Modern insulation for walls inside a country house. How to insulate a country house quickly, easily and with a minimum budget How to properly insulate an internal partition in a country house
Read also
“How to choose the right insulation for walls inside a country house?” - a question that worries many owners of a garden plot. The comfort of any home largely depends on its ability to retain internal heat. The walls in a private house must be sufficiently insulated to prevent sudden temperature changes when the weather changes. This is relevant not only for a building intended for year-round living, but also for a small garden house. After all, summer residents often have to wait out rain, cool nights and even spring and autumn bad weather in light buildings.
The need for insulation
Insulating walls in a dacha allows you to solve a number of problems and make using your garden house more convenient.
Creating a comfortable microclimate
By creating a reliable heat shield, significant temperature fluctuations can be avoided. Air temperature indicators can vary within very significant ranges, not only during the cold season. Even in summer, daily fluctuations can reach tens of degrees, which immediately makes itself felt in an uninsulated country house. According to the requirements of SNiP for residential premises, the temperature of the floors should be 25-27 o C, the walls - at least 18 o C, and the total air temperature in the room - about 22 - 25 o C. And since garden house during the summer season it becomes a habitat for gardeners and gardeners, then all of the above provisions of SNiP can be applied to it in full.
Increasing the service life of a building
One of the most important technical characteristics of construction and finishing materials is frost resistance. Initially, you might think that we are talking about their ability to withstand external cold. However, this is not entirely true: frost resistance and thermal conductivity are completely different indicators.
Frost resistance is the ability of a material to withstand a certain amount of freezing and thawing without visible destruction and loss of its strength qualities. In this regard, the frost resistance of a material is measured by the number of freeze/thaw cycles. For example, this indicator for brick is about 50 cycles.
Accordingly, the number of cycles directly affects the service life of construction and finishing materials, and, therefore, the house itself. Therefore, effectively working insulation of wooden walls allows you to reduce the number of frost cycles and increase the operational life of a garden building.
Internal or external insulation?
For a long time, there have been debates among experts: how to properly insulate the walls of a home? More precisely, which method is better suited for country house construction: insulating walls from the outside, or insulating wooden walls from the inside. Supporters of both technologies present a lot of arguments “for” and “against”, the most weighty of which can be called.
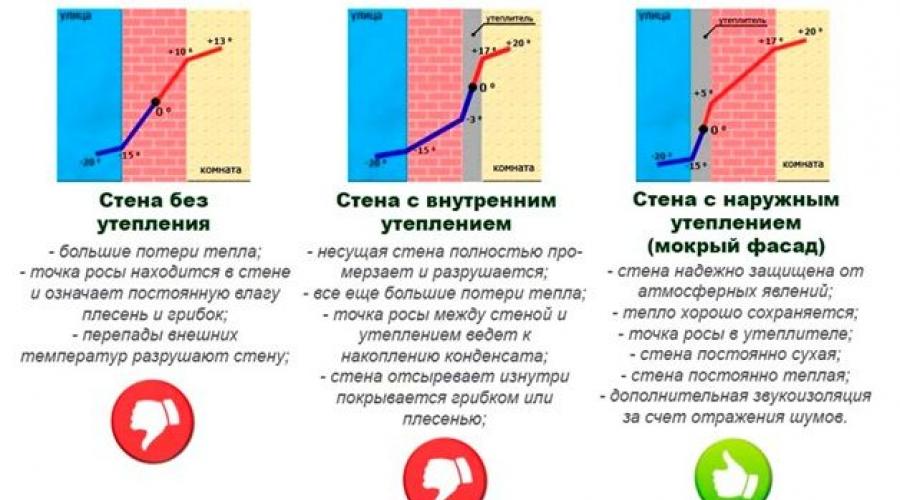
Dew point offset
One of the unpleasant effects accompanying internal insulation is the shift of the “dew point” into the building. With this, at first glance, beautiful and even romantic name, builders refer to the place of condensation of moisture vapor contained in the air.
Dew point - the place of external walls or roofs where warm air interior spaces encounters cold surfaces. In this place, the transformation of air vapor into dew droplets - condensation occurs.

The intensity and location of vapor condensation largely depend on which thermal insulation method is chosen. Insulating wooden walls from the inside leads to them freezing to a great depth, right down to the junction with the insulation. As a result, the dew point shifts into the space between the inner surface of the load-bearing wall and the thermal insulation material. Dampness accumulates in this place, which causes the appearance of fungus, mold, and premature destruction of the wood.
It will be very difficult to remove moisture from under the insulation. In this regard, it is not recommended to insulate walls in a wooden house from the inside without installing a vapor barrier membrane and performing a number of other technical specifications. If thermal insulation is installed outside the house, the external walls will be protected from the effects of cold, and the point of moisture condensation will shift to their outer side.
Advantages of internal insulation
However, installing thermal insulation material outside country house is not always possible without complex and expensive work. For example, if the facade of the building is finished decorative material- siding, tiles, lining, etc. - before installing the insulation, you will need to dismantle exterior finishing. After the outer layer of thermal insulation has been laid, it will need to be protected a reliable layer waterproofing, after which we can begin finishing the façade.
If the external installation of insulation can still be justified for a permanent house intended for year-round use, then for a small country house such work, which takes a lot of time and effort, will be impractical. In the latter case, it will be much easier to insulate the walls from the inside wooden house. Country house building used as living quarters only for a small part of the year, mainly in summer period. In this regard, the risk of condensation due to sudden temperature changes between warm indoor air and cold wall surfaces is reduced. Before you insulate the walls from the inside in a private house, you should take a responsible approach to choosing insulation for interior works.
Selection of thermal insulation material
Today on the finishing materials market there is huge assortment various heat insulators. Understanding this diversity is not so easy even for a finishing specialist, not to mention ordinary people who decide to insulate a country house from the inside with their own hands. Therefore, the question of how to insulate the internal walls of a wooden house from the inside is not at all rhetorical.

Since different thermal insulation materials have different operational and technical characteristics, before purchasing you must carefully read their instructions for use. When choosing insulation, special attention should be paid to the thermal conductivity of the material and to recommendations for its installation.
All types of thermal insulation, which can be used to insulate the walls of a wooden house from the inside, are divided into:
- Mineral fiber.
- Foam-polymer.
- Foil.
Mineral insulation
Mineral wool and heat-insulating materials created on its basis have excellent thermal protective properties. Such materials are created on the basis of mineral raw materials - glass (glass wool), basalt or granite (rock wool), slag (slag wool). The density of mineral insulation can be different - from 50 to 200 kg per cubic meter. Depending on this indicator, lungs can either be formed from mineral wool rolled materials, or compact compact slabs are pressed.

The mineral insulation is attached to the load-bearing surface using dowels, wooden slats or a frame profile. Due to the low mechanical strength, it is not recommended to use construction adhesive for installing mini-slabs - there is a high probability of delamination of the material. Among operational features mineral wool should also be especially noted for its fear of dampness. When wet, mineral fibers stick together and lose thermal insulation properties. Therefore, when externally insulating a building, it is necessary to take special care to create effective waterproofing. For the same reason, mineral wool is excellent for the interior walls of a wooden house, where it is not in danger of being damaged by precipitation.
Among other advantages of the material, one can note its non-flammability. Mineral wool can easily withstand heating up to 1000 o C and is not subject to ignition when exposed to open fire.
When working with mineral wool, it releases a lot of dust and tiny particles of glass, stone or slag. In this regard, when working with mineral fiber insulation, it is necessary to use protective clothing and goggles. This will help prevent insulation particles from getting on the skin and mucous membranes.
Foam insulation
Expanded polystyrene as insulation for walls inside a country house can also be an excellent solution. Among its main advantages are lightness, sufficient strength, ease of installation and low price. Expanded polystyrene, more commonly known as polystyrene foam, has long been successfully used to create thermal protection for buildings. In terms of their thermal insulation properties, foam insulation is not inferior to mineral wool, but they are not afraid of moisture. When wet, polystyrene foam does not lose its technical qualities. Sheets of foam plastic are quite easy to install - for this you can use both fasteners (screws, dowel-nails) and adhesives.

