Internet safety effective programs. Computer security programs. What to do then
Read also
The number of Internet users in Russia is growing rapidly: in the fall of 2014, the monthly audience of Runet reached 72.3 million users, which is 62% of the Russian population. The volume of user data on the Internet is also increasing, because today you can do almost everything online: from payment to utilities before purchasing air tickets. At the same time, the number of cyber threats is growing. Last year, Heartbleed, Shellshock, leaking photos of naked celebrities from iCloud, and many other events in the IT field thundered throughout the world. At the same time, Russians are at greater risk than foreign users: according to Kaspersky Lab, in the second quarter of 2014, Russia ranked first among the countries in which users were at greatest risk of infection via the Internet.
But is knowledge about how to counter cyber threats increasing? Especially considering that today you can lose much more as a result of hacking your account than at the dawn of RuNet? Many experts believe that a huge number of users still neglect basic rules, essentially nullifying with their carelessness all the efforts made by online services to improve security.
We analyzed how Russian users ensure their security on the Internet, and also found out how often they encounter fraud. The online survey, conducted with the participation of the research company Nielsen, involved 1,783 people aged 15 to 64 years old who live in cities with a population of over 100 thousand people and access the Internet at least once a week.
Checking connection security
One way to protect your login and password when working with various Internet services is to use an encrypted connection using the HTTPS protocol. You can check whether an Internet resource has a secure connection enabled in address bar browser; as a rule, it is indicated by a padlock icon (depending on the type of browser). This check allows you to further ensure that the site is not a phishing site.The study showed that when entering personal data in mail and social networks, in almost half of the cases, users do not check for the presence of a secure connection icon. But when making online payments, people check their secure connection almost twice as often. In general, we can say that users of online services do not attach special significance presence or absence of a secure connection icon.
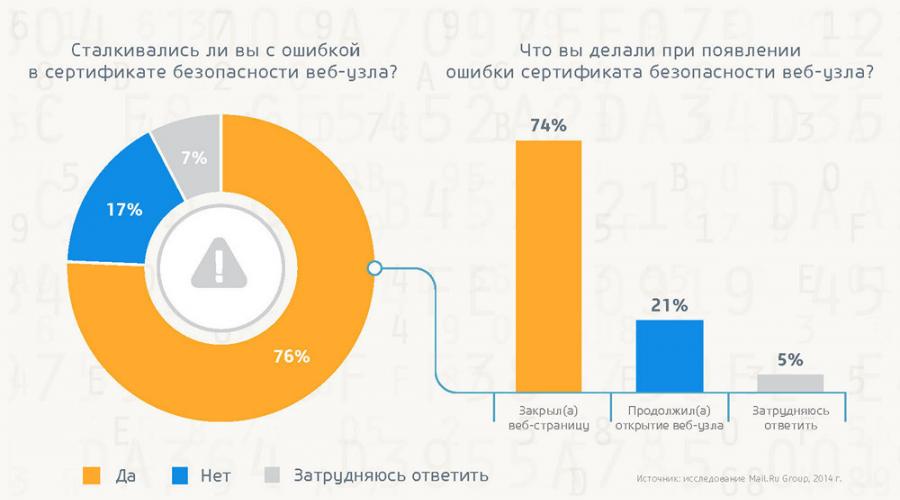
Sometimes, when visiting various websites, users encounter an error message about the website's security certificate. The presence of such errors may mean that they are trying to deceive the user or want to intercept information transmitted to the server. When an advertisement appears, it is recommended to stop working with the suspicious resource. The majority of users (three quarters) encountered such messages. At the same time, 21% of them continued to work with the site. Interestingly, users under the age of 34 are almost 2 times less likely to pay attention to a security certificate error and continue working with the site.

To access both email and social media, users typically use browser bookmarks or links on a quick access page. This method is safer, since in this case the user is protected from typos that could lead to a fraudulent site. However, every tenth user types the address into the browser line.

