Subtleties of attic floor insulation. Insulation of the attic floor using wooden beams and a reinforced concrete slab Ceiling pie of a frame house with a cold attic
For this it is necessary all heat sources, coming from the house, block heat insulator - attic floor insulation - put a "fur coat" on the house that keeps the house warm, and not give it to the attic.
There must be an attic cold - have the same air temperature inside as well as outside.
Then the snow will not melt on the roof, gathering in the snowdrifts, and icicles won't fall on the head.
ATTENTION! Need to remember Golden Rule: if you don’t want to climb onto the roof again clear the snow from it And knock down icicles- necessary properly insulate it.
After all, the purpose house roofs - act as an “umbrella” over the house (under no circumstances are they “hot water bottles”!). The role of a “hot water bottle” is played by heating in the house. And the most important task - separate the "hot water bottle" from the "umbrella".
At all delete or close all sources of heat entering the roof of the house- because she must confirm her "title" - cold roof.
In houses with cold attic roofs only insulated attic floor being the floor of the attic above the ceiling of living quarters.
Roofs with a cold attic, which are discussed in this section of the site, contain:
- attic covering with roof,
- external attic walls performed with holes- for ventilation with outside air through openings in the walls;
- insulated attic floor top floor.
Before starting work - space in the attic should definitely ventilate.
Natural ventilation(ventilation) attic performed via under-eaves and ridge vents. Lower (under-eaves) vents serve as a supply air, A upper (under-ridge) vents serve exhaust ventilation - thereby creating necessary draft.
ATTENTION! Application in cold attics solid structures, dividing sections of the building(long support panels, high purlins or ribs, etc.) NOT ALLOWED.
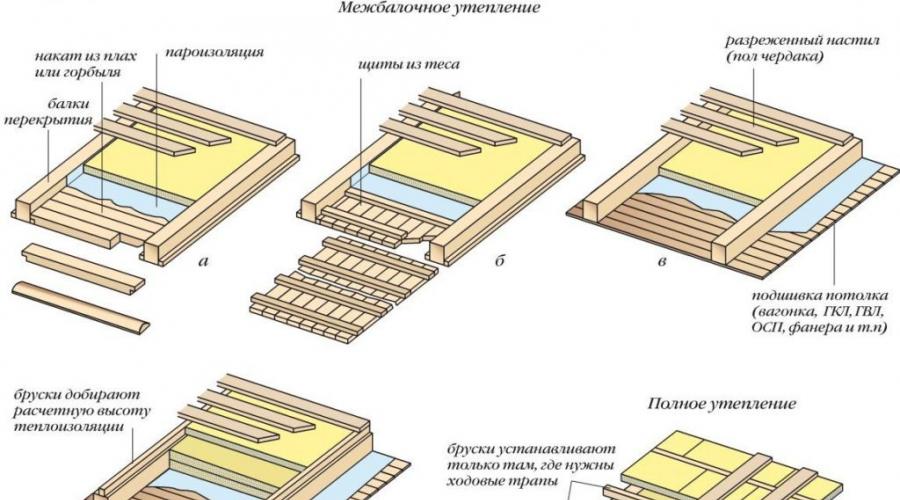
Insulating the floor For attic space can serve coatings (see table 1 below):
- polystyrene foam boards, foam plastic boards PSB-25, fiberboard, foam silicate(foam concrete is not an insulating material);
- construction felt, mineral slabs, rolled mineral wool;
- expanded clay gravel, fuel slag And pumice.
Before performing work on insulation attic floor need to:
- Go through and check all roof and ceiling joints for the presence of cracks (to protect against leaks).
- All gaps must be filled (tow).
- All wooden structures must be covered with fire retardant and anti-rot solutions.
During repairs coverings from asbestos cement sheets need to PAY ATTENTION on the gaps (cracks), formed by waves of asbestos-cement sheets. If there are such, then they MUST BE COMPLETED lime mortar with an admixture of fibrous substances.
For sealing junction points asbestos cement sheets for walls and parapets necessary check the presence of protective aprons, A to the pipes - collars made of galvanized roofing steel. Overlap of dissimilar elements coverings for aprons it should be not less than 15 cm.
To maintain normal temperature and humidity conditions in a private home, it is necessary to ensure reliable protection from the penetration of cold air. It is necessary not only to insulate the walls and ceiling of the basement, but also to insulate the attic floor with effective materials on wooden beams.
Types of attic floors
In a private home you can use the following types horizontal structures:
- prefabricated reinforced concrete;
- monolithic reinforced concrete;
- on metal beams;
- on wooden beams.
For construction wooden house most rational solution There will be an option to cover it with wooden beams. The tree has higher thermal insulation characteristics than concrete, but still the thermal insulation is insufficient.
Insulation technology
How to insulate the attic floor so that there are no problems in the future? In general, the technology for do-it-yourself thermal insulation is almost the same. But the methods of its installation depend on the specific situation.
Insulation of the attic floor is carried out in the presence of a cold attic. Thermal protection of the structure is carried out from above, since in this case the thermal insulation is most competent. But in some cases, another scheme is used - protection from the outside warm air.
The answers to the question why insulation from the ceiling side of the upper floor is undesirable can be the following disadvantages of thermal protection from below:
- the insulation only protects the ceiling, and the ceiling remains cold;
- doing work from below with your own hands is quite labor-intensive;
- the point of condensation moves inside the floor pie, which can lead to rotting of the structure along the wooden beams.
It is also important to maintain the correct order of all related materials.
When insulating, you need to remember one rule: the vapor barrier is always located on the warm air side, and the waterproofing on the cold air side.
Incorrect placement can lead to the following problems:
- insulation getting wet;
- condensation on the ceiling surface;
- rotting of the ceiling of a cold attic along wooden beams.

