Synopsis of a lesson in social science "banks of the Russian Federation and the Russian banking system." Lesson summary on social studies 'Banks of the Russian Federation and the Russian banking system'
Social science. Full course preparation for the exam Shemakhanova Irina Albertovna
2.6. financial institutions. Banking system
financial institution is a financial intermediary between lenders and borrowers or between investors and savers (pension funds, insurance companies, etc.). Financial institutions provide lending and money transfer services and influence the functioning of the real economy by acting as intermediaries in the conversion of savings and other Money into investments. Part financial institutions includes:
1. Business finance(all enterprises of material production and part of the non-productive sphere, in a market economy operating on the basis of commercial calculation). Commercial calculation- a method of managing the economy, the purpose of which is to obtain maximum profit at minimum cost.
2. Nonprofit Finance(Non-commercial activity does not pursue the goal of obtaining certain income, these incomes are used for the development of the institution itself). Sources of financial resources: budget resources; off-budget state funds; means of the population; monetary deductions from various commercial structures, receipts of funds for work and services performed in accordance with contracts; proceeds from the sale of products, including funds from the sale of tickets for mass events; income from the rental of property; income from training, etc.
3. Finance public organizations include: finances of public, including trade-union organizations; political finance and social movements; finances of special trust funds; charitable foundation finance.
Money - a special commodity that performs the role of a universal equivalent in the exchange of goods.
Basic functions of money
1) the measure of value: express the price - the monetary form of the value of the goods;
2) medium of exchange: act as an intermediary in the acts of purchase and sale of goods;
3) accumulation medium: money withdrawn from circulation is used as a store of value (gold, securities, real estate, currency, etc.);
4) instrument of payment: are used to pay off various obligations (wages, taxes, etc.);
5) world money: are used for settlements on the world market (gold, dollar, euro, pound sterling, ruble) as a universal means of payment and purchase, as well as a universal materialization of wealth.
Law monetary circulation - the amount of money in circulation depends on the sum of the prices of goods sold for cash and on credit, on mutually dependent payments and on the velocity of money circulation. money supply- a set of cash (paper money and small change) and non-cash purchasing and payment means that ensure the circulation of goods and services owned by individuals, institutional owners and the state. Non-cash funds: credit money; check; bill; banknotes (bank notes); electronic money.
The financial market includes: a market where the law of supply and demand determines the price of financial assets; the market of banking loan resources in the banking system that has developed in the country; securities market (stock market) - a market where the emission (issue) and purchase and sale of securities of shares, bonds and derivatives of them is carried out.
Stock Exchange - an organized market in which transactions with securities and other financial instruments are carried out and whose activities are controlled by the state. Stock exchange functions: raising funds for long-term investment in the economy and financing government programs; purchase and sale of shares, bonds of joint-stock companies, bonds of state loans and other securities; setting during the course of trading the rate of securities circulating on the stock exchange; dissemination of information on securities quotes and on the state of financial market.
Banking system - set various kinds national banks and credit institutions operating under the general monetary mechanism. The banking system includes a central bank, a network of commercial banks and other credit and settlement centers.
Credit and financial institutions of the banking system
1. The central bank (or the aggregate banking institutions acting as a central bank), which is legally assigned a monopoly on the issue of national banknotes and a number of special functions in the field of monetary policy. The Central Bank provides loans to commercial banks, keeps cash reserves of other credit institutions, performs settlement operations and exercises control over the activities of other credit institutions.
2. Commercial banks are credit institutions of a universal nature that carry out credit, stock, intermediary operations, organize payment turnover on the scale of the national economy. These banks are organized on a share (joint-stock) basis, according to the form of ownership they are divided into state, joint-stock and cooperative.
3. Specialized credit financial institutions are engaged in lending to certain areas and industries economic activity:
- investment banks (carry out operations for the issuance and placement of securities);
- savings institutions (accumulate the savings of the population and invest money capital mainly in financing commercial and housing construction);
– insurance companies (the most important channel for the accumulation of monetary savings of the population and long-term financing of the economy);
– pension funds(form the insurance fund of the economy, finance the economy and the state);
- investment companies play the role of an intermediate link between individual money capital and corporations operating in the non-financial sphere. The main area of capital investment of investment companies are shares of corporations.
