Installation of a single-pipe heating system using polypropylene pipes. Installation of a single-pipe heating system using polypropylene pipes - single-pipe system Thermal power of the air curtain
For organizing heating one-story houses influenced by a lot of factors, which makes it possible to implement various systems heating, optimal in specific conditions. The main thing is the purpose of the housing ( permanent residence or only seasonal holidays). In addition, the materials from which the structure is constructed, its parameters, terrain, etc. are taken into account. In small summer houses heating stove or electric types, and in large country cottages, far from settlements, – liquid-solar.
The autonomy of the heating system from external energy sources (electricity, gas, etc.) is of great importance.
There are several types of private heating designs one-story house:
- Gravity;
- Single-pipe;
- Two-pipe.
Gravity option
Gravity heating scheme. Click on photo to enlarge.
It is the simplest and most primitive. Consequently, such a system is cheap and not too difficult to implement, since it depends on the layout of the home. But this is where its disadvantages lie. It is a large metal pipe connected to the boiler and passing throughout the house (this is a prerequisite), through which the coolant flows.
The disadvantage of this scheme is the need for massive pipes with a large cross-section in diameter, since installing thinner ones or adding batteries to the system leads to a decrease in heating efficiency due to a decrease in the water flow rate. In order to increasing efficiency For this heating system, not one, but two pipes are installed in the house, which causes even greater inconvenience to the residents.
Single-pipe arrangement
This option is also easy to assemble and install, so you can install it yourself. It largely replicates the gravity system, but differs from it in the presence of a circulation pump - there is also a pipe (but already equipped with heating radiators), a boiler and a pump, which can be either separate or integrated into the boiler. It is the pump that is responsible for the water cycle in the system.
The optimal one is closed system, the design of which does not have an expansion tank (separate), which is facilitated by the presence on the market of boilers with integrated tanks. This solution makes it possible to prevent the formation of corrosion spots, which is very important if there is no anti-corrosion coating on the metal.
Two-pipe scheme
This layout is optimal for a one-story house. It consists of a boiler to which 2 are connected metal pipes– for supply and return flow. Hot water is supplied to the first, and cooled water is supplied to the boiler from the second. This arrangement is not only simple and convenient to use, but also allows you to heat the room with maximum efficiency and use energy rationally. It has only one drawback - high price installation, but over time it pays off.
Such heating schemes allow you to save considerable money on heating, are reliable, and are also relatively easy to install and easy to use. And most importantly, they relieve homeowners from having to wait for the start of the heating season.
Two-pipe heating circuit

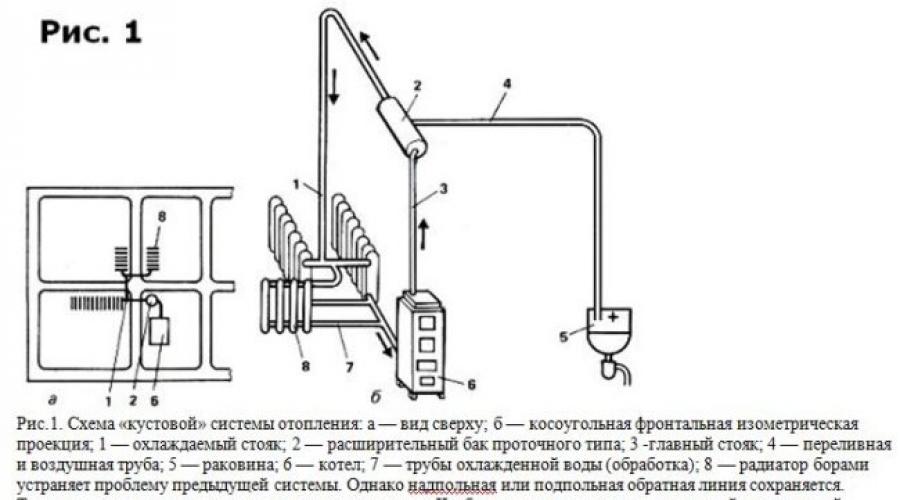
Diagram of a cluster heating system. Click on photo to enlarge.
