Do-it-yourself radiant wiring of a home heating system. How does a radiant heating system work? Diagrams and wiring options Radiant heating system in an apartment building
Read also
Beam wiring: features and elements
Modern multi-apartment residential buildings and private cottages of any number of floors are increasingly equipped with horizontal heating systems. A necessary element of such a scheme is one or more (in apartment building– in each entrance) vertical two-pipe risers, with branches/entrances to separate rooms/apartments on each floor. Further laying of pipelines is carried out in a “horizontal” way.
When installing such systems, builders invariably face the problem of the complexity of installation. heating pipes to the radiators. The pipelines of the vertical systems, laid along the walls from top to bottom, did not particularly disturb the residents. Horizontal pipes laid openly along the walls, become a factor interfering with the normal process of operation of the premises and do not fit well into their interiors. Therefore, various methods of horizontal hidden laying are used.
Pipeline layout in a branched dead-end circuit.
The minimum lengths of pipes and hydraulic resistance of the circuit are leveled by mutual crossing of pipelines, leading to an increase in the thickness of the screed (each centimeter costs from 40 rubles/m2).
- Dead-end scheme with pipelines in the screed or under the baseboard.
Pipeline layout diagram for a two-pipe dead-end system.
The lack of crossing of pipes in the diagram is offset by the need to make holes in the walls (in the given diagram you need to drill five holes).
- Layout of pipelines according to the scheme with associated movement of water (Tichelman scheme).
Pipeline layout according to the Tichelman scheme.
Here, the first radiator of the heating circuit has the shortest “supply” length and the longest “return” length, the last radiator is the opposite. The hydraulic resistance experienced by the coolant when flowing around the devices of the circuit is constant, which makes it possible to balance any number of radiators in a branch.
Pipeline layout for a collector-beam system.
The prevalence of this scheme is constantly growing. The pipes here are laid in the floor screed in pairs (“supply” plus “return”), approaching each radiator from the collectors (respectively, “supply” and “return”). The advantage of the scheme is ease of installation (no crossing of pipes and wall holes). The disadvantage is increased costs due to high pipe consumption and additional costs for collectors.
An additional advantage of the beam scheme is the use of small diameter pipes. An apartment (floor of a private house) will require the use of pipes d=25 and d=32 mm for the perimeter wiring diagram. Accordingly, the thickness of the screed and the diameter of the tees that connect the radiators will increase. The cost of such an element is comparable to the price of the pipe.
The use of radial routing, which increases the length of the pipes, provides the final benefit by reducing their diameter.
When using collector-beam wiring, a common method is to lay pipes in the floor in a screed, the thickness of which is 50-80 mm. Plywood is laid on top, covered with finishing floor covering(parquet, linoleum). This thickness of the screed is quite sufficient for free “monolithization” of the intra-apartment (intra-house) radial wiring of the heating system.
Connecting radiators with a collector-beam circuit.
Metal-plastic or cross-linked polyethylene pipes (PEX pipes) are used, laid in a corrugated pipe or in thermal insulation. PEX pipes have an undoubted advantage here. According to SNiP, only unbreakable connections can be “mortared” into concrete. PEX pipes are connected using tension fittings, which are permanent connections.
Even without fittings, not every metal-plastic pipe is uniquely suitable for laying in a floor screed. Manufacturers' products suffer from a serious defect: layers of aluminum and polyethylene delaminate under the influence of repeatedly changing coolant temperature. After all, metal and plastic have different coefficients of volumetric expansion. Therefore, the glue connecting them should be:
- internally strong (cohesive);
- adhesive to aluminum and polyethylene;
- flexible;
- elastic;
- heat resistant.
These requirements are not met by all adhesive compositions even from well-known European manufacturers of metal-plastic pipes, which delaminate over time; the inner layer of polyethylene in such a pipe “collapses,” reducing its cross-section. Normal operation the system is disrupted, and the location of the malfunction is almost impossible to find - usually the “sin” is due to malfunctions of thermostats, pumps and other products with moving parts.

In light of the above, we recommend that readers pay attention to metal-plastic pipes from VALTEC, which uses American adhesive from the DSM concern, which ensures the strength of the metal/plastic connection, adhesion and the complete absence of delamination.
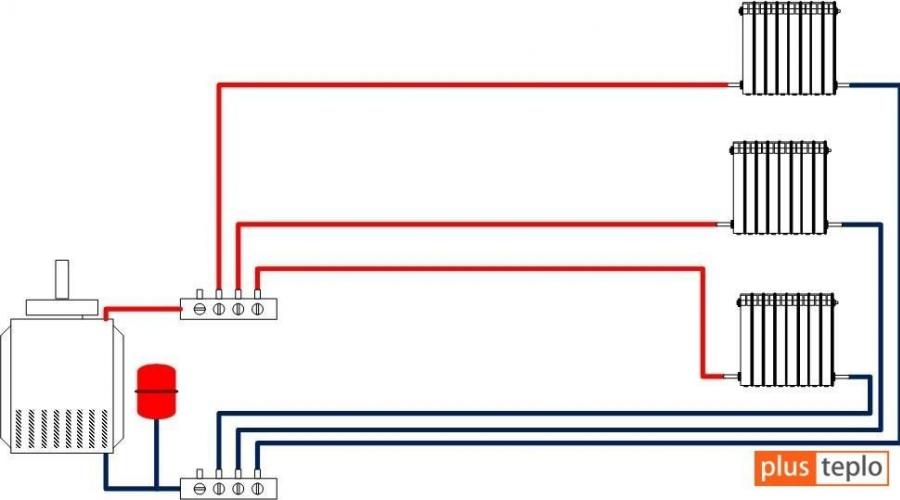
In an apartment with horizontal radiant heating distribution (on the floors of private houses), distribution manifolds (supply and return) are installed, collecting all supply and return pipelines at their outlets. They are placed in specially designed metal cabinets, often built into the partitions of bathrooms and opening inside them.
Manifold cabinet with thermal energy metering unit.
Collectors can be complete, consisting of sections of thick pipes with outlet pipes, or assembled on tees. The materials for these devices can be:
- plastic;
- nickel plated brass;
- copper;
- stainless steel.
Many famous manufacturers heating equipment(VALTEC and others) produce ready-made manifold blocks that combine supply and return manifolds, manual adjustment valves (on the supply manifold), thermostatic valves (on the return manifold), automatic air vents, drain valves and mounting brackets.
Complete collector block.
The task of individually adjusting the thermal regime of each single-radiator branch of a collector-radiant heating system is solved by tuning valves with built-in flow meters. The branches are of different lengths, and the coolant tends to flow the shortest way with minimal hydraulic resistance. It flows more intensely around short branches, warming up the radiators installed there more strongly.
Adjustment valves on the supply manifold change the flow of water (antifreeze), narrowing their nominal passages in short circuits, and widening them in long ones. Setting up is a painstaking process, and the setting valve is not intended to quickly shut off or open the coolant flow along the circuits. This function is performed by thermostatic valves.
Thermal valves on the manifold – “return” – are valves that smoothly shut off the flow manually or automatically. The radiant heating system is easily hydraulically balanced.