From the book Civil Code of the Russian Federation the author GARANT author author unknownBank guarantee BANK GUARANTEE - a written obligation of one person - a credit or insurance organization (guarantor), accepted by him at the request of another person (principal), to pay a third party - the principal's creditor (beneficiary) in accordance with
From the book Encyclopedia of a Lawyer author author unknownBanking secrecy BANKING SECRET - a kind of trade secret; intentionally concealed information (information) that has actual or potential commercial value due to their unknown to third parties in the absence of free access to them on
authorChapter 1. How the banking system works. Loan documents Where do interest come from, or how does the banking system work? I must say that bank employees, like doctors, are very fond of expressing themselves in complex and incomprehensible terms. One of the purposes of this book is to dispel this
From the book Shield from creditors. Increasing income during a crisis, paying off debt on loans, protecting property from bailiffs author Evstegneev Alexander NikolaevichWhere does interest come from, or how does the banking system work? I must say that bank employees, like doctors, are very fond of expressing themselves in complex and incomprehensible terms. One of the goals of this book is to dispel this terminological fog and get to the bottom of it. To start
From the book Finance: Cheat Sheet author author unknown50. INTERNATIONAL CREDIT AND FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS
From the book Social Science: Cheat Sheet author author unknown34. BANKING SYSTEM Banks are financial institutions that, on the basis of a license, have the right to carry out banking operations, including profit by providing funds to customers at interest (bank loans). There are two types of banks:
From the book Great Soviet Encyclopedia (BA) of the author TSB From the book Great Soviet Encyclopedia (SS) of the author TSB From the book International Economic Relations: Lecture Notes author Ronshina Natalia IvanovnaLecture No. 8. Monetary and financial instruments and institutions of international economic relations 1. Balance of payments and its types. Russia's balance of payments and its external debt The balance of payments is the ratio between all payments that a country has made to others.
author 
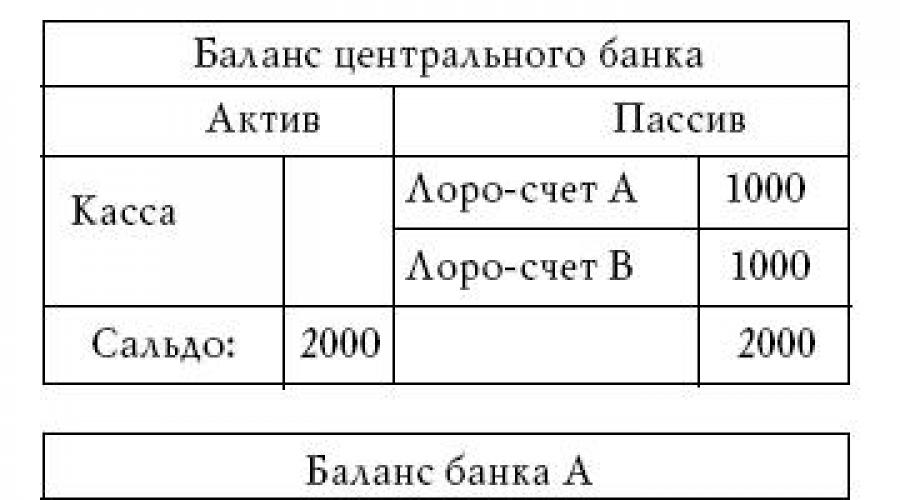
Correspondent banking system The central bank is the main link in the banking system We will first describe the Western banking system. This solution was found on the way to create a two-tier banking system with correspondent links. In order to
From the book Monetary circulation in an era of change author Yurovitsky Vladimir Mikhailovich 
Multi-level branch banking system A two-level correspondent banking system developed in the West in the twenties and thirties. At the same time, an alternative banking system developed in the USSR - a multi-level branch banking system.
From the book Monetary circulation in an era of change author Yurovitsky Vladimir MikhailovichThe Crisis of Accounting and the Banking Fiscal System
From the book Encyclopedia of Etiquette by Emily Post. Rules of good tone and refined manners for all occasions. [Etiquette] author Post PeggyFINANCIAL ISSUES Regardless of the degree of splendor of the ceremony and the number of guests at your wedding, the success of the celebration is determined not by the amount you are going to spend, but by the atmosphere that you manage to create. Therefore, it is so important to carefully consider all the details of the wedding
Banks- financial institutions that, on the basis of a license, have the right to carry out banking operations, including profit by providing funds to customers at interest (bank loans). There are two types of banks: commercial banks and the Central Bank. central bank- a state bank that issues (prints state money), regulates money circulation, stores the country's gold and foreign exchange reserves. Commercial banks- non-state, private commercial banks that receive income for the performance of certain functions. Commercial banks have licenses to operate and operate within the laws of the Russian Federation.
