Commercial banks and their operations. Commercial banks

Read also
1. Bank as a special type of enterprise. Functions of commercial banks.
2. The main operations of commercial banks: economic content and types. Banking products and services.
3. Banking resources and capital.
4. Ensuring sustainable development of commercial banks.
1. Bank as a special type of enterprise. Functions of commercial banks
The bank acts as a special type of enterprise, whose activities are aimed at meeting the needs of market participants. It is a credit institution that regulates the payment turnover of economic entities in cash and non-cash forms. creates its own specific product:
Payment means issued at the macro and micro levels. Without money, the products of labor cannot be exchanged, the reproduction process cannot be continued. The issuance of cash is a monopoly of the bank, it is produced only by the bank, making it a specific product banking system;
Accumulated free resources, which are transformed from temporarily unused into working ones;
Loans provided to bank customers as capital;
Various services.
Modern commercial banks are the main link in the banking system, providing direct services to enterprises and the public. Regardless of the form of ownership, they are independent subjects of the economy, their relations with customers are built on a commercial basis.
According to Russian banking legislation, a bank is a credit institution that has the right to raise funds from individuals and legal entities, place them on their own behalf and at their own expense on the terms of repayment, payment, urgency and carry out settlement operations on behalf of clients. Non-bank credit organizations carry out only individual banking operations.
Thus, commercial banks, unlike special credit financial institutions carry out comprehensive service clients are credit institutions universal type performing a wide range of financial transactions and services. Unlike financial dealers and brokers, CBs are characterized by a double exchange of promissory notes; unlike investment companies and funds, they assume unconditional credit obligations, mainly with a fixed amount of debt.
CBs act as specific credit institutions, which, on the one hand, attract temporarily free funds from the economy; on the other hand, they satisfy various financial needs of enterprises, organizations and the population at the expense of these borrowed funds. economic basis the activity of the bank in the accumulation and placement of credit resources is the movement Money.
The functions of a commercial bank include:
— accumulation (attraction) of funds in deposits;
- their placement;
- settlement and cash services.
CBs organize the process of cash flow, implement the monetary policy of the Central Bank, regulate the overall liquidity of the economy, and make payments and settlements.
Type of commercial bank (universal, sectoral, special purpose, regional, etc.) is determined along with the content of its activities, as well as the degree of development of the country's economy, credit relations, money and financial markets.
2. The main operations of commercial banks: economic content and types. Banking products and services
The operations of a commercial bank are a concrete manifestation of banking functions in practice. According to Russian legislation, the main banking operations include:
1) attracting funds from legal entities and individuals in demand deposits and for a specified period;
2) granting loans on its own behalf at the expense of its own and borrowed funds;
3) opening and maintaining accounts of individuals and legal entities;
4) making settlements on behalf of clients, including correspondent banks;
5) collection of funds, bills of exchange, payment and settlement documents and cash services for customers;
6) management of funds under an agreement with the owner or manager of funds;
7) purchase from legal entities and individuals and sale to them of foreign currency in cash and non-cash forms;
8) carrying out operations with precious metals in accordance with the current legislation;
9) issuance of bank guarantees.
Non-bank credit organizations are entitled to carry out banking operations, with the exception of the operations provided for in paragraphs 1, 2, 3 and 9. Valid Combinations other banking operations for non-bank credit institutions are established by the Bank of Russia.
commercial banks, in addition to the banking operations listed above, are entitled to carry out the following transactions:
Issuance of guarantees for third parties, providing for the fulfillment of obligations in cash;
Acquisition of the right to claim the fulfillment of obligations from third parties in cash;
Providing consulting and information services;
Leasing to individuals and legal entities of special premises or safes located in them for storing documents and valuables;
Leasing operations and other transactions in accordance with the law Russian Federation.
All banking operations and transactions are carried out in rubles, and in the presence of an appropriate license from the Bank of Russia and in foreign currency.
A credit organization (including commercial banks) is prohibited from engaging in production, trade and insurance activities.
All operations of a commercial bank can be divided into three main groups:
Passive operations - operations to raise funds in banks, the formation of the resources of the latter;
Active operations - operations through which banks place the resources at their disposal to generate profits and maintain liquidity;
Active-passive operations - commission, intermediary operations performed by banks on behalf of customers for a fee - a commission.
The passive operations of the bank include:
— attraction of funds to settlement and current accounts of legal entities and individuals;
— opening urgent accounts of citizens, enterprises and organizations;
— issue of securities; loans received from other banks, etc.
All passive bank operations related to raising funds, depending on their economic content, are divided into:
Deposit, including obtaining interbank loans;
Issuance (placement of shares or securities of the bank).
The active operations of the bank include:
- short term and long-term lending production, social, investment and scientific activity enterprises and organizations;
— provision of consumer loans to the population;
— acquisition of securities;
— leasing;
— factoring;
— innovative financing and lending;
— equity participation of the bank's funds in economic activity enterprises;
- loans to other banks.
Bank's active operations economic content divided into:
Loan - operations for the provision (issuance) of funds to the borrower on the basis of urgency, repayment and payment. Loan transactions related to the purchase (accounting) of promissory notes or the acceptance of promissory notes as collateral are accounting (accounting and loan) transactions;
Settlement - operations for crediting and debiting funds from customer accounts, including for paying their obligations to counterparties;
Cash - operations for receiving and issuing cash; more broadly - operations related to the movement of cash, as well as the formation, placement and use of funds on various active bank accounts (including the Cashier account and correspondent accounts with other banks) and accounts of commercial bank customers;
Investment and stock. Investment operations - operations by the bank investing its funds in securities and shares of non-banking structures for the purpose of joint economic and financial and commercial activities, as well as placed in the form of term deposits in other credit institutions. A feature of the investment operations of a commercial bank from credit operations is that the initiative for the first comes from the bank itself, and not its client. This is the investment activity of the bank itself. Stock transactions - transactions with securities (other than investment).
Stock transactions include:
Operations with bills of exchange (accounting and re-discounting operations, protest operations of bills, collection, domiciliation, acceptance, endorsement of bills, issuance of bill of exchange orders, storage of bills, their sale at auction);
Operations with securities listed on stock exchanges.
Warranty. operations for the issuance by the bank of a guarantee (surety) of payment of the client's debt to a third party upon the occurrence of certain conditions; also generate income for banks in the form of commissions.
Degrees of riskiness - risky and risk-neutral,
The nature (directions) of the placement of funds - for primary (operations related to the placement of funds on a correspondent account, at the cash desk, with the issuance of loans to customers, other banks, some other operations), secondary (operations related to the allocation of funds to the reserve and insurance funds) and investment (operations on investing the bank's funds in its own portfolio of securities, in fixed assets, on participation in the economic activities of other enterprises and organizations);
The level of profitability - for operations that generate income (high-yield and low-yield, generating stable or unstable income), and not generating income (the latter include cash transactions, on a correspondent account, on the deduction of funds to the reserve fund of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, the issuance of interest-free loans, prolongation and deferral of loans, when interest on loans is not paid).