Often there is not just one heating device installed in a room, but several. It is irrational to connect a separate two-pipe loop-branch to each radiator during collector-beam wiring. It is better to lay a separate branch to each room, which will bypass several heating devices inside the room, implementing a dead-end or parallel circuit.
Scheme of combined heating system wiring.
Such a system is calculated as a beam system. Branches that supply several radiators with coolant are subject to a separate calculation as dead-end or passing. IN modern systems radiators are equipped with thermal valves (temperature regulators) that can be adjusted by users different temperatures, based on the current requirements for comfort in the room. It becomes difficult to maintain temperature stability in the room.
It turns out that you can get rid of instability while simultaneously reducing the cost of connecting radiators by connecting them according to the so-called. "pass-through scheme".
“Walk-through” radiator connection diagram.
The thermal valve is installed only on the first radiator in the circuit, regulating the coolant flow through all heating devices connected in series. They are perceived as one radiator. Balancing difficulties will arise with multi-section devices (10 or more sections).
The radiant heating system is optimal choice heat supply method for houses with a large number of rooms and utility rooms or for buildings with several floors. Thanks to its installation, the efficiency of equipment operation and the quality of heat transfer are significantly increased, since there is no unnecessary heat loss. In the photo you can see what one of the options for a collector circuit for heating a house looks like.
The principle of operation of beam wiring is simple, but has a number of features. It involves the location of several heating collectors on each floor. from which they organize the laying of pipelines for direct and reverse supply of coolant (in more detail: “Laying heating pipelines according to the correct scheme”). If a radial distribution of a heating system is being created, the instructions for such a scheme regulate the installation of structural elements in a cement screed.
Radiant heating of a private house is a structure consisting of several main elements:
- Heating boiler. This device is the starting point, since from it the hot coolant is directed into pipelines and radiators. The power of the heating unit must correspond to the heat output of the heating equipment. There is the following nuance here: the radial layout of the heating system, unlike other pipeline layout options, has a greater degree of heat loss, which must certainly be taken into account when calculating equipment parameters.
- Circulation pump. According to the peculiarities of its design, radiant heating distribution is of the closed type and its operation requires forced circulation of the coolant liquid. For this purpose, a special pump is installed that creates a certain pressure and pumps the liquid. As a result, the required temperature conditions are ensured, guaranteeing efficient operation of the heating system.
- high efficiency of coolant distribution;
- the possibility of differentiated regulation of the coolant flow through each circuit, up to the complete shutdown of individual circuits or radiators without negative impact on other heating circuits;
- the ability to automate the process of room temperature control, easy integration into Smart Home systems by installing programmable sensors in individual rooms;
- mandatory forced circulation of the coolant makes it possible to reduce the gap between the temperature of the coolant leaving the boiler and the “return” coolant;
- A well-performed calculation of such a radiant heating scheme using underfloor heating circuits allows you to even abandon the use of radiators.
- heating boiler;
- supply line;
- entrance at the collector.
Design, advantages and disadvantages of a radiant heating system
Wiring heating pipeline must be carried out before starting internal repair work. If this is not done, then you will need to tear off the screed, lay pipes and re-fill the floors with a special solution.
- on all circuits, collectors must be equipped with thermostatic valves and devices that regulate coolant flow;
- When implementing a pipe layout for a heated floor system, thermostatic heads and electrothermal actuators are used. Thanks to these devices, the heated floor structure immediately responds to changes in air temperature in the room, maintaining comfort and coziness in it;
- when choosing the type of distribution system, you need to know that it can be made according to a standard or custom design. Professionals advise giving preference to the second option. In individual systems, then not only does the boiler function normally, but there are also no significant temperature changes, and fuel is consumed economically. Warm floors made using an individual radial distribution scheme can be installed in any building.
- the ability to hide the laying of pipelines and other equipment elements;
- lack of connections and, as a result, weak points between the collector and heating radiators;
- easy installation of the system and performing the work yourself, even without special skills. The number of connections is minimal and therefore assembly is completed in the shortest possible time;
- stable operation heating structure. In the case of using the beam distribution method, there is no possibility of hydraulic shocks. Especially this problem relevant in the case when imported plumbing fixtures are to be installed, for which the boundary pressure is 3 atmospheres;
- to repair or replace damaged sections of the pipeline, it is enough to turn off the circuit beam, and the entire system will continue to function as before;
- the equipment is affordable, as are all its components;
- simplification of the design and installation process of a heating structure due to the use of pipes of the same diameter coming from the comb.
The radiant heating system is characterized by efficiency, performance, inexpensive price, safety and comfort. This scheme can be used in any building for any purpose, from your own home to a large office building.
Comfortable life in a warm country house depends not only on the boiler. Everything matters here: from the diameter of the pipes to the heating distribution. The tee system is fading into oblivion: too little efficiency and “sluggishness”. It is impossible to set the temperature in the rooms at different levels, nor to carry out repairs in winter without evicting household members.
Elements of a manifold heating circuit
Radiant heating of a private house is a structure consisting of several main elements:
- Heating boiler. This device is the starting point, since from it the hot coolant is directed into pipelines and radiators. The power of the heating unit must correspond to the heat output of the heating equipment. There is the following nuance here: the radial layout of the heating system, unlike other pipeline layout options, has a greater degree of heat loss, which must certainly be taken into account when calculating equipment parameters.
- Circulation pump. According to the peculiarities of its design, radiant heating distribution is of the closed type and its operation requires forced circulation of the coolant liquid. For this purpose, a special pump is installed that creates a certain pressure and pumps the liquid. As a result, the required temperature conditions are ensured, guaranteeing efficient operation of the heating system.
When choosing a circulation pump for radiant heating, you should pay attention to a number of parameters, including the length of the pipelines and the materials used to make the radiators. In addition, the power of the pump is not one of its most important characteristics; the speed at which the liquid will be pumped should be taken into account
This parameter shows the volume of coolant moved by the circulation device per unit of time
In addition, the power of the pump is not one of its most important characteristics; the speed at which the liquid will be pumped should be taken into account. This parameter shows the volume of coolant moved by the circulation device per unit of time.
Collector(it is also called a comb). It is also an important element of the radiant wiring of the heating system. The comb is assigned the function of a distribution device designed to centrally supply heating radiators with coolant (more details: “Distribution comb of the heating system - purpose and principle of operation”).
The radial circuit of a heating system always contains a variety of thermostatic or shut-off and control elements. They provide required consumption carrier of thermal energy in each branch of the structure. The installation of thermometers and air removers operating in automatic mode will help create additional conditions for more efficient operation of the heating structure without unnecessary costs.
Collectors on the domestic market are offered to consumers in a wide range. The choice of a specific device is based on the number of designed heating circuits or connected radiators. Combs are made from various materials– this can be brass or steel, as well as polymer products.
Cabinets. The radiant heating scheme requires that all the elements included in it be located in special structures equipped for them. Distribution manifold for heating. shut-off valves, pipelines must be placed in manifold cabinets with simple design. They can be built into niche walls or external, but at the same time they are distinguished by functionality and practicality.
Manifold cabinets and blocks
In an apartment with horizontal radiant heating distribution (on the floors of private houses), distribution manifolds (supply and return) are installed, collecting all supply and return pipelines at their outlets. They are placed in specially designed metal cabinets, often built into the partitions of bathrooms and opening inside them. It is also possible to install distribution manifolds in specially designed wall niches. Often the collector unit is combined with a heat metering unit in one collector cabinet.

Manifold cabinet with thermal energy metering unit.
Collectors can be complete, consisting of sections of thick pipes with outlet pipes, or assembled on tees. The materials for these devices can be:
- plastic;
- nickel plated brass;
- copper;
- stainless steel.
Many well-known manufacturers of heating equipment (VALTEC, etc.) produce ready-made manifold blocks that combine supply and return manifolds, manual adjustment valves (on the supply manifold), thermostatic valves (on the return manifold), automatic air vents, drain valves and mounting brackets.

Complete collector block.
The task of individually adjusting the thermal regime of each single-radiator branch of a collector-radiant heating system is solved by tuning valves with built-in flow meters. The branches are of different lengths, and the coolant tends to flow the shortest way with minimal hydraulic resistance. It flows more intensely around short branches, warming up the radiators installed there more strongly.
Adjustment valves on the supply manifold change the flow of water (antifreeze), narrowing their nominal passages in short circuits, and widening them in long ones. Setting up is a painstaking process, and the setting valve is not intended to quickly shut off or open the coolant flow along the circuits. This function is performed by thermostatic valves.
Thermal valves on the manifold – “return” – are valves that smoothly shut off the flow manually or automatically. The radiant heating system is easily hydraulically balanced.
Features of a radiant home heating system
However, there is one more point that should not be overlooked. This is adjustment or regulation. It is carried out precisely in regulating the taps located on the manifold. But it’s also worth saying that such a system is inconvenient because you have to constantly adjust the modes, which is not always possible physically. In addition, if you have a fairly large building, then it is better to abandon this idea.
 The fire is the first direct descendant of radiant heating, and the Russian stove is a vivid example of this. Large, occupying a significant space, it was capable of heating the house with its infrared radiation, or, simply put, with living heat. If the room is warm, then heat radiation as such does not occur, and the person feels comfortable. And if it has cold walls, ceilings and other interior items, to a greater extent, it is on them that the infrared rays, emitted by humans. Surely, anyone can remember the chills running through the body, it would seem, in a warm room. This is radiant heat exchange, on the principle of which the radiant heating system of a house is built.
The fire is the first direct descendant of radiant heating, and the Russian stove is a vivid example of this. Large, occupying a significant space, it was capable of heating the house with its infrared radiation, or, simply put, with living heat. If the room is warm, then heat radiation as such does not occur, and the person feels comfortable. And if it has cold walls, ceilings and other interior items, to a greater extent, it is on them that the infrared rays, emitted by humans. Surely, anyone can remember the chills running through the body, it would seem, in a warm room. This is radiant heat exchange, on the principle of which the radiant heating system of a house is built.
Review of diagrams and components of the heating system
At the first stage, you need to choose the operating principle of the heating system. Even 20-25 years ago there was practically no alternative - they made a gravitational open system. Therefore, the question of how to properly install heating came down to choosing the diameter steel pipes and their correct slope. But the appearance on the market of basic elements closed system significantly expanded the possibilities for choosing a scheme.
Gravity heating system
Gravity heating circuit
The main source of water heating for it is a solid fuel boiler (it can run on diesel or waste oil). Installation of gas models is impossible, since their normal functioning implies increased pressure in the pipes. Self-installation of a heating system with gas boiler Maybe. But in this case, a solid fuel housing is used, into which a special gas burner is mounted.
Before properly installing heating in a private home, you need to select its main components. In addition to the boiler, the following elements are required:
- Pipes. For this type of heating, you can use plastic models (polypropylene, metal-plastic) or steel. It is best to choose a large diameter - from 40 mm. In this way, the overall hydraulic resistance can be reduced;
- Expansion tank. Necessary to stabilize the system in case of overheating of the coolant;
- Shut-off valves. Its installation is mandatory, since during repair or maintenance work it will be necessary to shut off the coolant flow in a certain area of the system;
- Feeding unit. Required to add coolant. For optimization purposes, it is often included in the design of the expansion tank.