Functions of banks: work with deposits. The main source of income for banks are deposits - this is a trust for the storage of funds from firms and individuals for a certain percentage to the bank. Deposits are: short-term (up to 1 year), medium-term (from 1 to 3 years) and long-term (from 3 to 10 years); lending to organizations and individuals. Most often, banks provide money for the purchase of real estate (housing and land), cars and household appliances. Loans are either guaranteed or non-guaranteed. To obtain a guaranteed loan, the bank takes the client's property as collateral. No collateral is required for non-guaranteed loans. All commercial banks operate on the terms of temporality (money is given for a certain period), payment (for a loan, the bank takes interest on the total debt) and repayment (money is provided for a while); provision of bank cells (depository) for storing valuables. The Bank may provide the opportunity to store valuables and money in safe boxes, the keys to which are kept by customers; implementation of leasing services. Leasing is the purchase by a bank of equipment and real estate and leasing it to a client for long term. Leasing is popular with small businesses - they cannot immediately buy expensive machines or machines, so they rent them from the bank (leasing). The bank receives interest for the lease, after the expiration of the contract, it again leases the equipment to other customers; investment in other industries. Investments - investments of funds in various sectors of the economy with the aim of making a profit. By receiving deposits for safekeeping, banks can temporarily manage the money of their customers. Banks can invest in investment projects, for example in real estate, build new houses, sell them and get additional income; factoring and consulting. Factoring - financial services that the bank provides to the client: the purchase of the client's debt by third parties for 80% of the debt and the collection of this debt and interest from the debtor in its favor. Consulting - financial advice and training; issue or purchase of securities(shares, bonds, bills); currency conversion- exchange of the currency of one country for the monetary units of another (for example, the exchange of rubles for dollars); making money transfers within the country and abroad.

Bank. What is it?
A bank is a financial and credit organization that performs various types of operations with money and securities and provides financial services to the government, legal and individuals. A bank is a commercial legal entity that: 1. was established for profit, 2. has the right to carry out banking operations, 3. has the exclusive right to raise funds from legal entities and individuals for the purpose of their subsequent placement on its own behalf; as well as for opening and maintaining bank accounts of legal entities and individuals, 4. does not have the right to carry out production, trade, insurance activities.

The emergence of banks.
Antiquity
Moneylenders who provided
borrowing money at interest
appeared in ancient times.
Banking still existed
in Babylonia in the 8th century BC. e.; there
practiced issuing cash loans for the purchase
seeds with debt repayment after the sale of the crop.
Temples in Egypt, Greece and the Roman Empire
accepted cash deposits and put them into circulation.
The centers of banking in the Middle Ages were
Italian republics, Holland, some
German states, and later - England.
AT Ancient Greece meals accepted deposits for safekeeping in order to make payments at the expense of depositors. They were also given valuable documents, contracts, disputed amounts for safekeeping. The Greek bankers loaned out the capital entrusted to them against the security of movables, slaves, houses and lands. At the same time, ancient Greek temples were serious competitors of private bankers, which lent money from their temple treasures. large sums both to individuals and public enterprises. The inviolability of temple treasuries allowed them to attract significant contributions from individuals, rulers, and cities.
In the time of the Ptolemies (in the 2nd century BC), in Thebes Hermontis, Memphis and Siena, there were "royal banks", managed by refectories, into which various state fees, income from state factories flowed and which made various payments at the expense of the state, for example , the issuance of salaries to soldiers.
AT Ancient Rome the bankers were called mensarii and argentarii. Argentaria accepted deposits, gave loans, through them it was possible to transfer money to another city.

Middle Ages
In the Middle Ages, due to the diversity of local monetary systems, the trade of money changers was developed. Then they began to give money capital for safekeeping and were entrusted with making payments. The shops of the money changers were located in the market squares, where they conducted their trade at a table covered with green cloth. Money changers in Italy gradually began to be called bankers.
So-called montes pietatis competed with the activities of individual bankers - special banks created in various Italian cities to provide cheap small loans to those in need. The first such institution arose in Orvieto (1463), the second - in Perugia (1467).
