What is plaster
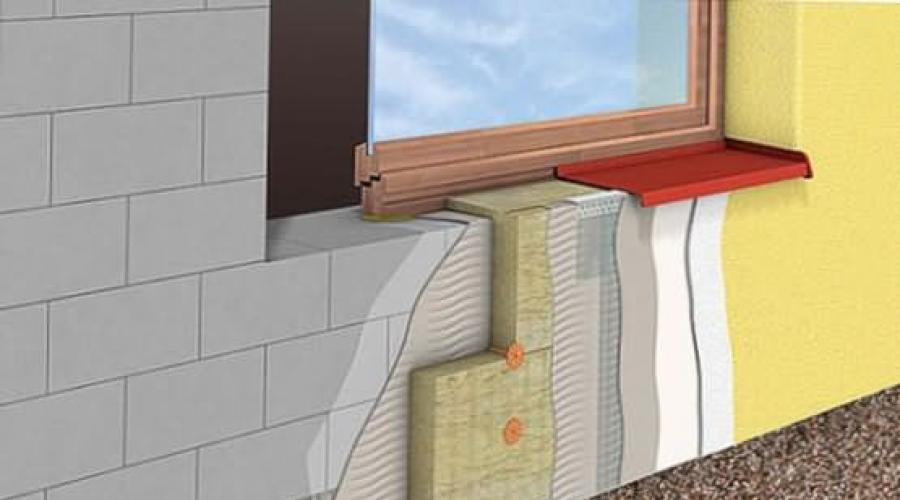

2 main types of plaster are described when repairing an apartment. Visual leveling and plastering on lighthouses.
Types of plaster: the main secrets of choice
What is plaster, what is it for, and what are plasters? These questions are of interest to every person who has decided to make not just an ordinary repair, but a good professionally performed repair!
After the erection of walls, partitions and roofs, it's time to start finishing work. The classic option is their plaster.
Despite the emergence of many new materials, plastering and walls remains the most popular way to decorate the interior. Its indisputable advantage is the minimum thickness and durability of the coating, which is often an important criterion in the requirements for the method of finishing.
The building, with high-quality plastering and painting, always looks fresh and modern, and its diverse textures will allow you to recreate any style in the room.
What is plaster? Let's try to understand this article.
These types include finishing walls with ready-made gypsum boards - the so-called dry plaster, applying plaster mixtures to the walls - “wet”, or monolithic plaster.
Dry plaster
Dry plaster
Factory-made sheets are used exclusively for wall cladding indoors. The dimensions and operational materials allow us to carry out work in a short time with a high quality end result.
For installation, a galvanized profile is used, which is fixed to the walls by level using special brackets.
When placing a profile, the dimensions of the sheets are taken into account. Fastening drywall to the profile is performed with self-tapping screws. The joints and fasteners are leveled with putty, followed by stripping. For final leveling, abrasive meshes of different grain sizes are used.
Advantages:
- The speed of work. Efficiency, in which the result is achieved, is primarily associated with ease of installation and the absence of "wet" processes.
- Tolerance to the qualifications of the performer. The relative ease of installation and the quality of modern materials make it possible to do without the cost of highly paid specialists.
- The possibility of erecting partitions and multi-level surfaces. The design of profiles and fastenings of plasterboard sheets provides for the installation of partitions without walls.
Disadvantages:
- Exposure to weather conditions.
- In some cases, insufficient strength.
Monolithic plaster
The work of applying a plaster solution to the walls in order to level or give a certain color or texture is called monolithic plaster. The result of such work is a layer resistant to mechanical and atmospheric influences.
Main advantages:
- versatility
- durability
- minimum occupied space
Disadvantages:
- weighting of the structure
- extended terms due to the need to dry each layer
- price
The varieties of wet plaster include ordinary plaster and decorative.
Ordinary plaster is a smooth leveling layer. The main purpose is to prepare the walls for further painting or wallpapering.
To give the walls a look that matches the overall design of the building, a special type of monolithic plaster is used - decorative plaster.