Whether vapor barrier and waterproofing is needed depends on the chosen insulation.
Choice of insulation
Methods for insulating the ceiling of the upper floor of a beam in a private house are very diverse. When doing the work yourself, the insulation is placed between the joists and provides reliable thermal insulation and noise protection. There are many options for insulating a structure, the most common of which are:
- insulation with mineral wool;
- laying expanded polystyrene (foam plastic or penoplex) on wooden beams;
- filling with expanded clay;
- insulation with sawdust;
- filling the ceiling space with foam.
Each of these options has its own characteristics and advantages.
 Insulation with mineral wool between joists
Insulation with mineral wool between joists Mineral wool insulation
The material is available in two versions: plates and rolls. Insulating the attic floor with mineral wool has the following advantages:
Styrofoam


Foam plastic has become one of the most common materials for thermal insulation. It has earned its place in the top three thanks to its very attractive price. The use of this insulation in individual house provides the following benefits:
- high degree of protection;
- resistance to rotting and mold and mildew;
- low degree of water absorption;
- ease of installation and no need for complex tools and protective equipment;
- Not heavy weight The material does not allow excessive load on the structure and allows for insulation from below.
Extruded polystyrene foam
 More often this material is called more in a short word- penoplex. Being the closest relative of foam plastic, penoplex is devoid of most of its disadvantages. In the process of improving performance characteristics, the cost has increased. The material is produced fireproof, it has sufficient strength for use as a base for flooring and is light in weight for use in ceiling construction.
More often this material is called more in a short word- penoplex. Being the closest relative of foam plastic, penoplex is devoid of most of its disadvantages. In the process of improving performance characteristics, the cost has increased. The material is produced fireproof, it has sufficient strength for use as a base for flooring and is light in weight for use in ceiling construction.
Do-it-yourself installation is quite simple. This issue is discussed in detail in the article. The text discusses options for using both penoplex and polystyrene foam for different types floor structures.
For people who decide to build their own wooden house, the naturalness of the materials is usually important. Here penoplex, like foam plastic, loses to other types of insulation due to its artificial origin.
Expanded clay or sawdust
 Insulation wooden floor
Insulation wooden floor If you decide to use it completely in the house natural materials, these two types of insulation will become irreplaceable assistants. They do not have high heat-protective characteristics, like previous types, but provide reliable protection from the cold with a sufficient layer thickness. Sawdust can be obtained almost free of charge; expanded clay is also an inexpensive material.
Insulation of the attic floor can be carried out by non-professionals and does not require special skills. The application is limited by the physical characteristics of these materials: they cannot be used for thermal protection from below.
Foam for thermal protection