In Genoa, creditors who gave credit to the government of the Republic of Genoa in connection with the war with Algeria and Tunisia (refers to 1148), formed a partnership, to which the republic transferred the collection of certain taxes to secure interest and repay the loan. This method was then repeated for following loans; in this way many partnerships arose, the capital of which was made up of shares. In 1250, all these partnerships were combined into one.


new time
The first banks, which were the forerunners of modern banks, arose in Florence and Venice (1587) on the basis of a money change business - the exchange of money from different cities and countries. The main operations of the banks were the acceptance of cash deposits, the provision of loans to the state, merchants and non-cash payments. The essence of the latter was to transfer the amount from one account to another in the banker's books in the presence of both clients. Later banks were organized on this principle in Amsterdam (1609) and Hamburg (1619). This was a primitive form of banking. Banks served mainly trade and settlements; they were insufficiently connected with production, with the circulation of industrial capital. They did not develop such an important function as the issuance of credit money.

Englishman William Peterson, proceeding from the fact, carefully concealed from everyone, that only about a quarter of all the deposits entrusted to him were in cash in the Amsterdam Bank, he came to the conclusion that it was not at all required full coverage specie of all obligations issued by the bank. He proposed a project of the Bank of England, the main capital of which would be placed in government interest-bearing papers that would serve as collateral for its credit operations. In 1694, the British government, being in a difficult financial situation, accepted this project. The Bank of England was created in the form of a joint stock company.
Among the banks founded in the XV-XVII centuries, there are those that continue their activities. Among them:
- the oldest bank in the world Siena Monte dei Paschi di Siena
(founded in 1472),
- Hamburg Berenberg Bank (1590),
- Swedish Sveriges Riksbank (1668),
- English C. Hoare & Co (1672),
- Japanese Sumitomo Mitsui (1683),
- English Barclays Bank (1690)

The first Russian banks
appeared in 1754, the first
State Bank of Russia was
founded in 1860, which
after the reform
Witte turned into a single
emission center of the country.
The first joint-stock design bureaus appeared in 1864. They produced mainly short-term loans to industry and trade. Mortgage banks were created in the 70s. 19th century, provided long-term loans secured by land and buildings.

Current position
Banks of the modern type arose on the basis of relations in connection with the needs of reproduction, the circulation of industrial and commercial capital. The destruction of natural economy, the growth of trade and commodity exchange sharply increased the importance of cash payments and credit. The transition to wage labor on a large scale led to the fact that an increasing part of the income was paid in cash. There was a regular money circulation, turnover and Maintenance taken over by the banks.
As the volume of production and circulation grew, the role of banks in all countries increased. Free cash resources appeared, which were accumulated and directed to industrial and commercial capitalists in the form of loans. With the development of commodity-money circulation in all sectors of the economy, the influence of banking capital expanded more and more. New functions were added to the listed initial functions, in particular, such as the management of interest-bearing capital.
Banks, as collectors and accumulators of capital, began to serve the entire production process and were able to influence it. From small institutions for the safekeeping of money, from modest intermediaries, banks have become active participants in the increase of industrial capital and active stimulators of the development of social production.
In addition to the traditional tasks of banks - the organization of money circulation and credit relations - their functions also include the financing of the national economy, insurance operations, the purchase and sale of securities, and in some cases intermediary transactions, investment operations, and the acquisition of obligations on guarantees. In addition, credit institutions provide consultations, participate in the discussion of national economic programs, and keep statistics.
The evolution of finance and the banking system has led to the ubiquity of cashless payments, which has significantly changed the nature of banking operations. Not only cash became money, but also bank debts to customers, as in the form accounts on customer accounts, and in the form bank receipts - banknotes .

By lending, banks can create new money. In essence, with non-cash payments as money, the bank transfers to the borrower its obligation to pay - the borrower becomes the bank's debtor, and the bank is the borrower's debtor. The total balance is not disturbed [but bank debts play the role of money and we pay our obligations with them.
The central bank can limit the total amount of credit in the economy by setting reserve requirements.

Bank types
Distinguish:
- central banks that state regulation banking and money supply.
- commercial banks engaged in entrepreneurial banking activities;
- universal banks, carry out all main types of banking operations;
- investment banks specialize in investments, most often in securities;
- savings banks, specialize in attracting funds from the population;
- specialized banks, specialize in one or more banking operations.