Radiator kit for single-pipe heating system
The gravity system in most cases is made of one pipe (Leningrad). In order to properly install the heating radiator, it is necessary to install a bypass on each of them. This also needs to be taken into account when purchasing components and compiling general scheme installation
In addition to these components, the installation of pressure gauges is required. If this device is not provided in the boiler design, it should be installed on the outlet pipe.
To install a heating radiator, be sure to include a Mayevsky tap in it. It is necessary to eliminate air jams in system.
Diagram of a forced circulation heating system
Closed heating circuit with solid fuel boiler
It is much more difficult to install a heating system with forced circulation. The difference lies in the creation of increased pressure in the line. This helps to increase the length of pipelines and optimal temperature conditions operation of the entire system.
It is best to consider the configuration of this circuit using the example of a harness solid fuel boiler. Since most gas models have the vast majority of components included in the design (circulation pump, expansion tank, etc.). Therefore, in order to install a heating system yourself, in addition to the boiler, the system must contain:
- Circulation pump. He will create required level coolant pressure;
- Closed expansion tank. Serves as a compensator when the pressure in the system increases above critical;
- Security group. Partially duplicates the functions of the expansion tank. If the pressure is too high, the air vent and drain valve will reduce it, removing excess air and coolant from the system;
- Shut-off valves;
- Feeding unit.
How to install a heating system yourself closed type, and most importantly - which pipe layout to choose? Experts recommend installing a two-pipe system, since in this case the radiators will be connected in parallel, which will ensure uniform temperature distribution throughout the system.
Installing a forced-type heating system is much easier than with natural circulation. In addition, the first is the only option for houses with medium and large areas.
Manifold selection
The radiant heating system includes a collector (comb). This element looks like a pipe. It has pipes for inlet and outlet of coolant. For a beam circuit, two types of collectors should be installed.

The first of these will be the input comb. A pump is connected to it, as well as a coolant distribution valve. It can be three- or two-way. The valve contains a thermometer. It is installed in the collector housing. The device transmits information to the valve. It opens or closes the valve, mixing hot liquid into the circuit.
The outlet manifold collects the cooled coolant, which returns to the boiler. The heating device heats it up again. Additionally, a balancing flow controller can be installed on this pipe. The collector group ensures the stability of the system. It is responsible for optimizing and balancing the heating of the coolant in the system.
Single-pipe horizontal

The simplest version of a single-pipe horizontal heating system with a bottom connection.
When creating a heating system for a private house with your own hands, a single-pipe wiring diagram may turn out to be the most profitable and cheapest. It is equally suitable for both one-story houses, and for two-story ones. In case of one-story house it looks very simple - radiators are connected in series to ensure consistent flow of coolant. After the last radiator, the coolant is sent through a solid return pipe to the boiler.
Advantages and disadvantages of the scheme
First, we will look at the main advantages of the scheme:
- ease of implementation;
- excellent option for small houses;
- saving of materials.

Single-pipe horizontal heating circuit is an excellent option for small rooms with a minimum number of rooms.
The scheme is really very simple and understandable, so even a beginner can handle its implementation. It provides for a serial connection of all installed radiators. This is an ideal heating layout for a small private house. For example, if this is a one-room or two-room house, then “fencing” a more complex two-pipe system does not make much sense.
Looking at the photo of such a circuit, we can note that the return pipe here is solid, it does not pass through the radiators. Therefore, this scheme is more economical in terms of material consumption. If you don’t have extra money, this type of wiring will be the most optimal for you - it will save money and allow you to provide heat to your home.
As for the shortcomings, there are few of them. The main disadvantage is that the last radiator in the house will be colder than the very first one. This is due to the sequential passage of the coolant through the batteries, where it releases the accumulated heat into the atmosphere. Another disadvantage of a single-pipe horizontal circuit is that if one battery fails, the entire system will have to be turned off at once.
Despite certain disadvantages, this heating scheme continues to be used in many small private houses.
Features of installation of a single-pipe horizontal system
Creating water heating for a private house with your own hands, the scheme with single-pipe horizontal wiring will be the easiest to implement. During the installation process, it is necessary to mount the heating radiators, and then connect them with pipe sections. After connecting the very last radiator, it is necessary to turn the system in the opposite direction - it is advisable that the outlet pipe runs along the opposite wall.

A single-pipe horizontal heating circuit can also be used in two-story houses, each floor here is connected in parallel.
The larger your home, the more windows it has and the more radiators it has. Accordingly, heat losses also increase, as a result of which the last rooms become noticeably cooler. You can compensate for the temperature drop by increasing the number of sections on the latest radiators. But it is best to install a system with bypasses or with forced circulation of the coolant - we will talk about this a little later.
A similar heating circuit can be used for heating two-story houses. To do this, two chains of radiators are created (on the first and second floors), which are connected in parallel to each other. There is only one return pipe in this battery connection diagram; it starts from the last radiator on the first floor. The return pipe coming down from the second floor is also connected there.
Radiant heating system for a two-story house is the best choice
At the moment, a more efficient and economical floor heating system for two-story private country houses than a two-pipe radial scheme simply cannot be found. By choosing the equipment correctly, as well as calculating all the nuances and performing installation as required by the instructions, you can ensure comfort and coziness in your home.
It is important to point out the fact that the main heating devices in a radial double-circuit system are traditional radiators. Regardless of the size and material (and this can be either cast iron or aluminum), such units must be installed correctly:
Regardless of the size and material (and this can be either cast iron or aluminum), such units must be installed correctly:
- Heating radiators must be installed only under window openings;
- All heating radiators must be mounted at the same height;
- The fins of the battery are located only vertically - otherwise normal coolant circulation will be impossible;
- It is imperative to provide drainage system, through which the coolant will be replaced.

Two-pipe heating system for a house with two floors
The boiler also means a lot (see how to choose a gas heating boiler)
For normal operation of the double-circuit system, it is important to choose modern and efficient boilers. Such equipment (and even equipped with automation) will make it possible to ensure optimal heating of each room two-story house, significantly saving fuel and finances and getting hot water
Heating system of a two-story building, two-pipe radiant heating circuit not only quite productive and efficient, but also demanding for the first launch.
For example, before starting direct operation, it is important to correctly balance the system and adjust the fluid flow for each loop of supply and return pipelines. This is the only way to achieve fuel savings and ensure the highest possible level of heating
Modern heating systems
 Enough has passed since the days of the Russian stove a large number of time, and although she is ideal option radiant heating of the house. but at present, installing it in a city apartment is nonsense. But technology is also developing every day, so all heating systems, including radiant ones, installed both in private houses and apartments, are mostly the most modern and adapted to the needs of each person.
Enough has passed since the days of the Russian stove a large number of time, and although she is ideal option radiant heating of the house. but at present, installing it in a city apartment is nonsense. But technology is also developing every day, so all heating systems, including radiant ones, installed both in private houses and apartments, are mostly the most modern and adapted to the needs of each person.
Heating systems are primarily divided according to how pipes are routed from the collector to the radiators. These are several types of systems such as;
- Single-pipe;
- Two-pipe;
- Radial;
The principle of radiant heating is that wiring from the collector, the main coolant distributor, is intended for each radiator separately. This is the most significant advantage in this system - radiators can be turned on and off, either individually or as a group.
In addition, the heat supply valve can be adjusted. For example, if the kitchen does not require such an amount of thermal radiation, due to the work household appliances, serving as an additional source of heat, then the valve can be screwed on. This can be done so that heat flows into the kitchen, but not in such quantities as into the rest of the rooms. The same can be done with those rooms that are not used for their intended purpose, but they should retain heat. By regulating the heat supply, fuel economy also increases. and due to this, the heat meter readings are also encouraging.
How is a multi-storey building heated?
- Operating principle of the elevator unit
- About the heating system multi-storey building
The heating system of a multi-story building is of particular interest; it can be considered using the example of a standard five-story building. It is necessary to find out how heating and hot water supply function in such a house.