Main negative quality expanded polystyrene - high flammability. It is easily ignited by open fire and burns with the release of asphyxiating gases. In this regard, when insulating the walls of a wooden house from the inside, special attention should be paid fire safety. Polystyrene foam must not be placed near potentially flammable places - in kitchens with gas stoves, near stoves and heating boilers, electrical panels.
Among modern foamed thermal insulation materials, polyurethane foam can also be mentioned. It is applied using special equipment in which chemical components are mixed to release polyurethane foam. It is applied under pressure to the surface to be insulated, resulting in a monolithic, firmly adhering thermal insulation layer.

The absence of joints, cracks and other cold bridges makes polyurethane foam unusually effective in terms of maintaining a comfortable temperature inside a wooden house. The main disadvantage of this method of insulation is its high cost, reaching 500 - 700 rubles. per m 3. In addition, it is impossible to obtain polyurethane foam at home: this requires expensive equipment and skills to work with it.
Foil insulators
These materials are perhaps best suited for insulating the walls of a wooden house from the inside. This is due to its high heat-saving performance. The most common type of foil insulation is penofol. It is based on a sheet of polyethylene foam with a thickness of only 0.5 - 1 cm. Thanks to this, after installing the penofol on the wall, excess space is not “eaten up”. This is especially true for small interior spaces of country houses.
High thermal insulation qualities are achieved by applying polyethylene foam to the surface metal foil, which prevents heat loss through external walls. Foil reflects up to 85-90% of everything infrared radiation emanating from heat-heating devices located in the room. The closed structure of polyethylene foam and the absence of pores make it possible to retain heat well due to the low thermal conductivity coefficient.
Specifications
Before you insulate the walls of a private house using this or that material, you should thoroughly familiarize yourself with the technical conditions for its use. When installing internal thermal insulation, you should try to select insulation in such a way that its vapor permeability rate is lower than that of the outer wall. This will prevent the accumulation of excess moisture under the thermal insulation material due to its timely removal through the wall. This can be achieved by installing a vapor-permeable membrane between the load-bearing surface and the heat insulator, or by selecting insulation with the appropriate technical characteristics.

Installation of different materials also has its own characteristics: if the insulation is installed incorrectly, the entire thermal insulation effect can be negated. Using mineral wool it should be protected with a layer of hydro- and vapor barrier due to its high hygroscopicity. Minfiber absorbs moisture from the air and retains it inside itself, which leads to loss of thermal insulation qualities. When fastening sheets of foam plastic or foil insulation, special attention should be paid to carefully sealing the joints between them. To do this, you can use sealant, elastic putty or tape.
When attaching polystyrene foam boards to the wall, it is necessary to ensure that they fit as tightly as possible. If there remains between the wall and the foam air gap, it can become a “cold bridge” through which cold air.
Features of summer house insulation
Each of the thermal insulation materials has its own technical characteristics, based on which its minimum permissible thickness is determined. During the construction of capital residential buildings For this purpose, SNiP summary tables are used, which indicate the thermal conductivity standards of walls for a particular region.
In relation to country houses, when choosing the thickness of thermal insulation, you should initially decide whether the room will be used only in the warm season, or sometimes there will be a need to spend the night in it in winter. If the owners plan to spend their weekends at the dacha from time to time in the winter, then the walls of the house must be thoroughly insulated in accordance with all the requirements of building regulations.
If the building is designed only for the summer season, then it will be quite sufficient to insulate the walls of a wooden house from the inside so that they can withstand a drop in temperature to 0... - 5 o C. This is quite enough to maintain a comfortable microclimate in the room during the first September frosts , during the last harvest. The video shows how to properly insulate a room with your own hands.
Having become familiar with the operational and technical features of a particular material, you can create an effective one with your own hands. thermal protection your country house. This will make temporary living in it much more comfortable, even during bad weather.
Insulation of a country house is necessary due to the fact that most buildings located outside the city are not heated from the central heating system. heating system, or boilers running on gas, but using solid fuel boilers, or conventional heating stoves.
Such heating is effective, but labor-intensive. In order for the resulting thermal energy to be used as rationally as possible, it is necessary to take care of insulating the walls of the country house. The best way to do this will be discussed in this article.
From this material you will learn where to insulate the dacha - from the outside or from the inside. The answer to the question: “Which insulation to choose?” will also be given. We will consider such materials for do-it-yourself home insulation as mineral wool, extruded polystyrene foam, penoizol and foil penofol.
1 Where is it better to insulate: inside or outside?
It’s worth mentioning right away that if you want to arrange as much as possible effective insulation country house with, then the required result can be obtained only through its comprehensive insulation. Especially if we're talking about about insulating a country house made of wood with your own hands.
There are a huge number of ways of heat loss in a house with low thermal insulation. These are both windows and attic floor, and doorways, and walls.
But there are often cases when the budget for a dacha thermal insulation project allows you to choose only insulation from the outside or from the inside of the house. Let's figure out which option is better to give preference in this case.
To be able to easily understand all of the following, you first need to understand the concept of thermal inertia. For example, a dacha built of brick, for summer day stands in the sun at an air temperature of +35 degrees.
During this time, the brick walls warm up so much that the warmth of the walls will be felt even 3-4 hours after sunset.

Based on this, brick is a material with high thermal conductivity, as well as - it absorbs the sun's rays for a long time, increasing its temperature, and when the ambient temperature decreases, it also gives off its heat back for a long time.
1.1 Insulation of cottage walls exclusively from inside the house
In construction, there is one key rule, which is formulated as: “designing the external structure (walls) of a house, the layers of the wall should be arranged in order of decreasing their thermal insulation and increasing vapor barrier properties from the outside to the inside of the building.” That is, the outer contour of the walls should have the lowest thermal conductivity.
If a layer of thermal insulation material, contrary to these requirements, is located inside the house, then both points will be violated of this rule. Of course, insulating the walls from the inside will give quite a tangible result, but the microclimate inside the room will significantly suffer.
There is a great risk that the humidity and dampness of the air in the house will increase significantly due to the unnaturally high vapor barrier, which is promoted by most types of thermal insulation, especially foil, materials.
Internal insulation of dacha walls is usually done with your own hands by installing heat-insulating material on the surface of the walls, and then covering it with plasterboard.
This technology is often performed incorrectly, both because one of the key factors that must be adhered to so that internal insulation with your own hands does not bring all the above problems is the strongest possible connection of the thermal insulator to the wall and tight connection of the joints.

This is important due to the high thermal inertia brick wall. Over the course of 5-10 days of severe sub-zero temperatures, the outer surface of the walls of the house will cool down very much, and the brick will turn into a serious source of cold, working to cool the inside of the house, which has a higher temperature, and, as a result, provokes heat exchange.
If you are insulating a wall inside a house with your own hands, then it is very important that the thermal insulation is made as tightly and monolithically as possible, since any gaps in the connections of the thermal insulation material with the wall and with each other will contribute to the appearance of cold bridges.
The bridge of cold is a place that has greater thermal conductivity than the main part of the house structure. Cold bridges are a serious reason for reducing the effectiveness of wall insulation, even if it is made using the highest quality thermal insulation materials.
If cold bridges have appeared, then the brick or wooden wall of the dacha will give off cold through the insulation (even if it is), as a result of which the layer of plasterboard with which it is lined will cool.
When drywall is cooled below the dew point temperature, due to the temperature difference, moisture will condense on it, which over time will turn into mold or mildew. This situation especially often happens in the corners of the most poorly heated rooms.