Sometimes distinguished:
- "Retail Bank" ("Retail Bank") - focused on working with individuals.
- "Captive Bank" ("Pocket Bank") - a subsidiary bank of a large industrial or banking structure, the main purpose of which is to service the operations of the parent company.

the role of the bank in the modern economy
The main functions of the Central Bank are:
1) monetary regulation of the economy;
2) issue of credit money;
3) control over the activities of credit institutions;
4) accumulation and storage of cash reserves of other credit institutions;
5) lending to commercial banks (refinancing);
6) credit and settlement services of the government;
7) storage of official gold and foreign exchange reserves;
main function central bank is credit regulation.


Bank operations
Banking operations are divided into passive and active.
Passive operations are called operations through which banks form resources of money capital, active operations are operations through which they use these resources in order to make a profit [ .
Banking transactions include:
- attraction of funds from individuals and legal entities in deposits and deposits (on demand and for a certain period);
- placement of attracted funds on its own behalf and at its own expense;
- opening and maintaining bank accounts of individuals and legal entities;
- making settlements on behalf of individuals and legal entities, including correspondent banks, on their bank accounts;
- collection of funds, bills of exchange, payment and settlement documents and cash services for individuals and legal entities;
- purchase and sale of foreign currency in cash and non-cash form;
- attraction to deposits and placement of precious metals;
- issuance of bank guarantees;
- implementation of money transfers on behalf of individuals without opening bank accounts (except for postal orders).

Banking system
Banking system- a set of different types of national banks and credit institutions operating within the framework of a common monetary mechanism.
The banking system includes central bank , network of commercial banks and others credit settlement centers .
central bank conducts the state issue and currency policy, is the core of the reserve system.
Commercial banks carry out all types of banking operations.

Structure of the banking system
In countries with developed market economies, two-tier banking systems have developed. The top level of the system is represented by the central bank. At the lower level, there are commercial banks, divided into universal and specialized banks (investment banks, savings banks, mortgage banks, consumer credit banks, industry banks, intra-production banks).
The banking system does not include non-bank credit and financial institutions.
Types of banking systems
International practice knows several types of banking systems:
- distributive centralized banking system;
- market banking system;
- banking system in transition.
Distributive (centralized) banking system: the state is the sole owner, the state monopoly on the formation of banks, a single-level banking system, a single bank policy, the state is responsible for the obligations of banks, banks are subordinate to the government, the head of the bank is appointed by the central or local authorities of higher governments. Banking activities are regulated by legal documents.
the market-type system is characterized by the absence of a state monopoly on banking activities. Banking competition is typical for the banking system in market conditions. Issuing and lending functions are separated from each other. The issue of money is concentrated in the central bank, lending to enterprises and the population is carried out by various business banks - commercial, mortgage, savings, etc. Commercial banks are not liable for the obligations of the state, just as the state is not liable for the obligations of commercial banks.

banking infrastructure
Banks, as elements of the banking system, can only develop successfully in cooperation with other elements and, above all, with the banking infrastructure. The elements of the banking infrastructure include:
- legislative norms (defining the status of a credit institution, the list of operations performed by it);
- internal rules for conducting transactions (enforcing the implementation of legislative acts and protecting the interests of depositors, customers of the bank, its own interests in general, methodological support);
- construction of accounting, reporting, analytical base (computer processing of data, management of the bank's activities on the basis of modern communication systems);
- structure of the bank management apparatus.
Despite the fact that banks have existed for a long time, the question of the essence of the bank is debatable. The following main aspects of the activities of banks are distinguished:
- money store;
- institution, organization;
- economic management body;
- exchange agent;
- credit company.
The new economic encyclopedia gives the following definition: “A bank is:
- a system that serves to accumulate (money, information, etc.);
- a credit and financial organization that accumulates funds and savings, provides loans, performs cash settlements, issues and records bills of exchange and other securities, issues money, transactions with gold, foreign currency and other functions.
AT federal law“On Banks and Banking Activity”, the concept of a bank is as follows: “A bank is a credit institution that has the exclusive right to carry out in the aggregate the following banking operations: attracting funds from individuals and legal entities to deposits, placing these funds on its own behalf and at its own expense on terms of repayment, payment, urgency, opening and maintaining bank accounts of individuals and legal entities.