The main types of decorative plaster are divided according to the composition of the plaster mixture and the appearance of the resulting facing.
The main element of the mixture is a binder.
- Plaster on limestone traditional material tested by time. The solution is prepared by mixing milk of lime and coarse river sand. In ready-made dry mixes on the market, there are also synthetic fibers that serve as reinforcement.
- Acrylic-based plasters are distinguished by exceptional adhesion and elasticity, and are resistant to atmospheric influences. The compositions of this category are indispensable when applied to old paintwork.
- Polymer-based plasters are non-combustible "breathing" plasters modified by the addition of polymers that increase the mechanical properties of the plaster layer.
- Silicone-based plasters have increased resistance to mechanical and aggressive atmospheric influences, they are not subject to decay.
Plaster in the classification by external features:
Colored decorative plaster
Colored decorative plaster
Colored plasters contain an acrylic-based binder, quartz sand and a dye. Usually they are presented in the form of ready-to-use plastic mixtures.
Smooth colored plaster is used when finishing door and window openings, interior walls and ceilings.
For facades of buildings, colored plaster is used in combination with various technologies that give a variety of effects. The most common and beloved were "bark beetle" and "pebble".
stone plaster
stone plaster
The creation of a stone decoration begins with the marking of stone rows on a prepared wall.
Using a marking cord, indicate the location of the seams. In the next step, the selected type of plaster coating is applied.
After setting, the mixture is "cut" into stones. Having fixed the rule by marks, with the help of a cycle, the plastic solution is removed to a depth of no more than a third of the layer thickness.
When preparing the solution, granite or marble chips are chosen as the main filler. Stone plaster is used for finishing structural elements of buildings - foundations, corners, columns, etc.
Terrazit plaster
Terrazit plaster
Terrazitic plaster mixture is used in facade cladding to imitate rock materials.
Considering it and its weight, the surface is prepared by applying a relief. On a fresh preparatory layer, a wavy grid of shallow furrows is made. The lines are made using any suitable tool and placed horizontally in 3-5 cm increments.
On concrete surfaces, a relief pattern is achieved with a hammer and a chisel, making a notch for better adhesion of the plaster layer to the base.
To prepare the solution, cement, slaked lime and mica are used. Quartz sand and stone chips are added as a filler.
The application of the decorating layer is carried out on a pre-moistened wall. The work is carried out in two stages: the first is sprayed. Then, after 15-20 minutes, they begin to apply the main decorative layer. The next step is the processing of terrazitic plaster by sanding. The result is a smooth sparkling surface.
The effect of the chipped is obtained by driving special tools into the seized covering: scarpel, tongue, chisel. The coating process is completed using a sandblasting machine.
Sgraffito - plaster
Sgraffito - artistic plaster
Sgraffito is a type of plaster in which a relief coating with a pattern or pattern is obtained.
The manufacturing technology of such a decorative coating consists in applying several multi-colored layers with the subsequent removal of their parts to obtain an ornament.
Each layer is applied with subsequent leveling and compaction with a trowel. The number of layers may vary. To give improved strength characteristics, 5-6 layers are used.
Next, a drawing is applied to the plastered wall. This is done using a stencil and pigment powder or chalk, poured into a gauze swab. After placing the picture, they begin to sample the solution. First, along the contour, then in the right places of the drawing, layer by layer is removed with a cutter or scraper.
Thus, sgraffito is a counter-relief, the skillful use of which guarantees a wonderful addition to the design.
Venetian plaster or liquid marble
Venetian plaster or liquid marble
Venetian plaster is a material that uses marble flour and an acrylic or lime-based binder in its composition.
The secret of manufacturing lies in the application of many thin layers with a unique texture of a chaotic pattern.
This texture of the plaster gives an extraordinary visual depth and glow when light is reflected at different depths of the coating.
The multi-layer process, which includes the technology of ironing and polishing each layer, requires high qualification and expensive materials. The result of labor-intensive work will be a five-millimeter cladding layer with a mother-of-pearl effect, superior in environmental friendliness and aesthetics to any of its kind.