To ensure that the internal insulation of a country house does not bring more disadvantages than advantages, it is necessary to strictly follow the following recommendations:
- The optimal insulation for insulating walls from the inside is foil-coated thermal insulation material like penoplex; it is best if the foil is done on both sides. Double-sided foiling significantly reduces the heat exchange between the cold wall and the facing material, as a result of which condensation is either minimal or does not form at all;
- Arrangement of a thick facing layer with. If drywall is used, then it optimal thickness should be about 5 centimeters. Such cladding, due to its size, will prevent intensive cooling of the air inside the room due to freezing of the walls in winter, even if cold bridges are present.
1.2 Insulation of cottage walls from the outside
External wall insulation is one of the most common and universal options for partial thermal insulation of a country house with your own hands. And, in fact, the only correct option.
The low thermal conductivity of insulation helps maintain the optimal internal temperature of a brick or wooden wall throughout the cold season.
The wall will not freeze due to the fact that the insulation prevents the penetration of cold from the outside, and the wall is warmed up from the inside by warm air.

For example, in practice, this plus, taking into account our knowledge of the thermal inertia of walls, results in the following. After opening the window to ventilate the house with cold winter morning, you will get instant heating of the air entering the house, since the heated walls will give off their heat inside the house.
As a result, even if the window is open for an hour, the temperature in the house will drop by a maximum of 2-3 degrees. Similar ventilation, when the insulation is located outside the walls of the house, will most likely provoke a decrease in the temperature of the house by 7-8 degrees.
An additional advantage of high-quality external thermal insulation, provided that the insulation is installed as tightly as possible and covered with a layer of plaster and external cladding, is the complete absence of any air convection, cold bridges and drafts.
2 Types of insulation
Question: “Which insulation to choose?” is very multifaceted, moreover, each individual case requires an individual choice, and it is impossible to say exactly which insulation is objectively the best. Let's look at the basic requirements that a truly high-quality insulation must meet.

- Thermal insulation properties. The higher the material thermal insulation characteristics, the thinner the cladding layer will be, as a result of which both finances and free space.
- Hydrophobicity The lifespan of the insulator directly depends on how much moisture the heat insulator absorbs. The presence of internal moisture contributes to the accelerated destruction of insulation. It is important that the material has water-repellent properties.
- Fire resistance. High-quality insulation should not be subject to combustion and be self-extinguishing.
- Lifetime. It is important that over time the insulation does not decompose, does not lose its thermal insulation properties, and does not harbor microorganisms, midges and rodents.
- Safety. This factor acquires maximum significance when it comes to materials for thermal insulation of a country house from the inside. The insulation should not have any negative effect on the human body;
- Soundproofing. High-quality insulation materials, as a rule, have good soundproofing properties. We are talking about foamed foam and mineral wool products.
- Price. How much insulation costs is often one of the leading factors when choosing a thermal insulation material. It is important that the cost of insulation is optimally correlated with its functional characteristics.
Let's figure out which insulation is best to use to insulate a country house with your own hands. The following materials meet the above requirements:
- Mineral (basalt) wool;
- Foamed polystyrene foam;
- Foil penofol;
- Liquid penoizol.

If you are not limited on funds, then the best option for insulating your dacha with your own hands is mineral wool. According to the thermal conductivity parameter this material is one of the best insulation materials. It does not burn, does not rot, has excellent soundproofing properties and vapor permeability, which helps maintain optimal microclimate indoors.
Mineral wool can be used to insulate walls with your own hands, both inside and outside the house. Weak side mineral wool insulation is unsatisfactory moisture resistance.
Manufacturers are trying to solve this question using various hydrophobic additives with which mineral threads are impregnated at the creation stage, however, in order to be completely sure that the insulation will not collapse due to moisture accumulation, it is necessary to equip a high-quality waterproofing layer.
If you do all the work yourself, then an important factor is the maximum simplicity of the insulation. The best option in this case is foil penofol or expanded polystyrene foam.
These materials have good thermal insulation properties, and at the same time, they are quite inexpensive. Penofol with double-sided foil is excellent for internal insulation of house walls, while polystyrene foam should be used for external wall insulation.
2.1 Features of insulating a country house with foam plastic (video)
If the dacha is a favorite place not only for summer holiday, but is also often visited during the cold season, then the premises of the country house will have to be well insulated. But who said that insulation (it would be more correct to say thermal insulation) should only serve in winter? It is no less necessary in the summer heat - the rooms will be kept comfortably cool on the hottest days.
For thermal insulation work, you can use different materials. Moreover, the modern range of insulation materials is so rich that it allows you to choose the best option not only in terms of performance characteristics, but also in cost, depending on the family budget. However, it is still always recommended to “bet” on high-quality thermal insulation material, and it must meet a number of important requirements.
In this publication, we will try to figure out which insulation for walls inside a country house looks preferable and why. Let us dwell on another important issue - what thickness of thermal insulation will ensure comfortable conditions in the house at any time of the year.
Requirements for insulation for residential buildings
Any material selected for repair or construction of residential buildings must meet certain physical and technical requirements, sanitary standards, and also be safe to use. Insulation is no exception.