Heating diagram for a two-story house.
In a five-story building it is implied central heating. the house has a heating main inlet, there are water valves, and there may be several heating units.
In most houses, the heating unit is locked, which is done to achieve safety. Despite the fact that all this may seem very complicated, the heating system can be described in simple words. The easiest way is to take a five-story building as an example.
The heating scheme for the house is as follows. After the water valves there are mud traps (there can be only one mud trap). If the heating system is open, then after the mud traps through the inserts there are valves that are located from processing and supply. The heating system is designed in such a way that water, depending on the circumstances, cannot be drawn from reverse side at home or from delivery. The whole point is that central system heating apartment building operates on water that is superheated, the water is supplied from a boiler house or from a thermal power plant, its pressure ranges from 6 to 10 kgf, and the water temperature reaches 1500°C. Water is in a liquid state even in very cold weather due to increased pressure, so it does not boil in the pipeline to form steam.
When the temperature is so high, the hot water supply is turned on from the back of the building, where the water temperature does not exceed 700°C. If the temperature of the coolant is low (this happens in spring and autumn), then for the normal functioning of the hot water supply this temperature cannot be sufficient, then the water for the hot water supply comes from the supply to the building.
Now you can disassemble the open heating system of such a house (this is called an open water intake), this scheme is one of the most common.
Types of radiant heating system
A visual diagram of the heating system in a private house.
A radiant heating system in a private house can be installed with either forced or natural circulation of the coolant. Currently, a system with natural circulation is used very rarely, since it requires the use of pipes with a very large diameter, which is not very convenient for a private home. In addition, this system is equipped with an expansion tank, the installation of which is necessary at the highest point of a two-story house, which again is not entirely convenient. But at the same time, a radiant heating system with natural circulation will help save on installation, since it will not require additional expensive equipment (pumps, temperature sensors, air vents, etc.).
The collector heating system with forced circulation is the most widely used; its main advantage is the artificial circulation of heat through pipes. For these purposes, a special pump is installed in the supply or return line. Forced circulation makes it possible to reduce the temperature difference between the water inlet and outlet, and also simplifies the heating system itself, which makes it more compact and helps to avoid unnecessary consumption of materials. This heating system is absolutely independent of the design of the house and the location of the heated rooms in it. The hydraulic resistance of the pipeline and the length of the branches do not play a special role. And by installing modern automatic devices, you can change the temperature depending on weather conditions and individual wishes of residents. All these advantages make this system universal.
Selection of pipes for the heating system
The most common for installing heating systems in two-story houses are metal-plastic pipes. This is primarily due to the fact that no sediment is deposited on products made of polymer materials and they are resistant to corrosion. A fairly low price is another advantage of metal-plastic pipes. All connections are made without welding using threaded or pressed connections, which simplifies installation as much as possible. However, such pipes have one drawback - a high coefficient of thermal expansion, which improper use may lead to leaks.
Pros and cons of radiant heating systems
The disadvantages of radiant heating in a house include:
- a large number of materials and, as a result, higher cost;
- the need for a special place for the collector block.
The advantages of the beam system are:
ease of installation due to the small number of connecting elements;
hidden gasket pipes in the floor;
hydraulic stability, which is especially important when using imported plumbing fixtures;
the ability to turn off each radiator individually, while all others are operating as normal;
temperature control in each separate room;
the system is balanced, all rooms are heated evenly.
When developing a project for a radiant heating system, it is necessary to detail it as much as possible; this will significantly simplify installation and help avoid problems in the future. It should also be noted that actual costs will always exceed planned costs; this must be taken into account when drawing up estimates. But, in spite of everything, the radiant heating system is highly efficient and can create maximum comfort in a living space.
Types of beam wiring
Method 1. With forced water circulation
Previously, a radiant heating scheme equipped with pumps that pump water was not very popular due to high cost details. But now the price of equipment has dropped significantly, and more and more people are choosing it.
The main difference from the gravitational scheme is that liquid (water or antifreeze) flows from the boiler to the batteries and back not due to the difference in temperature and pressure, but with the help of pumps.
This results in the following benefits:
- there are no restrictions on the geometry and number of rooms in housing construction;
- heating can be installed in rooms of any size;
- To connect radiators and collectors, you can use pipes of any length, laid without a slope.

One of the elements of a radiant heating system with forced circulation is a pump
Advice! Despite the fact that the circulation pump can be installed at any point in the system, it is advisable to do this on the return manifold before supplying coolant to the boiler. There the liquid temperature is the lowest, which has a positive effect on the service life of the equipment.
Method 2. With natural water circulation
In this case, the coolant moves due to gravity: the heated water becomes less dense and lighter, therefore it is displaced to the upper point of the system, after which, as it cools, it flows through the collectors and radiators, and then returns to the heater.
The gravity beam heating system has the following features:
- During installation, an open expansion tank is required, installed at the highest point. It compensates for the thermal expansion of the coolant and prevents an increase in internal pressure in the pipelines.
- A radiant heating network with natural circulation does not require the installation of expensive electrical equipment, which significantly reduces estimated cost works
- Heating with natural circulation is completely energy independent. Even if there is a power outage, which often happens in summer cottages or in rural areas, you will not be left without heat.

IN gravitational system heating pumps are not used
Beam wiring features and elements
The heating system using radiant radiation is most optimally suited specifically for apartment buildings, or private houses with more than one floor and many rooms. This significantly increases the operating efficiency of all equipment as a whole and guarantees high-quality heat supply and significantly reduces the amount of heat and energy indicators.
 The principle of operation of a radiant heating system is quite simple, but it has some features. For example, if a building has several floors, then installation of a collector is implied on each floor. Moreover, in many cases, not one, but several collectors are installed, and pipes are laid from them, and the direct and reverse supply of coolant is organized. It is also worth noting the fact that radiant heating of a house only works effectively if the house is well insulated. due to which the least heat loss occurs. If the house is insulated from the inside. and outside - problems with heating basically infrared radiation will not be. If it’s the other way around, all the heat will go to heating the walls, window panels, floors, and so on.
The principle of operation of a radiant heating system is quite simple, but it has some features. For example, if a building has several floors, then installation of a collector is implied on each floor. Moreover, in many cases, not one, but several collectors are installed, and pipes are laid from them, and the direct and reverse supply of coolant is organized. It is also worth noting the fact that radiant heating of a house only works effectively if the house is well insulated. due to which the least heat loss occurs. If the house is insulated from the inside. and outside - problems with heating basically infrared radiation will not be. If it’s the other way around, all the heat will go to heating the walls, window panels, floors, and so on.
But in itself, the radiant heating system is complex design. combining basic and additional elements necessary for quality work. This can include;
- Boiler. which is almost the main element. It is from this that heat is supplied to the pipes, and through the pipes to the radiators.
- Circular pump. which creates a certain pressure in the pipes, with the help of which the coolant circulates, and is maintained optimally comfortable temperature indoors. It also guarantees the efficient operation of the entire heating system;
- The collector (or in other words, the comb), is another most important element in a radiant heating system. It is, as it were, central, and it is from it that there is a uniform supply and distribution of heat to all rooms of the house;
- Closet. where all elements of the heating wiring must be hidden. The manifold cabinet hides the distribution manifold itself. pipes and shut-off valves. It is a fairly simple design, but very functional and practical. They can be located both outside and built into the wall;
What is the difference between tee wiring and radial wiring?
Such installation is quite complex, which increases the risk of breakdowns in the event of installation errors or sudden pressure changes in the heating system.

