How to build a frame house with a shed roof: step by step instructions from A to Z

Shed roof, according to modern architects, is of the main decisive importance in the development of not only economy class housing, but also stylish. After all, the forces and costs that usually go to the construction of a multi-slope can now be directed to the exterior. For example, building a pool in front of the house or adding a barbecue terrace. And the rest of the shed roof is not inferior at all in anything.
Therefore, it does not mean at all that a house with a pitched roof will turn out to be unsightly or too simple. On the contrary, by playing with the slope and direction of such a structure, roofing material and interior space, you will get a unique architectural design that no one you know will definitely have. And our website will make such a house inexpensive in construction and modern both inside and out!
Architectural Benefits of Shed Roofs
Of course, where gable roofs have existed for thousands of years, everything unusual seems ugly and ridiculous. But the Eiffel Tower in France in the early years of construction embarrassed the locals with its "simpleness".
The fashion for shed European villas came to the Russian expanses quite recently. And until now, individual architects are rebelling against this trend, calling mono-pitch roofs exclusively "barn" and arguing that clients do not even look at such projects.
But in fact, not only the customers of their future “dream house”, but self-builders with golden hands are increasingly making the roofs of their buildings precisely pitched, with different angles, directions and combinations with other roofs. Because, apart from the more dynamic look that only a sloped plane can give, shed roofs are actually more functional and even economical.
Most often in world practice, shed roofs can be found in Finnish houses, which are known for their pleasant combination of modesty and restraint:
 .
.
In warm and hot countries, houses with a shed roof are especially popular: no insulation is needed from the inside, the design always looks original, and such a roof is much cheaper in terms of costs. So the northern countries began to adopt this useful fashion.
For example, not so long ago, a new type of residential building was created in Norway - high-tech, with a shed roof with a slope of 19 °. It generates its own energy thanks to solar panels on the roof: the atrium has enough thermal mass to accumulate enough heat during the day and release it all night. And not only to give, but also to provide the whole house with electricity.
And for water heating of walls and floors, rainwater heated by the sun is used, which flows down the shed roof directly into the drain. With an ordinary gable or hip roof, all this would not have been possible to realize!
Is it worth it to make a “one-slope” for a residential building?
Until recently, shed roofs could not be called popular in Russia. It so happened historically that due to the winds and heavy snows in this country, it was gable roofs that proved to be the most practical, which were sharp in snowier regions, and gentler in more windy ones.
And purely visually, the indigenous population is accustomed to seeing roofs with a slope of at least 30-40 ° on houses, where there is a traditional attic for storing a variety of things. And shed roofs carry such inconveniences:
- An incomprehensible space at the upper Mauerlat. You don’t use it under the attic, but the attic turns out to be unusual. Leave it without an attic - then the entire geometry of the interior will seem broken and cause discomfort.
- On a shed roof, rainwater exerts twice as much pressure as on a gable roof. Why? It's simple: all the liquid that gets on it flows along one slope until it falls to the ground. And if you take and break this slope in half, a “house”, now the water will be divided at the ridge into two streams. And this is twice the amount and influx. This is why shed roofs are problematic in terms of leaks, especially if the choice of roofing material is wrong.
- A shed roof is one integral plane, and this is a real sail. That is why, during storms and strong winds, it is precisely such roofs that suffer in the first place.
- The need for a strong truss system. The load here is always distributed less than that of a gable roof, and therefore the rafters will have to be made thicker and stronger.
- A sophisticated ventilation system, which is sometimes not paid any attention at all, and then they are surprised at the short service life of such roofs.
- Another disadvantage of such a roof is that it will have to be cleaned during heavy snowfalls, otherwise the roofing material and the building system may break. And on ordinary days, on the contrary, the snow itself descends from such a roof, and not like an avalanche, but gradually.
- Unpopularity of experiments. Even more: neither the rich nor the poor want to risk their own investments in construction, and the designers completely fall into despair from any unusual roof.
Because of all these reasons, shed roofs in our country in 99% of cases are found only in baths, garages and summer country houses. Although at the same time, in a region with little snow and not very windy, such a roof could bring many bonuses, including the same unusual stylish design.
Frame houses with a pitched roof are considered the most energy-efficient. This does not take into account the fact that the area of the southern wall in such a house will be the largest, and the northern wall - the smallest. Now see the difference with gable projects? Moreover, the northern side itself is still being built without windows, and serves as one of the walls of the utility room: a boiler room, a boiler room or a supply room, where garden tools are stored. But the presence of an attic under the roof in private construction is already considered obsolete.
A shed roof is remarkable in that it has:
- Simple design. So simple that with a small private construction, they don’t even make particularly accurate calculations for it. There is no need to adjust the slopes to each other, to achieve the identity of their weight and load on the walls. There is no need for complex support systems, which are often found in other types of roofs.
- High practicality. In addition to the main functions of the roof, with a minimum angle of inclination, it is also used as an open area for a variety of purposes.
- Reliability. Due to its simplicity and unpretentiousness, such a roof is actually also the most reliable among all others.
And from the practical aspects, we highlight the following:
- The ability to arrange a house without an attic and the problems associated with it.
- The original geometry of the ceiling, which is used as a separate design element.
- The absence of a ridge and cracks under it.
- The ability to drain rainwater and snow from the roof in only one direction - where the slope is inclined. This is important if people are walking right in front of your house (like on the streets of the city) or if you have laid out a beautiful garden and do not want to flood it in the rain.
And, of course, the simplicity of construction work:

Know-how: shed roof combinations
There is one new architectural fashion: the gable roof, which consists of two single-slope, but not joined at the ridge. And technologically, we are still talking about two separate shed roofs, which are built according to all the rules. And in the middle they place either a flat part or an open terrace between the two halves of the house. An incredibly successful and functional solution, we note, which allows you to add more natural light to the house.
Shed roof houses are recognized all over the world as the most favorable in terms of energy saving. Which is not surprising, because the cube also takes the first place in this regard, and what then is such a house, if not a cube?
Now we will reveal a secret to you: it's all about compactness. Any structure is said to be compact if it has, as far as possible, the minimum area of all external surfaces. So, a house is sometimes built according to rather intricate projects, when almost every room has three external walls, plus an even more complex roof. And sometimes it happens that the rooms have only one such wall, and the roof is generally shed.
What is the point? The fewer such external surfaces that come into contact with cold outdoor air, the warmer the house itself will be. That's why compactness is so important in construction!

In this design, everything is simple: shed roofs are built according to the same patterns, but are based on two parallel Mauerlat-runs. And the main plus is that such a non-spacer construction does not “push apart” the walls of the house with its pressure, which means that there are already much less strength requirements for the frame structure itself. True, in such a house there must be at least two internal walls.
And in modern architecture, a new style has recently appeared: roofs united into a single whole, which have a slope in different directions.
Modern frame house: from the foundation to the roof
A frame house with a shed roof is a structure made of lumber and fixed wood panels. The frame of such a house itself must be built either from metal or from hardwood timber. It is solid, while the rafters on the roof should be made just from conifers. Now let's explain.
The fact is that solid woods tend to keep their geometric shape and not change over time: they do not dry out, do not shrink, do not twist. And, of course, in bending, due to such properties, they work poorly. But conifers are just good because they do an excellent job with dynamic loads, which is why the walls are made static and strong, and the rafters are more flexible and withstand both shrinkage of the house and a slight deflection due to snow.
Although wonderful houses are obtained on a metal frame:

Foundation for a frame house
Under a small one-story house, the easiest way is to make a columnar foundation. But, if you are building a solid two-story frame house with a shed roof, the technology will be a little different.
The fact is that a simple columnar foundation is no longer suitable here. A frame house, worse than any other, endures seasonal ground movements, subsidence of the earth, or other similar problems, and therefore experienced builders advise making a slab foundation for it. This one takes all the dynamic loads on itself, and the integrity of the frame is preserved.
Therefore, for a two-story house, make just such a foundation:

Or a more modern insulated Swedish stove:

Technologies of frame construction of walls
In total, there are two main technologies for frame construction.
Frame and panel technology
In this case, the frame house is built from various individual building materials: beams, cladding, insulation, interior decoration, vapor and waterproofing. All this is attached to the frame in its sequence, and as a result, we have a house that is no worse than a timber building in terms of quality.
Here is a good example of construction using this technology:

And the main components of a house built using this technology look like this:
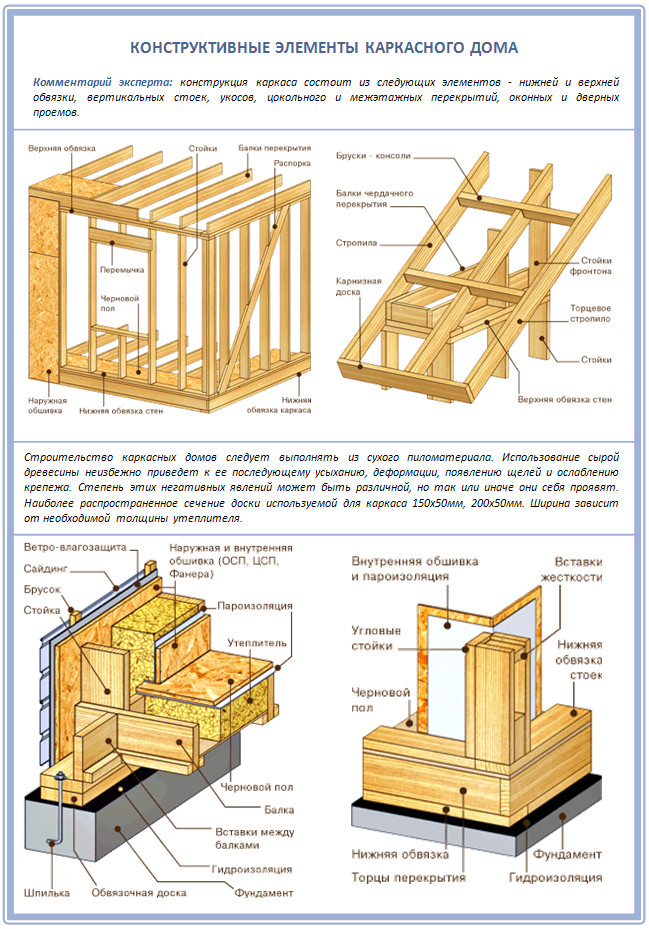
Frame-panel technology
To assemble such houses, a detailed project is initially made, according to which shields of the required size are already manufactured in the factory. We are talking about multilayer panels, which already initially include inner lining, insulation and all types of insulation. All you have to do is attach these shields to the frame of your house, which only takes two days in total. As a result, the whole house, from design to roof arrangement, is built in just a week.
So, insulated SIP panels are the most popular in frame-shield technology. SIP is a wall panel designed to carry longitudinal loads. A frame house based on Canadian technology, which just involves the use of SIP, turns out to be especially warm and integral.
And when building a frame house from such material, the following question arises: should the roof be made from the same material, or is it still traditional? With beams, rafters and lathing? The fact is that everything here is decided by the length of the overlap.
So, with small spans, up to 5-6 meters, the shed roof of a frame house may well be from SIP. It will be already insulated, durable and easy to perform. Moreover, SIP has good bending strength. But for large spans, it is better to build a traditional floor and reinforced rafters. After all, you can’t make a complex roof out of SIP, but just a shed roof is easy enough:

It is only important to know how to properly connect floor beams with such walls:

Shed roof device on a frame house
A shed roof in the design world is also called a monoslope. Modern architects see a house with such a roof somehow differently than a shed or hip roof: lighter, airier and more stylish.
A shed roof behaves remarkably where spans are from 6 to 8 meters. Usually, the slope of the slope is made to the north, and large windows are equipped in the southern facades. Often, external insulation of such a roof is practiced: on top is extruded polystyrene foam, which is filled with a cement screed, and on top of it is a roofing carpet.
What is also good, the drainage system in such a roof is simplified and is needed only on one side, and not on two or four at once. But this is not necessary: on a slope oriented to the south, solar collectors are often equipped abroad.
Step 1. Design
A shed roof of any format always differs from a gable one in that here the rafters are not connected in the ridge, but are attached to the walls of the building with both ends. Those. there is no skate at all. The only exception is the run on which the layered rafters are attached, but it never exceeds the level of the entire slope in height.
If you are building using frame-panel technology, then it will be easiest for you to create a wall difference:
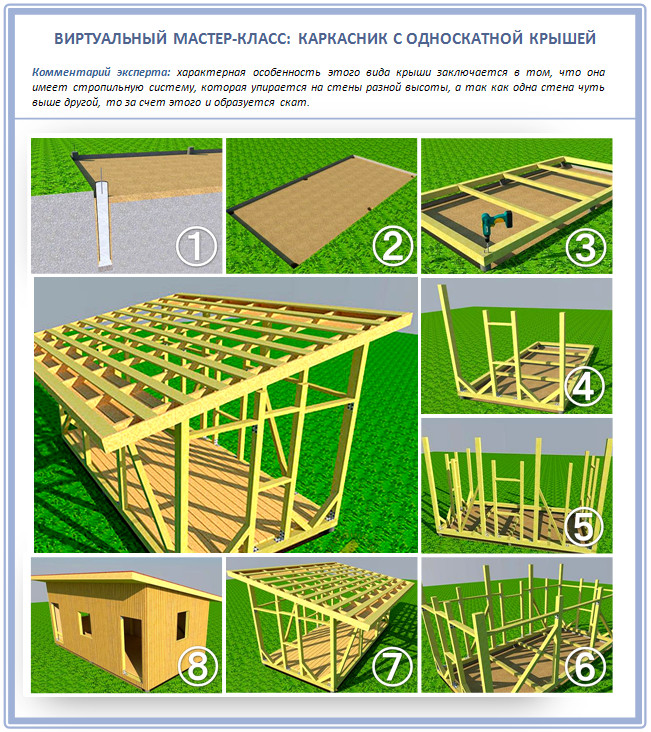
But if you use sip panels or the walls are already made at the same height, then you will have to make roof trusses.
Slanted rafters in a pitched roof are made when the building has an internal strong partition. After all, the longer the rafter leg, the more there is a danger of its deflection or eversion. And therefore, if it is possible to support such rafters, you need to use it.
In this case, a run is attached to the carrier partition:

Now we make the rafters twice as short - so that each of them rests on the wall with one end, and on the run with the other. And be sure to check the angle of inclination of such rafters with a laser level - it must completely match. And outwardly, such a roof will not differ from simpler shed roofs.
But in general, the shed roof rafters can be in all of these options:
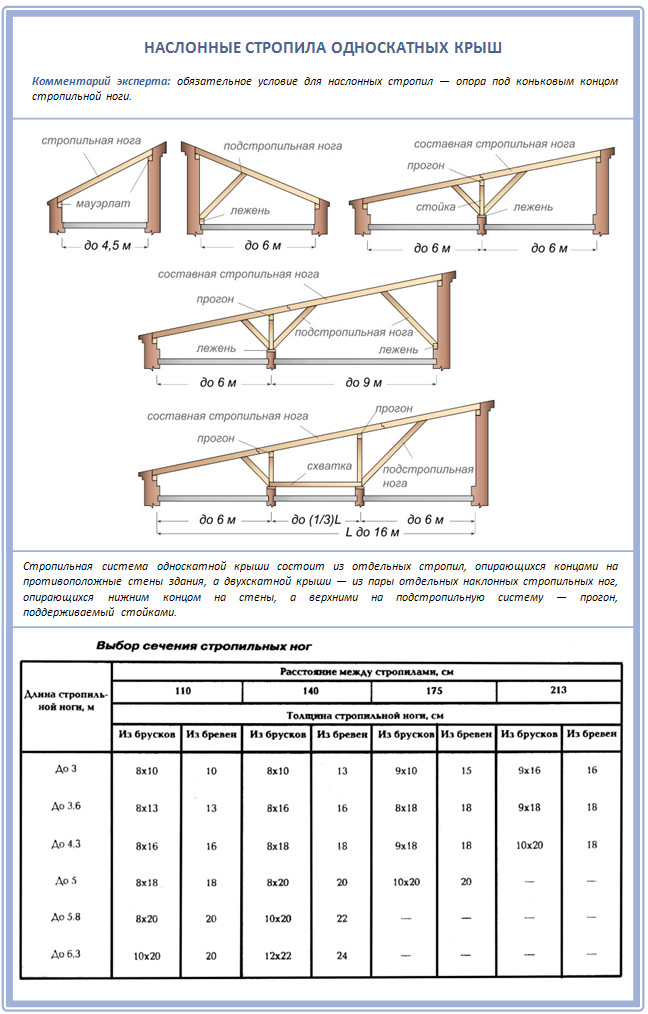
Although the rafters in the shed roof of a frame house can be generally non-expanding:
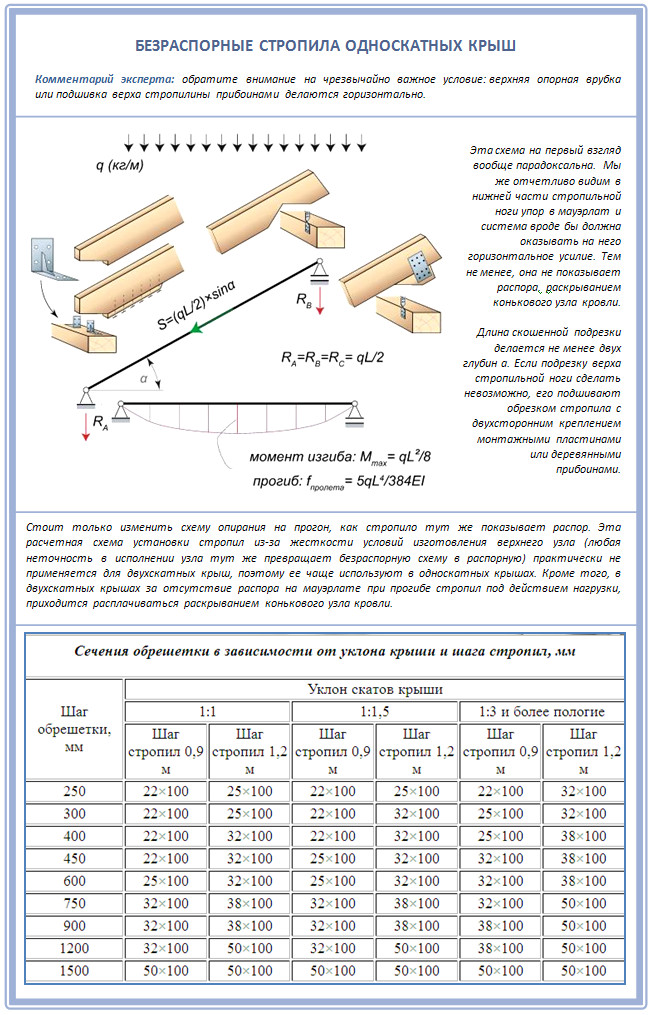
Hanging rafters are good because they can be built directly on the ground, in the form of ready-made farms. After all, their main difference from the layered ones is that the load is now transferred to the rafter triangle itself, and not to the walls of the building. And this is quite reasonable, because most often shed roofs are arranged just on small buildings, such as a bathhouse, a garage or a change house. And the walls of those usually do not please with a special fortress.