Its difference from a single-pipe is that instead of one pipe through which the supply occurs hot water, and cold selection, there are two. Each of them performs only one function.
The first picture shows a cluster system, characterized by the installation of pipes for hot and cold water at the same level as heating appliances. This allows you to achieve minimum flow by moving the pipes. Its location allows you to simultaneously heat several rooms in the room. This arrangement is suitable for southern regions, because the warm climate allows you to efficiently heat rooms, regardless of long interruptions in the combustion of fuel under the boiler.
There are differences in two-pipe heating systems for one- and two-story buildings. In the first case, pipes supplying hot and cold water, as well as a riser, are one and the same thing. In a two-story building, there is a clear distinction between these components. For example, in railway cars, hot water is supplied from above, and cold water is discharged from below.
A similar system can be implemented in a residential building by running a pipe with cold water right next to the floor. But this is hampered by doors, which can be bypassed in two ways:
U-shaped piece of pipe - to go around them from above;

Figure 3 (Schemes of two-pipe single-story systems heating). Click on photo to enlarge.
Installation under the floor - in this case, the inconvenience is to avoid connections in the underground space.
After all, the pipes will have to be laid under the floor (possibly the entire line) and insulated in order to avoid freezing in the cold months. Consequently, if a leak occurs, it will not be possible to detect it in time and eliminate it. For pipes with hot water the optimal place will be the space under the ceiling (about 50 cm from the ceiling). One of the disadvantages is heat loss through the ceiling. This can be solved by installing pipes in the attic with careful insulation, but you will have to sacrifice aesthetics and drill holes in the ceiling.
Figure 3 (options “b” and “c”) shows the location of the outlet pipes next to the pipes for supplying hot water. Such a system is appropriate if it is not possible to place discharge pipes from below. Figure 3 (option “d”) shows a diagram of the installation of hot water pipes under window sills, as well as above heating appliances. This decision, provided that the underground and above-floor lines are preserved, eliminates the disadvantages of the previous layout, but leads to slower heating of the entire system and necessitates the installation of a flow-through expansion tank(Figure 3, option “d”).
Self-installation of a heating system
Initially, you need to purchase all the components of the water heating system, and then begin its installation:
- Boiler - its type and characteristics depend on the dimensions of the building and other factors;
- Radiators;
- Pipes, as well as the required number of connecting components;
- Pressure gauge;
- Circulation pump - it is only necessary if a heating circuit with forced-type water circulation is installed;
- Shut-off valves.
The boiler power is determined depending on the area to be heated. As a rule, a 25 kW boiler is enough for a building with an area of up to 200 m². Most often, a gas boiler is installed as the simplest and relatively affordable one, but only if its installation does not cost too much.
If the choice fell on the stove, then you need to create a circulation system ( natural type). The stove must be located on the same floor as heating elements, install pipes large diameter subject to min shut-off valves. Installation of a coil-type boiler takes place in the furnace itself, which ensures rapid heating of water.
The efficiency of this system is ensured by a relatively short line. The choice of pipes must be approached very responsibly and focus not only on the diameter, but also on the material. When purchasing rolled metal pipes, you need to take care of protection against corrosion, which requires purchasing products made of galvanized or stainless steel.
Ideally you need to purchase copper pipes, because this material is optimal from the point of view of installing water heating. But the high cost prevents them wide application. The same applies to the rest of the system components. The installation of the heating system begins with installation heating boiler, after which comes the turn of pipes and batteries in pre- drilled holes in the ceiling, walls and floor. At the end, all elements are connected shut-off valves, final inspection and test run of the water heating system.
Time-tested and sufficient effective way provision comfortable stay The heating in a private house is two-pipe. This heat supply design allows you to regulate the degree of heating of each room individually, without changing the temperature in other rooms.
A two-pipe heating system for a private house can be used regardless of the number of floors of the building. Distinctive feature This heating method consists in separating the forward and reverse movement of the coolant along the contours of the structure. Read also: "".
Heated liquid from the boiler enters the system through the supply pipeline, it is distributed through radiators, coils and supplied to the “warm floor” system. After going through these elements heating structure, the cooled coolant is discharged back into the boiler using a return pipe.