How to choose plaster
It is logical to assume that with all the variety of methods and materials for plastering, the consumer has a question - which plaster is better?
There can be no single answer. This is explained by the fact that it is possible to decide on the choice of the “correct” plaster only by knowing the specific operating conditions and the method of carrying out the work.
Not the last role in the choice is played by the cost factor. The latest fashion trends have brought with them the latest materials, sometimes many times more expensive than their counterparts, quite complete in every sense.
When creating an interior design, the question of the harmony of the combination of styles and materials remains relevant. Agree, not always a "cool Venetian", creating palace chic, will be appropriate in a residential apartment. Conversely, spacious halls and living rooms can look much more attractive with suitable wall decoration.
Therefore, which plaster to choose depends on the interior of the room and the effect you want to achieve.
Plastering technology
Compliance with the rules when preparing the surface and applying plaster is a guarantee of durability and preservation of the appearance of the coating.
The necessary conditions for the best adhesion are thorough cleaning of the wall from building dust and dirt, as well as moisturizing. In cases where soot needs to be removed from the walls, a 3% solution of hydrochloric acid is used.
For plastering walls, lime-gypsum mixtures are used. They are applied to a reinforced shingle.
When plastering on concrete panels, a preparatory layer of laitance is applied first. Such a liquid solution will give the surface the roughness necessary for better bonding of the base with the plaster layer.
Any plaster coating consists of several layers. The first layer serves as a leveling layer and is called a spray. The second layer is the primer, and the last one is the finish coat. For simple ordinary plaster, this is limited.
In decorative plaster, there can be several finishing layers - up to 8, and they are called nakryvka. The total thickness of the layers should not exceed 20 mm. When correcting irregularities exceeding this size, cement mortars with a reinforcing mesh are used.
It should be noted that regardless of the type of plaster, the work must be done in one go over the entire surface of the wall. Otherwise, coating defects associated with minor changes in color and texture are possible.
Work is carried out from top to bottom along pre-set beacons. To apply the next layer, it is important to make sure that the previous one has hardened.
Cracks must be prevented. This happens when the layer dries quickly in high air temperature or when exposed to direct sunlight. Therefore, in the hot season, they resort to periodic moistening of the treated wall.
To apply the plaster mixture to the slopes, use a trowel or spatula. Alignment is carried out with the help of a bevel according to the established rules. To work with large even walls, a plaster ladle and a long trowel are used.
The types of plaster are so diverse that you can carry out repairs of any complexity and bring any idea to life!
Overview of plasters: what are plasters, which plasters are better, which plaster to choose, description of plasters
Wall plastering work
The article describes the types of plaster, the features of working with the most "complex" types of plaster. before you start finishing the walls, it is necessary to carry out preparatory work, which boils down to cleaning the walls from the previous coating and eliminating irregularities.
After you have freed the surface of the walls from old wallpaper, paint, etc., you can proceed to plastering. It is quite difficult to independently correctly calculate the material and estimate the terms of work, therefore it is advisable to invite specialists. You should not neglect qualified advice, since the most important thing depends on plastering - the geometry of the room.
For work on plastering a room, a mixture is suitable, which is made up of two types of components: the first have inert properties, the second are binders (this is, for example, gypsum or cement). The dry mixture is diluted with water, resulting in a solution that covers the walls. While the plaster has not hardened, you can create various artistic elements, such as stucco or arches, if this is included in the design of the room. After the coating becomes hard, the walls are ready for finishing work. The drying time of the surface depends on the properties of the applied solution, temperature and humidity in the room, as well as on the number of applied layers. If plastering is planned in several layers, each subsequent layer is applied after a certain time: if cement mortar is used for work - from 2 to 6 hours, if plaster - from 7 to 15 minutes.
Consider the types of plaster
one. " acoustic plaster».