Beam wiring diagram
Radial heating distribution involves laying pipes from each radiator to a special switchgear- a collector or, as it is also called, a comb. Naturally, here the pipe flow increases significantly. In addition to pipes, each radiator will require its own shut-off valves - valves, thermostats, tees and others small parts, and some of them must be installed on both pipes - supply and return.
But, despite the high consumption of components, such a system makes it possible, in the event of an emergency, emergency situation quickly turn off any radiator, group, separate room or entire floor. The heating system can continue to operate during this time and heat the rooms.
In addition, when radiating pipes, as a rule, they are hidden under the floor covering, regardless of its material
This gives an additional chance to make the floor warm, which is so important in houses where basement not insulated. A one-piece pipe, without joints, made of cross-linked polyethylene and laid under the floor, eliminates the risk of leaks, and all repairs, if required, are carried out directly at the radiator connections or in the collector
Natural and forced circulation of coolant during radial distribution - which is better?
Heating of any building can be carried out by natural circulation of coolant or forced. A radiant heating system for a two-story house may well function in both cases.
Natural and forced circulation of coolant during radial distribution
With natural circulation of the coolant, operating the heating system is, of course, easier and cheaper. There is no need to purchase a circulation pump, various sensors, thermostats, etc. This system is well suited if long-term construction is underway and the building is not connected to a centralized power grid or for country house, if residence in it is not permanent.
But on the other hand, a heating system with natural circulation involves the installation of large-diameter pipes and the necessary slope when laying them. As well as the installation of an expansion tank, which should be located at the highest point of the building, this is usually done in the attic. And since the attic is not always insulated, it becomes necessary to insulate the tank itself in winter time and constantly monitor the state of the coolant in it.
Radiant heating of a house with forced circulation of coolant is increasingly gaining fans. If in the recent past such a system was a novelty for the average consumer, now circulation pumps are often installed in houses, citing the fact that such equipment allows increasing the temperature in the house while reducing financial costs for energy. And indeed it is.
Many have encountered this effect, when the supply pipe has a fairly high temperature, but the return pipe is slightly warm, and as a result, the house is quite cool. When installing a circulation pump, the temperature of both pipes is made the same, which increases the overall temperature in the room at the same cost of gas, wood or electricity, and possibly less. In this case, the pump can be installed on any pipe – supply or return. Its function is to quickly move the coolant under a certain pressure, as a result of which the formation of air pockets is eliminated, and all heating devices warm up evenly.
When building houses, you need to think about the functionality of the heating system. It is one of the most expensive to construct, but the comfort and convenience of living for residents in the winter season depends on it. In addition to the cost of the system itself, an important factor in a private home is also the cost of fuel. Traditional heating systems are being replaced by newer ones that require in various ways gaskets One of these variations is radiant heating. These systems are quite complex and require properly executed design and installation. Character traits, the rules, advantages and disadvantages should be considered separately.
Design diagram
Radial system design
In most modern housing, heating pipes are laid parallel to the walls. But this wiring method is ineffective in large buildings with several tiers. The fluid transferring heat begins in short terms lose energy, as a result of which the temperature in rooms located next to the boiler room will be higher than in remote ones. To correct this drawback and ensure uniform heating, a radiant heating system for a private home was invented.
 Visual representation
Visual representation Heating differs significantly from the tee heating traditional for most buildings. The main difference is the need to install a manifold cabinet in which necessary equipment, providing circulation.
In this design, several separate circuits are created, which are connected in parallel with heating elements: radiators, heated floors. Moreover, pipe routing is carried out in the process overhaul on the floor of the building. Thus, each of the heating elements is filled with coolant from a separate heating circuit, and each radiator will have approximately the same temperature.
Unlike tee wiring, radial wiring requires a significantly larger number of pipes, but fewer connecting components. Therefore, their installation complexity is approximately equal. Since parallel wiring is considered more reliable, it is more difficult to make a mistake during execution, and leaks and depressurization occur less frequently.
Pros and cons of the beam system
Like other types of wiring, beam wiring has a number of advantages and disadvantages. Moreover, before installation, you should familiarize yourself with all the positive and negative sides and features of use. This will avoid complications and problems in the future. It's worth starting with the cons.
 Switchboard
Switchboard Disadvantages of the beam system
The main disadvantages of this wiring scheme include:
- The need to purchase and lay a significant number of pipes. For each heating element in the house, you will need at least 2 pipes, which must be connected into a single network, connected through a system of fittings.
- A significant number of pipes makes installation highly complex. Therefore, when building a house, heating installation is extremely expensive.
- Beam wiring can be installed exclusively covertly. A traditional tee system is usually installed along the walls, however, due to the large number of inlet and outlet pipes, a radial tee system can only be laid under the floor. An alternative is to fix the pipes in the walls, but this significantly increases the amount of material required and the complexity of the work.
- Lack of docking modules. When laying pipes, be sure to avoid bends and joints. It is in such areas that breakthrough most often occurs. And since the repair of radial wiring is significantly complicated due to the need to tear off the floor covering, it is easier to prevent problems.
- If available big number rooms that require different temperatures, then each of the pipelines must be equipped with a separate pump for forced circulation.
Pros of the beam system
The main advantages include ease of use. A significant amount of equipment is included with the system to make heating control as simple as possible.
- Using a manifold cabinet, you can easily regulate the temperature of each specific radiator. Also, you can easily completely stop the flow of liquid to any of the radiators, without turning off the others.
- Each supply and discharge pipe goes exclusively to one heating element. This allows the use of small diameter pipes. They are easy to disguise under floor coverings. And also slightly heat the house.
- Taking into account the use of hydraulic arrows, which are a container with a large capacity, it can be arranged in different rooms different temperatures.
- Economical. The energy loss of the coolant during movement is much lower. In addition, the floor warms up, which then transfers heat to the atmosphere.
- Allows you to effectively distribute heat even to the most remote rooms.
How is the radial system organized?
The most important element in organizing such systems is the collector assembly. If it is necessary to carry out wiring on each of the floors, you will need to place one on each of the floors.
 Forced circulation pump
Forced circulation pump During installation, the collectors are placed in special cabinets, which provide the ability to regulate the operation of the system. When laying, it is necessary to ensure a minimum number of pipe joints, which significantly increases the safety and stability of the equipment.
Also, it is necessary to choose the right heating boiler, taking into account power, heat and electrical energy, efficiency factor taking into account heat loss by the system. Regardless of the type of fuel that the boiler consumes during the heating process, the need for calculation is mandatory.
Rules for choosing a forced circulation pump
The main application of radiant circuits for home heating systems is a horizontal arrangement, with coolant supplied from below. To ensure operation, it is necessary to use a circulation pump, which ensures forced circulation of the coolant through the branches of the network.
Using a pump can significantly reduce the temperature difference at the inlet and outlet of the circuit. As a result, the efficiency of the beam system is significantly increased, providing greater compactness and lower material costs.
Choosing this type of unit is based on several parameters:
- performance;
- pressure height.
To select the right pump, it is necessary to take into account the width of the pipe lumen, the length and height level relative to the pump itself. All calculations are carried out in advance.
How to properly install a circulation pump
- Wet powered pumps are installed horizontally.
- The thermostat device must not be brought as close to hot surfaces as possible to avoid distorted readings.
- Installation is usually carried out on the return sections of the system to ensure normal operation of the system and to prevent excess temperatures. Row modern pumps can also be installed near the boiler and work at high temperatures without problems.
- If there is no mechanism for eliminating excess air on the heating circuit, you should definitely choose a pump with the ability to remove gases.