Active-passive operations of banks are often called services. There are settlement services related to the implementation of domestic and international settlements, trust services for the sale and purchase by a bank on behalf of clients of securities, foreign exchange, precious metals, mediation in the placement of shares and bonds, accounting and consulting services for clients, and others.
Commission operations - operations carried out by banks on behalf of, on behalf of and at the expense of customers; generate income for banks in the form of fees.
These include:
Accounts receivable collection operations (receipt of money on behalf of clients on the basis of various monetary documents);
Transfer operations;
Trade and commission (trade and intermediary) operations (purchase and sale of securities, precious metals for clients; factoring, leasing, etc.);
Trust (trust) operations;
Operations to provide clients with legal and other services.
All bank operations are divided into:
Liquid and illiquid:
Operations in ruble and currency terms;
Regular (committed by the bank periodically, constantly reproduced by it) and irregular (carrying for the bank a random, episodic character);
Balance and off-balance. The term "off-balance-sheet transactions" refers to a wide range of transactions, which, as a rule, are not reflected in officially published bank balance sheets or are given below the line in the "contra-accounts" ("off-balance sheet" accounts) section. Off-balance sheet operations can be carried out by banks both for the purpose of raising funds (passive operations) and their placement (active). In addition, if banks conduct off-balance sheet operations for a certain fee (commission) on behalf of the client, then they are classified as active-passive operations or banking services.
Quite often there is an identification of the concepts of banking operations, a banking product and a banking service.
A service, unlike embodied goods, is always a process during which its producer and consumer interact. We can talk about banking services only within the framework of the “client-bank” relationship. A banking service is one or more bank operations that satisfy a specific customer need. In addition, the services of commercial banks can be defined as banking operations on behalf of the client in favor of the latter for a fee.
The main characteristics of banking services include:
— intangible essence of services:
- services do not accumulate, but banks create reserves of funds that are managed by the banker:
- the provision of banking services is regulated by law:
- the sales system (providing banking operations and services is exclusive and integrated, since all branches of one bank perform the same set of banking operations and services.
A banking product is a set of banking financial transactions to solve any customer's needs, which can be positioned as a new banking service or a combination of traditional banking services, built into a technological chain that allows solving a specific customer problem and satisfying his demand in complex services.
For example, a banking product - a "salary project" can consist of three operations:
– issuance by the bank of plastic cards for employees of the enterprise;
- setting credit limits plastic cards in the amount of 1-2 salaries of an employee;
- installation of an ATM at the enterprise.
3. Banking resources and capital
The bank's resources consist of borrowed funds and equity. Equity is funds owned directly by the bank, as opposed to borrowed funds, which the bank has attracted for a while. The peculiarity of the bank's own capital in comparison with the capital of other enterprises is that the banks' own capital is approximately 10%, and in enterprises about 50%. Despite its small share, the bank's own capital performs several vital functions.
Protective function -
means the possibility of paying compensation to depositors in the event of the liquidation of the bank. A significant share of the bank's assets is financed by depositors. So main function share capital of the bank and equivalent funds is to protect the interests of depositors. Equity allows you to maintain the solvency of the bank by creating a reserve of assets that allow the bank to function, despite the threat of losses. It is important to keep in mind that most of the bank's losses are covered not by capital, but by current assets. Unlike most firms, the bank's solvency is maintained by part of its own capital. A bank is considered solvent as long as its share capital remains intact, that is, as long as the value of its assets equals the sum of its liabilities, minus its unsecured liabilities plus its share capital.
operational function.
To start successful work the bank needs start-up capital, which is used to purchase land, buildings, equipment, as well as the creation of financial reserves in case of unforeseen losses. Equity capital is also used for these purposes.
regulatory function.
In addition to providing a financial basis for the operation and protecting the interests of depositors, banks' own funds also perform a regulatory function, which is associated with a special public interest in the successful functioning of banks, as well as with laws and regulations that allow government bodies control the operations.
The structure of banking resources of individual commercial banks depends on the degree of their specialization or, conversely, universalization, the characteristics of their activities, the state of the market for loan resources, etc.
The structure of the bank's own funds is heterogeneous in terms of qualitative composition and varies throughout the year depending on a number of factors, in particular, on the nature of the use of the profit received by the bank.
The bank's own funds are made up of authorized capital and profits. The bank's own capital is the basis for increasing the volume of its active operations. Therefore, it is extremely important for each bank to find sources of its increase. They can be: retained earnings of previous years, including bank reserves; placement of additional issues of securities or attraction of new shareholders.
Equity management plays an important role in ensuring the sustainability of liabilities and the profitability of banks. One of the ways to manage the bank's own capital is the dividend policy. In conditions of financial instability and underdevelopment of the stock market, many Russian banks ensure the growth of own capital by accumulating profits. Large banks widely use the issuance of shares as a effective way attraction of financial resources.
The authorized capital of Russian banks is formed at the expense of share contributions (share bank) or funds received as payment for shares (joint stock bank).
The bank's reserves are formed at the expense of the bank's profit and include:
The reserve fund, which, in accordance with Russian law, is created in the amount established in the bank's charter in relation to the authorized fund, but not less than 10% for banks accepting deposits from the population. The fund is designed to cover large losses;
The reserve fund for the depreciation of securities is intended to cover losses arising from a fall in the price of securities;
The loan allowance is used to cover potential loan losses and is charged to the bank's expenses;
Fund economic development is formed in the amount established at the meeting of shareholders and is intended for the development of the bank (acquisition of real estate for the bank, equipment, incentives for employees, etc.).
Additional capital is formed due to the difference between the selling rates of common and preferred shares and their face value.
Retained earnings - the accumulated amount of profit that remains at the disposal of the bank. At the end of the period (year, quarter), the sum of all the effective accounts of the bank is credited to the profit and loss account. Part of these funds is directed to the payment of dividends, taxes, and the formation of reserve funds. The remaining part - retained earnings - is a cash fund managed by the bank's management and the meeting of shareholders.
Attracted funds occupy a predominant place in the structure of banking resources. In world banking practice, all attracted funds are divided into deposits and other attracted funds according to the method of their accumulation. The main part of the attracted funds of commercial banks are deposits. Deposits are accepted only by banks that have such a right in accordance with the license of the Bank of Russia.
Other borrowed funds are resources that the bank receives in the form of loans or by selling its own debt obligations on the money market. They differ from deposits in that they are purchased on the market on a competitive basis. The initiative to attract them belongs to the bank itself. They are mainly used by large banks. Usually these are significant amounts, due to which the corresponding transactions are considered wholesale.
4. Ensuring sustainable development of commercial banks
Sustainable development of the banking system is the most important condition for its effectiveness.
The stability of the bank is its dynamic state, which provides the necessary degree of protection from the adverse effects of external and internal factors. The economic stability of the bank is largely determined by financial results its activities, the ratio of risk, liquidity and profitability.
The term "liquidity" (from Latin liquidus - liquid, flowing) in literally words mean ease of implementation, sale of transformation material assets and other assets into cash. Bank liquidity implies the ability to sell liquid assets, acquire funds from the central bank and issue shares, bonds, certificates of deposit and savings, and other debt instruments. This is the bank's ability to ensure timely fulfillment of its liabilities in cash. The bank's liquidity is determined by the balance of assets and liabilities of the bank's balance sheet, the degree of correspondence between the terms of the placed assets and the liabilities attracted by the bank. The bank's liquidity norms are usually set as the ratio of various items of balance sheet assets to the total amount or to certain items of liabilities or, conversely, liabilities to assets.