Passwords used
Obviously, it is recommended to create unique passwords for the most important services. After all, hacking third-party resources is the main way to steal accounts. Large services are constantly working to strengthen their security, while many small forums, torrent trackers, and online stores neglect such things - and hackers, knowing this, attack them. If, when registering on a weakly protected resource, a person specified the same password that he uses for mail, then if the resource is hacked, the hacker automatically gains access to the mailbox. The results of the study indicate that 12% of respondents use the same passwords for all accounts. 36% of respondents use different passwords for the most important ones, and the same ones for the least important ones.
According to the results of our research, the average RuNet user has three email accounts. Below we will separately consider the use of the main box (the only one or most often used for personal purposes) and the additional one.
Since it is quite difficult to come up with different passwords for all accounts, many experts recommend using unique passwords for the most important ones, including email and social networks, and the same ones for the rest. However, 24% of email users use the password from the main mailbox on other resources, of which about 2/3 of email users use the same password on social networks (62%), 27% in online stores, 25% in additional mail box.
Ideally, passwords should be changed once every three months. However, only a fifth of respondents do this. It is noteworthy that 22% of study participants never changed the password for their main mailbox, and every third one never changed their password for their secondary mailbox.


According to modern security standards, a strong password must consist of at least eight characters and be a combination of letters in different case, numbers and special characters, chosen at random or in a manner understandable only to the user. Only 26% of respondents use a password consisting of symbols, letters and numbers. For most users, the password consists of only letters and numbers. 37% of respondents use only lowercase letters in their passwords. Moreover, among owners of relatively short (less than 8 characters) passwords, such carelessness occurs almost one and a half times more often than among those whose passwords consist of 8 characters or more (44% and 32%, respectively). 43% of respondents use passwords between 6 and 8 characters long. 27% - from 9 to 10 characters. Only 26% of users have passwords longer than 10 characters.

Almost a third of users use a random set of letters as a password (29%), and another 27% use a word they made up themselves. 17% prefer to use in password Russian word, typed in Latin letters, which is an unsafe option, since attackers also know how to switch the keyboard layout. Among those whose passwords contain numbers, 17% use their date of birth (their own or a loved one’s), 5% use a phone number.

Most users remember passwords from email and social networks by heart, about 30% write them down on paper. Only 3% of users use special applications for storing passwords.

The quality and frequency of password changes depend mainly on the user. However, today Internet services have the opportunity to influence the level of complexity of the passwords specified. Many resources do not allow the creation of a short
- password without numbers. So, for example, it is impossible to create a password in Mail.Ru Mail:
- shorter than six characters,
- matching the login,
- only numbers or numbers and dots and at the same time shorter than 10 characters,
- being a dictionary word.
Security measures when using online services
We were also interested in what security measures users of various Internet services take: what password recovery methods they use, how they treat links in their email, and how they assess the security of their accounts. Separately, questions were asked about the security measures that users most often resort to when making online payments.By far the most in a safe way password recovery is considered to be linked to the number mobile phone. This method of recovering the password from the main mailbox is used by 68% of respondents. There are fewer of those who link an additional mailbox to their phone number - 41%. Most often, a secret question is used to recover the password for an additional mailbox, which is much less secure compared to binding to a phone number, since, in fact, it is another password.

One of the common methods of hacking accounts is phishing. A typical example: the user is sent a link to a website disguised as an authorization page on some popular resource. The person enters a username and password, which are immediately sent to the attacker. Therefore, when clicking on links that come from unfamiliar senders, you need to be very careful: it is better not to open them at all. Or at least check the website address. The results of the study indicate that users are wary of links sent to their main email inbox: 74% in such cases always carefully check the address before clicking on the link. But at the same time, people are less careful about the security of an additional account: they change their password less often, use a phone number link less often, preferring a security question for recovery.

Let's consider what security measures users most often resort to when making online payments. First of all, they study information about an online store on the Internet (60%). 27% try not to make purchases in stores with free hosting. 17% check the certificate of authenticity issued to the site. Another 17% use a virtual keyboard to protect themselves from keyloggers.