The main criteria for choosing thermal insulators that you need to pay attention to include:
- Environmental Safety. Materials should not only help create a comfortable temperature regime in the house, but also not harm the health of its inhabitants. Therefore, during operation, the insulation should not spoil in any way the healthy atmosphere in the rooms.
- Energy saving characteristics. The insulation must have the lowest possible thermal conductivity.
- Fire safety. Most building materials, including wood, which you cannot do without when building a house, are flammable. However, the danger of modern products made on a synthetic basis lies not only in the possibility of rapid fire. An equally terrible phenomenon is the release of toxic combustion products. Therefore, when choosing insulation, you should pay attention not only to its flammability class, but also to its smoke-generating abilities. The heat insulator should ideally be non-flammable (NG) or have minimal flammability (G1) (many materials are far from this). The smoke-forming ability is designated by the letter “D”, and its lowest level is D1, which is what you should strive for.
- Soundproofing capabilities. You should not think that this quality is not so important for country houses - after all, there is peace and quiet all around... Even if you move away from a noisy city, you can get a neighbor who likes to listen to loud music, which in silence will be heard very loudly. long distance. It is impossible in dachas to prohibit neighbors from using power tools, working in personal carpentry workshops, or using equipment to cultivate the site. Other disturbing factors could be a busy highway passing nearby, a railway line, etc.
- Vapor permeability of the heat insulator. With this parameter, since we are talking about insulation from the inside, special care is needed. In fact, when the material is “breathable”, it is generally not bad. But if the vapor permeability of the walls themselves is lower (and this is usually the case), then saturation of the insulation placed in the room with moisture cannot be ruled out. This means that reliable vapor barrier and efficient ventilation rooms. In conjunction with this criterion, the hygroscopicity of the material, that is, its ability to be saturated with moisture, should also be considered. It certainly should be minimal.
- Durability of the material. This factor is also worth paying special attention to, unless, of course, there is a desire to carry out repair work every three to five years. To avoid making a mistake in your choice, you should not purchase insulation from an unverified manufacturer, even if it has a suitable price. In this case, it is better to overpay, but have confidence in the warranty periods specified by the manufacturer.
- The ability of insulation to retain its original shape. This quality can be referred to as the strength of the material. During operation, the insulation is subject to different loads - dynamic, vibration, statistical and others. Under the influence of these influences low quality materials may become deformed or decrease in size, forming “gaps” in the thermal insulation. And the entire insulation system will become ineffective.
- Resistance to biological and chemical influences. When insulating a private home, an important factor is the absence of unwanted “guests”, such as insects and rodents. Therefore, it is worth choosing a material that will not become a favorable environment for their habitat. In addition, the components of the insulation should not be subject to rotting or decomposition under chemical influence. They should not serve as a breeding ground for microflora - mold, mildew, moss, etc.
- Compatibility with building wall material. In order for the insulation to “work” as expected of it, it must combine well with the base material that is intended to be thermally insulated with it. In addition, when choosing the thickness of the insulation, it is also necessary to take into account the thickness and material of the walls of the building. This will be discussed in detail below.
Varieties of modern thermal insulation materials
In order to insulate the walls of any private house from the inside, you can use one or more types of thermal insulation materials. To understand which of them is most suitable for a particular structure, it is necessary to consider the characteristic features of each of them.
So, the following heat insulators are most often used to insulate walls:
- Mineral wool - glass and basalt, for example. This material goes on sale in rolls and mats.
- Expanded polystyrene - produced in rigid slabs.
- Ecowool. This insulation is made from natural cellulose and is sold in bulk or in the form of mats. The loose version of the material can be applied to the walls using the “wet” spraying method or simply poured into the cavity.
- Polyurethane foam and penoizol. These insulation materials are sprayed onto the walls to form a seamless, continuous coating.
You may be interested in information about what characteristics it has
To take the first step towards choosing a material, you should first consider them positive sides and obvious disadvantages:
| Illustration | Name of insulation | Advantages of the material | Disadvantages of the material |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basalt (stone) wool | - flammability class NG; - has low thermal conductivity; - a modified version of the insulation does not absorb moisture. | - hygroscopicity of conventional, unmodified insulation; - high price. |
|
| Glass wool | - has good thermal insulation characteristics; - high vapor permeability; - affordable price. | - belongs to the flammability class G1 (low-flammability); - hygroscopic; - insufficiently high stability of shapes, poor resistance to vibration influences, tendency to gradual caking; - is not environmentally friendly. |
|
| Ecowool | - environmentally friendly insulation; - low thermal conductivity; - long service life; - resistance to biological damage. | - is a low-flammable material - G1; - hygroscopicity; - when laid dry (in bulk), there is a tendency to caking, and therefore requires periodic replenishment of the thermal insulation layer. |
|
| - low thermal conductivity; - moisture resistance; - light weight of the slabs; - non-toxic under normal temperature conditions; - has a long service life; - has high mechanical strength; - resistant to biological influences. | - flammable (no matter how much they say otherwise); - when melting and burning under the influence high temperatures highlights toxic gas, dangerous to human life; - not vapor permeable (which, by the way, in certain conditions can be regarded as an advantage). |
||
| Polyurethane foam | - moisture resistant; - has markedly low thermal conductivity; - forms a continuous seamless insulating layer; - long service life; - non-toxic under normal conditions. | - belongs to the flammability group G1 (low-flammability); - not vapor permeable (the controversial nature of the defect has already been discussed); - required for application special equipment and experience working with it; - quite high cost of the material and work on its application. |
The table below shows comparative characteristics that allow us to evaluate the parameters of the above materials at the “digital level”:
| Name of material | Density, kg/m³ | Coefficient of thermal conductivity, W/(m×°С) | Vapor permeability mg/(m/h/Pa) | Moisture absorption kg/m² |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glass wool | 15÷40 | 0.039÷0.046 | 0.4÷0.6 | 0.55÷1.0 |
| Basalt wool | 30÷50 | 0.035÷0.042 | 0.4÷0.6 | 0.1÷0.5 |
| Extruded polystyrene foam | 35÷45 | 0.030÷0.035 | 0.0÷0.013 | 0.01÷0.05 |
| Polyurethane foam | 30÷80 | 0.024÷0.030 | 0.0÷0.005 | 0.01÷0.05 |
| Ecowool (mats) | 33÷75 | 0.038 ÷ 0.045 | 0.3÷0.5 | 0.3÷0.8 |
It is necessary to clarify that today modified insulation materials with improved technical and environmental characteristics. However, their production is carried out only by large manufacturers who are highly responsible for the quality and potential capabilities of their products. Naturally, the cost of such products is much higher, but they will also last longer without harming either the building itself or the health of the house’s residents.
You might be interested in information on how to do it correctly
The parameters of such thermal insulation materials will be presented below.
Basalt thermal insulation
This type of insulation materials is called differently stone wool, since they are produced by melting gabbro-basalt rocks. Products made from these raw materials could be called the best option for thermal insulation of surfaces inside the house. If not for one nuance that will be mentioned.
Basalt insulation has very low thermal conductivity. Stone-based materials are more suitable for insulating residential premises, as their fibers are more elastic. Thanks to this quality, the mats have a higher density and also have high strength characteristics. The fibers have a sufficient degree of elasticity and therefore are not as brittle as glass wool.

Basalt insulation is manufactured in rolls and mats. Some material options are equipped with a layer of aluminum foil, which can enhance insulation by reflecting heat flows into the room. In addition, the foil becomes a vapor barrier, which is of particular importance in such conditions.
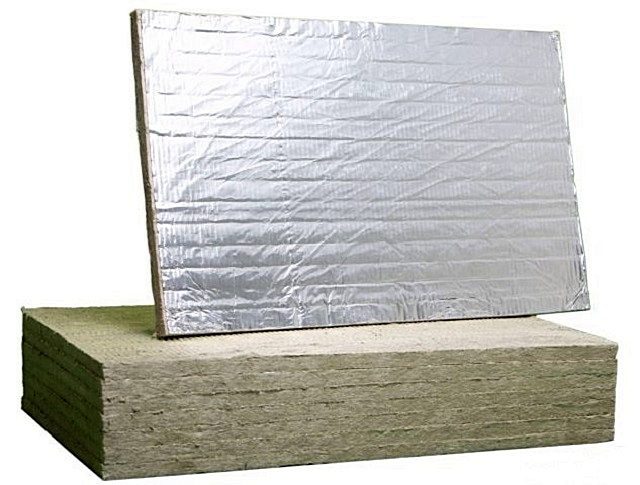

And now - about that very nuance that still calls into question the expediency of such a process as. Let's consider whether it is acceptable to use mineral wool for insulation from the inside?
In general, the optimal structure of an insulation structure is one in which the vapor permeability of each subsequent layer (in the direction from the room to the street) is higher than that of the previous one. In such a situation, water vapor will simply escape unhindered into the atmosphere. Mineral wool placed indoors does not fit these requirements.
The fact is that with such a structure of the thermal insulation “pie”, the dew point will be precisely in the thickness of the mineral wool or on the border between it and the wall. That is, this is where condensation will form during the cold season. Since the vapor permeability of mineral wool will always be higher than that of any wall material, and a high concentration of water vapor in a room is a normal phenomenon, gradual wetting of both the insulation itself and the wall cannot be ruled out.
The solution is to provide an insulating layer reliable vapor barrier from the side of the room so that water vapor simply has no chance of penetrating into the mineral wool. And plus, the house must have effective ventilation. Under such conditions, mineral wool will show all its advantages.
The general characteristics of this insulation were shown in the table above. However, large manufacturers produce improved versions of products, while the technical characteristics of insulation vary in their performance.
« Knauf»
« Knauf" - this is a famous German manufacturer various building materials known to Russian consumers for their quality. The company has been supplying its products to Russia for decades and has established the production of materials directly on the territory of the Russian Federation. And these products fully comply with GOST requirements and sanitary and epidemiological standards, which is confirmed by numerous quality certificates.

« Knauf» supplies to the Russian market several brands of basalt insulation, both universal and intended for different areas of the building. For example, the “Insulation” line of insulation products is a professional-class product and is used for thermal insulation of various objects. For private buildings, the manufacturer has provided a separate line of products that takes into account not only the thermal insulation capabilities of the material, but also the “human factor” - these are “TeploKNAUF House”, “TeploKNAUF Dacha” and “TeploKNAUF Cottage”. All heat insulators are vapor permeable and non-flammable (NG).
Their remaining operational characteristics are presented in this table:
It should be noted that the line of insulation materials produced in the form of slabs has been expanded with the products “Cottage+” and “House+”. They differ from the materials named in the table by their thickness of 100 mm.
"Rockwool"
The Rockwool company is constantly working on modifying its products, improving their characteristics. All lines of basalt insulation from this manufacturer belong to the NG class, that is, non-combustible materials.

