variable type. This type combines all types of climatic influence, including precipitation, wind currents, etc.
- Loads of a special type. This group takes into account climatic influences with high strength. This characteristic must be taken into account in seismically active zones and in zones where manifestations of storm winds or hurricanes are possible.
Permanent loads

The size of the rafters for the roof must begin to be calculated from the total weight of the "pie" of the roof. To get the final value, you need to calculate the weight per square meter of each of the materials used. In most cases, the roof will consist of the following components:
- interior decoration (in the case of a mansard roof, the finishing material and fasteners are taken into account);
- rafters (the weight of a standard rafter is 150x50 mm in size, this parameter can be adjusted in the future);
- insulation;
- hydro-wind insulation (taking into account the weight of films and membranes);
- crate, mounted from boards of small thickness (most often 25 mm).
- counter-lattice (often a bar 30x50, 40x50 or 50x50 mm);
- roofing (the weight per square meter of the roof can be found on the manufacturer's website).
When proceeding to the addition of all calculated data, it is recommended to add another 10% to the result, that is, multiply the final result by a constant factor of 1.1. This approach allows you to leave a margin of safety for the roof.
Snow loads

It is imperative to take into account snow loads, since in many regions a long-term influence of precipitation in the form of snow is possible. To prevent owners from breaking the roof under a mass of snow, it is required to calculate the possible load in advance.
To increase the convenience of calculations, a formula was derived for substituting coefficients from building codes and regulations. The formula looks like this:
where F is the value of the total snow load, P is the load per square meter, k is a correction factor depending on the slope of the roof slope.
The weight of snow on 1 square meter of the roof must be determined directly at the construction site. Each region has an average value of precipitation intensity, data can be found from building codes SNiP 2.01.07-85 *.

This type of load has a very high level of criticality, because it can affect the roof with intense winds, regardless of the angle of the roof. Even a small angle of inclination makes it possible for the roof to fall off under the influence of aerodynamic loads. Too much slope can cause the entire roof to experience strong wind pressure on the surface.
To calculate the effect of wind force on the roof, there is also a special formula in which there is a dependence on correction factors:
where V is the wind load, R is an indicator selected based on the regional position of the house, k is an adjustment factor that depends on the height of the structure.
After summing up all the loads, you get the total load per 1 square meter of the roof.
The pitch of the rafters is the distance between the rafter legs. The average value of this parameter in private construction is usually one meter, however, the exact figure is selected based on the full calculation of the bearing capacity of the selected roof system.
To independently calculate the distance between the rafters, you must follow the following algorithm:
- It is necessary to decide whether the space between the rafters will be insulated. If yes, then the step of the rafters will be equal to the width of the insulation minus 2 cm. If not, then the step is taken arbitrary within 1 meter.
- Based on the design scheme of the rafter system, we determine the length of the rafter.
- Next, we will use the program "Calculation of wooden beams" and substitute the data into it: the total load, step and cross-sectional size (initial value 150x50 mm). We look at the results, if the program indicates that this section is not enough, then we change the height of the beam (the width slightly affects the result), for example, up to 200x50 mm. You can also change the distance between the rafters if there is no insulation or roll material is used.
At first glance, the calculation of the roof rafters seems complicated and incomprehensible, but after spending just a few hours you can figure everything out, thereby accurately choosing the right size of the rafter legs.
Rafter dimensions
The minimum rafter size for the roof of a house should be 50x150 mm (40x150 mm), usually 50x200 mm rafters are used. For large roof spans, 50x250 mm rafters or double rafters can be used, that is, two boards are connected together with nails. It is also possible to use bars with dimensions of 100x150 mm. To know exactly what size of rafters you need to perform a calculation. To do this, the entire load is collected (see above), which affects the rafter and the required section is calculated.
If there is no desire to do the calculation, then you can use the tabular values, at least it's better than taking sizes at random.

Given the pitch of the rafters and knowing the length, you can determine the size of the section of the rafter. This option is not accurate and it is desirable to confirm it by calculation!