In addition to users' knowledge of possible security measures, we were interested in their opinion on how secure their email and social media accounts are. Almost half of users believe that their accounts are safe. About a third are concerned about the insecurity of their email accounts, believing that their mailboxes are “not secure at all” or “rather not secure.” On average, the security of the main and additional boxes is rated equally.


Experience with fraud
Today, tens of thousands of people face online fraud every day. “Fraud” means theft of an account password and/or sending spam on behalf of the user in the mail, social networks, as well as fraud in online payments (for example, debiting funds from a card). Many experts believe that most often users suffer due to their own carelessness or inattention, nullifying the efforts of Internet companies to improve security. This is confirmed by the results of our study. A quarter of the study participants experienced the theft of their main mailbox password, and 9% experienced it more than once. 17% of respondents had their password for an additional mailbox stolen.
Our respondents are more likely to encounter fraud on social networks than when using mail or making online payments. Almost half of social network users (48%) had their passwords stolen, 58% received fraudulent messages, and half experienced spam being sent in their name.


Basically, users became victims of fraud for three reasons: they used simple passwords, downloaded viruses, and went to fraudulent sites. When making online payments, use simple password less likely to cause fraud.

Online fraud: who experiences it? Socio-demographic profile of the user
People aged 15-34, single or unmarried, are most likely to experience online fraud. There are slightly more women among them than men. People over 45 years of age most often claim that they have not encountered online fraud. They are usually married or in a civil partnership. There are slightly more men among them than women.

conclusions
In general, it can be stated that users still do not carefully monitor their security on the Internet. Thus, almost two thirds of users of online services have ever become victims of fraud (64%). Among the reasons, victims most often cite a simple password, a downloaded virus, or a transition to a fraudulent site. Almost half as often, users report that they suffered due to the use of one password on several services or because they responded to a fraudulent message. Among the victims of fraud on online services, there are more users aged 15-34 years old who are not married.When entering personal data (for example, login or password), almost half of users of online services (mail, social networks) do not check for a secure connection.
Every fifth user has never changed their main password mailbox, and every third - from additional. Users rarely resort to changing their password on social networks: 38% change their password no more than once a year, and 18% have never changed their password at all.
Almost a quarter of email users use the password for their main mailbox on other resources, of which 62% use social networks, 27% use online stores, and 25% use a secondary mailbox.
Users tend to be less careful about the security of the additional mailbox compared to the main one: they change the password less often, less often use linking a phone number, preferring a security question to restore an account.
Just a quarter of users use the most secure password, which consists of symbols, letters and numbers. For 43% of users, the password length does not exceed eight characters; the password consists of letters and numbers (without using special characters). Just over a third of users (37%) use only lowercase letters in their passwords. If we talk about the numbers used in the password, 16% choose their own or a loved one’s date of birth. As for the alphabetic elements of the password, every sixth user chooses a Russian word typed in Latin letters, 8% - last name, first name or patronymic, 7% - several words in a row.
29% of users use a random set of letters as a password and 27% use a word they made up themselves.
43% of respondents use passwords between 6 and 8 characters long. Just over a quarter (27%) are between 9 and 10 characters. However, it can be assumed that this is mainly due to the fact that today many online services do not allow the user to enter a short and too simple password (for example, when registering in Mail.Ru Mail or when creating a new profile in Odnoklassniki, the user will not be able to enter a password less six characters and consisting only of letters).
To recover the password from the main mailbox, most users (68%) use a link to a phone number.
Users are wary of links sent to their main email inbox: almost three-quarters of respondents (74%) in such cases always carefully check the address before clicking on the link.
1) Do not send confidential information (bank card number, PIN code, passport data) through social network messengers. It is better to delete letters with scanned documents immediately after sending or receiving them; there is no need to store them in the mail.
3) Turn off Wi-Fi when not in use. Protect yourself and save battery power. Be sure to disable the feature automatic connection to Wi-Fi on your phone or tablet.
4) Don't trust unverified Wi-Fi connections that don't ask for a password. Most often, it is these networks that attackers use to steal users’ personal data.
5) Do not access online banks and other important services through open Wi-Fi networks in a cafe or on the street. Use mobile internet.
6) Remember: banks, services and stores never send letters asking you to follow a link, change your password, enter your bank card number and secret confirmation code, or provide other personal data!
7) Disable Siri on iPhone. Most likely, you don’t use it, but scammers have already learned how to withdraw money through online banking using voice commands.
8) Create several email addresses: personal, work and entertainment (for subscriptions and services).
9) Create a complex password, different for each mailbox. We wrote about how to do this.
10) Wherever possible, enable two-factor authentication.