So decide: if your building is not distinguished by the monumentality of the walls, make hanging rafters, and if it is more or less strong and there is an inner wall, then layered. The choice is pretty easy!
Step 2. Mauerlat cutout
Decided? Then specify the future angle of inclination of such a roof and make a template for the rafters:
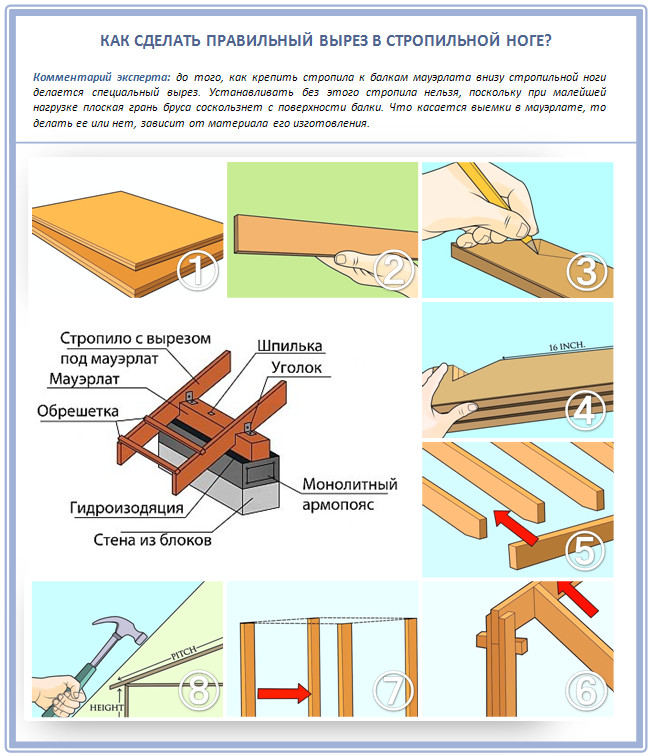
And the cut itself needs to be made in order to support the rafters of the shed roof on the Mauerlats. The main task of the Mauerlat is to compensate for the horizontal unevenness of the walls. That is why, when laying it, be sure to arm yourself with a building level.
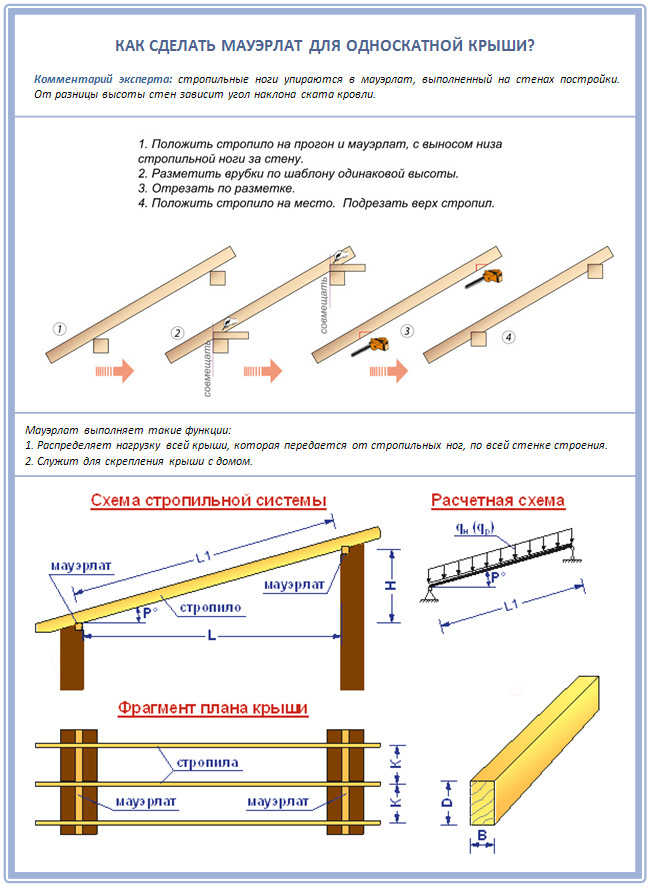
Step 3. Making rafters
For this task, you will need the following fasteners:
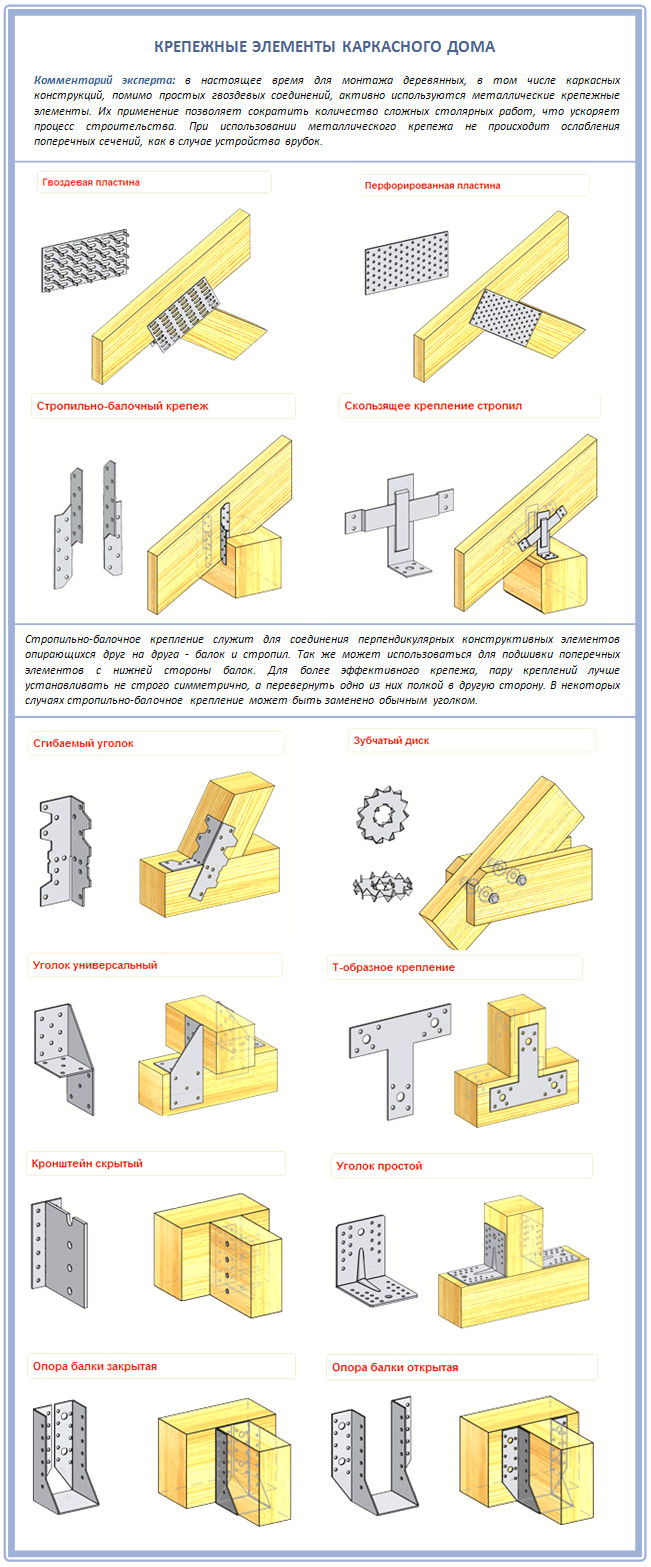
And how difficult your rafters will be depends on what load is planned for them. The higher, the rafters should be more reinforced from the inside:

Step 4. Calculation of the crate
As soon as you fix the rafters, go to the crate. The smaller the slope of the shed roof, the more often the crate should be (up to a solid one):

Step 5. Roofing
For a slight roof slope, use soft tiles, which are generally most common on frame houses:

And on steeper slopes - whatever your heart desires, just calculate in advance the weight of the roofing for the whole house and foundation:

It remains only to lay the selected roofing and arrange a spillway. Which, fortunately, in a shed roof is done on one side only:

Step 6 Glazing
Since relatively recently, a new fashion has appeared in frame construction: cleanliness, conciseness and a lot of glass surfaces. What is most easily achieved precisely through frame technology, for which the presence of a single-pitched roof instead of massive and clumsy multi-pitched ones is a real outlet:

The easiest, according to modern architects, way to bring more light and lightness into a frame house is to make transparent inserts into the roof or completely transmit some part of it. For example, above a covered veranda or part above an attic. And in fact, we are not talking about glass at all, but just about modern roofing polycarbonate, which is more often used monolithic or corrugated. There is a separate article about this on our website, but here we will note only some technical points.
When choosing the thickness of the polycarbonate that you are going to use for the construction of the roof, calculate in advance the climatic and static loads. You have probably seen a photo where beautiful, durable greenhouses have completely broken roofs in the spring? And all because when buying, the owners decided to save on quality, without calculating, such tons of snow fall in harsh Russian winters. You wouldn't want something like that to happen to your roof, would you? After all, replacing the top of an ordinary greenhouse is not difficult, but replacing the roof of a house is a real problem.
You need to fasten profiled polycarbonate sheets to the roof using the same fastening that is used for the metal profile. These are self-tapping and self-drilling screws of the STSD type. The sheets themselves are fastened together with special profiles, which are equipped with EPDM rubber seals. All this is necessary so that such a beautiful roof does not leak. There is also a special connecting aluminum profile for sale - for P-6066 polycarbonate. It consists of a special clamping bar and a sealant, but it already needs to be fixed with self-tapping screws directly to the pipe or crate.
In addition, if you have leftover polycarbonate (after all, standard sheets are produced), use it for glazing utility rooms:
And the excess from another roofing cannot be applied in this way.
A house with a shed roof, built using frame technology with a competent approach, will be the most modern and stylish!