There are two approaches to characterizing liquidity. Liquidity can be understood as a "stock" or as a "flow". "Stock" characterizes the bank's liquidity at a certain point in time, its ability to meet its current obligations, especially on demand accounts. As a "flow" liquidity is estimated for a certain period of time or for the future. To assess the total liquidity of a commercial bank, it is necessary to consider stationary liquidity (“stock”), current liquidity (“flow”) and prospective liquidity (“forecast”) in the system.
The liquidity of the bank's balance implies a momentary assessment of the state of the bank on a certain date, therefore, the liquidity of the balance is component bank liquidity. At the same time, the balance sheet of a commercial bank must ensure the presentation of analytical and synthetic accounting data in a form acceptable for calculating the total liquidity of the bank. If the second condition is not met, a situation may arise when, having a sufficiently liquid balance sheet on a certain date, the bank is nevertheless completely or partially illiquid.
The liquidity of a bank underlies its solvency. Solvency is the ability of the bank to meet its obligations in due time and in full amount (to depositors for the payment of deposits, shareholders for the payment of dividends, the state for the payment of taxes, personnel for the payment of wages).
The liquidity and solvency of a commercial bank is influenced by a number of factors that can be divided into macroeconomic and microeconomic ones.
To the main macroeconomic factors, which determine the liquidity and solvency of a commercial bank, include: the geopolitical and macroeconomic situation in the country; set of legislative, legal and legal regulations banking activities; the structure and stability of the banking system; the state of the money market and the securities market, etc.
The main microeconomic factors include: the resource base of a commercial bank, the quality of investments, the level of management, as well as the functional structure and motivation of the bank.
In foreign practice, the general liquidity reserve is divided into primary and secondary. The primary liquidity reserve is considered as the main source of the bank's liquidity. At the same time, assets included in the item “cash and debts of other banks” appear in the balance sheets as primary reserves, which include funds on the accounts of required reserves, funds on correspondent accounts (deposits) in other commercial banks, cash in a safe and checks, as well as other payment documents in the process of collection. The share of primary reserves is estimated by the ratio of cash assets to the sum of deposits or to the sum of all assets. Secondary liquidity reserves are highly liquid earning assets that can be turned into cash with minimal delay and negligible risk of loss. These include assets that typically comprise a portfolio of government securities and, in some cases, funds held in loan accounts. The main purpose of secondary reserves is to serve as a source of replenishment of primary reserves.
The total liquidity reserve of a commercial bank depends on the required reserve ratio established by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation and the level of liquidity reserve determined by the bank independently for itself. Each commercial bank strives to create a minimum reserve of liquid funds and ensure the maximum credit potential, based on its liquidity, reliability, and profitability. Liquidity is closely related to the profitability of the bank, but in most cases, achieving high liquidity is contrary to ensuring higher profitability. The most rational policy of a commercial bank in the field of liquidity management is to ensure optimal combination liquidity and profitability.
Banking activity is constantly accompanied by risk. Risks in banking practice are the danger (possibility) of losses in the event of certain events. Risks can be both purely banking (internal), associated with the functioning of a credit institution, and external, or general. The most common financial risks are: the risk of insolvency of the borrower, credit risk, interest rate risk, currency risk, unbalanced liquidity risk. The most important way overcoming or minimizing risks is their regulation, i.e. maintaining optimal ratios liquidity and solvency of the bank in the process of managing its assets and liabilities.
A significant increase in the risks associated with banking puts the problem of "risk - liquidity" in the center of banking operations management.
The analysis of liquidity, profitability and the level of risk of the bank should be carried out in a complex. A high level of profitability, as a rule, is associated with high-risk operations. The potential to obtain the maximum possible benefit increases as the degree of risk increases. The higher the liquidity of the bank, the lower the profitability and vice versa: the lower the liquidity, the higher the expected profit and necessarily the risk.
The main method for managing the liquidity and solvency of Russian commercial banks (in terms of internal and external audit) is their compliance with the economic standards of the Bank of Russia. At present, to ensure economic conditions sustainable functioning of the banking system The Central Bank of the Russian Federation, in accordance with Instruction No. 110-I, establishes a number of economic standards for the activities of commercial banks:
Minimum size authorized capital for newly created and the minimum amount of own funds (capital) for existing banks;
Capital adequacy ratios;
Liquidity ratios;
The maximum amount of risk per borrower or group of related borrowers;
Maximum size of large credit risks;
The maximum amount of risk per one creditor (depositor);
The maximum amount of loans, guarantees and guarantees provided by a credit institution to its participants (shareholders, shareholders) and insiders;
The maximum amount of attracted cash deposits (deposits) of the population;
Standards for the use of own funds of credit institutions for the acquisition of shares (shares) of other legal entities.
An analysis of the bank's income and expenses makes it possible to study the performance of a commercial bank, and, consequently, to evaluate its effectiveness as a commercial enterprise. Banking performance analysis begins with an analysis of income and expenses, and ends with a profit study.
Gross income of the bank is usually divided into interest and non-interest. The stable and rhythmic growth of the bank's income testifies to its normal operation and qualified management. Bank interest income is the accrued and received interest on loans and securities. Non-interest income - income from investment activities (dividends, income from participation in joint activities enterprises and organizations, etc.); income from currency transactions; income from commissions and fines received; Other income. The analysis of the bank's expenses is carried out according to the same scheme as the analysis of its income.
The bank's gross expenses are also divided into interest and non-interest. The bank's gross expenses include: a) operating expenses (commission fees paid for services and correspondent relations; expenses on operations with securities; expenses on operations in the foreign exchange market); b) expenses for ensuring the functioning of the bank (expenses for the maintenance of the administrative apparatus; business expenses); c) other expenses (fines, penalties, forfeits paid; interest and commissions of previous years, etc.).
Profit is main indicator bank performance. Quantitative and qualitative assessments of profitability are made in order to determine the financial stability of the bank. The amount of profit in itself is far from being an exhaustive indicator. It must be compared with other indicators characterizing the bank's activities. Analysis financial activities bank is carried out simultaneously with the analysis of the liquidity of the bank's balance sheet, and on the basis of the results obtained, a conclusion is made regarding the reliability of the bank.
The financial condition of the bank is a complex concept, which is characterized by a system of indicators reflecting the availability, placement and use of financial resources.
The internal audit of the bank involves the assessment, control and analysis of the main activities of the bank by the bank itself, its ideas about the efficiency of work, the feasibility of conducting certain banking operations and services, their profitability, and so on. External audit is carried out by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, other commercial banks, tax office, audit firms and other organizations, as well as clients (real and potential) of a commercial bank.
Important for the bank's activities is not only an internal analysis of its activities, but also a comparison of the results of work with other banks. In a market economy, it is also important to trace the trends in the development of the banking system as a whole at the national level. Today in Russia there is a shortage of analytical information about the work of commercial banks. Therefore, the rating of banks is important as a basis for studying their activities.