Advantages two-pipe system heating are obvious:
- ease of adjusting the supply of coolant to each heating battery (read: " ");
- can be used not only in residential one-story buildings, but also in multi-storey buildings;
- It is possible to install a system even of considerable length.
Features of the two-pipe heating system
It is possible to install a two-pipe heating system, not only with natural circulation of a liquid heat carrier, but also with forced movement using a special pump. The choice of circulation method is usually influenced by the layout of the forward flow pipe, which can be upper or lower.
The upper wiring method involves laying a straight pipeline at a considerable height, which ensures sufficient pressure to move water through heating batteries without using a pump.
The two-pipe design with top wiring looks more aesthetically pleasing and allows the direct current pipeline to pass over doorways throughout the building, as in the photo. It can be hidden under decorative finishing elements.
If two-pipe is selected horizontal system heating with a lower version of the distribution of the supply pipe, it is located below the window sill (read: ""). Then there are no problems with the placement of the expansion tank open type in a heated room. It can be placed in any convenient place, but above the level of the straight pipe. True, in this case you cannot do without the use of a circulation pump. It is also impossible to create a passage through the entrance doorway.
When a two-pipe heating system is created for a one-story house and the boiler is mounted close to the entrance to the house, heating circuit should be laid around the perimeter to the door or divided into two independent lines, each of which has its own direct pipe and return pipe.
The circulation pump is located in the return pipeline so that heat coolant at the outlet of the heating boiler did not damage the device. Expansion tank membrane type With closed camera usually placed near the boiler.

A do-it-yourself two-pipe heating system is made using main pipes with a diameter of 25-32 millimeters, but if the system has a significant length, products with a diameter of 50 millimeters or more are used (more details: "").
To connect radiators, use one of existing schemes connections. The most effective are the lateral and diagonal options. Bottom connection They are used very rarely - when installing batteries of small height, in which the main straight pipe is located above the radiators. For this reason, preference is given to floor-standing boilers.
Two-pipe systems in a two-story private house
Creating two-pipe heating two-story house, a number of nuances should be taken into account (more details: " "). So, if the heated rooms on both floors are not separated by constantly closed doors, then the flow of heated air from the first floor will rise to the second (read: ""). As a result, the microclimate in the house will not be comfortable, since the rooms below will be cool, and the rooms above will be hot and stuffy.This problem can be solved in one of two ways:
- on the top floor, instead of radiators for heating, heated floors are installed;
- distribute the number of batteries so that approximately 2/3 of the sections are installed on the ground floor.

In addition, if a two-pipe heating system is designed multi-storey building(from 3 floors or more), it is advisable to place on the lower level rooms that require less stable heating - a library, kitchen, laundry room, living room (read: " "). But bedrooms and children's rooms should be on upper floors, since they require more heat (read also: " ").
Features of creating a two-pipe heating system:
- You should install a boiler that has enough power to heat all rooms in the house. The work is carried out strictly according to the instructions.
- The expansion tank is mounted in a place specially prepared for this purpose. An open-type container with an upper direct supply wiring method is located in the attic or attic. When the tank is installed in an unheated room, it is insulated and a signal pipe is installed, which will warn that the tank is full. A pipe is cut into the top of the tank and led into the bathroom to drain excess liquid if necessary.
- The circulation pump is mounted in the return pipe in front of the boiler.
- Experts recommend when self-installation first study an example of calculating a two-pipe heating system and make the appropriate calculations.
- To remove air trapped in the system, Mayevsky taps are installed.
- When installing a straight coolant supply pipe, ensure a stable slope of approximately 1 centimeter for each linear meter. It is done in the direction away from the heating boiler. When arranging the return lines, they act in a similar way; a two-pipe heating system in a private house provides for this, but the slope is made towards the heating unit. Therefore, the highest point of the return pipe should be located at maximum distance from the boiler.
- Having completed the installation, pressure testing is carried out and the system is filled with liquid coolant. The heat supply to the batteries is adjusted using taps and the temperature is observed to remain stable for one to two days.
Heating installation in a private house begins after installation in it roofing covering and installation of windows and doors.