Polyurethane foam insulation is sufficient new material in construction. At self-construction buildings this method can provide high speed work and reliable protection from the cold. You can read about insulating a building, including attic floors, with foam in the article.
This provides big choice materials for insulation and significantly save on construction.
The insulation of a wooden floor is carried out between the joists, and therefore does not require high strength heat-insulating material: the main load from people, furniture and equipment will be borne by boards or timber.
A large percentage of heat loss occurs precisely through the ceiling of the upper floor, which is why it is so important to choose the right insulation and follow the installation technology.
A room in the attic of a private household is used for various purposes: storing temporarily unnecessary things, installing equipment or furnishing living rooms. Depending on what it is used for free space under the roof, choose the method of installing the attic floor.
What is an attic
The attic space is limited by the roof slopes and the ceiling of the residential floor. This place is often used to create additional living space.
There are two types of attics in private households:
- Residential. It is called an attic. It can be equipped with a living room, study, bedroom, library, etc. The height of the room in this case should be at least 220 centimeters. In addition, it must be provided with ventilation, daylight, perform insulation of the slopes.
- Non-residential. This attic space is usually used to accommodate technical equipment, storing old or unnecessary things. In this case, a 2-meter height will be sufficient, and there is no need to provide natural lighting. Instead of insulating the slopes, they insulate the attic floor.

When making a decision to repair or rebuild a house, you need to decide in advance for what purpose the attic will be used in order to make calculations and a design for the floor. The list depends on this necessary materials and the gap between the beams. They must provide the required strength and load-bearing capacity.
Functional purpose of floors
The design of the attic floor depends on the parameters of the structure and the purposes for which it is planned to use the under-roof space. The attic functions as a kind of air gap that separates cold roof from heated floors.

The floor in the attic performs a number of tasks:
- carrier. The floor, located between the upper residential floor and the attic space, is assigned a load-bearing function, so it is made reliable and durable, since people will move on it, they plan to place equipment on it and arrange storage areas;
- insulating. In a cold attic, the temperature differs little from that outside the house. In this case, the floors in the attic have a thermal insulating function, thereby preventing the air from cooling to residential floors. To retain heat, the attic floor needs to be insulated. It is advisable to entrust such work to professionals.
Features of the device and design of floors
Since attic floors perform two functions - load-bearing and insulating, they have a multi-layer structure. Each of the elements of the “pie” complements each other, which ensures the structure being created long term operation, strength and ability to withstand heavy loads.

