Insulation of an existing flat roof with mineral wool slabs. Methods of thermal insulation of flat and pitched roofs from the inside. Choosing a method of insulation depending on the base
Read also
The answer to the question is there a need for insulation? flat roof, should definitely be positive. Any schoolchild knows the law of convection, according to which warm air rises up. As a result, maximum heat loss occurs through the roof structure. However, this is not the only reason for the need for insulation.
A cold surface without insulation, when in contact with heated air, will lead to its sharp cooling, resulting in the formation of condensation, which will destroy the roof. This process proceeds slowly and imperceptibly, but in the end it can cause a complete collapse of the entire structure.
In the case of a combined roofing option, condensate will drain into the interior.
An insulated flat roof creates a cozy atmosphere in the rooms located directly below it.
Features of insulation of flat roofs
Flat designs are divided into classic and inverse
The classic version is often called soft roof. His components are load-bearing slab, on which it is placed above the vapor barrier layer thermal insulation material. It, in turn, is protected from the effects of rain, melt water, and snow by a carpet of waterproofing coating created on the basis of rolled bitumen-containing materials.
A traditional flat roof is a kind of multi-layer cake, the main layers of which are:
- Floor slab
- Fastening insulation material
- Vapor barrier layer
- Insulating layer
- Waterproofing
- Additional insulation
Traditional flat structures are widely used in residential and industrial construction. For example, most residential high-rise buildings have just such a layout. Classic roofs can be used or not.
The inversion type of flat roof is an improved design solution of the traditional version. It is arranged according to the following scheme:

- Gravel layer - its thickness should be at least 50 mm.
- Filter material
- Insulation layer (for example, extruded polystyrene foam)
- Carpet waterproofing
- Screed
- Floor slab
The fundamental difference between the inversion design and the classical one is the location of the layer of insulating material above the waterproofing, and not under it. This design feature allows you to protect the waterproofing carpet from the negative effects of solar ultraviolet radiation, significant temperature fluctuations, freezing and thawing, and mechanical damage. As a result of the listed advantages of the inversion layer arrangement, the service life is significantly increased compared to the service life of traditional soft roofs.
The design feature of the inversion roof makes it possible to use it as an operational one: it can be used to organize recreation areas, parking lots, summer cafes, pedestrian zones, etc.
Thermal insulation requirements
 The load-bearing part of a flat roof is the covering slab. It is made on the basis of reinforced concrete or corrugated sheets.
The load-bearing part of a flat roof is the covering slab. It is made on the basis of reinforced concrete or corrugated sheets.
The roof slope is created in various ways: using reinforced concrete ties, structurally, by filling with expanded clay, etc. The main feature of a flat roof structure is the increased requirements for all its elements.
The layer of thermal insulation material will be affected different types loads: snow, wind, installation, operational, etc. For this reason, particularly stringent requirements are imposed on the material in terms of their physical and mechanical characteristics.
Since it is impossible to completely prevent the penetration of moisture into the roof structure, the thermal insulation layer must certainly be hydrophobized.
Single-layer and double-layer thermal insulation
Single-layer thermal insulation system
Its main distinguishing feature is that it is based on insulation for flat roofs of the same density. When planning the creation of an exploitable roof, as already mentioned, installation is carried out above the heat-insulating layer concrete screed. The use of such a system is advisable in case of repair of an old structure or during construction storage facilities, industrial buildings, garages.
Double-layer thermal insulation system
Its structure is completely different. Upper layer should be made on the basis of an insulating material characterized by increased density and significant strength. Its main task is to redistribute mechanical load. The thickness of this layer should be 30-50 mm.
The purpose of the bottom layer is to perform the main heat-insulating function. Its thickness remains within the range of 70-170 mm.
This design significantly reduces the weight of the roof, thereby reducing the load on the floors. This point is extremely important when renovating old buildings.
Today, the construction market offers new generation materials that combine the quality characteristics of both layers. The upper edge of such insulation is characterized by significant rigidity, while the lower edge is much softer. Installation of such slabs takes very little time and is not associated with any difficulties.
The importance of vapor barrier for high-quality roof insulation
The vapor barrier layer laid on the base must have excellent vapor-retaining properties in order to prevent vapors rising from the interior to the roof from penetrating the insulation. As you know, as insulation becomes saturated with moisture, its thermal conductivity decreases. In addition, steam accumulations lead to the formation of swellings in the waterproofing carpet, which over time provoke the destruction of the coating. For this reason, the issue of choosing a vapor barrier must be taken very seriously. It comes in two types:
Film - polyethylene or polypropylene film is used for insulation. The main disadvantage of these materials is the presence of seams: moisture can seep through them.
Fused - created on the basis of materials of the welded type - for example, bitumen or polymer bitumen. The absence of seams when constructing such a vapor barrier guarantees the tightness of the coating. Its other advantages are the significant thickness of the deposited layer and increased tensile strength.
Thermal insulation materials
When constructing a layer of thermal insulation, a variety of materials are used: they all differ in physical and mechanical properties and method of installation.
 The most affordable insulation, still used in private and urban construction, is the use of backfill materials. The main ones are perlite sand and expanded clay. The main and, perhaps, the only advantage of using these materials is their low cost. In all other properties, they cannot compete with modern gas-filled polymers and fiber insulation.
The most affordable insulation, still used in private and urban construction, is the use of backfill materials. The main ones are perlite sand and expanded clay. The main and, perhaps, the only advantage of using these materials is their low cost. In all other properties, they cannot compete with modern gas-filled polymers and fiber insulation.
Absolute horizontality of flat roofs is unacceptable.
In accordance with technological requirements, they must have minimum slope 2-4 degrees. Choosing as insulation expanded clay, it is extremely difficult to level the surface in such a way as to create a smooth slope and achieve the same screed thickness across the entire roofing plane. Working with expanded clay significantly increases costs and increases construction duration.
 Insulation based mineral wool
in most cases, it does not have a sufficient level of strength to create a full-fledged base for a waterproofing carpet. For this reason, in order to strengthen it, new Constructive decisions. In this case, a screed device is used above the insulation. It helps to distribute the load evenly and create a base of the required rigidity for laying a waterproofing carpet. There are two types of screeds:
Insulation based mineral wool
in most cases, it does not have a sufficient level of strength to create a full-fledged base for a waterproofing carpet. For this reason, in order to strengthen it, new Constructive decisions. In this case, a screed device is used above the insulation. It helps to distribute the load evenly and create a base of the required rigidity for laying a waterproofing carpet. There are two types of screeds:
- Prefabricated screed– created from flat or asbestos covering the insulation slate sheets. The installation of such a coating is quite expensive and significantly increases the cost of the work carried out.
- Wet screed- essentially it is a simple cement-sand mortar. It is a more budget-friendly option, but has one big drawback: its use can lead to moisture in the insulation. For this reason, when choosing this method, a separating layer based on kraft paper or glassine is placed under the screed.
Another disadvantage of this method is the significant drying time of the cement-sand composition. If waterproofing is applied to a mixture that has not completely dried, bubbles appear on the surface of the finished roof, significantly reducing the service life.
It is obvious that the screed is by no means the perfect way obtaining a rigid base in case of choosing not very durable insulation. In addition to increasing the financial costs associated with construction, it also increases the weight of the coating, increasing the load on the floors.
For this reason, it is recommended to choose very durable thermal insulation slabs made from mineral wool, which is obtained from basalt rocks. In their production it is used special technology with double orientation of fibers, significantly increasing their rigidity.
 Rigid slabs based basalt fiber
have a number of advantages:
Rigid slabs based basalt fiber
have a number of advantages:
- ease of installation;
- excellent thermal insulation properties;
- increased fire safety.
- A significant disadvantage of fibrous materials is their significant hygroscopicity. If the waterproofing layer is damaged due to cracks formed in the screed, moisture penetrates into the insulation layer. As materials with a fibrous structure become wet, they lose their thermal insulation characteristics, resulting in insulation becoming of lesser quality.
The listed materials are used for insulation of flat roofs of classical design.
When insulating inversion roofs materials such as foam glass or extruded polystyrene foam. Their advantages over mineral wool are non-hygroscopicity and high mechanical strength.
 Foam glass– relatively new heat insulating material, which has become widespread in the creation of flat structures due to its exceptional qualities.
Foam glass– relatively new heat insulating material, which has become widespread in the creation of flat structures due to its exceptional qualities.
The distinctive properties of foam glass are:
- resistance to high temperatures;
- mechanical strength;
- resistance to ultraviolet rays;
- non-susceptibility to biocorrosion;
- excessively long service life (it is practically unlimited);
- preservation geometric shape– achieved due to the low coefficient of thermal expansion.
As a result of the presence of the last of these qualities, the mechanical loads exerted on the waterproofing membrane are significantly reduced, as a result of which the material retains its quality characteristics throughout its entire service life.
- Its disadvantage is considered to be its high price compared to other insulation materials.
Extruded polystyrene foam (or extruded polystyrene foam) is a new achievement in the field of thermal insulation technologies. The material has a uniform structure and is composed of completely closed small cells (0.1-0.2 mm). During its production, polystyrene granules are mixed under high pressure and at high temperature, a special foaming agent is introduced into the composition, and then extruded from the extruder. We can confidently say that in terms of quality characteristics this material has no analogues in the world. Extruded polystyrene foam has:

- the lowest thermal conductivity among analogues;
- resistance to chemical agents;
- increased compressive strength;
- resistance to the formation of mold and mildew;
- steam and waterproof.
According to the results of a number of studies, the degree of water absorption of the material is a maximum of 0.2 percent by volume. It is also important that moisture does not penetrate inside: only the cells located on the surface are filled. Thanks to this quality, when installing thermal insulation on a flat roof, there is no need for additional protection of the material.
Subtleties of insulation fastening
When choosing any material, a necessary condition is its strong attachment to the base. For this purpose, two methods can be used:
- Bonding to bitumen. This process is labor-intensive and quite expensive. Its use is advisable only if there is a concrete base, since in this case there is no need for more expensive specialized dowels and drilling holes for them.
- Mechanical fastening method using special telescopic dowels. Their special feature is a very wide cap, thanks to which the fastening elements do not pierce the waterproofing carpet and the tightness of the roof is not compromised.
There is a construction rule, according to which the waterproofing carpet is attached to the insulation using the same method in which it is mounted to the base.
At mechanical fastening As a vapor barrier, it is recommended to use a polymer-bitumen fused material. Thanks to its elasticity, small holes, which are made by dowels on which the insulation is attached, are tightened without consequences.
When using two-layer insulation, the slabs are laid “staggered”: the joints of the slabs forming the bottom layer must be covered by the top ones. If this requirement is observed, the formation of “cold bridges” can be avoided. At least two dowels are used to fasten each insulation board.
Properly carried out insulation will provide a cozy and comfortable atmosphere inside the house.
CONCLUSIONS:
- The need for insulation is due to maximum heat loss through the roof structure.
- The fundamental difference between the inversion design and the classical one is the location of the layer of insulating material above the waterproofing.
- Particularly stringent requirements are imposed on insulating materials in terms of their physical and mechanical characteristics.
- When installing roofs in use, a concrete screed must be laid on top of the insulation layer.
- Insulation of a flat roof can be done by laying one or two layers.
- The vapor barrier layer laid on the base must have excellent vapor-retaining properties in order to prevent the insulation from moistening.
- When constructing a thermal insulation layer, different materials are used, differing in physical and mechanical properties and installation method.
- For insulation classic roofing Expanded clay, mineral wool, and rigid slabs based on basalt fiber are used.
- When insulating inversion roofs, foam glass or extruded polystyrene foam is used.
- When choosing any material, a necessary condition is its strong attachment to the base.
- Fastening is carried out by gluing to bitumen or mechanically using special telescopic dowels.
How to insulate a flat roof with mineral wool, see the video.
Every owner of a private home faces roof insulation work. Those who are doing this work for the first time will face a long process of becoming familiar with different technologies and studying the properties of modern materials. The task of roof insulation is to create a cake from insulation and waterproofing films. Regardless of the type of roof structure, the durability and efficiency of insulation is determined the right choice materials and compliance with the sequence of laying each layer roofing pie.
Why do you need to insulate your roof?
A third of a home's heat loss occurs through the roof. Therefore, high-quality roof insulation primarily saves money on heating the house.
The infrared photo clearly shows that there is no heat loss through the insulated roof
Insufficient waterproofing and insulation of the under-roof space leads to the formation of dampness. She penetrates load-bearing elements roof frame, resulting in a reduced service life.
Insulating a pitched roof allows you to turn the attic into a full-fledged living space.
Common materials for roof insulation
All materials used for roof insulation are divided into two types:
- Cotton (or fibrous). This group includes basalt (stone) wool, glass wool, and slag wool. Products of this type have different characteristics of rigidity, density, crease resistance and are produced in the form of rolls or plates. Cotton insulation is considered non-load-bearing materials.
- Foam. These materials are made from foamed polymers and are available only in the form of slabs. They have high rigidity and are classified as load-bearing materials.
Features of cotton materials
Cotton insulation has the ability to transmit moisture vapor, but should not get wet. To prevent water condensation from being retained in the thickness of the material, its fibers are coated with a water repellent. Thanks to this, moisture is not absorbed by the fibers, but flows out or is ventilated by air currents.
Mineral wool
Due to its vapor permeability, mineral wool is considered the best material for insulating roofs with wooden rafters, as it promotes the natural exchange of moisture between wood and air.
 Basalt wool is produced in the form of slabs, which are conveniently mounted in cells between the rafters
Basalt wool is produced in the form of slabs, which are conveniently mounted in cells between the rafters But the ability to transmit moisture vapor also has a negative side: it is necessary to use a waterproofing film to protect the insulation from the roof side and a vapor barrier film to protect from warm, humid air from the living quarters.
Condensation will accumulate on the waterproofing film. If it lies close to the cotton insulation, then moisture will penetrate into its thickness. This will lead to the insulation getting wet and mold appearing in it. Therefore, when using conventional vapor-proof films for waterproofing, it is necessary to leave a gap of 2–3 cm on each side between the insulation and the film. This space is called the ventilation gap. After condensation, moisture will be removed from the surface of the waterproofing membrane natural circulation air.
Instead of conventional waterproofing films, you can use a superdiffusion membrane. This material allows you to do without a ventilation gap, which will simplify the process of installing insulation. Such a film will save space and allow you to lay insulation over the entire height of the rafter beam, completely filling the cells.
Basalt insulation
Mineral wool often means basalt insulation. However, due to the special arrangement of the fibers, basalt wool has higher thermal protection and is practically not susceptible to the formation of fungi and mold. This dense material does not cake, does not compact, and is not subject to combustion over time.
 Basalt wool retains heat better and does not react with oxygen, which usually causes mold to form.
Basalt wool retains heat better and does not react with oxygen, which usually causes mold to form. Basalt wool is most often used to insulate pitched roofs by installing it in the cells of the rafter structure. The advantage of all cotton materials with this installation method is the ability to completely fill the cells without cracks or cold bridges.
This material has also become widespread by analogy with basalt insulation. It is available in both rolls and mats different thicknesses(up to 150 mm). Therefore, you can always select the material in accordance with the configuration of the roof frame cells to minimize waste during cutting. But in terms of density, thermal conductivity and compression resistance, glass wool is inferior to basalt insulation.
 Glass wool has worse thermal insulation properties, but is cheaper
Glass wool has worse thermal insulation properties, but is cheaper The main argument that allows glass wool to compete with basalt insulation is its low price. Therefore, many craftsmen prefer this material, despite the well-known ability of glass wool to slide down the slope over time, forming cracks and severely irritate the skin when working with it.
Slag wool
Made from blast furnace slag. Of all cotton materials, it has the widest operating temperature range (up to 300 o C). Slag wool also has the greatest hygroscopicity, so it is not used for insulating facades.
 Slag absorbs water well, so it must be carefully protected waterproofing coating
Slag absorbs water well, so it must be carefully protected waterproofing coating Slag wool has the most “dirty” base, therefore it is not recommended for use in residential premises. This material is usually used for insulation of industrial buildings and pipelines.
Plate materials
For the production of slab materials they use different types polymers. These are polystyrene, foam plastic, polyurethane.
An important characteristic of slab materials is rigidity and vapor permeability. The technology for using insulation in the pie also depends on this. warm roof. The ability to transmit moisture vapor depends on the method of molding polymer foam boards in production:

To insulate the roof between the rafters, slab foam materials are not used, since it is difficult to cut the material precisely according to the cell dimensions. The inevitable cracks will become bridges of cold. In addition, if the rafters are not mounted taking into account the dimensions of the material, a large amount of waste will appear during cutting.
Pitched roof insulation technology
A pitched roof can be insulated in the following ways:
- Installation of insulation between rafters.
- Formation of a continuous layer of insulation on top or under the rafters.
- Combined method.
Insulation between rafters
The easiest way is to install insulation with single-layer ventilation using a superdiffuse membrane. For this method, insulation is purchased, the thickness of which is equal to the depth of the cell:

 Superdiffusion membrane is attached closely to the insulation
Superdiffusion membrane is attached closely to the insulation If you have an old waterproofing film and you plan to use a film with low vapor permeability (microperforated film) for padding underneath, then the gap between the insulation and the film should be on both sides. To do this, it is necessary that the panel is not completely recessed into the cell, but with a distance of 2–3 cm from the edge. The same gap must be left on the attic side. The thickness of the insulation should be 5 cm less than the depth of the cell. The support for the panel can be padded slats around the perimeter of the cells or pieces of wire stretched over nails:
- A thin strip (2 cm) is placed along the upper edge of the cell, and nails are driven in at a distance of 2 cm from the upper edge of the beam.
- Nylon threads or wire are wound crosswise around the nails. Now, when laying the insulation into the cell, the necessary gap will remain between it and the film.
- Exactly the same operation is performed after installing the mineral wool panels. The threads on the bottom side will prevent the material from sagging or moving in the cell.
 To create a ventilated gap, the thickness of the insulation must be less than the depth of the cell between the rafters
To create a ventilated gap, the thickness of the insulation must be less than the depth of the cell between the rafters Insulation with foam slabs must be done in two layers. This is done in order to cover the gaps at the joints. In this case, the joints of the slabs of the second row should be shifted relative to the joints of the first row.
It is necessary to select the thickness of the foam insulation so that it does not extend beyond the rafters. If the material (or two layers of it) protrudes from the cells, the rafters must be extended with timber.
Video: laying mineral wool between rafters
The disadvantage of insulation between the rafters is the presence of cold bridges along the perimeter of the cells. Therefore, many owners use combined insulation methods, additionally installing a layer on top or under the rafters.
For insulation over rafters, foam boards that have sufficient rigidity are ideal. This material copes well with the load that it will experience under the roofing material, so most often in new buildings a continuous layer of insulation is mounted on top of the rafters from the outside. This is much more convenient than screwing panels from the inside. In addition, you can save inner space. And if you do not combine the laying of slabs with insulation between the rafters, then the open parts of the timber inside the attic will be an original element of the interior.
 Foam insulation is not afraid of moisture, so there is no need to waterproof the under-roof space
Foam insulation is not afraid of moisture, so there is no need to waterproof the under-roof space If extruded slabs are used, then there is no need to put a vapor barrier under the insulation and lay waterproofing on top. The work is carried out according to the following principle:

Combined insulation technologies
The most common method of combined insulation during repairs is insulation under and between the rafters. This option is the described insulation method with one ventilation duct and an additional continuous layer below.
This technology uses cotton materials:

This design is the simplest, easiest to implement and cheapest. Installation of an additional layer on top of the rafters is most convenient; it is performed during a deep inspection of the roof with subsequent replacement of the roofing material. For houses in harsh climatic zones most effective way insulation will be a combination of all three methods.
Video: insulating the roof of a cottage with a layer of foam plastic 20 cm thick
Thermal insulation of flat roofs
The same materials are used to insulate a flat roof. There may be limitations in the use of foam insulation if the coating is subject to high fire safety requirements. They carry out work both outside and inside. The insulation can be single-layer or multi-layer.
If you plan to insulate a flat roof on both sides, then first install an external roofing pie, and after a season, if there are no leaks, perform internal insulation. Flat roofs can be traditional or used. The choice of material and technology for forming the roofing pie depend on the type of roof.
 Traditional and used flat roofs are insulated differently
Traditional and used flat roofs are insulated differently For traditional structures, the roofing pie consists of the following layers:
- Base. This can be a concrete slab or metal profile.
- Vapor barrier layer.
- One or two layers of insulation.
- Waterproofing.
The composition of the pie for an exploited roof:
- Only a concrete slab can act as a load-bearing base.
- Waterproofing film.
- Insulation.
- Drainage geotextiles.
- Crushed stone bedding.
- Finish coating.
Insulation methods: single-layer and double-layer thermal insulation
For external insulation they use a lot different materials having a porous structure (for example, foam concrete or expanded clay). But the most popular are extruded polymer foams and mineral wool. Due to its low cost, mineral wool is a priority for many craftsmen.
 Mineral wool is often used to insulate flat roofs due to its lower cost.
Mineral wool is often used to insulate flat roofs due to its lower cost. For single-layer insulation, dense material is used. Depending on the type of base, insulation of a flat roof with mineral wool is performed as follows:

It is allowed to lay mineral wool on a metal profile without a leveling layer using flat slate.
 The bottom layer of mineral wool should be thicker and less dense than the top
The bottom layer of mineral wool should be thicker and less dense than the top But in this case, the thickness of the lower insulation should be twice as large as the distance between extreme points neighboring profile waves.
Video: how to simultaneously insulate and waterproof a flat roof
Rules for laying foam materials:
- The slabs are laid on the metal profile with their long side across the profile waves.
- The sheets are laid with seams staggered and the jointing should be similar to brickwork.
- When laying in multiple layers, the top seams should not coincide with the bottom ones.
Methods for attaching slabs to the base
The following methods are used to fix the material:

Thermal insulation of a flat roof from the inside
If necessary, the flat roof is insulated from the inside. Typically, such work is performed when the roof does not have an attic space. The technology is simple; all the difficulties lie in the need to constantly keep your arms extended upward. But, unlike outdoor work, there is no need to rush, and the work can be done at a moderate pace:

High-quality insulation roof largely depends on what material you decide to use. Cotton insulation always requires mandatory installation ventilation ducts. Extruded foam boards make installation technology easier, but they are more expensive. On large areas this difference can result in a significant amount. At the same time, polystyrene or polyurethane foam are ideal for insulation on top of the rafters, and mineral wool fills the cells efficiently when insulating between the rafters. Therefore, before making your final choice, you must carefully weigh all these factors, taking into account your financial capabilities.
Flat roofs are less popular in private buildings compared to pitched roofs. They are mainly used in the construction of multi-storey residential buildings and industrial facilities. According to statistics, only 5% of private houses and cottages have a roof of this type.
But during construction outbuildings, garages, terraces this type roofs are used quite often. A flat roof is influenced by various types of loads: precipitation, wind, temperature changes, sun, installation loads, etc. Therefore, insulating a flat roof is a complex undertaking that requires a thorough approach.
Thermal insulation technologies
The method of insulation and the sequence of work depends on the type of flat roof. They are traditional and inversion. Inversion roofs are usually used. Traditional roofs do not perform additional functions.
Thermal insulation of a traditional roof
The “roofing pie” of a traditional type roof is made of the following layers:
- concrete base or metal profile;
- vapor barrier;
- insulation material;
- waterproofing layer.

The sequence of layers for thermal protection inversion roof somewhat different. IN in this case The insulation system looks like this:
- load-bearing base;
- waterproofing;
- insulation material;
- geotextiles;
- backfilling with crushed stone;
- finishing coating.

Operated and non-operated roofs
Unused roofs serve only the main protective function.
The surfaces of exploited roofs can additionally serve as a garden, terrace, sports ground, or recreation area. Therefore, the insulating structure of the roof in use must be especially strong and reliable. When installing a single-layer insulation system on such a roof, a concrete screed must be placed on top of the insulation.

Green roof.
Single and double layer insulation
Depending on the number of layers of insulation, the insulation system can be two-layer or single-layer.
With a single-layer system, the thermal insulation layer is made of insulating material of the same density. In this case, the heat insulator must be sufficiently dense and durable.
This design is usually used when reconstructing an old roof or during the construction of warehouses, industrial buildings and garages.
When installing a two-layer insulation system, two layers of insulation are laid. The bottom layer has the main heat-protective function. It has a greater thickness compared to the top layer and high thermal insulation characteristics. In this case, the strength of the material can be relatively small.
The top layer of insulation additionally has the function of redistributing the load. Its thickness is smaller, but the density and compressive strength should be high.
The two-layer design makes it possible to achieve high strength of the insulation system at a relatively light weight. As a result, the load on the floors is reduced.
Material selection
When choosing insulation for a flat roof, you need to take into account the following material characteristics:
- strength;
- density;
- thermal insulation properties;
- Fire safety;
- soundproofing characteristics.

The following materials can be used for thermal insulation:
- mineral basalt wool, due to the air in the structure, the material has high thermal insulation properties, and the insulation fibers adhere tightly to each other, providing it with high tensile strength;
- ecowool - a cellulose material that is treated with fire retardants to make the insulation non-flammable;
- polyurethane foam - a modern sprayed heat insulator that forms a uniform surface without seams;
- extruded polystyrene foam - popular insulation, which has good thermal insulation qualities, is not afraid of moisture, is easy to install, and is affordable;
- foam concrete - modern material, as strong as concrete and light as foam.
Laying vapor barrier
When insulating a traditional roof, be sure to lay it on top of the base. vapor barrier material. If this is not done, the insulation will gradually accumulate moisture and lose its thermal insulation properties, air pockets will form, and the roof will deform.

Polyethylene and polypropylene films or built-up bitumen materials can act as a vapor barrier. The lack of films is the presence of seams. Bituminous materials form a homogeneous, tear-resistant surface.
The vapor barrier must be laid not only on a horizontal surface, but also on the wall just above the level of the insulation.
Installation of insulation
After laying the vapor barrier layer, you can proceed to the installation of insulating material.
Thermal insulation with mineral wool
Not every type of mineral wool is suitable for insulating a flat roof. The material must have sufficient strength to withstand the loads during installation and operation. Therefore, special high-strength mineral plates are used.
Installation of insulation can be done in two ways: dowels or bitumen. The process of attaching to bitumen is quite complex and expensive. That's why this method Installation of slabs is advisable when laying on a concrete base. Then you won’t have to buy specialized dowels, which are more expensive, and drill holes in the concrete.