11) Change passwords regularly, update your browser and spam filters.
12) Install and update antivirus programs. Outdated versions may not guarantee protection against malware. Several new viruses appear in the world every day, so an antivirus needs to receive information about methods to combat them as often as possible.
13) Click on the links received in messages from strangers - the right way fall for the bait of cyber scammers and infect your device with viruses. A dangerous link can also come from a hacked friend, so it’s better to find out what he sent you and whether you need to open it.
14) Don't run unknown files, especially with the .exe extension
15) Carefully check link addresses, logos, text and sender of messages.
16) Never respond to spam.
17) If you receive a request via messenger from a friend asking you to urgently send money, do not send anything! First, call him back and make sure that the account has not been hacked by intruders.
18) Read Kevin Mitnick's book "The Art of Deception." Mitnik - a cult figure in the environment information security, his book, like his life story, is both fascinating and instructive. You will learn how cybercriminals gain people's trust by manipulating their feelings.
19) A minimum of personal information: do not publish your home address online, do not write what time you are not at home, do not describe your regular route, do not boast about large purchases, and generally try not to advertise your level of income.
20) Do it regularly backup data. Follow the 3-2-1 rule: create one primary copy and two backup copies. Save two copies on different physical media, and one in cloud storage(Google Drive, Yandex.Disk, special solutions from Acronis). Don’t forget to backup all devices: smartphones, tablets, computers/laptops.
21) To never lose money on invisible payments, do not buy additional services by mistake and definitely pay for what you need, always read the rules before checking the “I agree” checkbox and proceeding to payment.
22) If in your security question you indicated your mother’s maiden name, which is now publicly available on her social media pages, be sure to change the security question.
23) Set a safe mode for the child. To do this, create a separate account on the website of the search engine of your choice or use children's search engines: Gogul or Sputnik.children.
24) Talk to your child about the Internet: agree that he will inform you about unwanted information found. Explain that not all information on the Internet is reliable, and teach them to consult with you on any unclear issue.
25) Do not download dubious applications or try to do so from unknown links. Use only official stores App Store, Google Play and Windows Market.
26) Advice for users Google Chrome, Firefox and Opera: if you travel frequently and access the network from a laptop in in public places, install a special browser extension to access the Internet safely. We recommend. By default, this plugin provides a secure connection for Yahoo, eBay, Amazon and some other web resources. You can also add sites of your choice.
28) When purchasing from online stores, maintain healthy skepticism. Remember: the price cannot be too low, especially if you are counting on purchasing original brand products.
29) Study the history of the store online, check for contacts, find out if you can come there and meet in person. When reading reviews, pay attention that they are different. Custom reviews are written by people who have to do this many times a day, so such texts seem to be written according to a template.
30) See how sellers react to reviews. Please note Special attention to negative ones: if they are worked out, this good sign(and the situation must be specific, contain the order number, etc.).
31) Pay safely! The classic case is that you will be redirected to a secure page (the address begins with “https://”). If not, it's better not to risk it. According to acquiring rules, the seller’s website must contain information about who accepts the payment. Read it and compare it with what is written on the next page.
32) Get a separate (virtual) card for online payments.
33) If you use your regular card to pay online, do not store large sums of money on it.
34) Connect your bank to SMS notifications about all transactions on cards and accounts. This way you can quickly notice if your card is compromised and block it.
35) The pages for entering confidential information of any serious service are always protected, and the data is transmitted in encrypted form. The site address must begin with “https://”, next to which there is a closed green padlock.