The construction of the floor in the attic requires the presence of the following layers:
- Finish floor. This name is given to the floor covering, which is laid on a rough base. If it is an attic, then when installing the finished floor, linoleum, laminate, parquet, etc. are laid. IN non-residential premises the finishing floor covering may be missing.
- Rough base. It is a boardwalk that is mounted on logs. The subfloor is lined with edged boards 4–5 centimeters thick or, to save money, with unedged boards.
- Lags. These are durable, smooth wooden elements, laid perpendicular to the floor beams to create flooring. When installing an attic floor on wooden beams, insulation is placed between the joists, which is protected from below with a layer of vapor barrier, and covered on top waterproofing material. If you do not use insulating layers, then repairs will be required in a few years.
- Beams. The frame of the floors is built from thick and strong beams, which are either mounted on the projections of the walls or built into them. They must support the entire weight of the structure. A flat roof can also be made using wooden beams, which is quite practical.
- Headlining. From the side of the rooms, the ceilings are decorated finishing material, For example, natural wood or drywall.
Types of attic floors
To construct the ceiling of a cold attic, materials differing in weight, durability, cost and load-bearing capacity are used.
There are several types of floors depending on what they are made of:
- Wooden elements. For their manufacture, you can use beams with a cross-section of 150x150 or 200x200 millimeters. The advantage of this option is that the tree is quite durable and at the same time relatively lightweight material, so wooden elements do not put additional load on the foundation of the house. In addition, their big advantage is their low price and availability. But such an attic floor is used when the size of the building does not exceed 6 -10 meters, since it maximum length lumber.
- Metal products. Metal I-beams are distinguished by their strength and ability to withstand heavy weight without deformation. But they weigh quite a bit, so wooden houses They are used extremely rarely, but for brick and aerated concrete buildings they are the best option.
- Reinforced concrete products. Molded floor beams made from reinforced heavy-duty concrete are used to multi-storey buildings, since they are heavier and the same length.
Of all the above types of floors, in private low-rise housing construction, in most cases, preference is given to wooden beams. They have optimal ratio between price and quality. If the calculations are carried out correctly and the technology is followed, repairs to the ceiling will not be required in the coming years. Ventilation is also necessary in the attic of a private house, the arrangement of which will require additional knowledge.
Requirements for the device of the pie
Since the safety of staying in the house depends on the quality of installation and repair of attic floors, a number of requirements are imposed on their arrangement.
To know the maximum value permissible load that the structure can withstand, it is necessary to perform the appropriate calculations, and then, based on their results, they begin to develop a project from which it will be clear how to properly insulate the attic floor in the house.

The requirements relate to:
- Load capacity. It directly depends on the material used to make the beams and the gap between them.
- Distances between load-bearing elements. Maximum permissible value for this parameter in accordance with building codes equals 4 meters.
- Resistance to temperature changes. It is necessary that the beams can withstand such changes without problems. The fact is that the difference between the air temperature in the residential floors and in the attic always exceeds 4 degrees.
- Isolation. The attic floor covering of a cold attic should protect the premises of the household from the penetration of cold and moisture from the under-roof space.
During the design process, you should take into account the requirements for the beams used to arrange the floor in the attic so that the result is reliable and durable. The distance between them must be calculated based on the loads exerted on them.
Technology for creating an attic floor using wooden beams
If you have experience construction work You can mount the ceiling of a cold attic using wooden beams yourself. This process is performed at the final stage of roofing work.
The sequence of actions will be as follows:
- Installation of load-bearing beams. For a small private house, wooden floors made from timber with a cross-section of 150x150 or 200x200 millimeters are suitable. They are laid on concrete or brickwork walls
- Installation of lag. They are placed on the edge perpendicular to the beams in increments of 60 centimeters. The logs are made from boards with a cross section of 150x50 millimeters.
- Laying thermal insulation. The insulation is placed between the joists - it will protect against the penetration of cold from the attic.
- Installation of rough and finished floors.
- Covering load-bearing beams on the side of the room to decorate the ceiling surface.
When insulating the attic floor, you should not forget about installing hydro- and vapor barriers.
Are you insulating your house for winter and don’t know how to insulate the attic floor using wooden load-bearing beams? Having gained experience in this matter, I will definitely convey technical points thermal insulation, and I will also describe step by step the procedure for carrying out the work.
Why insulate an attic?
We must not forget that a significant part of heat loss occurs through the roof. Therefore, when constructing buildings with cold attics, it is very important to pay attention to proper thermal insulation of the ceiling between the heated room and the attic.