Recently, many people use acoustic plaster, especially if the apartment being finished is located in a panel house. This type of plaster significantly reduces the noise level in the room. For its preparation, aluminum powder is used, which is added to the main components of the mixture, which gives the surface porosity, improving its sound-absorbing properties.
This method of plastering is good because you can create a special design of the room. When working, plaster of various colors and textures is used, inexpensive in price and easy to use.
3. Textured plaster.
At the heart of the mixture, in addition to the main components, fillers are used, such as mineral crumbs, cotton fibers, etc. In addition, materials with astringent properties on a synthetic basis are added to the mixture. A huge plus of this type of plaster is that it perfectly masks wall defects.
4. stone plaster.
Already the name of this type of plaster speaks for itself: its main component is crushed stone. Even a home craftsman can work with this type of coating, and it will serve for a very long time.
5. Latex plaster.
These coatings include material such as artificial latex. If you use silicate plaster, then you are guaranteed durability and resistance to dirt. When working, it should be noted that the walls before applying the solution should be additionally treated with plaster with mineral components.
6. " Vanguard - F»
This mixture has properties such as strength, vapor and water resistance, which makes it suitable for use on a wide variety of surfaces: concrete, fiberboard, brick, etc.
7. Structural plaster.
The peculiarity of this mixture is that small pebbles or quartz chips are added to the main components of the dry mixture. The solution can be prepared on a water basis, which is especially good for interior decoration. Structural plaster has a high degree of plasticity, which allows you to create ornaments. In addition, walls plastered in this way can be washed. A ready-made dry mix can be purchased at a store at a very affordable price.
How to apply structural plaster correctly?
Stage one, preparatory. Release the walls from the previous coating, wait until they are completely dry Stage two - primer. The application protects the wall from mold and swelling. Stage three: plastering. There is room for creativity here. For example, if your plans include creating a cave or grotto effect in a room, you need to use a spatula and coarse-grained plaster when working.
8. Venetian plaster.
The difference between this type of plaster and others is that after drying it seems that the walls are covered with marble. The mixture resembles a thick mass in consistency, which contains marble flour, emulsion and lime. Before application, it requires careful preparatory work: priming the walls.
Stages of work with "Venetian plaster"
1. Cleaning and walls. Ideally, the wall should be absolutely clean and even. When priming the surface, you can use acrylic paint.2. After the primer has dried, the plaster can be applied. When working, a spatula is used, which is applied with a coating in several layers. Each previous layer should dry well.3. Wax coating. This type of plaster requires special protection with white wax, which is applied after the coating has dried.
So, after completing the work on plastering the walls, you can proceed to the next stage of work - finishing ....
What kind of plaster happens, types of plasters and which one is better in composition (snip and gost)
One of the most important stages of finishing the premises, during cosmetic or major repairs, is plastering. In order to determine the scope of work and understand the variety of mixtures for plastering offered by the trade, you should understand what kind of plaster is and what is right for you.In general, plaster is understood as a layer of a special mixture that is applied to all walls, partitions, columns, and in some cases, ceilings.
What is plaster for? First of all, this finishing layer allows you to even out the unevenness of the walls, and also protects any building from the damaging effects of natural precipitation and wind. In addition, the plastered surface retains heat much better in the cold season, and in hot summers it reduces the cost of air conditioning.
Types of plasters
According to their functional features, all types of plasters can be divided into:
- heat-shielding;
- acoustic;
- waterproofing;
- special (acid-resistant, X-ray protective);
- decorative plaster.

Designed for thermal insulation of rooms or communications. To achieve better insulating properties, it is carried out with the addition of various fillers, for example, foam glass, granulated polystyrene foam, expanded perlite (a mineral of volcanic origin) or vermiculite (hydromica). Such plasters are otherwise called warm. Due to the filler, which has a low weight and a significant volume, such plaster is quite light and allows you to create an optimal comfortable microclimate inside the room. Its use often makes it possible to refuse the use of additional insulation of the facade with sheets of expanded polystyrene or mineral wool.