IN modern construction to the aesthetics of the premises are put forward increased requirements, which in relation to heating systems involve the installation of heating system communications hidden from view. The pipes are “hidden” in wall grooves or in the floor screed, which is more convenient. If it is not possible to install heating lines in the floor screed (for example, the floor may be wooden), they are installed in the walls.
Blitz conclusion! Installation of home heating is necessary, or rather convenient, to be carried out at the stage of plastered walls, but without a concrete floor screed.
Installation of heating radiators
“Accurate” installation of heating radiators is best done on an already plastered surface, which will avoid their incorrect installation relative to the wall surface.
The optimal option for installing heating radiators may be:
- A radiator is hung on a plastered wall.
- At hidden gasket pipes in the walls, the boundaries of the grooves are outlined.
- The radiators are removed from the hangers and “moved back” sufficiently long distance from the place of work. Agree that extra scratches and abrasions on radiators will not add value to them!
- Grooves are cut in the walls for laying the pipeline.
- The radiators are hung in their places, and then the heating pipes are laid out and connected to the radiators.
- The pipes are fixed in grooves at the points where they exit the wall with alabaster or cement mortar.
- After the solution hardens, the radiators are again disconnected from the system, removed and taken to a storage location that is “safe” for their appearance.
Heating system installation country house“on top” of finishing work can also be done in a hidden way. For this purpose, boxes are used, fixed along the baseboard at the bottom of the walls. In the absence of a specialized structural elements for hidden installation of heating in a private house, you can use a regular plastic box suitable cross-section for electrical work.
Attention! When installing heating systems, it is necessary to ensure that the system does not form high raised “slides” in which air can accumulate, preventing the coolant from passing through the system. For example, when a heating system pipeline bypasses a door opening, it must be done in the floor, and not create an additional huge loop above the top point of the doorway.
If such “humps” are forced to “emerge,” it is necessary to install automatic air valves at their highest points.

Installation of the heating system of a private house must be carried out in warm rooms, since in technical documentation majority polymer pipes The manufacturer declared an operating “installation” temperature of >+5 O C. Operating at lower temperatures leads to an increase in the fragility of the pipe material, reducing the efficiency of welding polypropylene pipes for heating systems and soldering copper pipes.
Important! Optimal time installation of heating in a private house should ensure the possibility of putting the system into operation before the onset of frost.
Pipe routing when installing heating in a private house
Since currently heating systems for private houses with forced circulation coolant in them, then in this section, in order not to spray too much, we will focus on a closed two-pipe heating system with forced circulation.
Methods for arranging pipes when connecting heating radiators to the boiler:
- beam circuit (collector version);
- tee circuit;
- mixed (combined scheme.
Installation of heating in a private house with radial (collector) wiring involves connecting each heating radiator to a pair of collectors with separate pipes: supply and return. Each collector, in turn, is connected to the boiler (or other collector) by a pair of pipes: supply and return.
Installing heating with a collector group gives the heating system some positive and negative qualities:
- the possibility of differentiated regulation of the degree of heating of each radiator or group of radiators;
- lack of connections in the floor and walls (a solid pipe is used from the collector to the radiator);
- it is necessary to allocate space for installation of the manifold cabinet;
- correct installation of the manifold group above the level of the main pipelines, which usually run in the floor, allows you to install air valves on the manifolds;
- significantly increasing cost compared to other installation schemes.


Installation of heating and water supply systems using the tee method involves parallel connection radiators to the supply and return pipes, which usually run just above the baseboard along the walls. If such “main” pipes are of a significant length, it should be possible to install pipes of larger diameter at the beginning of the system (from the riser).
 "Tee" or parallel circuit installation of heating system radiators
"Tee" or parallel circuit installation of heating system radiators IN country houses most common heating system. This is due to the lack of centralized or non-existence in most rural areas main gas pipelines. Boilers are used for heating small sizes working on solids, liquid fuel, electrical energy And natural gas supplied in cylinders. Most commonly used water heating, characterized by simplicity and reliability, compactness and hygiene. The main equipment for this method includes the following elements:
- hot water boiler;
- radiator batteries;
- water pipes;
- expansion tank;
- shut-off and control valves.