The rating of banks is a system for assessing their performance, based on the financial performance and balance sheet data of the bank. The rating of the bank as a whole consists in the derivation of a free assessment in all areas that have been analyzed. Rating score can be made by a special rating agency on the basis of an agreement with the bank.
In world banking practice, two approaches to assessing the activities of commercial banks prevail based on:
Analysis of the system of indicators of a particular bank and comparing them with similar indicators of first-class banks;
Plan
Introduction
Main part
1. Commercial banks and their operations
2. Central Bank and its functions
Conclusion
Bibliography
Introduction
On the basis of credit, credit relations, the credit mechanism, a credit system-banks arises. Bank is not an agency acting as an appendage of the Ministry of Finance, but an economic institution involved in attracting and allocating financial resources.
The totality of credit and financial institutions that accumulate and lend funds form the credit (banking) system of the country.
The modern credit system is a system of a wide variety of financial institutions operating in the loan capital market and carrying out the accumulation and mobilization of income. A two-tier banking system has been adopted in a market economy. The upper level is represented by the central, as a rule, state-owned bank, which does not directly lend to enterprises and the population, but regulates the country's money circulation and manages the entire banking system existing in the country. The second level is occupied by many independent commercial banks, which do the main job of accumulating savings and placing loans. Commercial banks - independent organizations, they are not administratively subordinate to the central bank, although they are obliged to follow the instructions of the central bank within the limits established by law.
Along with banks, at the second level of the credit system, there are specialized non-banking institutions (pension, insurance, investment funds, savings and loan associations, credit unions, etc.), whose activities are mainly reduced to the accumulation of monetary savings of the population, the provision of loans through bonded loans enterprises and the state, capital mobilization through the issue of shares, the provision of mortgage and consumer loans, etc.
In economically developed countries, specialized non-banking institutions play an important role in the accumulation of savings of the population and are important providers of loan capital. Non-banking financial institutions lead an acute competition for attracting savings from all segments of the population, both among themselves and with the banking sector.
One of essential conditions effective functioning of a market economy - the presence of a stable and actively working monetary system of the country. This paper will consider the essence and functions of commercial banks, their types. Since the basis of the entire credit system of the country are commercial banks.
1. Commercial banks and their operations
Commercial banks form the basis of the entire credit system of the country. Modern commercial banks are banks that directly serve enterprises and organizations, as well as the population - their customers. Commercial banks are the main link in the banking system. Regardless of the form of ownership, commercial banks are independent subjects of the economy. Their attitude towards customers is commercial in nature. The main purpose of the functioning of commercial banks is to maximize profits. bank profit is the difference between the percentage that banks receive for the money they lend. And the percentage that they pay for the money provided to them, minus the costs associated with the activities of the bank.
According to banking legislation, a bank is a credit organization that has the right to raise funds from individuals and legal entities, place them on its own behalf and at its own expense on terms of repayment, payment, urgency, and carry out settlement operations on behalf of customers. Thus, commercial banks carry out (should carry out) comprehensive customer service, which distinguishes them from special non-banking credit institutions that perform a limited range of financial transactions and services. Unlike a bank, credit institutions carry out only individual banking operations.
A commercial bank, like any other bank, performs the following functions:
& mobilization of temporarily free cash and savings and their transformation into capital. By accumulating money and savings in the form of deposits (deposits), banks turn them into loan capital and use them to provide loans. Thus, with the help of banks, savings are turned into capital;
& providing loans to individuals and legal entities. The direct provision of temporarily free funds as a loan by their owner to the borrower in practical economic life is difficult. Banks, by receiving funds from end creditors and lending them to end borrowers. Act as an intermediary;
& Creation of credit money - issuing a loan, banks carry out non-cash deposit-credit emission. Having provided the client with a loan, the bank credits a certain amount of money to his account, i.e. creates a deposit, the owner of which can receive cash or carry out non-cash payments- in any case, there is an increase in the amount of money in circulation. The stock of money in circulation increases when the banks lend, and decreases when the loan is repaid;
& cash handling and customer service. Acting as intermediaries in payments, banks perform operations for their customers related to settlements and payments;
& issue, purchase, sale of payment documents and securities. By performing this function, banks become a channel for directing savings to productive purposes.
In addition, in accordance with Russian banking legislation, commercial banks, in addition to the banking operations listed above, are entitled to carry out the following transactions:
ü issuance of guarantees for third parties, providing for the fulfillment of obligations in cash;
ü acquisition of the right to claim for the fulfillment of obligations from third parties in cash;
ü provision of consulting and information services;
ü Leasing to individuals and legal entities of special premises or safes located in them for storing documents and valuables;
ü leasing operations.
In accordance with their functions, banks perform certain operations, which are divided into passive, active and commission.
Passive Operations- these are operations through which banks raise funds, form their resources.
Banking resources are divided into own and borrowed. The sources of own funds are the share capital (authorized fund), the reserve capital formed at the expense of profit, and retained earnings. The required amount of equity capital is regulated. The Central Bank sets the minimum required authorized capital reserves and the maximum ratio of own and borrowed capital. So, today the minimum size of the authorized capital in Russia is set at 100 million rubles.
Despite its small share, the bank's own capital performs several vital functions.
protective function. A significant share of the bank's assets (approximately 88%) is financed by depositors. Therefore, the main function of the bank's equity capital and equivalent funds is to protect the interests of depositors. Equity allows you to maintain the solvency of the bank by creating a reserve of assets that allow the bank to function, despite the threat of losses.
Operational function. To start the successful work of the bank, start-up capital, which is used to purchase land, buildings, equipment, as well as the creation of financial reserves in case of unforeseen losses. Equity capital is also used for these purposes.
Regulating function. Own funds also perform a regulatory function, which is associated with the special interest of society in the successful functioning of banks, as well as with laws and regulations that allow government bodies to control ongoing operations.
Equity management plays an important role in ensuring the sustainability of liabilities and the profitability of banks. One of the ways to manage the bank's own capital is the dividend policy.
However, the predominant part of banking resources are borrowed funds, which are used to provide loans and purchase securities. Investors are the owners of funds and lend them to banks for a certain percentage fee. The attracted funds are made in the form of deposits (deposits) and are debt obligations(liabilities) of the bank.
Deposits- the main source of banking resources, however, in addition to attracted deposits, the source of banking resources can be loans received from other banks and loans from the central bank.
Cash placed individuals for storage and income purposes, constitute a contribution. Income on the deposit is paid in cash in the form of interest. The deposit is returned to the depositor at his first request. Banks ensure the safety of deposits and timely fulfillment of their obligations to their depositors. Attracting funds to deposits is carried out on the basis of an agreement between the bank and the depositor. To ensure the guarantor of the return of citizens' funds attracted by banks and compensation for the loss of income on invested funds, a fund may be created compulsory insurance deposits.
Contributions can be:
1. Demand deposits - a deposit, the issuance of which is provided at the first request of depositors;
2. Term deposit - a deposit, the return of which is made after the expiration of the term specified in the agreement.
Under a bank deposit agreement of any kind, the bank is obliged to issue the deposit amount or part of it at the first request of its depositor. Exceptions are deposits made by legal entities on other terms of return stipulated by the agreement.