- It is advisable to mount it as close as possible to the expansion tank.
- Before installation, it is advisable to clean the system of all solids.
- Before launching the beam system, it is imperative to conduct preliminary testing with water.
 Installation of a circulation pump
Installation of a circulation pump Is it possible without a pump?
The operation of the system can be ensured without purchasing and connecting a pump and a number of devices to remove excess air, but it is necessary to ensure compliance with certain conditions, which are extremely difficult to implement. It is necessary to select pipes with a large diameter and install the expansion tank at the maximum height from the floor.
This method can be used in rooms with small dimensions to ensure sufficient heat in the room. However, choosing between forced or natural water supply is required during the calculation process.
Selecting a distribution manifold
This device has a second name - distribution comb. It received it for the function it performs - supplying a liquid that conducts heat to each individual heating element, radiators, heated floors and others. Also, the coolant is returned to certain holes on the way back, after which it is supplied to the boiler or mixed with the contents of the pipes to reduce the temperature.
 Distribution manifold
Distribution manifold The number of simultaneously supported pipes reaches 12. In some models, for complex radiant heating systems for a two-story house, their number may be greater. Each manifold is connected to a ball valve, which allows you to regulate the flow of liquid to each radiator. This is necessary to regulate the amount of coolant that flows through the branches.
Which pipes to choose
There are a number of aspects that determine performance characteristics future pipeline. You should make your choice after you decide where the network will be installed: under a camouflage coating or in a cement screed.
During the work, you will need to bend the pipes in a certain way, at a non-standard angle. For this reason, it is advisable to use a material with a sufficient degree of flexibility so as not to increase the number of joints. The best option is pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene.
 Pipes
Pipes Moreover, the design must have a layer of airtight material. Otherwise, the smallest oxygen particles contained in the coolant may escape. As a result, rusting of the boiler and radiators is observed.
Also, it is worth paying attention to the following points:
- Beam distribution does not require the use of pipes standard diameter. The optimal clearance is from 24 to 32 millimeters.
- It is worth choosing products that are sufficiently protected from mechanical damage. Most often, they are filled with cement, but it is necessary to prevent excessive pressure on the network.
This requires checking the integrity and connections of all pipe elements. After which you can launch. This is required to prevent leaks during operation.
Beam wiring diagram
When choosing a scheme, preference is usually given to a floor plan. The network is carried out under a masking covering on the floor. The collector is usually mounted in a pre-prepared niche in the wall. An alternative is a special cabinet.
Most systems require the installation of a circulation pump, but there are options when several of them are not required, or they are mounted alternately on each of the rings. A supply and discharge container is attached to each element of the system. Then, under cement screed pipes from the collectors are placed and then connected to the heating element.
It is desirable that the duration of all pipes be approximately equal. Otherwise, the system will need to be additionally equipped with a circulation pump and sensors for temperature control. There are two main ways to organize heating: with forced circulation and without. It is worth describing each of them in more detail, with all their inherent features.
Method 1 with forced water circulation
This type of system, which is equipped with pumps for forced movement of liquid, was previously considered extremely expensive. However, with the advent of cheap and reliable pumps, such heating with pumps has increasingly become used in apartment buildings and private buildings.
The most important difference is that the coolant (water or antifreeze) circulates between the heating boiler and radiators not using gravity, temperature and pressure differences, but through the use of a special pump.
 Natural heating scheme
Natural heating scheme There are a number of positive aspects:
- The system can be installed in a room of any complexity and geometry.
- You can install radial wiring in rooms with large areas.
- For laying, pipes of almost any diameter can be used, provided that they are located at right angles.
It is advisable to install the circulation pump on the back of the pipes going to the distribution manifold to prevent overheating of the equipment and rapid failure.
Method 2 with natural water circulation
In a system without the use of circulation pumps, fluid movement is ensured by gravity. A hotter liquid has a lower density, due to which it moves upward, then, over time, returns to the collector and batteries, and then to the radiators.
The installation has the following features:
- During installation, it is necessary to provide space for the expansion tank open type, which must be placed in the highest place. It is required to compensate for the expansion of the coolant due to heating and prevents the pressure from increasing too much.
- In this case, the purchase and installation of circulation pumps is not required, which reduces the cost of work.
This type of heating does not require electrical energy, which is convenient for dachas and other country houses.
Radiant wiring and heated floors
In addition to connecting to radiators, you can use a radial circuit to organize a “Warm” floor type system. If you draw up a project correctly, taking into account everything possible options, you don’t have to buy radiators, making the floor the basis of heating in the house.
In this case, the heat will be distributed over the entire area of the room, without heating some areas, as well as rising air flows. This results in a reduction in the amount of moving dust.
However, before installing such a system, several factors must be taken into account:
- If the floor is made of concrete or wood, then a heat insulator must be placed underneath.
- Then, arrange the set of pipes in the form of a serpentine.
- Before concreting, it is required to test the system with water at normal pressure for 24 hours.
- After that, position the screed.
For each of these circuits it is required to provide distribution manifold with sensors. To prevent pipes from being squeezed, it is advisable to secure them with fittings or brackets.
 Warm floor
Warm floor Options for wooden houses
If you plan to place such a system on the floor in wooden house, then it is advisable to provide a number of holes in wooden beams ceilings Moreover, the slots should be slightly larger in diameter than the pipes themselves in order to prevent additional pressure on the pipeline.
Installation features
All such systems are installed and designed for a specific house, taking into account the dimensions, area, number of rooms and floors, planned coolant, radiator and some other parameters.
However, there are a number of rules that must be followed during installation. The use of a beam system in an apartment building is not permitted. Because the coolant circulates through vertical risers, which connect all rooms into a single network. Due to the connection of several collectors to the system, the liquid will not circulate to the upper floors.
 Installation process
Installation process In private homes, you can install a radiation system if you follow these recommendations:
- All manifolds that provide coolant circulation for radiators must be equipped with valves that would prevent the formation of plugs.
- The circuit must be equipped with an expansion tank with a volume of 10% of the total amount of liquid circulating through the pipes. The best option is to use a membrane tank.
- The tank is attached to a pipeline that connects the outlet tank with the heating element.
- If you plan to attach multiple pumps, make sure they are positioned horizontally. Otherwise, they will break, requiring expensive repairs or replacement.
Preparing for installation
Before all work, a project must be drawn up. It is especially important to consider the formation of the drawing. It should be quite detailed, with all calculations and dimensions. If it is impossible to do it yourself, you can hire specialists.
Also required:
- Select locations for batteries.
- Select the type of radiators and the number of sections.
- Make a list of necessary materials and equipment.
Installation of a radiant heating system
Collective radiant heating systems are installed under the floor. In this case, several recommendations must be followed.
The subfloor or base can be the foundation of the building, onto which a heat insulator is attached, after which the pipeline is placed. After which, the pipeline from pre-purchased and cut segments is connected. To prevent it from rising when pouring concrete, it is advisable to attach it in any of the following ways.
After that, around the network you need to place up to 5 centimeters of foam insulation and nail it with dowels. After which, you can fill it with concrete, up to 50-70mm.
Analysis of arguments for and against
The system has both advantages and disadvantages that must be taken into account during design. You need to arrange the manifold cabinet, which takes up a lot of space, and choose the right pipes.
However, such a system has much more advantages and positive aspects. Therefore, many owners prefer to install pipes along the radial distribution of the heating system in an apartment building. This provides a lot of benefits.
Conclusions on the topic
This heating system is more energy efficient than any other. It consists of many components, and the pipes and wiring themselves “feed” heating elements and remove the spent liquid. The radial design allows for extremely efficient distribution of coolant.