36) Where to go if something goes wrong? The activities of online stores are controlled by the same organizations as regular ones: Rospotrebnadzor, the Society for the Protection of Consumer Rights. Be sure to write to Hotline Runet: www.hotline.site
37) Be careful when communicating online with strangers, they may not be who they say they are.
39) Do not repost compassionate announcements about a cute cat who is urgently looking for a home (and in the post - the owner’s phone number or card number where you can transfer money for the care of the animal). There is a high probability that these are scammers who decided to make money on compassionate and gullible citizens.
40) Logo of a famous charitable foundation does not mean that the money will go there - the account details can be falsified. If you want to help people, do it only for people you know personally or, for example, with a project
44) By following the link http://www.tcinet.ru/whois/ you can find out when the site was created. Attackers usually create one-day pages that are closed very quickly.
45) Lost the phone to which it is linked bank card? Block both your SIM card and your card immediately.
46) It is better not to use torrents: if you download illegal content, you are not only ripping off your favorite author, but you may also download a file infected with a virus.
47) Fraudsters create websites where you can supposedly watch or download the movie you like for free, but first you need to leave your phone number or send a message to a short number. This way, a significant amount of money can be deducted from your account for SMS, and the phone itself will end up in the spammers’ database.
48) Some applications and services have a free trial period (for example, 2-3 months), after which you must disable the service yourself. If you do not do this, the subscription may be automatically renewed and become paid, and money will be debited from the card specified during registration.
49) Do not participate in promotions with prizes where you have to pay for something and then ask several other people to do the same. It's a pyramid!
50) Always lock your computer screen, even if you are leaving “just for a minute.”