Interest on the amount of a bank deposit is accrued from the day following the day it is received by the bank, from the day preceding its return to the depositor - or its debiting from the depositor's account for other reasons.
The conclusion of a bank deposit agreement with a citizen and the deposit of funds to his deposit account is certified by a savings book. A bearer savings book is a security.
The bank can also provide various loans. Under a loan agreement, a credit institution - a lender undertakes to provide a loan to the borrower in the amount and on the terms stipulated by the agreement, and the borrower undertakes to return the amount of money received and pay interest on it.
The lender and the borrower may refuse to provide and receive a loan; lender - if there are obligations under which the loan granted to the borrower will not be repaid on time; the borrower must notify the lender of the refusal of the loan.
In case of misuse of the loan by the borrower, the lender may also refuse further lending under the agreement.
Active operations - these are operations through which banks realize the resources at their disposal. The financial resources provided by the bank form bank debts and are its assets.
The main type of active banking operation is the issuance of a loan (provision of a loan). However, it must be borne in mind that banks do not have the right to issue a loan for the entire amount of their deposits. A bank is required to keep a portion of its deposits in cash or deposits in interest-free central bank accounts. The minimum amount of a deposit that a bank must keep in the central bank or have in cash is called the required reserves. The amount of required reserves is determined on the basis of standard(rr), set by the central bank as a share (percentage) of the bank's deposits.
For example, if a bank's deposits amount to 100 million rubles, and the required reserve ratio is set at 20%, then the bank is required to keep 20 million rubles in the accounts of the central bank.
At first glance, it may seem that the amount of required reserves is a kind of insurance fund from which commercial banks can draw the funds they need in the event of large and unexpected withdrawals of money by their depositors. However, it is not. The fact is that deposits in commercial banks can be several times larger than the amount of reserves, i.e. reserves are partial, therefore, in the event of sudden and large withdrawals of funds by depositors, the presence of required reserves will not save commercial banks from bankruptcy.
The requirement to keep part of the liabilities in the form of reserves is explained by the need to control the ability of commercial banks to lend to their customers. The central bank, as a coordinating body, strives to prevent an excess or shortage of credit and thereby exert the necessary influence on the amount of money in circulation and on the macroeconomic situation as a whole. The actual reserves of the bank, as a rule, are greater than the required: these excesses are called excess reserves, which serve as a source of loans.
If the bank has 100 million rubles. actual reserves, he can issue new loans in the amount of 80 million rubles. (100 million rubles of actual reserves minus 20 million rubles of required reserves).
A very common active operation of the bank, a method of providing short-term loans is accounting of bills. Accounting for a bill is the purchase of a bill by a bank, the bank buys the right to receive money on the bill at the end of its term. For the fact that the bank advances the holder of the bill, he charges discount interest - discount. The discount is equal to the difference between the amount indicated on the bill and the amount paid by the bank when discounting the bill. At the expiration of the bill of exchange, the bank presents it to the debtor for redemption.
Active operations include investment activities bank - an investment by a bank of funds in private and government securities. By buying securities, banks provide an inflow of funds for a relatively a long period. In terms of income generated, investments are the second (after interest on loans) source of bank profits.
Commission transactions of banks - This different kind intermediary and trust services, for the provision of which the bank charges a commission. The range of banking services provided is constantly expanding. In particular, such commission transactions as leasing, factoring and trust are becoming more widespread today.
Leasing- this is banking activity for leasing machines, equipment, structures. Banks, instead of lending to the enterprise to acquire such funds, they themselves acquire and rent, retaining the right of ownership. In this case, the bank receives rent (leasing payments), and not loan interest. Lease payments in these recommendations mean the total amount paid by the lessee to the lessor for the right granted to him to use the property that is the subject of the contract.
The lease payments include: depreciation of the leased property for the entire term of the lease agreement, compensation of the lessor's payment for the borrowed funds, commission fee, fee for Additional services of the lessor, provided for by the leasing agreement, as well as the cost of the property to be bought out, if the agreement provides for the buyout and the procedure for paying the specified value in the form of shares in the composition of leasing payments. Leasing payments are paid in the form of separate installments.
When concluding an agreement, the parties establish the total amount of leasing payments, the form, method of accrual, the frequency of payment of contributions, as well as the methods of their payment.
Payments can be made in cash, compensation form (with products or services of the lessee), as well as in a mixed form. At the same time, the price of products or services of the lessee is established in accordance with the current legislation.
Leasing is a specific form of investment financing for enterprises.
Factoring- a type of banking activity, which consists in the fact that the bank buys from its customers their claims to debtors (buyers), paying them 60-90% of the amount of obligations in the form of an advance, with a final recalculation after repayment of the debt. The bank charges a fee for these services.
How is the demand for factoring changing in Russia? Factorings.ru conducted a study of the demand for factoring services among Russian companies in 2008 and 2009. “We analyzed data from 1,130 applications sent to factors from March 2008 to August 2009 through Factorings.ru. Applications for factoring services were transferred to factors directly via e-mail. The growth of interest in factoring from the business side is growing steadily - over the period under study it has grown at least three times.
Trust operations- execution by the bank various functions related to property management pension funds, storage of securities by proxy of the client. Banks receive a commission on trust transactions. By concentrating trust assets, banks have the opportunity to significantly expand the scope of their activities and influence, thus ensuring high profits for themselves.
The results of active and passive operations of the bank are reflected in bank balance sheet, which characterizes the ratio of its liabilities (debts of the bank) and assets (debts to the bank) on a certain date. Annual reports (balance sheets) of banks are published in the open press.
2. Central Bank and its functions
At the end of the 19th and the beginning of the 20th century, in most countries, the issue of banknotes was concentrated in one issuing bank, which became known as the central issuing bank, and then simply the central bank.
The most important principle of the functioning of central banks is their independence from government. The central bank does not set itself the goal of profit maximization inherent in commercial banks and does not compete with the latter. The main purpose of the central bank in a market economy is to ensure the stability of the banking and financial systems, control over money circulation countries, conducting a monetary policy that would ensure the achievement of macroeconomic goals, primarily without inflationary development of the economy.
The main purpose of the central bank in a market economy is to ensure the stability of the banking and financial systems, control over the country's money circulation, conduct a monetary policy that would ensure the achievement of macroeconomic goals, before the inflation-free development of the economy.
Traditionally, the central bank performs four main functions:
v monopoly issues banknotes.
v Is a bank of banks. The clients of the central bank are commercial banks.
v The Central Bank keeps the cash reserves of banks, through accounts opened by commercial banks in the Central Bank, carries out settlements between them, and, if necessary, provides credit support to commercial banks.
v The central bank holds accounts for the government and government agencies and acts as the government's creditor teller.
v Regulates non-cash issuance by commercial banks. The main instruments of influence of the central bank on the mass of money created by commercial banks are:
ü Operations on the open market - purchase and sale of government securities by the central bank;
ü Discount rate;
ü Required reserve ratio
The Central Bank also influences the activities of commercial banks, exercising supervision over their activities, setting various kinds of economic standards: the ratio between cash reserves and deposits, equity and borrowed capital, equity and assets, maximum size risk per borrower, capital adequacy ratios, etc.