I'll try below accessible language explain how attic insulation affects the internal microclimate and overall heat loss in the house:
- Purpose of the attic. Any unused attic under a sloping roof is, in fact, a buffer technical floor between the street and the living space. Its purpose is to smooth out significant changes in air temperature inside the house and outside;
- Temperature conditions. At any time of the year, during the day the air temperature inside the attic will be several degrees higher than outside. Thus, in winter there will almost always be negative temperatures, and on sunny summer days there will be intense heat;
- Heat losses in winter. When the temperature of any substance increases, its density always decreases. Therefore, in heated rooms, heated air from household heating devices, always rises up to the ceiling. If the ceiling has insufficient thermal insulation, then during the cold season, all the heat from the room will go outside through the attic;

- Excess heat in summer. On hot days summer days this process will occur in reverse. The air in the attic will become very hot from the hot roof in the sun, and then transfer its heat through the uninsulated ceiling into the apartment.
- Reverse air circulation. After touching an uninsulated ceiling, the heated air quickly cools down, and due to the increase in density, it sharply sinks down. Indoors, this leads to excessive reverse air circulation and the constant formation of drafts, which have an adverse effect on the health of residents;
- High humidity. When heated, humid air comes into contact with a cold, uninsulated ceiling, small drops of condensation may form under the ceiling. This will lead to an increase in air humidity in the house, and will also contribute to the appearance and development of mold on the walls and ceiling;

- Economic factor. Confirmed heat loss through an uninsulated roof is at least 20-30%. It means that proper insulation attic floors on wooden beams will save up to 30% of fuel during each heating season. Air conditioning in summer period, will also require lower costs;
- Damage from a “warm” attic. Among other things, the penetration of warm air into an uninhabited attic, from time to time, can lead to unpleasant consequences:
- As warm and cold air mixes, condensation will begin to form in the attic. Drops of water will settle on all surfaces, which will lead to rotting and destruction of the wooden supporting structures of the roof;
- From the warmth of the attic, snow masses the roof slopes will begin to gradually thaw. Thawed water will freeze as it flows down. This can lead to the formation of large icicles along the edges of the roof, as well as freezing of rain gutters and downspouts.

All the factors described are characteristic not only of residential buildings. They should be taken into account when designing and constructing any outbuildings on the site where the heating system will be used (for example, a garage, bathhouse, barn, etc.).
Stage 1: Selecting insulation
When choosing materials for ceiling insulation, you should be guided by several criteria. In addition to low thermal conductivity, attic insulation must have the following qualities:
- Moisture resistance and mechanical strength. The material should not be deformed or destroyed under the influence of mechanical load, and should not change its properties in the event of direct hit water;
- Heat resistance. The insulation must be absolutely non-flammable and should not be destroyed under the influence of high or low temperatures;

- Light weight. In order not to create additional load on the load-bearing structures of the building, the thermal insulation of the attic floor should be quite light, so you need to choose insulation with a low specific gravity;
- Vapor permeability. To ensure normal temperature and humidity conditions in residential premises, all finishing and Construction Materials must allow air and water vapor to pass freely;
- Environmental Safety. Insulation for residential buildings must be hypoallergenic and chemically neutral. It should not contain harmful volatile compounds or toxic substances;
- Lack of organic matter. I recommend using exclusively materials based on mineral or polymer based. They do not contain organic matter, therefore they are not susceptible to mold, and are not suitable for food for small rodents and insect pests.

Taking into account all these factors, several types can be used to insulate attic floors thermal insulation materials:
- Mineral wool. Produced in the form of rolls or rigid mats, from intertwined frozen fibers of molten sedimentary rocks. Mineral basalt wool is characterized by all of the above qualities, so it can be considered the most suitable material. Below I will give some recommendations for its use:
- Basalt wool itself is very soft. To avoid pushing it through or denting it while walking, you need to lay plank flooring on top of it in the attic;
- When choosing insulation, I advise you to give preference to rigid slabs that are covered on one side with aluminum foil;
- They need to be mounted with aluminum foil inside the room. It simultaneously reflects heat and acts as a vapor barrier layer.

- Glass wool. It has a similar manufacturing technology, only molten glass is used as the raw material for its production. I do not recommend using this material for insulating residential buildings for the following reasons:
- Glass fibers are more fragile, so they can break under load;
- The price of glass wool is much lower, but after creasing or getting wet, it partially loses its heat-insulating properties;
- Small particles of glass penetrate deeply into a person's skin and cause severe irritation.