Acoustic plaster belongs to the category of special ones, its main task is to reduce the level of extraneous noise in the room. Most often, these types of plasters are in demand in the construction of production workshops, cinemas, concert halls and sports facilities. They are indispensable in the case of an abundance of architectural curvilinear forms and allow you to replace suspended acoustic systems if their installation is not possible due to the building structure. And in everyday life, they make living in an apartment building much more comfortable, especially if the rooms are finished with hard materials (tiles, marble), which create additional boominess.
Pumice, expanded clay, slag or the same vermiculite with perlite can be used as sound-absorbing additives. The density of the plaster that provides the acoustic effect is 500-1300 kg / m, and painting or whitewashing reduces the level of protection from extraneous noise, and therefore is undesirable.

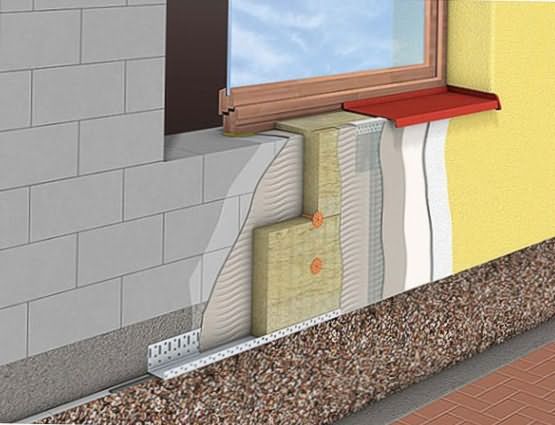
Waterproofing plaster, the composition of which most often includes some kind of waterproof polymers, is designed to make insulating layers in rooms or buildings with high humidity (bathrooms, basements, balconies, sheds).
Particularly high demands are placed on the plastering of pools and wells, because in this case the plastered surface is constantly in contact with water and experiences certain hydraulic loads. Acrylic, epoxy or polyurethane resins are usually used as the closure fluid. To enhance the water-repellent properties, special technologies are also used - applying the solution using a thincrete machine (cement gun).
Special plasters
Technologies for applying special plasters are standard. In order for the plastered surface to acquire the desired properties, special fillers are used. The need to use special plaster must certainly be noted in the design and estimate documentation, indicating its exact composition.

Special plaster mixes, first of all, include X-ray protective plaster, 4682-84 regulates the main properties of the barite concentrate used as the main component in this dry mix. Barite plaster is a fairly cheap alternative to lead screens used as shielding against electromagnetic ionizing rays. The thickness of the protective layer is usually maintained at about 50 mm, and, if a more massive layer of protection is required, barite plates are used.
When working with barite plaster, the ambient temperature should not fall below 15C. In addition, it is necessary to plaster the entire surface at a time, since it is forbidden to join X-ray protective plaster.

Also belongs to the category of special. It is most often involved in the finishing of workshops at chemical industry enterprises and in large laboratories, where aggressive acid vapors act on the walls of buildings.
Usually, plaster on liquid potassium glass is used to create an acid-resistant surface. Since liquid glass is destroyed under the influence of air, a layer of acid-resistant plaster is protected with a covering layer of a conventional cement-sand mortar, which is carefully rubbed using cement milk (iron). Additionally, quartzite and stone flour are added to such solutions for plastering the surface.

The most diverse type of plaster. It includes both the simplest structural plaster (used mainly for facade decoration), and such rather exotic types as flock (silk) plaster, textured plaster and plaster using marble chips. Venetian stucco looks especially advantageous in the interior, which, in terms of its artistic qualities, is an analogue of natural marble and requires special materials and highly skilled craftsmanship to make it.
Facade plasters and plasters for interior work
If we consider what kind of plaster is, depending on the conditions of further operation, then all plaster coatings can be divided into two classes: for facade and for interior work. For facade plaster, the fundamental properties will be its strength and durability. Since the plastered surface of the building is constantly in contact with the external environment, the plaster must have frost resistance, moisture resistance and inertness to ultraviolet radiation and atmospheric oxygen.