Despite the very wide variety of thermal insulation products from this manufacturer, for insulating the walls of a country house it would be optimal to opt for “ROCKWOOL LIGHT BUTTS SCANDIC” or “ROCKWOOL LIGHT BUTTS”

Special processing of the material during its production gives the blocks water-repellent qualities. Particularly convenient is the compact packaging - after opening it, the slabs quickly accept the specified original size. In addition, one edge of the slabs is made “spring-loaded” - for easy and tight installation between the sheathing drains.
The main characteristics of the “ROCKWOOL LIGHT BUTTS” heat insulator are as follows:
| Operating parameters of insulation | Indicators |
|---|---|
| Thermal conductivity coefficient (W/m×°C): | |
| - calculated value at t = 10 °C | 0,036 |
| - calculated value at t = 25 °C | 0,037 |
| - operational under conditions “A” | 0,039 |
| - operational under conditions “B” | 0,041 |
| Flammability class | NG |
| Fire safety class | KM0 |
| Vapor permeability (mg/(m²×h×Pa), not less | 0.03 |
| Moisture absorption when partially immersed | no more than 1kg/m² |
| Dimensions | 1000×600 mm |
| thickness | 50, 100 or 150 mm |
"TechnoNIKOL"
This insulation material is produced by a domestic manufacturer, which is well known to Russian consumers.

Modified basalt wool "TechnoNIKOL" is also non-flammable material(NG) what the manufacturer reports on its packaging. Thermal insulators of this manufacturer are manufactured under strict control, in accordance with established GOST standards, and also fully comply with the sanitary and epidemiological requirements of the Russian Federation.
This table presents the most popular options for TechnoNIKOL basalt insulation, as well as their technical characteristics:
| Material grade | Compressibility, %, no more | Vapor permeability, mg/(m×h×Pa) | Moisture absorption, kg/m² | Density, kg/m³ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| "Rocklight" | 0.037÷0.041 | 30 | 0.3 | 2 | 30÷40 |
| "Technolight" | 0.036÷0.041 | 20 | 0.3 | 1,5 | 30÷38 |
| "Heat roll" | 0.036÷0.041 | 55 | 0.3 | 2 | 25÷35 |
| "Technoacoustic" | 0.035÷0.040 | 10 | 0.3 | 1,5 | 38÷45 |
| "Technoblock" | 0.035÷0.040 | 8 | 0.3 | 1.5 | 40÷50 |
For insulating the walls from the inside of a country house, any brands of “Technoacoustic” are well suited as they have a low thermal conductivity coefficient and optimal density. In addition, “Technoacoustic” is designed to insulate the house from external noise, so it can be called a multifunctional material.
Glass wool
Glass wool is made from fibers obtained by melting broken glass and quartz sand, as well as other natural supplements. Phenol-formaldehyde resins are used as a binder to join glass fibers into a single structure. Slabs and mats acquire rigidity as a result of pressing with simultaneous heat treatment. The heat insulator obtained by pressing glass fibers into blocks or mats has fairly high dimensional stability, but not the most outstanding vibration resistance.

Glass wool is a good sound and heat insulator, is resistant to chemical influences and can withstand temperature changes. Its operating temperature range varies from -60 to + 180 degrees. However, if this is exceeded for now, the fibers themselves are not damaged, but their binding substance is destructured, so the structure of the mats is sintered, deformed or disintegrates.

Experts do not recommend using glass wool for insulation of residential premises. This is due not only to its high hygroscopicity. There is also the possibility of microparticles of fibers getting into the air in the room, which poses a rather serious threat to the health of the residents of the house. Therefore, if for some reason glass wool is chosen for insulation, then after installing it in the sheathing, the thermal insulation should be hermetically sealed with plastic film or vapor barrier membrane. However, as we have seen, basalt wool needs exactly the same protection.
"Isover"
"Isover" is a high-quality heat insulator produced using innovative equipment in accordance with all the requirements of existing standards.

“Isover” is produced in mats and slabs, so it can vary in density. The slab material has a higher density and can be used to insulate walls before plastering. Materials with increased density include “Isover OL-A” and “Isover OL-E”. But plastering mineral wool insulation is only permissible on the outside of the wall.
The manufacturer positions “Isover” glass wool as a non-flammable insulation material, that is, it belongs to the NG class.
There are several options for glass wool on sale, which are designed to insulate various parts of the house. The main characteristics of these products are as follows:
| Insulation brand | Thermal conductivity coefficient, W/(m×°C) | Compressibility, %, no more | Vapor permeability, Mg/(m×h×Pa) | Moisture absorption, kg/m² | Density, kg/m³ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| "Isover Light" | 0.035÷0.040 | 10 | 0.3 | 1,5 | 38÷45 |
| "Isover Standard" | 0.036÷0.041 | 55 | 0.3 | 2 | 25÷35 |
| "Isover Optimal" | 0.036÷0.041 | 20 | 0.3 | 1.5 | 30÷38 |
| "Isover Facade" | 0.035÷0.038 | 30 | 0.3 | 2 | 30÷40 |
In addition to the options mentioned above , Isover also produces other brands of insulation materials. Moreover, the company continues to develop and launch innovative products that can withstand the necessary loads in a certain area of the structure.
"URSA"
Another well-known brand of insulating materials is URSA products. The manufacturer uses innovative technologies in the production of its products, trying to minimize the disadvantages of glass wool. Thanks to this approach, URSA glass wool is characterized by increased durability and particular strength. The density of the slabs and mats greatly simplifies installation work.

Since URSA produces a large assortment insulation products, due to ignorance it will be difficult to choose the required material option. We give a hint - for thermal insulation of a country house, it is recommended to use insulation from the URSA GEO line. They are safe for the health of the residents of the house and are maximally adapted to the conditions of private construction.
The URSA GEO line includes the following products:
| Insulation type “URSA GEO” | Thermal conductivity coefficient, W/(m×°C) | Vapor permeability mg/(m×h×Pa) |
|---|---|---|
| "M-11" | 0.04 | 0.64 |
| "Mini" | 0.041 | 0.64 |
| "A private house" | 0.041 | 0.55 |
| "Universal plates" | 0.036 | 0.51 |
| "Light" | 0.044 | 0.35 |
| "Pitched Roof" | 0.035 | 0.55 |
| "Noise protection" | 0.04 | 0.6 |
| "Framework" | 0.035 | 0.64 |
In addition to those presented in the table, this series of materials also includes other insulation materials suitable for thermal insulation of private houses.
Speaking about any of the mineral wool heat insulators, one cannot help but mention their general disadvantages, which may well affect the choice of material.
- The binder in most brands is phenol-formaldehyde resins, which are toxic substance. Throughout the entire period of operation of the insulated structure, the emission of compounds harmful to humans will be observed. Some leading manufacturers claim that these components are no longer used in the manufacture of their products, as they have been replaced with environmentally friendly binders. It is quite difficult to verify this statement without special instruments, and you have to take it on faith. However, it is better to give preference to insulation materials labeled ECO.

- Another problem with mineral wool is rodents, which adapt well to this material, making their nests and making passages in it. It will be possible to get rid of these neighbors only by dismantling the casing and replacing the insulation with another version. If your country house has taken measures to protect against these ubiquitous animals, then you can purchase mineral wool for wall insulation. In another case, it is better to give preference to denser insulation or those options that mice bypass.
Extruded polystyrene foam
Many people think that extruded polystyrene foam is the same as the familiar polystyrene foam. But this is not true at all. Yes, the raw materials for their production are similar, but they differ from each other not only in appearance, but also in their technical characteristics. Until recently, inexpensive foam plastic was widely used for insulation of both internal and external surfaces. However, he has a large number of significant shortcomings, which caused the complete abandonment of this material in many countries around the world.
When starting a renovation, many, wanting to save money, prefer polystyrene foam, but before making your choice, you need to have an idea of its negative qualities.

- Flammability of the material. Polystyrene foam doesn't just burn - it melts and spreads over the surface, becoming a flame spreader. At the same time, such toxic smoke is released from the molten mass that just a few breaths can cause poisoning that is incompatible with life.
- Polystyrene foam (non-pressed polystyrene foam) is a polymer that is not chemically stable enough. And with prolonged use under the influence of temperature changes and other external factors, it also begins to release substances harmful to the environment - free styrene. These fumes will not be able to be contained by the plaster or brick layer, and they will penetrate into the premises.
- Polystyrene foam is breathable, and therefore mice can easily live in it. They not only easily gnaw through this material, but also make their nests in it. This is especially common when foam plastic slabs have a fairly large thickness of 70÷100 mm.
- Polystyrene foam is short-lived, it deteriorates quite quickly - it begins to crumble. As a result, the material loses its thermal insulation qualities.