- Expanded clay. This bulk insulation It is produced in the form of small round pellets of light brown or red color. Expanded clay balls are formed as a result of sintering special varieties of red clay under conditions high temperature.
Expanded clay has the following characteristic qualities:
- The internal structure of the material has many closed pores, so it has low thermal conductivity;
- Each pellet is covered on the outside with a dense glassy layer of baked clay, so moisture practically does not penetrate inside it;
- Small crumbly expanded clay pellets freely fill the entire volume, so they are convenient to use for insulating hidden cavities and hard to reach places in building structures;
- Thanks to mineral based, this material does not burn at all, does not emit harmful substances, is not susceptible to mold, and is not suitable for rodent food.

- Styrofoam. This polymer thermal insulation material is made by hot molding from small round granules of polystyrene foam. It is usually produced in sheets measuring 1000x1000 mm, which can be from 10 to 150 mm thick. The following features are characteristic of polystyrene foam:
- Of all existing species insulation, it has the lowest thermal conductivity;
- The foam contains no organic substances, so it is absolutely not afraid of water, does not rot and does not contribute to the formation of mold;
- By itself, polystyrene foam does not burn and does not support combustion, however, when exposed to high temperatures, it can emit toxic gases and acrid thick smoke;
- Due to the polymer base and closed porous structure, foam sheets do not allow air and water vapor to pass through. For this reason, it is not very good to use for insulating living rooms and rooms with high humidity air.

- Extruded polystyrene foam Abbreviated as EPPS. It has the same composition as polystyrene foam, but is made by hot extrusion from a molten mass of polystyrene foam. The technical characteristics of these two materials are also very similar, however, EPS still has some differences:
- Expanded polystyrene has a porous, uniform structure and a higher specific density;
- Due to this, it has higher thermal conductivity, but at the same time is more durable, and therefore is able to bear higher weight loads;
- For this reason, I recommend using it for insulating unheated attics that will be used for storing seasonal items or household equipment.

- Foil polyethylene foam. It is also called “Penofol” in another way. This roll material consists of thick foam polyethylene film, which is covered on one or both sides thin layer aluminum foil. I recommend using it in combination with other types of insulation, because by itself it has specific properties:
- The porous structure of polyethylene foam provides a low heat transfer coefficient, so it functions as an additional insulation;
- Polyethylene film does not allow air, drops of moisture and water vapor to pass through at all, so Penofol can be used as waterproofing;
- Mirror aluminum foil reflects infrared waves well thermal radiation. In other words, it does not allow radiant heat to pass through itself, and returns it back to the room.

- Wood sawdust. This one is cheap and available material, is still often used to insulate ceilings in bathhouses, heated barns or small country houses. It is applied to the wooden floor from the attic side, in the form of a homogeneous thick mixture of sawdust with a liquid clay solution. Despite the seeming primitiveness of this method, it has its advantages and disadvantages:
- Sawdust or small shavings can be bought inexpensively, or even taken for free, at almost any large sawmill;
- There can be no problems with clay either, so such insulation is easy to prepare with your own hands in the required quantity at any time;
- A mixture of sawdust and clay has a small specific gravity, and after hardening it becomes quite hard. Therefore, it does not place significant stress on load-bearing beams, and allows you to walk freely on it with your feet;
- Due to the mineral components, such a coating is permeable to air and steam, but due to sawdust, it may grow mold or be chewed on by mice.

All mineral-based thermal insulation materials, to one degree or another, are capable of allowing water vapor and air to pass through. To protect such insulation from the formation of condensation or moisture penetration from the outside, they must be installed using a vapor-permeable waterproof membrane.
Stage 2: Preparation of materials and tools
In addition to insulation, for the work you will need lumber, waterproofing, as well as the usual set of carpentry and carpentry tools:
- Two hammers: one medium, weighing 200-300 grams, and one heavy, weighing 800-1200 grams;
- Longitudinal and transverse hacksaw for wood. Instead of a cross saw, it is more convenient to use an electric cutting machine;
- A carpenter's plane, a large wooden mallet and a set of chisels;
- From electric tools you need to have a regular one household drill, and it is desirable to have cordless screwdriver with a set of replaceable nozzles;