System.
Another striking advantage of the scheme is the use of small diameter pipes. An apartment (floor of a private house) will be required to use pipes d=25 and d=32 mm for the perimeter wiring diagram. Based on this, the thickness of the screed and the diameter of the tees with which heating devices are connected become larger. The cost of such an element is comparable to the cost of the pipe.
When collector-
Scheme.
- flexible;
- elastic;
- heat resistant.
Manifold boxes and blocks
- plastic;
- nickel plated brass;
- copper;
- stainless steel

Supply to heating devices switched on collector wiring, can be created automatically adjustable. IN in this case on the thermal valves of the return manifold (position 2 in the figure "Complete manifold block") instead of the plastic cover manual control(position 4 in Fig. “Complete collector block”) a small electromechanical servo drive is installed, connected by a cable to an analog thermostat or controller. Heating devices are connected to heating pipes without any fittings at all (valves with a spherical shut-off element can be installed).
Conclusion
Publications on the topic:
Methods for filling closed heating systems. Standard errors made when performing this operation. Tips for choosing a size.
Heating system Leningradka with forced circulation: important points. “Tying” of a heating device for single-pipe heating, specifics.
Many property owners are thinking about how to implement an alternative heat supply for a private home. Home heating systems are a plus.
Radial heat distribution system
Manifold heating distribution
Excellent conditions in the house or on summer cottage are determined not only by the presence of a boiler. All heating elements become important. People are increasingly refusing the tee system, because it is very slow and uncomfortable. With its help, you cannot change the temperature and make repairs without creating inconvenience. Collector heating distribution, on the contrary, is gaining great popularity. Previously, it involved excessive costs, and because of this, few people wanted to buy it.
Differences between and tee systems.
The radial type heat supply distribution has the ability to connect heating devices to the distribution system. Pipes run from each point to the battery. There are two of them: the one that supplies the coolant and removes it. The heating device itself is a large technical device, which is why it is mainly stored in a specialized building.
A typical tee system takes into account a small number of pipes, but regardless of this, there will be many more connections. This will complicate the installation, and the possibility of failure of the unit has many chances.
When the collector is separated, the number of pipes becomes larger, but all joints are easy to reach, which means that removing the problem takes little time. Each individual branch of the heating system can simply be turned off and this will not cause disruption to the heating of other rooms. A radiant-type heating distribution installed in a couple-storey building usually has forced and gravitational circulation.
The key advantage of a radiant heating system is the availability of its installation under pipes. With a tee system, it is considered impossible to fit the pipes in an inaccessible place, because if repairs are necessary, the walls and floor will have to be destroyed.
Home collector wiring - circulation function
An alternative heating system that has a forced circulation function.
About 10 years ago this device A very small number of people could afford it. In our time, the cost of technical devices has decreased significantly, and this has made heating systems of this type generally available.
The key advantage of forced circulation is the unnatural circulation of coolant through the batteries. The water seal can be installed on both output and receiving paths. The radiant heating system does not require special construction of living rooms.
The actual circulation of the coolant in the heating system involves the use of large cross-section pipes and the installation of a specialized tank. Very often this is considered inconvenient, because the coolant recovery part should be installed at a higher point in the room.
The distribution of radiant heat supply with real coolant circulation makes it possible to save on additional elements. Parts that are very expensive are not needed for the actual functioning of such heating systems.
If the room works as a building in a country house, then the best choice would be a real circulation. Even without additional devices, the house will be heated very efficiently.
Radiant heating distribution in a private house - its advantages and disadvantages
Pros and cons of the heating system.
When creating a project for diluting heating system batteries, it is necessary to consider all the pros and cons of this type of heat supply to the room. Radiation-type heat supply wiring has disadvantages; anyone who is at least a little competent in this area knows them, but few are familiar with its good qualities. The disadvantages include: high consumption of materials for construction and, naturally, much higher costs than when constructing tee pipes; the need to allocate a significant amount of space for a specialized tank or block for it.

Also, collector wiring also has advantages, everyone knows that they undoubtedly exist, but problems arise with their clear definition. Very often you can hear that a radiant heating system is simply of better quality and that’s the end of it. Although she, for her part, provides a large number of purposes and good sides.
They consist in the elementary creation of a design for a heat supply device; pipes of the same cross-section can be used all the time, which is very convenient; banality of installation due to insufficient number of joints between pipes; possibility of uniform coolant circulation.
This is very important for people who use plumbing equipment, mainly imported from other countries, which mainly has three Atmosphere pressure. The radiant heating system is very rational and heats the home in exactly the same way.
The broken part of the pipe can simply be replaced with a new one, without resorting to dismantling the floor; the ability to turn off one of the batteries, while the others will still work fully; devices for regulating the temperature level in any room; such regulators can be mechanical or automated.
This heating system is good because of its flexibility and easy installation. automated system regulation.
Radiant heating system in a house with several apartments
Perimeter or collector wiring of the heating system: what to choose?

Being a variation of the methods of laying heating pipes of two-pipe horizontal systems of modern private and apartment buildings, the collector distribution of the heating system has a number of undeniable positive qualities. Each circuit of the system with such piping is separately connected to the heating manifold, which makes it possible to set a personal operating mode for it that meets the condition of a person’s comfort in a certain area of the room.
Heating pipes laid in the thickness of a concrete screed or under a wooden floor on wooden blocks must be reliable, eliminating (or minimizing) the likelihood of leaks, deterioration of throughput and other breakdowns.
Wiring diagrams for modern horizontal heating systems
Modern apartment buildings and private country houses of any number of floors are very often equipped with horizontal heating systems. A mandatory element of such a scheme is considered to be one or more (in a building with several apartments - in each entrance) vertical two-pipe risers, having branches/entrances into separate rooms/apartments on each floor. Subsequent installation of pipelines is carried out in a “horizontal” way.
When making such systems, workers invariably encounter difficulties in laying heating pipes to heating devices. The pipelines from the pipes of vertical systems, laid along the walls from top to bottom, did not disturb the residents very much. Horizontal pipes laid openly under the walls become an argument that interferes with the natural process of using the premises and do not fit well into their interiors. Due to this, different methods of horizontal hidden laying are used.
Branched dead-end wiring diagram with pipes in a screed

Routing of pipes and wires in a branched dead-end circuit.
Very short pipe lengths and hydraulic resistance of the circuit are leveled out by the mutual crossing of pipes and wires, leading to an increase in the thickness of the screed (each centimeter costs from 40 rubles/m2).
Perimeter wiring heating systems
- Dead-end scheme with pipelines in the screed or under the baseboard.

Pipeline layout diagram for a two-pipe dead-end system.
The lack of crossing of pipes in the diagram is offset by the need to make holes in the walls (in the given diagram it is necessary to drill five holes).
- Layout of pipelines according to the scheme with the associated movement of water (Tichelman scheme).
Layout of pipes and wires according to the Tichelman scheme.
Here the first heating device of the heating circuit has the shortest “supply” length and the longest “return” length, the final heating device is the opposite. The hydraulic resistance experienced by the coolant when flowing around the devices of the circuit is constant, which makes it possible to balance any number of heating devices in a branch.
Collector-beam wiring heating systems
Pipeline distribution diagram for the collector system.
The popularity of this scheme is regularly increasing. Here the pipes are laid in the floor screed in pairs (“supply” plus “return”), approaching each heating device from the collectors (based on this “supply” and “return”). The advantage of the scheme is ease of installation (no crossing of pipes and wall holes). The downside is very high costs due to excessive consumption of pipes and additional costs for collectors.
Another striking advantage of the scheme is the use of small diameter pipes. An apartment (floor of a private house) will be required to use pipes d=25 and d=32 mm for the perimeter wiring diagram. Based on this, the thickness of the screed and the diameter of the tees with which heating devices are connected become larger. The cost of such an element is comparable to the cost of the pipe.
The use of manifold wiring, which increases the length of the pipes, provides the final benefit due to a reduction in their diameter.
General requirements for the installation process of collector wiring
For collector distribution, a common method is to lay pipes in the floor in a screed; its thickness is 50-80 mm. Lay plywood on top, covered with a final floor covering (parquet, linoleum). This screed thickness is quite sufficient for free “monolithization” of the intra-apartment (in-house) collector wiring of the heating system. It is possible to lay pipes externally under walls under decorative skirting boards, entailing an inevitable increase in the length of pipelines. There are known options for laying collector distribution pipes in the space of a suspended (suspended) ceiling, in grooves.
Connecting heating devices with a manifold circuit.
Metal-plastic or PEX pipes (X-linked polyethylene pipes) are used, laid in a corrugated pipe or in thermal insulation. Pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene have an absolute advantage here. According to SNiP, only unbreakable connections can be “mortared” into concrete. Pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene are connected using tension connectors, which are classified as permanent connections. Metal-plastic pipes use crimp connectors with union nuts. “Monoliquing” them means violating SNiP. Each wedge pipe connection must be accessible for physical and technical maintenance (tightening).
Even without connectors, not every metal-plastic pipe is definitely suitable for laying in a floor screed. Manufacturers' products suffer from a serious defect: layers of aluminum and polymer ethylene delaminate under the influence of repeatedly changing temperature. After all, metal and plastic have different volumetric magnification coefficients. Due to this, the glue composition that unites them should be:
- internally strong (cohesive);
- adhesive to aluminum and polymer ethylene;
- flexible;
- elastic;
- heat resistant.
These requirements are not met by all adhesive compositions, even from popular European manufacturers of pipes made of metal-plastic, which delaminate over time; the layer inside the polyethylene in this pipe “collapses,” reducing its cross-section. The normal operation of the system is disrupted, and the location of the breakdown is usually impossible to find - in most cases, the “sin” is caused by breakdowns of thermostats, pumps and other products with moving parts.
In light of the above, we advise readers to pay their own attention to metal-plastic pipes from VALTEC, which uses American adhesive from the DSM concern, which ensures reliable metal/plastic connections, adhesion and the complete absence of delamination.
Manifold boxes and blocks
In an apartment with a horizontal collector distribution of heat supply (on the floors of privatized houses), distribution-type collectors (supply and “return”) are installed, collecting all supply and return lines from pipes at their own outlets. They are placed in specialized iron cabinets, very often built into the partitions of bathrooms and opening inwards. It is also possible to install distribution manifolds in intentionally constructed wall niches. Often, the collector unit is connected to the heat metering unit in one collector cabinet.