Complete protection, absolute anonymity, freedom of action. In reality this would be quite good, but in the virtual world - is it possible? We use programs from trusted publishers, browsers that protect our personal data, but is the Internet safe? Think about it.
Nothing is perfect, and the current vaunted Internet security can be questioned. What can you say about your passwords, huh? How confident are you that your card details, which you used in online banking or made a purchase on a site using HTTP encryption, are reliably protected? What do you think about cookies? We give free rein to skepticism and begin to figure out what’s what.
Your passwords do not guarantee online security
As a rule, many people use one password for almost all sites on which they are registered, email, social network, Internet banking, which is fundamentally wrong. Is it dangerous! But don’t panic if this is the case for you, because it’s unlikely that the average person will be of interest to attackers. Forget about people constantly watching you American intelligence agencies and hackers who only dream of taking advantage of your twenty thousand in your account. This is a criminal offense and no one will risk their skin for this.
Everything you do on the Internet can be used against you. Browsers such as Firefox or Google, although they collect certain information, are not your enemies, quite the contrary. But various companies that have their own websites in the vast world wide web, are potentially dangerous villains for you.
When you visit a company's website like this, even if you don't intend to buy anything, you start being followed. All your movements on tabs and links on the site are recorded. But then you leave, and the company doesn’t want to just let you go. Through so-called beacons, they can find out where you are going next. And here the collection of information begins, on the basis of which a virtual profile of a person is compiled. Because of this, you see annoying pop-up ads, and even the holy AdBlock doesn't block everything. Although large companies and deny such actions, rest assured, if they deny everything now, they are either already doing it, or nothing prevents them from doing it in the foreseeable future. This method imposing your services on users is very effective from a marketing point of view, since a person sees advertising more and more often. In any case, he will think about it at least once or twice, which already indicates that the system is working.
In fact, the owner of absolutely any site can see what a particular visitor did on his site. Of course, the site owner does not know who exactly he is watching, but if you draw a penis on the site with your mouse, the admin will definitely notice it. Unless, of course, he decides to watch your session.
Your social network profile alone can tell you about your interests, hobbies, what kind of music or color you like, what you eat, what you drive, and with the development of the internal payment system, how much money you spend and on what. Undoubtedly, social networks are convenient. We can communicate with someone by text or voice messages, we can exchange files, music, photos, correspondence with other people, we can create our own communities or join existing ones, and communicate with users based on interests. But there is always another side of the coin - so that you do not know the troubles with unexpected hacks and loss of information, as in real life, you need to provide yourself with reliable protection.
The password must be unpredictable
Internet security can be improved by changing passwords to more complex ones.. You can also use password generators, but in this case it is better to use an installed program, since otherwise the password will appear on the network once. It is important that passwords are not linked in any way to your identity. Why? Because the password can simply be selected based on information from open sources and social networks.
But how can you remember so many passwords and at the same time remember which one is from where? The answer is quite simple: either you create a password with many different characters (like this one: Mn€HrA8№tsya#grАt'vBadDm#nt()n), or make it unique, preferably some kind of nonsense that you don't forget, for example: “my cheetah eats purple candles", only in the English layout and between each word there is a number instead of a space.
Passwords – even though convenient way protection, but a problem for online authentication. We may use unique, exclusive passwords and store them on physical media, which can result in the loss of a lot of information. Or we can use an additional password manager.
In the best case scenario, in order to ensure your security on the Internet, you need double authentication. This is when they send you an additional SMS code to your phone or email. In any case, you should think about your safety on the Internet.
The Internet is teeming with dangerous viruses
It's no secret that a large number of users, especially in the Russian Federation, use pirated programs and games. By downloading this or that program from a dubious site, you expose your PC to viruses. There are sites that are truly reliable, but there are also those that are fake, that is, created only to purposefully infect users’ computers or simply install unwanted software.
A virtual virus, as in life, is transmitted from host to host - from computer to computer. It can be either passive or active. Passive ones do not reveal their identity; they can install malware in the background without your knowledge, which can cause irreparable harm to your PC. Active ones begin to act immediately as soon as you activate it, that is, you launch the installer, as a rule, activation begins from this moment. Then the virus itself causes damage to the computer.
In order to maintain your safety on the Internet, you must follow several rules. Firstly, be very careful when you are going to download free program or a game. You can compromise your Internet security in an instant by clicking on the wrong link or accidentally downloading a Trojan horse along with a program.