All the functions of the central bank are closely interconnected, and by performing them, the central bank carries out monetary regulation of the economy.
Conclusion
The development of the economy would be impossible without the existence of a credit mechanism, through which temporarily free funds are transferred to business entities in need of additional cash reserves.
The huge role and importance of banks in a market economy is associated with their ability to create new money in the process of lending (to carry out non-cash deposit and credit emission of money) and thereby influence the amount of money in circulation. By lending money, banks create new money. However, an individual bank has handicapped to expand their loans. He can't lend Moreover, that received from depositors, cannot lend the entire amount of deposits, because, in accordance with the requirements of the central bank, part of the deposits must be kept in the accounts of the latter. The ability of an individual bank to create money is limited by its excess reserves.
Whole banking system can lend and create new money several times its excess reserves.
Any bank can be characterized by the form of ownership, field of activity, size, types of operations performed. Banks operate on the basis of their own and borrowed capital. All operations to raise capital are called passive, and operations to place funds are called active. The bank's assets must be equal to the bank's liabilities (debts) plus the bank's equity. If assets exceed liabilities, then the bank is solvent. If assets are less than liabilities, this means that the bank's equity capital decreases and the bank becomes insolvent, i.e. bankrupt.
LITERATURE
1. Efimova E.G.: Economics for lawyers: textbook. - 2nd ed., Rev. and add.-M.: FLINTA: Moscow Psychological and Social Institute, 2001.-472p.
Our experts will help you write a paper with a mandatory check for uniqueness in the Anti-plagiarism systemSubmit an application with the requirements right now to find out the cost and possibility of writing.
A commercial bank is an organization different shapes property, which can perform passive operations to raise funds from customers, active operations and conduct settlement and cash services.
There are different types of commercial banks, but they all have the same features:
- this is a legal entity whose purpose is to make a profit;
- may be formed in the form of an LLC, joint-stock company or companies with additional liability;
- conducts banking operations on the basis of a license issued by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation;
- can generate income through certain operations (we will talk about this a little later).
Such a bank accumulates cash deposits of clients, giving them some kind of remuneration in the form of a fixed percentage of profits. Temporarily free funds are used by competent employees of the organization to issue interest-bearing loans to other customers and companies.
Thanks to such activities of banks, these savings of depositors are converted into capital, bringing different types commercial bank income.
Some people mistakenly associate banks with loans only. But this is not true, since a loan is a relationship between a borrower and a lender, which is regulated by a loan agreement and relates to the amount of the loan.
The Bank is only one of the parties to such relations, acts as an intermediary (credit company).
Types of banks depending on their functions

There are two main types of commercial banks:
- universal. Such an institution can carry out all types of banking operations: issue loans, keep deposits, conduct settlement and trust operations, etc.;
- specialized. They perform various kinds of operations only in a certain direction, while there are several types of specialized banks: savings, mortgage, investment, innovative. Let's talk about each of these types in more detail.
Savings bank - it stores the deposits of the population. The accumulated funds are later used to issue consumer loans to the population at interest.
A small profit (also in percent) is received by the deposit holder. In turn, deposits can be perpetual or on demand, therefore, the term for issuing a loan is also limited by time frames.
Investment banks are created for the purpose of buying different shares. The bank's resources are formed by selling its shares; such banks do not carry out deposit operations and do not lend to the population. But they help to meet the demand of industrial and other enterprises in fixed capital. Their role is in the issuance of bonds and shares of industrial companies.
The Innovation Bank specializes in investment policy, provides loans to enterprises to upgrade equipment, and finances scientific and technical programs.
The resources of such a bank are formed by issuing shares, attracting deposits and customer deposits. The same money can later be used to issue loans. Usually these are medium- and long-term loans.
Mortgage banks
Separately allocate mortgage banks. Here, everyone can get a loan for the purchase of ready-made real estate, take a loan for an apartment in a new building, construction of a residential building or production premises and much more.
Typically, interest rates on such loans are quite high, and the bank's customers are subject to rigorous assessment and verification for compliance with the requirements of the bank. Real estate transactions are very risky.
If necessary, such organizations may issue mortgage bonds. These organizations are of several types:
- land. In this case, you can get a loan secured by an existing land plot;
- ameliorative;
- utilities that provide loans secured by real estate in the city.
It is commercial banks that account for the bulk of all foreign exchange transactions. They not only meet the needs of the population in loans, but also engage in speculation at their own expense. In this market, all transactions are carried out on a large scale.
Goals of activity and sources of profit formation
Types of activities of commercial banks and their main goals:
- attracts depositors' funds and places them in storage for a certain period of time;
- places these funds on its own behalf, lending to individuals and legal entities;
- carries out settlements on bank accounts of customers, creates these accounts and services them (carries out settlement and cash services);
- engages in the purchase and sale of foreign currencies by bank transfer and in cash.
Since each such organization holds a large amount of borrowed funds, it faces an increased responsibility for the preservation of these funds to its contributors. Therefore, it is so important to choose the appropriate type of bank if you need to deposit a certain amount and devote enough time to check its reliability.
All operations of commercial banks can be divided into 2 types: active and passive. Active allow you to create new credit resources.
Passive - these are operations with the help of which the formation of the banks' own resources takes place, i.e. money already in circulation.
Thanks to them, organizations have the opportunity to purchase credit resources on the market. Such passive operations are carried out in certain forms:
- issue of securities of the bank itself;
- obtaining a loan from other legal entities;
- carrying out deposit operations;
- deductions from the bank's profits in order to form and increase funds.
Results
A distinctive feature of such organizations is their interest in making a profit from their activities, which forms their commercial interest in this system of relations.
They operate within their own resources and have the power to create their own money. But this possibility is somewhat limited.
AT federal law“On Banks and Banking Activity”, adopted by the State Duma on 07.07.1995, the following definition of a bank is given: “ Bank–a credit institution that has the exclusive right to carry out the following banking operations in aggregate: attraction of funds from individuals and legal entities to deposits, placement of these funds on its own behalf and at its own expense on the terms of repayment, payment, urgency, opening and maintaining bank accounts of individuals and legal entities persons".
The main functions of a commercial bank
The main functions of commercial banks include:
mobilization of temporarily free funds and their transformation into capital;
lending to enterprises, the state and the population;
issue of credit money;
implementation of settlements and payments in the economy;
issuing and founding function;
consulting, provision of economic and financial information.
Function accumulation and mobilization of temporarily free funds is one of the oldest functions of banks. Initially, commercial banks used only their own funds in their activities, but later it became clear that these funds were not enough and other people's, borrowed funds were needed, which predetermined the role of the bank as an intermediary in the redistribution of funds. In the future, banks began to look for opportunities to expand the channels for attracting funds by opening various deposits and accounts, inviting the owners of funds to pay the appropriate interest. As a result, the share of borrowed funds in relation to own funds increased immeasurably and amounted to 80% of the bank's total capital. Performing a function granting a loan, a commercial bank acts as an intermediary between entities that have free cash and entities that need it. He, accumulating money (the first function), has the ability to provide these resources to those in need the right amount and for the required period. Thus, lending to enterprises, industry, the state and the population is carried out. The performance of this function contributes to the expansion of production, the financing of industry, the creation of reserves, the increase in consumer demand, and the expansion of the financial activities of the government.