Traditionally used heating schemes
Depending on the type of pipe laying route and the connection of pipes to heating devices, the following systems are distinguished:
- Single-pipe. The coolant circulates through one pipe without the use of pumps. Performed on the highway serial connection radiator batteries, from the very last one the cooled medium (“return”) returns to the boiler through a pipe. The system is simple to implement and economical due to the need for fewer pipes. But the parallel movement of flows leads to a gradual cooling of the water; as a result, the media arrives at the radiators located at the end of the series chain significantly cooled. This effect increases with increasing number radiator sections. Therefore, in rooms located near the boiler it will be excessively hot, and in remote ones it will be cold. To increase heat transfer, increase the number of sections in the batteries, install different diameters pipes, additional control valves, and equip each radiator with bypasses.
- Two-pipe. Each radiator battery is connected in parallel to the direct supply of hot coolant and the “return” pipes. That is, each device is equipped with an individual return outlet. With the simultaneous discharge of cooled water into the common circuit, the coolant is returned to the boiler for heating. But at the same time, the heating of heating devices gradually decreases as they move away from the heat supply sources. The radiator located first in the network receives the hottest water and is the first to send the coolant to the “return”, and the one located at the end receives the coolant last with low temperature heating and is also the last to release water into the return circuit. In practice, in the first device the circulation of hot water is the best, and in the last the worst. It is worth noting the increased price of such systems compared to single-pipe systems.
Both schemes are justified for small areas, but are ineffective for extended networks.
An improved two-pipe system is the Tichelman heating scheme. When choosing a specific system, the determining factors are the availability of financial capabilities and the ability to provide the heating system with equipment that has the optimal required characteristics.
Tichelman heating feature
The idea of changing the operating principle of the “return” was substantiated in 1901 by the German engineer Albert Tichelman, in whose honor it received its name - the “Tichelman loop”. The second name is “reverse type return system”. Since the movement of coolant in both circuits, supply and return, is carried out in one, parallel direction, a third name is often used - “scheme with parallel movement of thermal fluids”.
The essence of the idea is to have the same length of forward and return pipe sections connecting all radiator batteries with the boiler and pump, which creates the same hydraulic conditions in all heating devices. Circulation circuits of equal length create conditions for the hot coolant to travel the same path to the first and last radiator and receive the same thermal energy.
Tichelman loop diagram:
The procedure for performing installation work
The work consists of the following operations:
- Boiler installation. Necessary minimum height the room for its placement is 2.5 m2, the permissible volume of the room is 8 cubic meters. m. The required power of the equipment is determined by calculation (examples are given in special reference publications). Approximately for heating 10 square meters. m requires a power of 1 kW.
- Hangment of radiator sections. The use of biometric products in private homes is recommended. After selection required quantity radiators, their location is marked (usually under window openings) and fastening using special brackets.
- Extension of the associated heating system line. Optimal application metal-plastic pipes, successfully withstanding high temperature conditions, characterized by durability and ease of installation. The main pipelines (supply and return) are from 20 to 26 mm and 16 mm for connecting radiators.
- Installation of a circulation pump. Mounted on the return pipe near the boiler. The insertion is carried out through a bypass with 3 taps. It is necessary to install a special filter in front of the pump, which will significantly increase the service life of the device.
- Installation of an expansion tank and elements ensuring the safe operation of the equipment. For a heating system with a passing coolant movement, only membrane expansion tanks are selected. Safety group elements are supplied with the boiler.
For lining with a highway doorways in utility rooms and utility rooms it is allowed to install pipes directly above the door. In this place, to prevent air accumulation, automatic air vents must be installed. In residential areas, pipes can be installed under a door in the body of the floor or bypassing an obstacle using a third pipe.
Tichelman scheme for two-story houses provides a certain technology. Pipe distribution is carried out with tying the entire building, and not each floor separately. It is recommended to install one circulation pump on each floor while maintaining equal lengths return and supply pipelines for each radiator separately in accordance with the basic conditions of the associated two-pipe heating system. If you install one pump, which is quite acceptable, then if it fails, the heating system in the entire building will shut down.