If the base is made of profiled sheets, then it is more convenient to fasten the slabs mechanically using adhesives or dowels. In the case where it is planned to install a cement-sand screed, it is not necessary to secure the slabs.
When choosing a mechanical method of fastening insulation for a flat roof, the vapor barrier must be made of weldable materials so that the resulting holes in the base can be closed.
When laying insulation in two layers, the lower slabs are coated with bitumen, and the upper ones are installed so that the seams between the slabs of the upper and lower layers do not coincide. This is necessary to prevent the formation of cold bridges.
Application of expanded polystyrene
The principles of roof insulation with extruded polystyrene foam are similar to insulation with mineral wool. At the same time, polystyrene foam boards have slot locks, which greatly simplify the installation process. To prevent moisture from entering, all seams are taped.

Waterproofing
To protect the roof from water, it is necessary to lay a waterproofing layer. Moreover, on traditional roofs it is installed on top of the insulation, and on inversion roofs - under the insulation. Laying a waterproofing membrane follows the same principle as installing a vapor barrier. Waterproofing can be made of rolled, fused materials or profiled steel sheets.

Polyurethane foam insulation
The stages of work described above can be skipped if you use modern material such as polyurethane foam as insulation. It is sprayed onto the insulated surface using special installations. The result is an even, sealed layer without seams. Additional vapor and waterproofing is no longer required. The material can be applied to almost any substrate. Service life - from 25 years. The disadvantages of polyurethane foam insulation are its high price and the need to call specialists.

How successfully the insulation of a flat roof will be completed depends on strict adherence to certain rules and generally accepted technology. Let's list some of them.
Following instructions
Any modern insulation system requires compliance with a number of rules established by the manufacturer. Basically, the procedure is the same everywhere. The difference lies in the details. Some types of insulation require the use of only certain adhesives. If you take another one, you will damage the surface. Therefore, when purchasing finished system Be sure to check the manufacturer's instructions.

Preparing the base
Before carrying out insulation work, the base must be carefully prepared. It must be cleared of ice or snow in winter and freed from moisture and debris in summer.
Correct installation process
Installation of insulation is carried out “by yourself”. You should start from the edge that is opposite the roof exit. You need to move along special inventory walkways to evenly distribute the mechanical load. The laying direction changes periodically.
The biggest loss of heat from houses and buildings occurs through the roof of the house. Lower floors This is hardly noticeable in buildings, but more heat is needed to heat the upper ones.
To insulate the roof, you need to choose best option material. It must not only be airtight, but also fire resistant and non-toxic.
Taking into account such requirements, mineral wool will be the best option.
There are varieties of mineral wool: glass and basalt. The latter is made from rock - gabbro-basalt. During production, carbonates are added to it, which allows you to regulate its acidity.

Basalt wool
A factor such as acidity is of great importance for mineral wool. The more acidic the cotton wool is, the less sensitive it is to water.
The type of cotton wool in which the acidity is higher is considered more durable. Synthetic, bituminous or composite clays are added to give shape. Glass wool does not require much explanation; its name speaks for itself.
This mineral composition, for the manufacture of which the same components are used as for glass (this can be broken glass).
The two types of wool differ in their properties. Glass wool is usually 15 microns thicker (from 3 microns), but basalt wool is several times longer.
The conclusion suggests itself: glass wool is more durable material, capable of withstanding more aggressive environmental factors than basalt. Also glass wool does not burn.
Insulating a roof with mineral wool is difficult when working on roof slopes with a rafter structure. In such cases, it is better to use thick cotton wool. To prevent moisture from accumulating under the roof, you need to use cellulose wool.
Advantages and features of mineral wool
Mineral wool has the following advantages:

- wide range of products. Mineral wool is produced in the form of slabs, rolls or mats. Due to this, it is possible to choose the option that is best suited for thermal insulation of a certain area of the building. Also, types of mineral wool differ in density: material in the form of slabs has high density, A roll insulation lighter;
- has high thermal insulation characteristics. Mineral wool has a porous structure. This material consists of small layers. Due to this, it retains heat well and also provides excellent sound insulation;
- fire safety of the material. Mineral wool does not burn and does not spread fire. For this reason, it is often used for thermal insulation of interfloor ceilings. Manufacturers of mineral wool claim that this material can withstand temperatures above 900 degrees Celsius;
- mineral wool does not deform, and this is a very important advantage. This material does not shrink, therefore, there is no formation of “cold bridges” that cause heat loss;
- frost resistance. This property allows the use of mineral wool for thermal insulation of external elements of a building;
- mineral wool is an environmentally friendly material. It is used for thermal insulation of health resorts and medical institutions, as well as children's rooms.
This insulation is produced in various forms - plates, cylinders, mats; You can buy cotton wool covered with foil.
Mineral wool has features that cannot be called positive. These include:
- low strength. This is due to the high porosity of mineral wool;
- to ensure a high level of thermal insulation, this material should be used together with a waterproofing film and a vapor barrier membrane;
- when using mineral wool with fiberglass, it becomes unsafe because formaldehyde is added to it;
- high hygroscopicity (therefore high waterproofing is done).
To attach such insulation, planks are nailed to the inside of the rafters (they are used to make a lattice), to which the cotton wool will be attached. On the outside, cotton wool is laid in one layer (the layers depend on the thickness of the wool).
After laying the insulation, waterproofing is applied. It is important at this stage not to confuse the sides of the insulation. The top layer does not allow moisture to pass through, and the bottom layer is an obstacle to steam.
The waterproofing is not stretched; an air space remains between it and the wool. There should be air space in front of the skate, which will create additional traction.
Insulation method
To start insulating the roof with mineral wool, you need to cut it (if necessary) so that it fits in size to the distance between the rafters.

If cotton wool is used, for example 10 cm, and the thickness of the thermal insulation is more than 10 cm, then another layer of wool is laid perpendicular to the rafters. There are two ways to strengthen the roof of non-residential premises.
The first is to insulate the floor, and the second is to strengthen the roof slopes. The first case does not require any special preparation or special costs.
There is no need to go around the rafters, as in the second case. Strengthen roof slopes non-residential premises, thus, it is expensive. A large amount of wool will be required, which must be strengthened by going around the rafters.
Mineral wool grades
Mineral wool is produced in the form of mats and slabs. It is used for thermal insulation of ceilings, partitions, roofs, partitions, as well as interior walls. When working with this material, as a rule, no special problems arise. Mineral wool can be laid not only on a flat surface, but also on a non-standard surface.