Modern economic theory considers banks as a special kind of financial intermediaries. Banks as special financial intermediaries are characterized by the following essential features:
Firstly, like any financial intermediaries, they exchange debt obligations, i.e. banks issue their own debt obligations, and the funds mobilized on this basis are placed on their own behalf in debt obligations issued by other issuers;
secondly, banks form their own liabilities on the basis of highly liquid and fixed deposits. Acting as a financial intermediary, banks assume unconditional obligations with a fixed amount of debt to legal entities and individuals;
thirdly, banks as depository financial intermediaries have high level"financial leverage", i.e. shares borrowed money in the passive structure. Banks form credit resources mainly at the expense of borrowed funds, which makes them dependent on external and internal factors and necessitates a special system of banking supervision by the central bank and other bodies;
fourthly, banks have the right to open and maintain settlement, current, currency and other accounts, issue non-cash means of payment and, on this basis, ensure the functioning of the payment system.
Banks like financial intermediaries, accepting cash deposits from different subjects of economic relations, lend them to other subjects for various terms. The former can return the money on demand or without notice, the latter usually need money for a long period. There are entities that have money they are willing to lend, but also want to get it back when they need it. At the same time, there are entities seeking to borrow money, but with the condition that they pay back the money only after a certain period. It is clear that these two groups cannot directly deal with each other. The bank's function consists of converting short-term deposits into long-term loans. The bank acts as an intermediary, accepting deposits, paying interest on them, and making loans, charging borrowers higher interest rates. Thus, the bank relieves the depositor of the need to investigate the reliability of the borrower.
Thus, the following functions of the bank can be distinguished:
- accumulation of funds;
- resource transformation;
- regulation of money circulation.
The purpose of banks in serving borrowers and depositors is to make a profit, and in this capacity they are similar to any commercial organization. How more money banks can lend, the more profit they will get. However, the bank cannot lend out all the funds it receives from deposits, as it is required to hold enough funds in liquid form to be able to meet depositors' repayment requirements. This is where the banker's dilemma lies: the more liquid the form in which funds are held, the lower the rate of return. Keeping cash, for example, i.e. the most liquid form of assets, does not bring profit to the bank.
Therefore, the bank must maintain certain proportions in the balance between maximizing lending and minimizing liquidity until the very end. low level in which it is safe to work. To some extent, this task is facilitated by official controls, but banks still have ample room to operate. The conflict of profitability and liquidity requirements can be seen as a direct result of the clash of interests between the two groups that give the bank its financial resources: shareholders and depositors. Shareholders jointly own banking property and are interested in receiving income on invested capital. Depositors provide the bulk of the funds used by the bank and demand security and the ability to withdraw their money from savings accounts without notice. good bank must be able to reconcile the interests of these groups, otherwise it will lose either investors or shareholders.
The role of banks is to ensure the concentration of free capital and resources necessary for simple and expanded reproduction, to streamline and rationalize money circulation.
Types and forms of banks
The banking system as a unity of constantly developing and interacting financial and credit institutions that perform banking operations both in full and in part, depending on the evaluation criterion, can be classified as follows:
- on form of ownership allocate state, joint-stock, cooperative and mixed banks. In a number of countries, the capital of the central bank belongs entirely to the state (Russia, France), sometimes the state owns about 50% (Japan, Switzerland);
- on legal form banks are divided into open and closed joint-stock companies and limited liability companies;
- on functional purpose - issuing (issuing money into circulation), deposit banks - accepting deposits from the population is their main operation; commercial banks engaged in all operations permitted by law;
- on the nature of the operations performed banks are divided into universal and specialized. If universal banks are more typical for Europe (risk reduction), then for the USA they are specialized, since it is believed that specialization increases the level of customer service, reduces the cost of banking operations;
- on number of branches- branchless and multi-branch;
- on service industry— regional, interregional, national, international; municipal banks are also regional,
- on scale of activity - small, medium, large, consortia, interbank associations.
Separately allocated banks special purpose who perform operations at the direction of the authorities executive power, are authorized banks, finance government programs.
The elements of the banking system also include banking infrastructure - enterprises and services providing information, methodological, scientific, personnel, communication services for banks.
Banks are the center of the financial system.
Bank- a special credit institution specializing in the accumulation of funds and placing them on its own behalf in order to make a profit.