Extruded polystyrene foam is made from the same raw materials as the familiar polystyrene foam. But in its production a completely different technology is used.
The fine-cell structure of polystyrene foam boards is created by melting polystyrene granules. Foaming and strengthening additives are added to the molten mass. Compositions that do not contain freons are used as foaming agents.
The advantage of extruded polystyrene foam is its high density. Thanks to this quality, the material is not attractive to mice. Plus, it is impenetrable to steam and air, so rodents do not make nests in it. The maximum they can do to harm it is to gnaw off its edges.
Extruded polystyrene foam is non-hygroscopic, has a distinctly low thermal conductivity coefficient, high compressive strength, and has good frost resistance. In addition, insulation is not susceptible to biological damage and chemical decomposition, so it is often used even for insulating the foundations of buildings.
However, as regards its flammability, this is a controversial issue. Manufacturers position polystyrene foam as highly flammable and self-extinguishing, that is, does not support combustion. Practice shows that it still ignites when exposed to open fire, is often capable of supporting combustion, and, just like polystyrene foam, emits toxic smoke. They are trying to combat this - many materials in this group undergo special treatment to increase their fire resistance. But it’s still a long way from being inflammable!

Extruded polystyrene foam has almost zero vapor permeability. And this factor is just right for insulating walls from the inside. That is, the laid layer of slabs itself becomes a good vapor barrier, and the structure of the material inside will definitely always be dry, that is, there is simply nothing to condense in it. True, this still does not eliminate the need to create a general hermetic vapor barrier under the finishing layer, or at least from hermetically “sealing” the seams between the slabs laid on the wall. The requirements for creating effective system ventilation - they are required for any type of internal insulation.
On construction market Both well-known and completely unknown manufacturers present their products. Sometimes you can find slabs that do not have any markings at all. It is clear that one cannot expect any guarantees from such materials. Therefore, if the choice is made on this particular insulation, then you should give preference to well-known brands.
"Penoplex"
The most popular on the Russian market is extruded polystyrene foam “Penoplex”. These are products of a domestic manufacturer, which produces several types of material that differ in some characteristics.

The names of the plates indicate their purpose - this universal material“Comfort”, “Roof”, “Foundation” and “Wall”. Accordingly, for thermal insulation wall surfaces two types of slabs are used - “Comfort” and “Wall”, performed with “Roof” slabs, etc.
Penoplex slabs (this is the colloquial name most often used) are produced in a wide range of thicknesses - from 20 to 100 mm (20, 30, 30, 50, 60, 80 and 100 mm). Linear dimensions - 1200×600 mm. Comfort type slabs can be produced in lengths of 2400 mm.
The main characteristics of the Penoplex thermal insulation material specified by the manufacturer are as follows:
— thermal conductivity coefficient – 0.030 W/(m×K);
— moisture absorption – no more than 0.2÷0.4% of the total volume;
— vapor permeability – 0.007÷0.008 Mg/(m×h×Pa);
— flammability group - G2 – G4;
— operating temperature range – from -50 to +75 °C;
— durability declared by the manufacturer is 50 years.
- "Penoplex S" is designed for thermal insulation of walls. Contains fire retardant components that reduce the risk of fire. High thermal insulation properties, minimal moisture absorption, resistance to temperature changes, as well as grooves provided for connecting the slabs, make the insulation of the walls of the house reliable and durable.
- "Penoplex Comfort" is universal option slabs that can be used in different areas buildings, from the roof to the foundation. In this regard, it can well be used to insulate the walls of a country house from the inside.
- "Penoplex F" is intended for thermal insulation of the foundation. Due to the fact that this insulated area of the building is located in the ground, the slabs are manufactured without the addition of fire retardants. Therefore, it is not recommended to use them for installation in other areas, since they belong to the G4 flammability group.
- “Penoplex K” is used for insulating roofs and ceilings, but it can also be used for thermal insulation of wall surfaces.
You may be interested in information about what kind of insulation
"Styrodur"
Styrodur extruded polystyrene foam boards are not as popular as Penoplex, although they also have decent technical characteristics.

Several types of this thermal insulation material are available for sale - these are 2500 C, 2800 C, 2800 CS, 3035 CS, 3035 CN, 4000 CS, 5000 CS. The difference between the slabs primarily lies in their density and compressive strength. The surface of all slabs is protected by a smooth, more durable layer of material, and Styrodur 2800 C and Styrodur 2800 CS are equipped with a grooved surface.

To prevent the formation of cold bridges at the joints of the slabs, there can be provided at their ends various options docking locks. This is also how the plates differ from each other.
Due to its strength characteristics, as well as different configurations of locks, this insulation is well suited for internal insulation of house walls.
| Name of characteristics and units of measurement | Digital marking of Styrodur insulation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2500 C | 2800 C | 3035 C | 4000 C | 5000 C | |
| Dry thermal conductivity coefficient, W/m×K | 0.029 | 0.029 | 0.029 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| Density (not less), kg/m³ | 25 | 30 | 33 | 35 | 45 |
| Moisture absorption in 24 hours, % of volume | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.07 | 0.07 |
| Compressive strength at 10% linear deformation (not less) | 0.2 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.7 |
| Surface of slabs | smooth | grooved | Smooth or grooved | smooth | smooth |
| Linear dimensions of slabs, mm | 1250×600 | 1250×600 | 1265×615 | 1265×615 | 1265×615 |
| Slab thickness, mm | 20,30,40,50,60 | 20,30,40,50,60 | 30,40,50,60, 80, 100, 120, 140, 160 | 30,40,50,60,80 | 40,50,60 |
| Operating temperature range, C | -180...+75 | ||||
| Flammability group | G2 | ||||
| Frost resistance | More than 300 cycles | ||||
Styrodur boards are produced only in light green color, so they are difficult to confuse with other similar materials. The heat insulator is non-toxic under normal operating conditions; freon is not used in its production. In addition, the material is odorless, so it can be used for insulation. internal surfaces residential buildings.
Polyurethane foam
Polyurethane foam, like effective insulation, appeared in the public domain relatively recently, but has already managed to prove its reliability in thermal and sound insulation of premises. Polyurethane foam is applied by spraying, for which special equipment is used. The material can be applied in several layers to achieve the required thermal insulation thickness.
The composition applied to the surface, after foaming and polymerization, forms a monolithic layer on it, as it expands and fills the space. In addition, the finished mass has excellent adhesive properties, so when sprayed, it is firmly fixed to almost any surface of the walls and ceiling.

This material is used for thermal insulation of both internal and external surfaces, and is especially suitable for use in regions with low winter temperatures. The thermal conductivity coefficient of polyurethane foam is very low, ranging from 0.025 to 0.030 W/m×K. That is, among the insulation materials under consideration, it is an absolute “champion” in this indicator.
Due to the fact that the structure of polyurethane foam decomposes under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, it must be installed under decorative cladding.

When insulating a house from the inside with this material, a frame structure is installed on the wall to secure the facing material. And between its racks and jumpers the composition is sprayed. After the polyurethane foam applied to the wall or ceiling hardens, the excess that protrudes beyond the frame, formed during its expansion, is cut off.
You might be interested in information on how to do it yourself
Polyurethane foam has a low moisture absorption index, therefore it retains its thermal insulation qualities at any ambient humidity. Vapor permeability is practically zero. And since the coating is seamless and continuous, you can even do without additional vapor barrier.
This material can belong to different fire safety groups - from G1 and even to G4, depending on the additives added to the composition. However, polyurethane foam, as a rule, does not become a source of fire and does not spread fire. It quickly chars, stopping the flow of oxygen necessary for combustion deep into its structure. But the gases formed during thermal decomposition are still not as dangerous as those of expanded polystyrene.
Excellent material for internal insulation. But it requires special raw materials and equipment for its application, as well as work skills. And the cost is very high. All this limits him wide application for such purposes.
Ecowool
Ecowool is a material that is not yet familiar to everyone, and therefore not so popular. But it is successfully used for insulating residential buildings both inside and outside. The main advantage of this insulation is its environmental friendliness. Ecowool is made from cellulose fibers that are processed boric acid, which protects the material from mold and makes it unattractive to rodents.
Slabs are formed from the fibers, or ecowool is sold in bulk and intended for installation using the so-called “wet” method - spraying.