Mediation in making payments and settlements is the next function of a commercial bank. Commercial banks ensure the functioning of the payment system by transferring funds. The high efficiency of the use of means of payment is evidenced by a gradual reduction in cash turnover and an increase in the share of non-cash payments. In foreign countries, non-cash payments account for over 90% of all payments, in Russia - about 64%. In order to implement this function, commercial banks open accounts for their customers and transfer funds.
Means of payment creation function in the form of bank deposits, which are used with the help of checks, plastic cards, bills of exchange, electronic transfers. This function appeared in commercial banks due to the development of credit money, the withdrawal of gold money from circulation and the transformation of banknote emission into deposit and check, which made it possible to expand non-cash circulation and reduce cash. The purpose of the banking system is to ensure that the amount of money in circulation corresponds to the needs for them, to maintain normal economic growth rates and high level employment.
The development of the lending function is the function of organizing the issue and placement of securities. It is carried out through investment operations and has greater value in an elastic credit system, which is necessary condition relatively stable economic growth rates. When bank loans are not available, expansion of production becomes impossible or will be delayed until the necessary funds are accumulated. Moreover, industrial enterprises will be forced to hold large amounts of money, which would be uneconomical, so commercial banks organize the sale of securities on the securities market, which makes it possible to redistribute funds. The expansion of the significance of this function led to the fact that banks, starting from the 20s of the XX century. become direct competitors to stock exchanges, through which the bulk of retail sales of securities are realized.
Thus, a bank is primarily a commercial enterprise, which is based on making a profit, and the implementation of functions occurs as a result of passive and active operations.
AT modern conditions by nature of activity commercial banks subdivided into specialized and general .
Specialized banks include banks engaged in certain types of lending. Such banks, in particular, include investment, mortgage, savings, etc.
investment banks engaged in financing and long-term lending to various sectors of the national economy. Through investment banks, a significant part of the needs of enterprises in fixed capital is satisfied. These banks mobilize the vast majority of their resources by issuing their own shares and bonds. They also play an active role in the issuance and placement of shares in industrial and other companies.
Mortgage banks provide long-term loans secured by real estate - land and buildings. They mobilize resources through the issuance of a special type of securities - mortgage bonds, which are secured by real estate pledged in banks. The clients of mortgage banks are farmers, the population, and in some cases - entrepreneurs.
savings banks specialize in the accumulation of monetary deposits of the population.
Universal Banks in the course of their activities carry out several of the above operations.
In countries with a developed credit system, a feature of modern banking is the implementation of many banking operations with a wide clientele. For example, the largest commercial banks in the UK use about 100 various kinds customer service operations, US commercial banks - more than 150 types of operations, Japanese banks - about 300 types.
Commercial banks carry out their activities in order to make a profit. Main sources of bank profits are:
excess of interest received by banks on loans issued over interest paid on deposits;
interest and dividends from investments in securities;
commissions on settlement, transfer, factoring, trust and other commission transactions;
from exchange transactions;
from foreign exchange transactions, etc.
Main operations of commercial banks
All operations carried out by banks are divided into passive and active.
Passive operations of commercial banks aimed at the formation of banking resources. In the practice of Russian commercial banks, passive operations include: accepting deposits (deposits); opening and maintenance of customer accounts, including correspondent banks; issue of own securities (shares; bonds), financial instruments (bills, deposit and savings certificates); obtaining interbank loans; obtaining centralized credit resources.
The purpose of the operations of a commercial bank is as follows:
provision of resources for the bank's activities;
formation of additional sources of funds for productive use in the economy;
increase in income of individuals and legal entities receiving bank interest on deposits;
growth of the bank's own capital;
creation of reserve funds for insurance of banking operations.
Basic passive operations commercial bank - deposit.
Deposit operations- these are fixed-term and perpetual investments of the bank's clients. AT treasures on demand placed in banks on various accounts opened by customers. They are intended for current settlements and can be fully or partially claimed at any time. Withdrawal of these deposits is possible both in cash and in the form of non-cash payments.
Term deposits - these are funds credited to deposit accounts for a strictly specified period with interest paid. The rate on them depends on the size and term of the deposit. Varieties of time deposits are deposit and savings certificates.
Deposit certificate - this is a written certificate of the bank on the deposit of funds, which entitles the depositor to receive at the end of the established period of the deposit and interest on it. The certificate of deposit is issued only to legal entities. The right to receive a deposit on a certificate of deposit may be transferred to another person. For individuals it is used savings certificate .
Active Operations
Active operations of a commercial bank are operations for the placement of borrowed and own funds of a commercial bank in order to generate income and create conditions for banking operations.
Active operations of a commercial bank are primarily credit operations, investment operations, operations property formation jar, settlement and cash operations, intermediary commission(factoring, leasing, forfating, etc.). All credit transactions can be grouped as follows 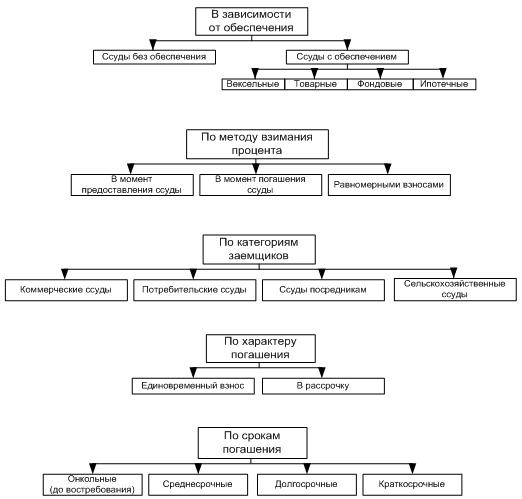
Another important active operation of banks is their investmentactivity, in the course of which banks act as an investor, investing resources in securities or acquiring rights for joint, economic activities. Preferred shares, bonds, government debt obligations, financial instruments (bills) can serve as such securities. Transactions with securities include transactions with securities that are quoted on the stock exchange. In this case, commercial banks may enter into agreements with the Central Bank of the Russian Federation for servicing operations with government short-term bonds.
In the structure of assets of commercial banks, the so-called highly liquid assets are distinguished: the balance of cash held by the bank and ensuring its payments in cash; reserve of means of payment on accounts with the Central Bank of the Russian Federation (correspondent and reserve accounts) and other commercial banks (correspondent accounts).
Other active operations are diverse in form and their development brings income to banks. These include operations with foreign currency, trust, settlement, etc.
Under the influence of increasing interbank competition, commercial banks are constantly expanding the number of their operations through operations that can be carried out not only by credit institutions. Thus, in the banking sector, leasing and factoring operations appeared in the group of active lending operations.
Leasing operations consist in the provision of machines, equipment, real estate and other elements of fixed capital to tenant enterprises on a long-term lease basis.