The main purpose of the bank
- mediation in the movement of funds from creditors to borrowers and in payments. As a result, free cash is converted into loan capital, which brings interest.Working in the field of exchange, the bank regulates the money circulation in cash and non-cash forms.
The main functions of banks:
- attraction (accumulation) of funds and their transformation into loan capital;
- stimulation of savings in national economy;
- credit mediation;
- mediation in payments;
- creation of credit means of circulation;
- mediation in the stock market (in transactions with securities);
- provision of consulting, information and other services.
Banks do not just form their own resources, they provide internal accumulation of funds for the development of the country's economy. Incentives for saving free funds of the population and capital accumulation are provided by the bank's flexible deposit policy in the presence of a favorable macroeconomic situation in the country.
Stimulating policy suggests:
- setting attractive interest rates on deposits;
- high guarantees of the safety of depositors' funds;
- a sufficiently high reliability rating of the bank and the availability of information about its activities;
- variety of deposit services.
Credit intermediation- the most important function of the bank as a credit institution. It ensures the effective redistribution of financial resources in the national economy on the principles of repayment, urgency and payment. Credit operations are the main source of income for the bank.
Payment intermediation- the original and fundamental function of banks. In a market economy, all business entities, regardless of their form of ownership, have settlement accounts in banks, through which all non-cash payments are made. Banks are responsible for the timely fulfillment of their customers' instructions for making payments.
Creation of credit means of circulation is the process of money production by the banking system. It is able to expand loans and deposits by multiplying the monetary base. Such extension money supply called multiplier effect.
Understanding this process requires an understanding of the main types of banking operations. All operations are divided into passive and active, which is reflected in the bank's balance sheet.
By liability banks reflect the attraction of funds - the formation of deposits, and for the asset- their placement by issuing loans or investing, for example, in securities.
All funds mobilized by banks in the financial market are its resources, that part of them that can be used to conduct active operations is called free reserve(or credit resource).
Thus, the activity of banks is of extremely important social importance. Banks organize the monetary process and issue banknotes.
The specific result of banking activity is a banking product.
banking product- these are special services provided by the bank to customers, and the cash and non-cash means of payment issued by it. The specificity of the banking product lies in its intangible content and limited scope of monetary circulation.
Bank types
The following main types of banks should be distinguished: issuing banks, commercial banks (specialized banks, accounting and deposit banks, savings banks, mortgage banks, cooperative banks, utility banks). In the vast majority of countries, the issuing bank is the central bank of the country.
In modern banking systems of developed countries, there are two main types of banks:
The group of commercial banks in various developed countries includes whole line institutions with different structures and different ownership relations. Not interpreted in the same way different countries and the very concept of "commercial banks". Their main difference from the central ones are the rights to issue banknotes. There are two types of commercial banks: universal and special banks.
Universal Banks carry out all or almost all types of banking operations: the provision of both short-term and long-term loans; operations with securities, acceptance of deposits of all kinds, provision of all kinds of services, etc.
special bank, on the contrary, specializes in one or a few types of banking operations. In some countries, banking laws prevent or simply prohibit banks from carrying out a wide range of operations. However, banks' profits from certain special operations can be so large that activities in other areas become unnecessary.
The predominance of one type of banks in the credit system of a country should be understood as a trend. In some countries where universal banks, for example, dominate, there are numerous special banks. Conversely, in countries dominated by specialty banks, especially last years, there is an increasing trend towards universalization. This happens both as a result of the liberalization of banking legislation in individual countries, and as a result of circumvention of existing laws by banks. An example is the practice of creating independent special banks that belong to large banks and expand the range of banking operations of the latter. The countries where the principle of specialization of banks prevails include the UK, France, the USA, Italy and, with a reservation, Japan. The principle of universalization dominates in Switzerland, Germany and Austria. However, in many developed countries, the statistical differences between these two types of banks are becoming increasingly vague and controversial, since even in those countries where, according to statistics, special banks dominate, in fact, many of them have already turned into universal ones. In any obstacles exposed public authorities on the way of universalization, there are loopholes. In the USA it is bank holdings. Similar examples exist in other countries. For example, the banking system in Hong Kong has three levels, which consist of three types of banking institutions, namely: licensed banks, restricted banks and withdrawing companies who are authorized to accept deposits from the public.