Many experts consider it expedient to install a common riser on two floors with separate piping on each floor. This will allow us to take into account the difference in heat loss on each floor with the selection of pipe diameters and quantities necessary sections in radiator batteries.
A separate associated heating circuit on the floors will greatly simplify the setup of the system and allow for optimal balancing of the heating of the entire building. But to get the desired effect, it is necessary to insert into the contour of the ride balancing valve for each of the two floors. The taps can be placed side by side directly next to the boiler.
Advantages and disadvantages of the Tichelman system
Main advantages:
- versatility for installation in rooms of various purposes, layouts and sizes. Possibility of installation large number devices. Optimal heating country houses with uniform heating for short-term overnight stays in winter time;
- there is no need for complex balancing with the installation of expensive adjustment equipment;
- uniform heating of all rooms in the building with the ability to adjust the heat output of each radiator;
- ease of installation and maintenance of the system;
- long service life and rare breakdowns.
Available disadvantages:
- high cost caused by the increased length of pipelines and the inability to use small diameters;
- It is not always possible to lay the loop around the perimeter of the house due to interfering architectural features (high windows and doorways, flights of stairs and other obstacles).
The emergence of modern circulation pumps with the ability to effectively pump coolants has made the associated heating system one of the most popular.
Having ordered installation work at Thermodynamics company you will definitely receive an additional discount on equipment and materials.
It is advisable to think through the heating system during the construction of the house. It is necessary to provide niches for risers in advance, and if necessary, a separate room for the boiler room. But even if the house has already been built, you can find a way out of any situation, especially since modern technologies they allow it. To begin installing the heating system, the house must have a roof and windows. Pipes can be laid hidden wiring, for example, install them in the floor, in screeds specially designed for this purpose. If it is not possible to do this, then you will have to lay it in the walls. It is more advisable to install the heating when the walls are already plastered, but the screed has not yet been poured, so that after installing the radiators you do not have to pick at the plaster and adjust the terminals. You can carry out installation in this way - first make pipe leads with a reserve, and after plastering the walls, hang and connect the radiators. But this method takes longer. For maximum accuracy, it is better to follow the following technology. First of all, you need to hang all the radiators, but you do not need to remove the film from them until the heating system is started. If the exits to the radiators will pass from the wall, then it is necessary to mark the boundaries of the grooves, remove the radiator and groove places for the pipes. When everything is ready, you need to hang the radiators back, route the heating pipes and connect them to the radiators. It is better to cover the places where the eyeliner comes out of the wall with alabaster. When the solution has hardened, the radiators can be removed and placed away from the place where they will pass Finishing work, otherwise even film will not save them from damage and dust. If the finishing work in the house is completed, there is still the option of installing hidden wiring. Heating pipes can be laid along the walls, below, in boxes specially designed for them. In professional language This installation of pipes is called “plinth wiring”. You can pay money and contact Western pipe manufacturers - you can buy from them ready-made system“plinth wiring”, with all materials and well-thought-out components. But, if you don’t want to pay extra money, you can do this wiring yourself. By the way, you can use plastic ones as boxes. These are often used to hide electric wires. If in heating system your house uses triple wiring, it is better to lay the pipes along the walls, but at the same time retreat 10-15 cm so as not to spoil them when you nail the baseboards. In the last century, heating systems had slopes towards the taps for drainage. Currently designs modern systems they do not allow this to be ensured, and there is no point in doing so. But main point, which must be taken into account when laying - there should be no large “humps” in the pipes, that is, you need to make sure that over time they do not appear in the heating system air jams. If this problem cannot be avoided, there is a way out - you need to install an automatic air vent at the top point. To go around a doorway with pipes, it is advisable to run them along the floor rather than lay them around the entire opening along the top, thereby creating a large loop. It is not advisable to install a heating system in cold rooms. As a rule, manufacturers of polymer pipes warn that you should not install them at temperatures below 7 degrees. The fragility of metal-plastic pipes increases during operation at low temperatures, welding of polypropylene pipes deteriorates, and it is not worth soldering copper pipes at all - low temperature it feels quite strong. Therefore, it is worth thinking in advance and calculating the installation so that the system is launched before the cold weather begins.