Mineral wool grade p-75
There are the following brands of mineral wool, which differ from each other in their density:
- P-75. Mineral wool of this brand has a density of 75 kg/m3. It is usually used for thermal insulation of horizontal surfaces that are not subject to heavy loads (some types of roofing, attic spaces). This brand of wool is also used for insulation of oil and gas pipes, as well as pipes of heating plants. Mineral wool of lower density is also produced, but it is used in cases where there is almost no load.
- P-125. This material has a density of 125 kg/m3. It is used for thermal insulation of partitions, ceilings, floors and interior walls of the room. Mineral wool of this brand creates good sound insulation. Therefore, when using it, you can not only insulate the building, but also create good sound insulation.
- PZh-175. This is a dense material with increased rigidity. It is used to insulate floors and walls made of profiled metal or reinforced concrete.
- PPZh-200. Mineral wool of this brand has increased rigidity. Used in the same cases as PZh-175. The difference between PPZh-200 and the previous brand is that it is fireproof.
How to cut mineral wool?
It is advisable to cut stone wool insulation special knife with a serrated blade or a hacksaw for metal. The tool used for these purposes must be well sharpened.

This is necessary to ensure that there are as few torn insulation fibers as possible. Many manufacturers of thermal insulation materials offer customers special tools for cutting. These are knives whose length is approximately 300 millimeters, as well as saws with straight teeth.
If you don’t have special tools, you can use a kitchen bread knife with a wavy edge and fine teeth. For cutting 50 mm thick mats and soft boards, you can use a regular mounting knife.
It is important to note that the thermal insulation material must cover the insulated space very tightly. Therefore, it is necessary to leave allowances before cutting.
Thermal insulation of the floor
Interfloor and attic floors are made from load-bearing beams or reinforced concrete. In the first case, the heat insulator is placed in the space between the floor beams, and in the second - on the surface of the slabs.

Insulation of the attic floor
First of all, it is necessary to install a vapor barrier. It will protect the thermal insulation from moisture and steam. Before installation vapor barrier film it is necessary to study the instructions for its use. If the vapor barrier is installed incorrectly, it will not perform its tasks.
Flat roofs are usually insulated with rigid mineral wool slabs, the density of which is more than 150 kg/m3. A layer of waterproofing is laid on top of it. The slabs must be laid very tightly to each other. In this case, the seams should not be located on the same line. The optimal thickness of the mineral wool layer is 25 centimeters.
You can also insulate interfloor and attic floors using sawdust. They are used together with sand, clay, lime and cement. The composition provides good thermal insulation.
Expanded clay is also often used to insulate the attic. This material contains a large number of pores, due to which the thermal insulation function is ensured.
When using these materials, financial costs will be lower, and the quality of thermal insulation will be no worse than in the case of mineral wool insulation. When choosing insulation, you should take into account the height and area of the building, the materials from which it is built and other parameters.
Video about thermal insulation of attic floors:
Insulation of pitched roofs
To insulate the roof with mineral wool, it is necessary to install steam-hydro- and thermal insulation. The pitched part of such a roof is a multi-layered pie. It can be installed both inside and outside the roof.
To create high-quality thermal insulation of the roof, you must perform the following steps:
- install a vapor barrier layer. It will protect the thermal insulation from air saturated with moisture;
- use mineral wool as a thermal insulation material;
- to protect the rafter system and insulation from precipitation, a layer of waterproofing should be installed;
- must be ensured ventilation gap. It is created by installing a counter-lattice;
- At the last stage, the roofing material is laid.

Laying a waterproofing membrane
- When insulating the roof of a building with mineral wool, you must ensure that it does not block the ventilation hole.
- If during installation work If a superdiffusion membrane is used, the heat insulator should be placed tightly on it. This is necessary so as not to block the ventilation gap.
- If a regular roofing film is used, then it is necessary to make two gaps: at the top and at the bottom.
- When laying mineral wool slabs in rows, care must be taken to ensure that the joints do not coincide with each other.
- In order for the insulation to fit tightly to the surfaces of the rafter legs, it is necessary to choose mineral wool of such a size that its width is slightly larger than the distance between the rafters.
- Mineral wool slabs must fit very tightly to each other.
- When insulating a roof with mineral wool, it is necessary to install a layer of waterproofing. In this case, it is necessary to monitor the quality of the connection of the waterproofing film.
Installation errors
Before installing mineral wool, you must perform the following steps:
- check the truss structure. If there are rotten elements, they must be replaced;
- treat the roof with antiseptics;
- check communication systems: water supply and electricity;
- It is best to insulate a pitched roof with material in the form of slabs or rolls, since they fit well onto the sheathing.
There must be a ventilation space between the mineral wool layer and the roofing material. When insulating a pitched roof in a private house, not only thermal insulation is provided, but also sound insulation.
Inexperienced specialists often make the following mistakes:
- You should not use a heat insulator whose width is less than the distance between the rafters. In this case, heat loss will occur through the cracks;
- You should not insulate the roof with material with a high level of humidity. It will cause rot wooden elements rafter frame;
- If you do not install hydro- and vapor barriers, the thermal insulation system will not work properly, and its service life will be significantly reduced.
Video on how to insulate a roof from the inside with your own hands:
It is a rare owner of a country estate in our latitudes who is not concerned about heat preservation issues. The number of wasteful people among domestic owners is decreasing at an astonishing rate. There are fewer people willing to easily throw away money to warm the air outside their own roof.
The idea of saving money has firmly taken root in minds concerned with the choice of “cruising” methods of saving. TO effective ways, allowing you to achieve a noticeable effect with minimum costs, refers to the insulation of a flat roof. As a result of well-executed thermal insulation, costs will be significantly reduced.
The insulation of flat roofs is carried out according to special rules that differ from the principles of thermal insulation of pitched roofs. The analogy can be traced only in the sequence of laying the layers of the roofing pie. Flat structures do not have rafter systems, among the elements of which it is convenient to place a thermal insulation layer.
There is nothing to nail the sheathing to, forming a ventilation gap to ventilate the components. Instead of channels for ventilation, if necessary, original vents are created due to partial gluing of the coating to the underlying base.
According to construction traditions, a flat roof is constructed by sequentially placing its components on top of each other. Traditional components include:
- Vapor barrier. Acts as a barrier to household fumes. Located on the side of residential, commercial, etc. premises.
- Thermal insulation. Prevents the passage of heat waves from the inside to the outside of the building and in the opposite direction. At the same time, it copes with the duties of a barrier to sound vibrations.
- Waterproofing. Covers the thermal insulation from the outside, protecting it from atmospheric water. It is laid in 4-6 rows depending on the size of the roof slopes that direct water to the water intakes, and on technical characteristics roofing material. Outer layer waterproofing of a conventional roof serves as a finishing coating. When constructing ballast roofs, gravel, soil and vegetation layer, paving slabs, etc. are laid on top of the waterproofing.
Violation of the sequence of layers and installation rules ends in failure for owners, who are forced to shell out considerable sums for repairs or even for a total reconstruction of the roof.