Oh, you Trojan horse!
A Trojan is a malicious program that penetrates a computer under the guise of legitimate software.
Secondly, it is necessary to acquire high-quality antivirus program, for example Kaspersky, but do not download a pirated version from the Internet, but buy a licensed one, because the official version will be updated in a timely manner and will be able to destroy the latest viruses, which will increase both your security on the Internet and the lifespan of your computer.
Spam on the Internet can be safe or dangerous.
Sometimes you receive emails with dubious content, tempting offers and links. This is spam. On this moment spam is filtered quite well and is either immediately deleted or sent to a separate section, from where you can personally delete it, if necessary. But there is always a chance that the filter may mistakenly consider the message you need to be spam.
Why spam? The term originated from Monty Python television productions in which actors dressed in Viking costumes would suddenly chant the word Spam at a marching pace.
The main rule is never, remember, never click on links in such messages. Under no circumstances, under any circumstances, click on anything in the email. These links lead to fake sites, by visiting which you open access to yourself and may be subject to data theft, hacking of your social network profile, etc.
Although spam does not always come with viruses and hackers. Often spam is simply advertising and intrusive. People are trying to sell their services using the wrong methods - mass mailing of advertisements. Such letters are extremely rarely useful.
Conclusion
This, of course, is not all that can be said about Internet safety. The topic deserves an entire book. In any case, if something on the Internet seems suspicious to you, then most likely it doesn’t seem suspicious to you. Be vigilant and careful on the Internet. Good luck!
Did you read to the very end?
Was this article helpful?
Not really
What exactly did you not like? Was the article incomplete or false?
Write in comments and we promise to improve!
An important issue today is security on the global network, and it concerns this problem absolutely everyone, from children to pensioners. Due to the massive arrival of users on the Internet, this problem is becoming increasingly relevant.
Not all users are ready to face the threats that await them in the Internet space. This review will focus on the issue of Internet security. After all, millions of users are facing this problem today.
Dangers on the Internet
In short, there are two potential possibilities for a virus to get onto your computer. The first option is due to the user's fault. Very often, users install unverified software and traveling through dubious Internet resources, they bring infection to their computer. The second option is the activity of Trojans and viruses. Using these tools, attackers can deliberately make your device a source of danger.
As a result, the computer may start sending spam, stealing passwords, and participating in DDoS attacks on websites without the owner’s knowledge. In some cases, the provider decides to forcefully disconnect the infected device from the global network. Thus, a user who has no idea about information security on the Internet will have a hard time.
Why do attackers seek to gain access to a user's computer?
Many users believe that no one needs access to their computer. But this is far from true. It used to be that hackers created viruses out of pure curiosity. Today the situation is completely different. Now viruses are written with commercial gain in mind. A couple of decades ago, hackers received satisfaction only from the fact that they could gain access to this or that information. Or, for example, remotely change the wallpaper and theme on the user’s desktop. Today, every possible effort is being made to keep the PC user in the dark. Meanwhile, the device will secretly perform some additional functions. Why is this needed?
As mentioned at the beginning of the article, hackers today are trying to gain access to user accounts and electronic payment systems. There are often situations when at one moment all funds are debited from your e-wallet, and all your contacts in the mail receive letters with spam and Trojans. Hackers today have a lot of options, for example, they can unite infected computers into a single network and launch an attack on government servers.
Another simple option to get money from the user is to block the operating system and demand a certain amount to unlock it. Moreover, even if you pay the required amount to the attackers, this does not mean that the computer will be immediately unlocked. Therefore, Internet security is one of the user’s priorities today.
How can attackers gain access to your computer?
Professional hackers use a number of methods to hack a personal computer. Users are in vain hoping for antivirus protection. Even if you have taken precautions in advance, there is still a chance of picking up a virus or malware. Therefore, before searching the Internet for information about maintaining security online, it is important to understand the very mechanism of viruses and Trojans appearing on a personal computer. The following will list the main ways they penetrate and gain access to the user’s personal information.
The first method hackers use is called social engineering. Through the use of tricks and psychological techniques, you open a letter sent by hackers containing a Trojan. It is noteworthy that if you run a virus on your computer, you with my own hands. Another popular technique is to offer free software. These are usually tricks containing many viruses and Trojans.
By the way, even in software from trusted sources, security holes often appear. The same applies to operating systems. Attackers seize every opportunity. Simply follow an unverified link and your device is at risk of infection.
Recently, another method of spreading a computer infection has gained popularity. This is the so-called phishing. Fakes of popular sites are created on the Internet. So instead official page your bank, you may end up with a fake copy of it. Let's not talk about what might happen next.
How to protect your PC?
Ideally, a user who has just purchased Personal Computer Before you start conquering the Internet, you must complete a whole range of operations. Below we will present several recommendations for safe browsing on the Internet. In the operating room Windows system There is a built-in firewall.