Loose ecowool is also used in dry form; most often this method is used for thermal insulation of horizontal surfaces, for example, ceilings or floors in the house. Another method of insulation is filling closed spaces (specially provided cavities) with dry ecowool. For example, in a frame partition sheathed on both sides with plywood sheets.

The “wet” method of application can be called the optimal installation option. However, this process is complicated by the fact that it requires special equipment. This means that you will have to invite a specialist for insulation.
Ecowool applied “wet” forms a monolithic seamless layer on the surface that reliably protects the premises from the cold. The material retains its thermal insulation qualities throughout its entire service life.
If you plan to do the insulation yourself, then the best option would be ready-made, molded slabs. They are installed between building sheathings in the same way as mineral wool, by surprise. Of course, with internal insulation, this will again require a reliable vapor barrier - ecowool has considerable hygroscopicity.
When installed dry, both on horizontal surfaces and when filling empty spaces, the wool may shrink over time. Therefore, when carrying out insulation, it must be well sealed.
Ecowool in its flammability belongs to group G1 (weak flammable material) due to special processing in the production process. When burned, cellulose does not release toxic products that are excessively dangerous to humans.
There are several varieties of this material from different manufacturers on the market. For example, it is worth paying attention to the Finnish manufacturer Termex.

Ecowool "Termex" goes on sale in packages weighing 13 kg and has the following characteristics:
— thermal conductivity coefficient 0.040 W/(m×°C);
— density, depending on application - 35÷79 kg/m³;
— sound insulation capabilities with a layer of 25 mm - 9 dB.
Ecowool freely allows water vapor to pass through, and for external insulation, you can’t think of anything better. But for the internal, this again becomes a problem, which has already been mentioned more than once above. Such a thermal insulation structure will require a very reliable vapor barrier. Ecowool has considerable hygroscopicity, and without such protection it can soon literally swell with water, losing all its insulating qualities.
* * * * * * *
In order for the insulation of a country house to be high-quality and safe, when choosing a thermal insulation material, it is necessary to carefully study its characteristics, as well as methods of application with all the nuances. It is recommended to purchase insulation famous manufacturers who have been working in the building materials market for a long time and have managed to gain authority.
As we have seen, insulation materials can be produced in a wide range of thicknesses. And the thickness of the layer of polyurethane foam or ecowool can be adjusted by the employee. In any case, you need to know what thickness of insulation will be guaranteed to cope with the task of reliable thermal insulation of walls assigned to it. And this issue should also be considered.
What thickness of insulation will be required?
Each home owner is able to make such a thermal calculation. Now we will “arm” him with an understanding of the calculation algorithm and a convenient online calculator.
What is the calculation based on?
Try to imagine any abstract insulated structure. Since our theme is a wall, we will leave this example.
So, a multilayer structure will include the actual wall of the house, made of one material or another. Often, it is finished on the outside. The same is true on the inside, as well as a layer of insulation, the thickness of which needs to be found.
So that the premises of the house are maintained comfortable temperature at any time of the year, this entire multilayer structure must have a certain total heat transfer resistance. And it consists of the resistances of each layer.
Here it is appropriate to make a reservation - the external façade finishing, organized according to the ventilated façade system, is never taken into account. It does not make any contribution to the overall insulating qualities of the wall.
Where can I get the necessary data?
What the total resistance should be is shown by its normalized value established by SNiP for each region, taking into account climatic features. This indicator can be easily clarified at any local construction organization. Or, what’s even simpler, identify it using the diagram map below. In this case, for further calculations it is necessary to take the value “for walls”, which are highlighted in purple.

The thermal resistance of any layer is easy to determine - to do this, the thickness of the salt (expressed in meters) must be divided by the tabulated thermal conductivity coefficient of the material from which this layer is made.
Rc =Hc/λc
Rc- thermal resistance of the layer, m²×K/W;
Hc- layer thickness, m;
λc- coefficient of thermal conductivity of the material, W/m×K.
It is clear that there is little point in taking into account layers that are too thin (for example, membranes). But some options for external and interior decoration are quite capable of influencing the overall thermal characteristics of the wall structure.
So, if you calculate all the thermal resistances of the layers planned for future construction and sum them up, this will still not be enough to achieve the normalized value. This very “deficit” should be covered by a layer of thermal insulation. The difference is known, the thermal conductivity coefficient of the insulation is also known, which means there is nothing stopping you from finding the desired thickness:
Well =Ry × λy
Well- required insulation thickness, m;
Ry- "shortage" thermal resistance which needs to be replenished with thermal insulation;
λy- thermal conductivity coefficient of the selected insulation material.
To make the task as easy as possible for the reader, a special online calculator has been compiled. When carrying out calculations, you don’t have to take into account the insulating qualities of the finishing layers - simply their thickness is left by default equal to zero. As for the rest, everything is simple and probably does not require much additional explanation.
The result will be immediately shown in millimeters - it’s more convenient. The obtained value is minimal, and it is usually reduced to standard thicknesses of insulating materials, somewhat rounded up.
Insulating a dacha is an activity that should not be postponed, but completed before the weather gets colder. You should know that the insulation procedure itself concerns many elements of the building, moreover, it can last several weeks. But something else is more important - to choose the materials and execution technology wisely, since this determines how effective the result will be. It is worth adding that with the help of the simple techniques described in the article, you can save a little on thermal insulation.
So, how to insulate a country house? Let’s immediately say that insulation can be of two types:
- external;
- internal.
Let's look at the features of each of them.
External insulation of the cottage
Such insulation can protect not only the room from freezing, but also the material from which the building is made. In this case, the “dew point” will shift towards the street, and condensation will form outside the elements made of wood, and under the ventilated facade (the moisture under it will soon dry out).
Let's look at how external insulation is produced.
Stage one. Material selection
In this case, it is better to use mineral or basalt wool. In the case of wooden structures (and country houses are often wooden), it is undesirable to use polystyrene foam, since it is vapor-tight and therefore does not remove steam from the surface. Mineral wool can have different densities and thicknesses. The denser it is, the easier it is to install and the longer it will retain its original properties. Loose insulation will slide and crumble, spreading dust harmful to the body. In short, you shouldn’t skimp on the quality of insulation material.

Note! The advantages of the material also include the fact that it does not burn and rodents do not “like” it, which distinguishes it favorably from the same foam plastic.
In addition to the heat insulator itself, the work will require a film that will be laid in 2 layers - one to protect against moisture penetration, the other for wind and water protection. The film is placed on wooden surfaces. What is characteristic is that it must be vapor-permeable and remove moisture from the wood to the outside through insulation. Wind protection is installed on top of the heat insulator, and it is absolutely necessary.

The outside insulation layer can be covered with any material, but a gap must be left for ventilation. This design is called a ventilated facade. Air will circulate between the facing surface and the walls, due to which moisture will be removed from the mineral wool. This will increase the service life of the building as a whole.
Stage two. Warming procedure
Below is an algorithm of actions for thermal insulation of a country house.
Step 1. First, the walls are treated with an antiseptic, in two layers. Extreme attention should be paid to the corners, as well as the crown located below. The ends of the logs should be treated with special care, because they are often the most susceptible to rotting. The application of the antiseptic itself is carried out in dry, warm weather, after which the walls are left for a couple of days so that the product dries completely.