There are usually three parties involved in a leasing transaction. In the person of the owner of the property - the lessor, providing the property for use on the terms of the leasing agreement, leasing companies or commercial banks most often act. The user of the property - the lessee is a legal entity (an enterprise of any form of ownership). In addition, the seller of the property participates in the leasing - the supplier, which may be a manufacturer or a trading company.
Usually, a potential lessee selects the supplier of the property he needs, but, not being able to acquire it, turns to the lessor, for example, a bank, with a request to participate in the transaction. The bank buys property from the supplier at its own expense and leases it to the lessee on the terms specified in the agreement. Thus, the bank provides the user with a financial service similar to a credit transaction. The Bank acquires property in ownership for the full cost, which is reimbursed by periodic contributions from customers.
Factorin d represents an assignment to the bank of unpaid debt claims arising between counterparties in the process of selling products, performing work, rendering services, and is a type of trade and commission operation combined with lending. Wherein we are talking, as a rule, about short-term requirements.
A commercial bank is a credit institution that has the exclusive right to carry out the following banking operations: attracting funds to deposits, placing these funds on its own behalf and at its own expense on the terms of repayment, payment and urgency, as well as opening and maintaining bank accounts of individuals and legal entities persons.
The main purpose of the functioning of commercial banks is to maximize profits.
The functions of a commercial bank include:
1. Mediation in credit. It is manifested in the ability of banks to act as intermediaries between those economic entities and the population that have temporarily free cash resources, and those who need them. The money resources of enterprises released in the process of circulation, savings and savings of the population are accumulated by banks, converted into loan capital and transferred to borrowers in compliance with the basic principles of lending.
2. Mediation in payments between independent entities and in transactions with securities. A commercial bank, on behalf of its clients, carries out operations related to settlements and payments in non-cash form.
3. Issue of credit money. A commercial bank issues credit funds of circulation by means of a deposit-check issue, the essence of which, when issuing a loan, is to credit it to the account of a business entity.
All functions are closely intertwined and allow a commercial bank to act as a body issuing means of payment for servicing the entire circulation of capital in the process of production and circulation of goods. But commercial banks do not have the right to issue cash banknotes on their own.
The main principles of the commercial bank activity are:
1. A commercial bank works with clients within the limits of actually available resources in the conditions of market relations;
2. The bank has a high degree of economic independence with full economic responsibility for the results of its activities, subject to the regulation of its work by indirect economic methods;
3. The Bank shall be liable for its obligations with all the funds and property belonging to it, which may be levied in accordance with the current legislation. The bank assumes all risks from these operations.
Currently, commercial banks can be classified according to a variety of criteria:
1. By form of ownership:
1.1 State
1.2 Private (stock)
1.3 Mixed
2. By the nature of the activity:
2.1 Universal
2.2 Specialized
2.3 Industry
3. By scale of activity:
3.1 Large
3.2 Medium
3.3 Small
4. By degree of independence:
4.1 Independent
4.2 Subsidiaries
The result of the activities of commercial banks are various kinds of services provided. They can be rendered to clients through a variety of operations, which can be grouped as follows: fig. 3
Fig.3. Grouping operations of commercial banks
Operations connected with the formation of bank resources are called passive. The resources of commercial banks can be formed at the expense of their own, attracted and issued funds. The formation of resources of commercial banks is shown in Figure 4.
RESOURCES OF COMMERCIAL BANKS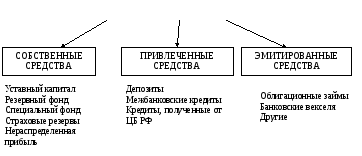
Fig.4. Formation of resources of commercial banks
The own resources of a commercial bank include authorized capital, reserve and special funds, insurance reserves and retained earnings.
The authorized capital is formed at the expense of the participants' own funds and serves to ensure its liquidity. fourteen
The reserve fund is formed from deductions from profits and serves as a source for recovering losses from active operations and paying interest on bonds and dividends.
Commercial banks can form separate special funds (economic incentives, production purposes). The procedure for their formation and use is determined by the Charter of the bank.
Insurance reserves are reserves, the formation of which is mandatory. They are included in the cost of services rendered by the bank.
Retained earnings is the part of profit remaining after taxation, deductions to reserve, special funds and dividend payment funds.
Attracted funds are funds transferred for temporary use to banks by business entities and the population. They make up a significant part of the resources of commercial banks. Deposits form the basis of attracted resources. This is a bank service related to attracting temporarily free funds of business entities and the population into deposits. Non-deposit sources of attracting resources include: interbank loans and loans received from the Central Bank of Russia.
Issued funds of banks are additional funds raised by customers. These include, for example, bonded loans, bank bills.
Operations related to the placement of banking resources for the purpose of making a profit are called active. These include:
accounting and loan operations, as a result of which the bank's loan portfolio is formed;
Investment operations that create the basis for the formation of an investment portfolio;
commission (intermediary) operations.
Lending - the most important species active operations. Bank loans can be classified according to the following criteria (Appendix 1.).
Bank lending is carried out with strict observance of the principles of lending (urgency of return, security, payment, differentiated approach).
The active operations of the bank include accounting (discounting) bills. This means the purchase of bills by the bank before their maturity. For this operation, the bank charges the client a certain percentage, which is called the discount percentage, or discount.
The discount is the difference between the amount indicated on the bill and the amount paid to the holder.
Investment operations - the activities of the bank to invest resources in securities in order to obtain direct (dividends, interest, profit from resale) and indirect income generated by expanding the influence of banks on customers through the ownership of a controlling stake in their securities.
Commission transactions are transactions that the bank performs on behalf of its customers and charges them in the form of commissions. The number of these operations is constantly growing. These include such services as settlement and cash services for clients, trust operations, foreign exchange operations, information and consulting services, issuance of guarantees and warranties, renting safes, etc. 15
In this chapter, the theoretical foundations of the functioning of the banking system in modern economy, disclosed the essence and principles of the organization of the banking system, identified the main factors influencing its development. It should be noted once again that the banking system means the historically established and legislatively fixed system of organizing banking in a particular country. It includes all banking and non-banking institutions that carry out individual banking operations. Legislation determines the structure of the banking system, establishes the scope of activities, subordination and responsibility for the various institutions included in the system. The banking system of the Russian Federation has a two-tier structure. The Central Bank occupies the main position in the banking system. The purpose of its activities is the development and strengthening of the banking system of the Russian Federation; protecting and ensuring the stability of the ruble exchange rate; ensuring the efficient and uninterrupted functioning of the payment system. The second level includes credit organizations and branches of foreign banks. The main part of this block is made up of commercial banks, the main and main purpose of which is to obtain the maximum possible profit. In turn, the Central Bank does not seek to maximize profits, this is the main difference between these levels. The two-level structure indicates the development of the banking system of the Russian Federation.
This is manifested at least in the fact that the Central Bank performs a controlling function in relation to other elements of the system.
This chapter identified the main factors influencing the development of the banking system, since their knowledge and changing their impact can further improve the development of the banking system.
The activities of the Central Bank and commercial banks were considered in detail. Further, this will help to identify the main problems of the functioning and development of the banking system, as well as to determine the main directions for improving the banking system and the prospects for its further development.