The third type of banking institutions for the withdrawal of deposits operates with various restrictions. Only licensed banks and banks with a limited license may be called banks.
Banks began in the 12th century. activity changed, whose functions included the exchange of money for a fee. Subsequently, they expanded their activities by accepting deposits for safekeeping. In 1587, the first public bank was opened in Venice, which marked the beginning of the creation of banks throughout Europe. The first state banks in Russia appeared in 1754.
These are institutions that combine cash and savings. Banking activities includes the following aspects:
1) banks act as financial intermediaries - accept deposits;
2) banks concentrate a significant part of the free capital available in the country;
3) banks buy and sell shares;
4) banks transfer capital into the hands of businessmen who need to expand their turnover;
5) banks provide loans to individuals;
6) banks own industrial enterprises.
Banking system
The state includes the Central Bank, state and commercial banks, special financial institutions (insurance, mortgage, savings).central bank
stands at the head of the credit system of any state. Historically, it emerged as an emission center and still occupies a special position in the economy. The main function of the Central Bank is to conduct a nationwide monetary policy. His clients are commercial banks, government organizations, credit institutions. In addition, to The functions of the Central Bank are:1) issue of money;
2) The Central Bank acts as a bank of banks - each commercial Bank must keep a certain amount on a reserve account (mandatory reserves - 15-20% of the amount of deposits);
3) The Central Bank provides credit support to commercial banks and regulates their activities;
4) The Central Bank is a banker and creditor of the state - it carries out cash execution of the budget by financing public expenditures, manages public debt, stores and forms gold and foreign exchange reserves, acts on behalf of the state in international financial organizations.
All functions of the Central Bank are closely interconnected, they create objective conditions for the regulation of the entire monetary system of the country.
Commercial banks
they concentrate the bulk of credit resources, carry out bank settlements, lend to economic entities, and provide financial services to enterprises and the public. The resources of commercial banks are formed from their own and borrowed funds. Own resources include authorized, reserve capital and profit, and attracted - demand deposits, time and savings deposits, interbank loans.Commercial banks use the received funds for lending to enterprises and the population, conducting transactions with securities, and investing. In addition, they carry out cash settlements, transactions with foreign currency and real estate.
This is a loan in cash or commodity form, provided by the lender to the borrower on a repayment basis. Allocate two types of loans(Fig. 10.1 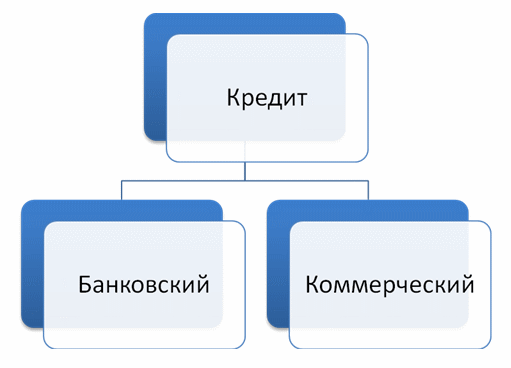 ).
).
commercial loan
- lending by entrepreneurs to each other when buying and selling goods through a promissory note.A bank loan is also divided into several types (Fig. 10.2  ).
).
Agricultural loan
- investment in agriculture. - long-term loan secured by real estate.State loan- the borrower or creditor is the state and local authorities in relation to citizens and legal entities.
International credit- relations between states, international banks and corporations.
The place and role of credit in the economy are determined by the functions it performs:
1) is a condition for the redistribution of temporarily free cash from one area of economic activity to another, providing a higher profit;
2) contributes to the concentration of capital, which is necessary condition stable development of the economy;
3) at the expense of the loan, the lack of own working capital subjects of the economy, ensuring the acceleration of capital turnover;
4) in the sphere of monetary circulation, it replaces cash payments with non-cash ones, simplifying the mechanism of economic relations.
Securities
security paper- this is a sold and bought financial document that certifies the property rights of the owner and gives him the opportunity to receive a certain income. The main properties of securities are:
negotiability - the ability to be bought and sold on the market and act as a payment instrument;
availability for civil circulation- the ability to be the object of various civil relations;
standardization - the presence of standard content (rights, forms, accounting rules, types of participants, places of trade);
documentation- availability of necessary details;
state recognition- provides confidence of buyers;
profitability - the ability to receive dividends or interest;
liquidity - the ability to quickly sell and turn into cash.
Securities have nominal