Step 2. Next, an insulating film with a vapor-permeable coating is attached to the walls (a mounting stapler is used for fixation). The coating of the sides of the film may vary. In this case, the porous side goes towards the wall (it absorbs and removes excess moisture), and the smooth glossy side goes towards the street. The film is attached with an overlap of 10 centimeters, all joints are taped with mounting tape.
Step 3. A vertical type of wooden sheathing is installed on top of the film (it is constructed from bars, the thickness of which is equal to the thickness of the insulating material). The step between the beams should be 4-5 centimeters smaller than the width of the mineral wool mats. In this case, the material will fit tightly to the sheathing and will be held there well even without additional fixation.

Step 4. We continue to figure out how to insulate a country house from the outside. Mineral wool slabs are laid on top of the film between the sheathing bars, pressing each of them a little. If necessary, the material is cut using regular knife. If the material is not hard enough or is poorly held inside the sheathing, then it can be temporarily fixed with slats. The final fastening of the mats is done using anchor nails.
Note! If thermal insulation is laid in several layers, then the new layer is laid with offset joints - that is, so that the sheets overlap the joints of the previous layer.
Another important point: all work related to the installation of mineral wool slabs must be carried out exclusively in a respirator and special protective gloves.

Step 5. A layer of wind and waterproof membrane is laid on top of the wool (staples are used again). It is important that the side with waterproofing “looks” towards the street. The material is laid with an overlap, the joints are still sealed with mounting tape.

Step 6. A ventilated frame is installed on the film. It is made from the same beams that were used for the sheathing. In this case, there should be a slight gap (about 50 centimeters) between the insulation and the frame for ventilation. The bars are installed to the previous frame using self-tapping screws, and if the surface of the walls is sufficiently flat, then perforated profile hangers can be used, thanks to which the distance to the frame can be adjusted.
- vinyl siding;
- imitation timber;
- metal profile;
- block house.

During finishing, you need to pay attention to ensure that there are no gaps left, otherwise moisture will seep through them into the structure.
Video - Sheathing and insulation of a wooden house
Is internal insulation necessary?
We find it difficult to answer this question, since approaches to insulation can be radically different. Thus, some builders do not favor internal thermal insulation, explaining this by the fact that ventilated siding, which requires the same costs, is much more effective, and there is less fuss with it. Let's try to find out if this is so.


How to insulate a frame house?!
Previously, we talked about what materials should be used when insulating a frame house and fully described the insulation technology; in addition to this article, we advise you to read this information
First, let's look at the main problems that may arise before insulating a country house. If you use materials intended for outdoor work, when insulating ceilings, walls, etc. internal surfaces, they will “eat up” a significant part of the free space. After all, high-quality thermal insulation is a mandatory sandwich (it is described above), the thickness of which can reach 80-100 millimeters. Another problem is that when a cold wall comes into contact with warm air in a building, condensation can form on its surface. Because of this, the air in the house will be constantly damp, and the materials used for insulation will begin to rot or lose their original properties.
Is it possible to avoid all these troubles? Yes, if you approach the issue wisely and do everything using the technology given below.
Stage one. Selection of insulating material
In this case, the requirements for the heat insulator are somewhat different than if the insulation was carried out outside.
Note! But the main requirement remains - minimum vapor permeability, although this parameter can be compensated by good vapor barrier.
Insulation for interior work must also be environmentally friendly - this is perhaps the most important point that you should pay attention to when purchasing. Next criterion– this is thermal conductivity, which determines what thickness of material needs to be installed. Obviously, it is not advisable to use thick insulation in a country house, because, as noted above, it will reduce the free space inside the building.

As a rule, mineral wool is used for insulation. It is environmentally friendly, and other characteristics have already been discussed at the beginning of the article. However, it is more suitable for outdoor use. Why? Because it has high vapor permeability. Moreover, it also has poor hydrophobicity - mineral wool absorbs moisture, which is why it breaks down faster. Therefore, extruded polystyrene foam is more suitable for internal insulation. This is an environmentally friendly and effective heat insulator with minimal vapor permeability. It also does not absorb moisture, which is also very important. Finally, an ordinary country house will require a much thinner layer than if mineral wool were used. Installation does not require the construction of a frame - the material is simply placed on glue.

Stage two. Wall insulation
The walls are insulated with one layer, and it is necessary that the surface be previously prepared. The sequence of actions is given below.

Step 1. Remove everything unnecessary from the room - furniture, decorative elements, mirrors, etc. Wallpaper (if any) must also be removed.
Step 2. Wall surfaces are cleaned of dirt. All detected irregularities are sealed with plaster.
Step 3. After hardening plaster mortar The walls are covered with two layers of primer mixture.
Step 4. The foam sheets are laid bottom up. Used for fixation special glue– it must be applied evenly over the entire back side of each sheet.

Dowels may not be used. The main thing is to ensure that the insulation fits tightly to the walls.

Step 5. The joints between the sheets are sealed with sealant or glued with reinforcing tape. It is worth remembering even before insulating a country house from the inside that polystyrene foam does not require additional installation of vapor barrier.

Step 6. A sheathing is constructed on top of the insulation, on top of which the previously selected finishing material will be installed.
Stage three. Floor insulation
Using polystyrene foam, the floor can be insulated both along the joists and when poured with concrete. In the first case, slabs of material are simply adjusted in size and placed between the joists. There will be no load on the slabs here, so almost any type of polystyrene foam will do.

But if the screed is to be insulated, then the heat insulation slabs must be very strong. Algorithm of actions for insulating the floor under concrete pouring as follows.
Step 1. A film is laid for waterproofing. This must be done with an overlap of approximately 100 millimeters.
Step 2. Insulation boards are laid.


Step 3. A reinforcing mesh is installed on top of it (you can use an ordinary solution to fix it).
Step 4. At the end, a finishing screed is performed (in most cases, a thickness of 60-80 millimeters is sufficient).

Stage four. Ceiling insulation
The ceiling can also be thermally insulated with polystyrene foam boards. The sequence of actions in this case will be as follows.
Step 1. The ceiling surface is cleaned of dirt; if necessary, uneven areas are sealed with plaster (the same as in the case of walls).
Step 2. The back side of each foam board is evenly coated with a special adhesive composition.
Step 3. The plates are glued to the surface one by one.

Step 4. Once the glue has dried, the slabs of material must be additionally secured with umbrella dowels.
Step 5. A putty mesh is laid on top of the thermal insulation material.
Step 6. The ceiling is covered with a layer of putty.

Video - Thermal insulation of a country house
Stage five. Roof insulation
As far as we know from school course physicists, streams of heated air always rise upward. Consequently, if the roof of a country house is not properly insulated, then most of the thermal energy will simply leave the building.

To carry out internal thermal insulation of the roof, you must first of all build a wooden frame (it will be somewhat reminiscent of the sheathing described above). To construct the frame, beams are used; they are attached to the roof with nails or self-tapping screws. Alternatively, instead of wooden frame you can use metal profiles (the same as when constructing a base for plasterboard structures).

Insulation material is placed between the bars. If mineral wool is used as such, then additional anchoring will be required. If we are talking about expanded polystyrene slabs, then it is quite enough to trim the material so that it fits tightly between the beams. Actually, ideally you need to lay two layers at once - mineral wool and expanded polystyrene. All this can be sheathed using thin sheets of chipboard.
Video - Roof insulation
Finally. Basic requirements for internal insulation
So we figured out how to insulate a country house. All that remains is to become familiar with the key requirements put forward for this process.
- A vapor barrier film is a prerequisite for high-quality thermal insulation. Moreover, you should not skimp on the film (in principle, the same as on the material that will be used to seal its joints).
- Before laying insulating material, all working surfaces must not only be thoroughly cleaned, but also coated with a special compound that will prevent mold in the future.
- The thermal conductivity of the material used should be minimal. Ideally, this indicator of the heat insulator should exceed that of the wall itself.
- The thickness of the insulating layer should be calculated with maximum accuracy, and should be based on the specific climate conditions in your region.
- During insulation (internal), you need to ensure that there are no voids left between the material and the surface of the walls. In order for the contact to be extremely tight, the glue must be spread evenly over the back side.
- To reduce humidity inside the building, it is recommended to take care of forced ventilation.