Note that the indicated layers, together with their laying sequence, are used only if it is necessary to retain the heat obtained by heating the premises.
The roof summer kitchen or storage shed country house equipment there is no reason to insulate. In such situations, the roofing pie includes only waterproofing if it is installed on a concrete base, or consists of a prefabricated screed and waterproofing if corrugated sheeting is used as the base.
Classification of insulated flat roofs
The external simplicity of a flat roof can lead to deep bewilderment for home craftsmen who want to quickly erect a roof over private property. Those who consider flat roofing a budget option will also be surprised.
If the roof is built wisely: with the proper number of waterproofing layers, with insulation of the required thickness, with parapets, drainage and its heating, in the end it will cost quite a lot, but also work flawlessly.

Flat roofs of the following categories are subject to insulation:
- Combined, they are hopeless. Their roof structure is combined with the ceiling. Insulation is carried out by laying thermal insulation with accompanying layers on top of the base. The advantage of combined systems is that they practically do not require winter clearing of snow cover. After all, the ceiling is regularly heated from the inside. Minor snow deposits can be easily removed by the natural force of the wind, which is why it is recommended to equip such roofs not with parapets, but with lattice fencing. Disadvantage: the condition of the roof is difficult to monitor. The slightest damage will result in leaks, followed by serious restoration of the roofing pie.
- Attics, having two subspecies within the category. Attic floor of the first subspecies is complemented by a light superstructure on top. It is clear that in such cases the ceiling should be insulated. In the scheme of the second subtype, the attic superstructure and the ceiling are independent structures. This means that insulation is acceptable for both of them. The advantage of attic structures is the free monitoring of the condition of the roof and timely detection. Owners can dry out the roofing pie by simply ventilating the attic. Among the significant advantages is the ability to carry out insulation upon completion of roof construction. The disadvantage lies in the impressive cost, which, however, pays off through long-term operation and rare repairs.
The second category of attic roofing systems means that the insulation can be located either within the superstructure or above the ceiling. However, the second option for laying insulation for a flat roof is a priority.
According to the second scheme between roofing covering and an air chamber is formed by the thermal insulation system. This is an attic that divides the structure into two parts with different temperature backgrounds.

The difference between the external and internal temperatures of the attic roof will not be as significant as it is with structures without an attic. The temperature change will not be so sharp and destructive. Plus a minimum of condensation, which is the secret to the longevity of attic roofs.
Analysis of technical nuances
The choice of method for insulating a flat roof is influenced by a number of circumstances, including the financial capabilities of the building owner, the required thermal insulation parameters and the load-bearing capacity of the building.
Almost all types of materials used to protect walls and ceilings are used as insulation: expanded clay, lightweight concrete, slabs made of mineral and synthetic materials. However, the list of popular options for insulating flat roofs is now topped by:
- Expanded polystyrene– a rigid material obtained by pressing and sintering styrene granules. Lightweight, fairly strong slabs are used as a layer on top of which the screed is poured.
- Extruded polystyrene foam- a rigid material obtained by mixing styrene granules with a foaming agent under the assistance of high temperature and pressure. Everything is mixed and conditioned in an extruder, and then squeezed out of it while simultaneously molding into slabs standard dimensions. It is used as a basis for installing a finishing roof and as a thermal insulation layer under a concrete screed.
- Mineral wool– fibrous semi-rigid and rigid material obtained by melting silicate rocks, metallurgical waste or mixtures thereof. Depending on the density, it is used as a basis for waterproofing or as a component of a multilayer insulation system.
Polystyrene representatives are attractive due to their closed structure of granules sintered together and minimal moisture absorption. The extrusion namesake of the previous representative has the lowest thermal conductivity. Mineral wool is easy to install. The advantages of all of these options include light weight, combustion resistance and stable insulating qualities.
The unfortunate drawback of mineral wool is that the procedure for insulating a flat roof with it from the outside must be timed to coincide with a period without rain. The thermal insulation installation stage must be completed on the start day without postponing some of the work to the next day. If mineral wool gets wet, it will have to be completely changed, because... the material will lose the insulating properties laid down by the manufacturer.

The type of insulation suitable for construction is determined in accordance with protocol SP 02.13130.2009, which regulates the adoption of measures to ensure the fire resistance of the facility under construction. The thickness of the thermal insulation is calculated according to the requirements of the collection of rules on thermal protection of structures SNiP 02/23/2003.
Manufacturers of roofing thermal insulation produce a range of materials with varying parameters of density, compressive strength, and thickness. Using the products supplied to the construction market, it is possible to arrange an insulation system with the necessary characteristics for any design scenario.

In addition to standard thermal insulation slabs, wedge-shaped slabs are produced from these materials and are used to organize the natural movement of atmospheric water to drainage facilities. They produce fillets that are installed along the lines where the vertical planes meet the horizontal surface of the roof.
Fillets prevent the formation of puddles and stagnation of water near parapets, adjacent walls, square chimneys, skylights, etc. It should be remembered that they cannot be considered as a worthy replacement for the insulation layer. It is obliged to solve only drainage issues.
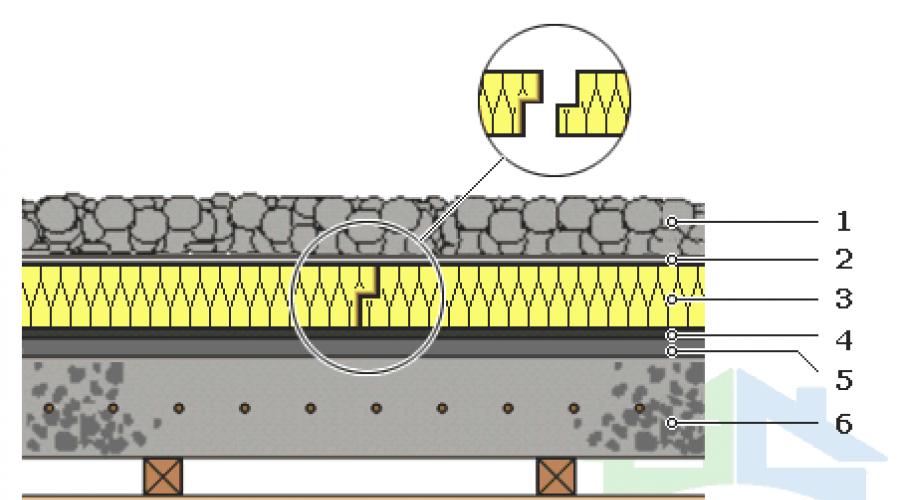
Choosing a method of insulation depending on the base
Insulated roofing systems are installed on profiled steel sheets or iron concrete base. Reinforced concrete bases include slabs, reinforced poured screeds and prefabricated screeds. Filling of cement-sand screed is carried out only according to concrete bases and only if the strength characteristics of the base are sufficient.