I must say that when choosing a plaster for the facade, it is necessary to take into account the type of material from which the walls of the building are made. For houses made of cellular concrete, porous and lightweight bricks of an enlarged format with a significant proportion of voids, the use of conventional lime-cement plaster mixtures is not recommended, since in this case massive cracking or even rejection of the plaster layer is observed.
For finishing such buildings, the market has long offered special compositions, most often based on gypsum with additives, their properties are optimized for application to material with a cellular structure. So before carrying out plastering work, be sure to consult with a specialist which plaster will best suit the walls of your house.
The plaster used for interior work is not exposed to rather harsh weather conditions. Therefore, when choosing it, preference is given to such quality as environmental friendliness. From this point of view, for interior work, water-based plasters are much preferable. After all, even if they contain polymers, they, when decomposed, do not form toxic decomposition products. An important factor for choosing the type of plaster for interior work is its decorative qualities. Although, it must be said that such a division is somewhat arbitrary and many plasters have a universal purpose, being used both indoors and for finishing the facade or basement of a building.
Simple, improved and high quality plaster
Any of the above types of plaster can be made in a simple, improved and high quality version. Simple plaster is used mainly in non-residential premises or when further finishing with other materials (for example, tiles or decorative panels) is planned.
Much more stringent requirements already apply to improved plaster. According to the snip, the plaster should not have a deviation from the plane of more than 2 mm. The evenness of the plaster is checked using special tools - rules, a plumb line and a special probe. Measurements are carried out in an amount of at least three for every 10 m2 of surface. Such plastering is most often performed outside the premises, but only if the building is not planned to be decorated with additional stucco.
For interiors, high-quality plaster is most often used. It is performed in several layers. First, a spray layer is performed, then primer layers and several finishing, covering layers. The usual thickness of high quality plaster is 20 mm.
Surface plastering is carried out along beacons - guides that allow you to perform the work flawlessly. Setting up beacons takes quite a long time and requires considerable scrupulousness. The cost of such work is significant, so high-quality plaster is produced in rooms that are subject to the most stringent requirements.
Dry plaster
All of the above types refer to monolithic or wet plaster, which is the most versatile. Its undeniable advantages are the absence of seams, a monolithic connection with the base surface and the possibility of finishing any, the most complex profile. But such plaster is laborious and requires highly qualified specialists to perform the work. In addition, finishing works can be carried out only after the plastered surface has completely hardened, which delays the construction time.
Dry plaster is deprived of all these shortcomings - gypsum boards, which are mounted with screws on a crate made of wooden bars or special aluminum guides. If the walls are even, then dry plaster sheets can also be fixed with glue. After sealing the joints, you can immediately begin finishing work. And if you choose dry plaster with a pre-finished surface, then finish the job by closing the joints with special overlays with decorative nails. Despite all the advantages, this type of finish has a very limited use, because it can only be used inside the building and only in those rooms that are not exposed to moisture vapor and temperature changes.
Stucco - what is it. what is plaster
What to do if the plaster is cracked. How to repair plaster
Types of surface treatment - plaster
How and from what materials to prepare plaster
Preparatory work for plaster work
Distinctive features of simple plaster
Features of improved plaster
Providing high plaster.
Application of decorative colored plaster
What is decorative plaster
The method of applying plaster with a mortar pump. The structure of the mortar pump.
Finishing, plastering works. Wall plastering. Types of plaster
Features of finishing with dry plaster
Carrying out plaster work. Foundation device for plastering works
Plastering stone and concrete surfaces
Plastering wooden planes
Rules for applying plaster on a mesh netting
Requirements for applying plaster
Plaster under the falcon and plaster under the rule
Surface plastering on beacons
Plastering technique. Stucco finish
Different ways of plastering the surface - manual and mechanized
How to plaster slopes and openings.
Organization of plastering works for the winter period
Carrying out internal plastering work
Production of external plastering works in winter
Methods for the manufacture of plaster solutions
Internal and external wall decoration.
Plasterer's tools