Box for collectors with heat energy metering unit.
Collectors can be complete, consisting of sections of thick pipes with outlet pipes, or assembled on tees. The materials for these devices will be:
- plastic;
- nickel plated brass;
- copper;
- stainless steel
Most well-known manufacturers of heating equipment (VALTEC, etc.) produce ready-made manifold blocks that combine supply and return manifolds, manual adjustment valves (on the supply manifold), thermostats (on the return manifold), automated Mayevsky taps, drain valves and mounting holders .

Complete collector block.
The task of personal adjustment of the thermal regime of each single-radiator branch of collector-heating systems is solved by adjustment valves having installed flow meters. The branches are of different lengths, and the coolant tends to flow along the shortest path with very little hydraulic resistance. It flows more intensely around short branches, warming up the heating devices installed there more intensely.
Adjustment valves on the supply manifold change the consumption of water (antifreeze), narrowing their nominal passages in short circuits, and widening them in long ones. Setting up is a labor-intensive process, and the setting valve is not intended to quickly close or open the flow along the contours. Thermostats perform a similar function.
Thermal valves on the manifold - “return” - are valves that slowly shut off the flow manually or automatically. The radiant heating system is easily hydraulically balanced.
Combined layout of heat supply pipes and wires
Often, there is not only one device installed in a room for heating the room, but several. It is impractical to connect a separate two-pipe loop-branch to each heating device during collector wiring. It is better to run a separate branch to any room, which will bypass several radiators in the middle of the room, performing a dead-end or passing circuit.

Combined wiring diagram for heating systems.
A system of this kind is designed as a beam system. Branches that supply several heating devices with heat carriers are subject to separate calculations as dead-end or passing. In modern systems, heating devices are equipped with thermal valves (thermostats), which can be adjusted by customers to different temperatures, based on the current requirements for comfort in the room. It becomes very difficult to maintain the stability of indoor temperatures.
It turns out that you can free yourself from instability, while simultaneously reducing the cost of connecting heating devices, combining them according to the so-called. "pass-through scheme".

“Walk-through” connection diagram for heating devices.
The thermal valve is installed exclusively on the first heating device in the circuit, regulating the flow rate across all gradually switched on devices for heating the room. They are perceived as one heating device. Balancing difficulties will arise with multi-section devices (10 or more sections).
Automatic collector-beam system
The supply to heating devices connected via manifold wiring can be created automatically regulated. In this case, on the thermal valves of the return manifold (position 2 in the figure “Complete manifold block”), instead of the plastic manual control cover (position 4 in the figure “Complete manifold block”), a small electromechanical servo drive is installed, connected by a cable to an analog thermostat or controller. Heating devices are connected to heating pipes without any fittings at all (valves with a spherical shut-off element can be installed).
Thermal valve servo drive dimensions.
A similar scheme has very high capital costs while providing high level comfort. temperature desired by the client environment can be set from the control panel of the room thermostatic valve, the signals of which are processed by servo drives on the thermal valves of the return manifold. The system can be controlled by a so-called chronothermostat, which provides the client with the ability to set a temperature control program for 7 days, differentiated by day of the week and time of day.
Conclusion
The heating system with manifold-pipe distribution provides the client with the possibility of hydraulic balancing and personal adjustment of the operating modes of the radiators. A certain increase in the length of pipes during collector wiring is compensated in advance by a decrease in their diameter and ease of installation.
Collector heating system for a private house - pros and cons
Radiant heating system
- Radiant heat supply: a simple scheme of actions
- Editing like aerobatics
- It is hardly possible to do without a circulation pump
Heating systems are challenging, especially when it is necessary to include both the personal tastes of the owners and the originality of the structure that needs heating. Those who live in apartment buildings are familiar with the pattern: the higher the floor, the less heat there will be, which means the degree of comfort will decrease, and it becomes worse health families living there. The reason is the methodical reconnection of heat exchangers to a single, passing and connecting riser. The consumption of purchased pipes allows you to save on them, but it is unrealistic to achieve a homogeneous temperature in all apartments. The temperature will also differ in the rooms, the details of the living space.

Time demonstrates that a radiant heating system is most optimal for balanced temperature regulation. To define it, the synonym collector is used. This system modern heating supply has proven itself with its own operating parameters and non-hazardous parameters for residents.
Radiant heating system is the best solution

Heating system diagram.
Anyone who owns their home naturally wants to organize a good system of excellent heating supply with their own hands. He must know for sure: great heating systems have not yet been invented, so you need to select what is the most functional and has received positive approval. You can give your own preference to the heating system, nicknamed. Its romantic-geometric name is absolutely explained: each heating device receives its own beam as a pipeline.
If the owner owns a comfortable, not very large and heavy house, which consists of two floors, then the scheme for constructing a heating system using collectors provides for the presence of its own collector on each floor. They are connected together in a parallel way, then a boiler is installed, then an expansion tank. This heating system is sometimes called two-pipe. And it is right. A pair of pipes runs through all the rooms that need to be heated. One line of pipes is formed for the direct movement of liquid - the other is responsible for the way back.
There are a considerable number of radiator heating pipe layouts, but due to their many advantages, two layouts have become especially popular: two-pipe and radial. Most often, any developer has to choose between these two systems (if it was decided to install radiators). Hoping to get recommendations from installers, you usually do not meet objectivity and everyone chooses what is more convenient for him.
And there is also the most pleasant phrase that every customer loves to hear: “well, you decide for yourself, but it doesn’t matter to us what to install.” Let's try to adequately understand the strengths and weaknesses of two-pipe and radiator radiator wiring

This is a consequence of the evolution of the single-pipe system, in which all the main disadvantages were eliminated. In this system, two pipes are connected in parallel to the radiator. One is feed, then feed, the other is reverse, then return. Hot coolant is supplied, and it will enter each battery at almost the same temperature. And in the opposite direction, the already cooled coolant flows by itself.
In a single-pipe system, we were faced with the fact that only one looped pipe was responsible for the supply and return. Therefore, the temperature difference between the first and subsequent batteries was more significant. And it was not possible to “level” the system so that each radiator was the same temperature.
What is a radiant heating scheme?

Let's now highlight the strengths and weaknesses of each heating scheme
Which heating is cheaper?
Most standout plus two-pipe system– this is the price. This system is cheaper than the beam one. Mainly due to the fact that fewer pipes are used and there is no need to purchase an additional distribution manifold. But a two-pipe system uses more fittings. At our last facility with an area of 300 square meters, the difference between the beam and two-pipe systems was 30,000. In both cases, metal-plastic pipes were used, as well as connections from the same company.
On the one hand, this can be written down as a disadvantage of the beam system. But on the other hand, for such an object, for many developers the difference of 30,000 will be insignificant.
Materials used
Polypropylene can be used for pipe routing in a two-pipe system. As we know, this is the most affordable type of pipe on the market. Now we will not list the advantages and disadvantages of this material. You just need to keep in mind that if the budget is limited, then you can use polypropylene
For beam distribution, only metal-plastic pipes or pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene with a thicker wall are used.
Number of joints
Here the radiant heating system has its clear advantage. Its main advantage is the absence of connecting parts in the concrete screed. All connections are located in the manifold and on the radiator itself. Accordingly, if something ever decides to leak, it will happen in a visible field and you can quickly fix everything.
For a two-pipe system, all connections are filled concrete screed and are recessed into the walls. This adds the possibility of some kind of leakage due to operation of the system. Although press and tension pipe connections are famous for their reliability, accidents actually occur quite rarely
It's a different matter if you use polypropylene. There are even more joints there and most of them are also located in an inaccessible area. This is truly a lottery. If suddenly the installer welded the joint sloppily, it may not leak immediately. It will last a year or two. And that's where the fun begins. So with polypropylene pipes When installing hidden, I would recommend being extremely careful.
Temperature adjustment
These systems have convenient ways temperature adjustment. Thermal heads on radiators are most often used. This is a relatively inexpensive and convenient adjustment option.
The advantage of the beam system is that you can install servos on the collector and regulate the temperature in each room using room thermostats. This option is already much more expensive, but at the same time more advanced.
What's the result?
An insignificant disadvantage of the beam system is that it requires space to install the collector. But in truth it is not always present. Plus, it is advisable to install the collector in the middle of the house.
If we consider these two systems in terms of efficiency and economy, then they have absolute parity. Both systems do their job remarkably well.
It’s just that if you have a limited budget, then you should look towards a two-pipe system. If desired, you can also use polypropylene. The beam system will add some convenience and peace of mind to you, that if something happens, nothing will leak under the screed.
It is important to understand the main thing. In both cases, your choice will be absolutely correct!