But the standard security measure does not provide the required level of security. Therefore, it is recommended to install a more reliable firewall. Whether you will use the paid version or the free one depends only on your capabilities. The next step should be to install antivirus and antispyware software.
After installation, update them and configure them automatic update. It is better to make the antivirus update run automatically along with operating system. Scan any installed program with an antivirus. When updates for the browsers you use appear online, try to download them immediately. To reduce the chances of hackers gaining access to various services, try to disable all unused components.
Information security lessons
Even if you have completed all the operations listed in the previous paragraph, do not forget about daily safety measures. First of all, do not open files downloaded from unverified sources. It is also better to immediately delete emails with suspicious content. Do not pay attention to offers of easy money, and especially do not send your logins and passwords to anyone. When registering, use complex passwords consisting of symbols, letters and numbers. Assign a new original password each time.
Be careful when using the Internet in public areas. The same goes for using a proxy server. With this connection, it is advisable not to make payments via the Internet. It is generally better to work with payment systems through special applications, and not through the official website. It's safer this way. Sites for adults are also undesirable to visit. On such Internet resources there is a high probability of catching a Trojan. Even if you use an unlimited tariff, monitor your Internet traffic. A sudden increase in traffic for no reason is a serious cause for concern. Compliance with these simple rules Working on the Internet will allow you to avoid many problems.
That's not all. There are a lot of dangers waiting for you on the Internet, so you shouldn’t forget about protection even for a second.
Precautionary measures
Below we will give a few more recommendations to ensure safe browsing on the Internet. If you like e-mail I received a letter asking you to send your password for verification, do not answer it. Banks do not carry out such checks. Today, all email programs have a feature that allows you to filter spam.
Activate it. You should also ignore messages about big wins or inheritances.
It is recommended to install programs that provide comprehensive PC protection. This is more reliable than using antivirus, antispyware and firewall from different manufacturers. And of course, it is worth considering that paid versions provide more reliable protection. Since the most common Internet browsers today are InternetExplorer and Opera, it is for them that there are the most viruses.
Try using alternative options internet browsers, such as GoogleChrome, MozillaFireFox and AppleSafari. Try not to use unlicensed software: it may initially contain viruses and spyware. If you often make purchases in online stores, try to use only proven options. The same rule applies to all online services. It is enough to follow these few simple requirements, and you can ensure your safety on the Internet.
Internet and children
IN last years observed big leap in development high technology. In this regard, more and more children are able to independently access the Internet. And if quite recently children on the Internet were mainly interested only in games, today the situation has changed somewhat. Surely you can guess what we are talking about.
Therefore, there is a need to ensure the safety of children on the Internet. It is extremely difficult to organize such protection, since the Internet is developing completely uncontrollably. It contains a lot of information that children should not have access to. You should also pay attention to the basic rules when working on the Internet. This way you can teach your child to avoid Trojans and viruses. Children are the most inexperienced users. They can easily fall for scammers. Therefore, it is very important to teach children to use this information resource correctly.
Teaching children how to use the Internet correctly
The main advice that can be given to all parents is to conduct at least the first sessions on the Internet with their child. It is advisable to use programs such as " Parental control" This will allow you to control the child’s actions. Limit independent use your child of mail programs. This can be extremely dangerous.
Recommendations
Try to organize your child’s work on the Internet in such a way that he shares his successes and failures with you. Encourage your child to tell you about anything that makes him worry. Also, take some time and tell your child about privacy, help him choose a password to register on information resources. Explain to your child that safe work on the Internet will allow him to avoid trouble.
Let him understand that you don’t need to give personal information about yourself to anyone on the Internet. Also tell him that there is no difference between actions on the Internet and in real life. Warn your child in advance that communication on the Internet may deceive his expectations, that in real life a person may not be at all who he claims to be. Be sure to install special software that allows you to control your children’s activities on the Internet.
Children from 14 to 16 years old
If your child is already a teenager, then it is unlikely that you will be able to tell him anything new about computers. But still, don’t forget about control. Remember the need to ensure information security. If your child has access to a shared computer, be sure to scan the computer for threats.
If all home devices are connected via a network, then the threat can develop into serious problem. You can always view your child's activity reports. Try not to create conflict situations, but calmly communicate with the child on this issue. Let your child understand that there are certain rules for using the Internet.
It is better to install a computer with network access in public areas. This will help hold the baby back a little. Also install software that will block your child’s access to unwanted Internet sites and make sure that no new programs appear on your computer. Don't let the children for a long time surfing the Internet can be addictive. That's all the recommendations. We hope that these tips will allow you to increase the security level of your home computer.