Method of installing an insulation system and characteristics required type thermal insulation is selected depending on the type of base:
- Insulation of a roof with a base of reinforced concrete slabs is carried out using mineral wool, covered on top with a prefabricated or cement-sand reinforced screed. The compressive strength of the insulating material should be 40 kPa or more. Deformation parameters are not less than 10%. When installing a two-layer insulation system, the compressive strength of the lower tier must be at least 30 kPa, upper tier from 60 kPa.
- Thermal insulation of a flat roof being repaired is carried out in two layers. The bottom layer is made up of slabs with compression resistance values from 30 kPa, similar data for the top layer from 60 kPa with the possibility of deformation changes of no more than 10%.
- An insulated roof using corrugated sheets must have a two-layer structure. The strength indicators of the lower tier laid on top of the corrugated sheet should be from 30 kPa, the same data for the layer laid on top from 60 kPa. Deformation limit 10%. If it is planned to install a bitumen-polymer roof on top, the material is laid directly on the thermal insulation system.
It is allowed to lay thermal insulation on galvanized corrugated sheets without a preparatory leveling layer of flat slate or DSP, if the thickness of the slab is twice the distance between the corrugations. The insulation must be based on the flat component of the profiled sheet with its own area of at least 30%.

Mechanical fasteners for insulated flat roofs are installed at the rate of 2 units per slab. If the roof is built on a concrete base, the covering and insulation are fixed simultaneously.
Along the interface lines with vertical surfaces, around chimneys and other penetrations, the frequency of installation of fasteners is increased. The insulation of flat structures on a profiled decking is attached separately from the waterproofing coating.

Rules for laying insulation
The principles of laying thermal insulation for a flat roof are closely related to the rules for constructing a roofing pie, because the insulation is its significant and most impressive part in terms of volume. We remember that the thermal insulation material can be covered with a cement-sand screed or serve as the basis for laying waterproofing together with the finishing coating.
When pouring a screed solution over the material, the surface is leveled to install beacons that determine the power of the thermal insulation system.

Specifics of thermal insulation device on a flat roof:
- Laying of thermal insulation boards begins from a corner located in the low area of the roof. If during the construction process the slope of the structure was not observed, then the first elements should be aligned with the installation site of the water intake funnels or gutter.
- Insulation slabs are placed on the profiled flooring so that their long side is perpendicular to the corrugations in order to install fasteners in different ridges.
- When installing multi-layer thermal insulation, the slabs are placed according to the principle of spacing the seams. Those. The layout of the slabs in each layer should resemble brickwork. In addition, the connecting lines and crosshairs of the upper tier should not coincide with the analogues of the lower row. To do this, the heat-insulating boards of the second tier are cut in the order proposed by the material manufacturer.
The cutting method given as an example, which has been repeatedly tested in practice, can significantly reduce costs.

Options for attaching thermal insulation boards
Fixation slab insulation produced in accordance with the type of roof being constructed. To attach a thermal insulation layer to a flat roof, the following methods are used:
- Mechanical. Fixation is carried out using so-called telescopic fasteners, the elements of which consist of self-tapping screws that are screwed into the base and pass through the thickness of the roofing pie. plastic mushrooms. IN concrete plates special anchors are hammered in and secured to the ties with screws with plastic sleeves.
- Adhesive. Thermal insulation and other components of the roofing cake are glued to hot bitumen-polymer mastic. The insulation is glued evenly; at least 30% of its area must be in contact with the base. The installation of roofing systems with bitumen or bitumen-polymer coating is not used during rainy weather periods, because... completely deprives the insulation of the opportunity to part with excess steam. Gluing can be done at any time of the year if the pie is completed with a roofing membrane that allows the excess fumes accumulated in the thermal insulation to pass through.
- Ballast. The insulation laid on a flat roof is simply covered with a waterproofing carpet, on top of which a gravel-pebble mixture is poured or paving slabs are installed on plastic supports. The components of the system lie freely, the pie is secured only along the perimeter and around the roof penetrations.
Ballast roofs include the now very popular green roofs. True, these are inversion systems, so the order of laying the layers of the cake is somewhat different from tradition. The insulation is laid on waterproofing, which at the same time serves as a vapor barrier.
The thermal insulation is covered by a geodrainage polymer membrane, produced specifically for roofs with landscaping. A soil-vegetative layer is arranged on the drainage layer.


Thermal insulation device from the inside
Laying insulation slabs from the inside of a structure with a flat roof is not very convenient in the physical sense. Not everyone will be able to maintain their ability to work for a long time with their arms extended upward.
But it is practical, because you can work regardless of rain, snow, strong winds, or scorching sun. It is also not necessary to carry out all thermal insulation actions in one day, because... the material will not get wet.
Work on laying thermal insulation from the inside proceeds in the following order:
- We screw a block, both or one of the sides of which is equal to the thickness of the insulation board, along the line where the ceiling and wall join. For internal insulation, lumber from coniferous species and polystyrene foam boards that hold their shape well.
- We install a similar bar made from a bar on the opposite wall.
- Glue the polystyrene foam board onto a hot bitumen mastic or glue to the ceiling and the side edge of one of the planks. Press the insulation firmly onto the mating surfaces. We fill the conditional strip with insulation boards completely. If necessary, we cut the edge slabs to actual dimensions.
- We screw the block onto the side of the heat-insulating strip we created, pressing it tightly against the mating elements.
- Pressing the polystyrene foam, we again form and glue the insulation strip.
- We alternate screwing the bars with gluing the thermal insulation until we fill the ceiling plane.
- We staple the plastic film to the bars and cover the ceiling with plasterboard or similar material.
Before laying thermal insulation with inside buildings, it is necessary to think through and calculate how, where and at what height to place electrical lighting fixtures.

Video instructions with examples of work
Compliance with the rules according to which it is required to construct an insulated flat roof guarantees long-term operation of the structure without the slightest problems.
There are many rules, but it is necessary to follow construction postulates in order to prevent premature repairs. A “conscientiously” equipped flat roof will be an excellent result of work and the pride of the owner.