- For fastening roll materials(waterproofing, vapor barrier), I recommend using construction or furniture stapler with a set of metal brackets;
- You will also need a straight metal ruler, a tape measure 3-5 meters long, building level and a simple rope plumb line;
- To work near the ceiling, it is most convenient to use a folding stepladder. If it is not there, you can adapt a high strong table or homemade goats from scraps of boards;
- Lumber will be needed wooden blocks section 62x62 mm, and planed edged boards thickness 25-30 mm;

- As a waterproofing layer, you can use a film of foamed polyethylene and a vapor-permeable waterproof membrane;
- To seal the joints of the panels, you will need metallized aluminum tape, which is usually used in ventilation systems;
- Each homeowner chooses materials for finishing the ceiling at his own discretion. This could be lining board, drywall, laminated OSB or plywood, or other finishing materials;

If you plan to use mineral or glass wool, then I recommend purchasing a special protective suit that is designed to work with these materials. Otherwise, from small fibers of glass, on open areas severe skin irritation may occur.
Stage 3: Filing the rough ceiling
During construction attic floor or erecting a sloping roof, you can do without expensive and heavy concrete slabs ceilings Instead, the entire load from the roof is carried by wooden load-bearing beams made of logs or timber, with a cross-section of at least 120x120 mm. They are usually laid on top of two main exterior walls, perpendicular to the long side of the house.
Such beams serve load-bearing structure for the ceiling of the top floor, and for the floor of the attic. The same beams will be used for installing insulation between residential building and the attic. This type of ceiling is called hemmed, because both the rough and the finished ceiling are hemmed from below to the load-bearing beams.
Before insulating the attic floor, you need to mount the rough ceiling:
| Illustration | Description of work |
 |
Installation draft ceiling. To hem the rough ceiling, you should use dry edged boards 25 mm thick, or plywood sheets 10 mm thick or more. |
 |
Hemming boards. They must be secured to the lower plane of the supporting beams and beams around the perimeter of the room. Hemming boards must be fastened without gaps or cracks, close to each other. For fastening, use galvanized self-tapping screws 5-6 mm. |
 |
Waterproofing. When the entire rough ceiling is hemmed to the load-bearing beams, panels of foiled polyethylene foam need to be secured to it from below. This can be done using a stapler. "Penofol" will perform the functions of heat and waterproofing. It should always be placed with a foil layer towards a warm room. |
 |
Sealing joints. To prevent moist air from the room from entering the insulation, the ends of the polyethylene film must be wrapped on the walls by 150-200 mm. The joints between the panels must be glued with metallized tape on an aluminum base. |
 |
Attaching the sheathing. From below, across the entire area of the rough ceiling, nail a counter batten made of wooden slats thickness 15-22 mm. It is needed to provide ventilation air gap between Penofol and the finished ceiling. The distance between the slats should be about 400-600 mm. In the future, a finishing ceiling covering will be attached to them from below. |
Before starting work, all wooden structural elements must be treated with antiseptic and fire-retardant impregnations. Antiseptics are needed to protect wood from rotting and mold development. Fire retardants give dry wood fire retardant properties.
Stage 4: Installation of thermal insulation
After filing the rough ceiling, the transverse load-bearing beams will be on the side of the attic. Insulation will be laid in between them.
Depending on the thermal insulation materials used, further installation technology may have some differences. Therefore, below I will briefly discuss the use of the most common types of insulation.
- Laying mineral wool. Mineral insulation materials, when wet, partially lose their properties. To prevent condensation from forming in the mineral wool, all insulation cake the ceiling of a cold attic must be permeable to air and water vapor:
| Illustration | Description of work |
 |
Vapor barrier. First, you need to lay a vapor-permeable waterproofing membrane on top of the rough ceiling. Its peculiarity is that it freely allows water vapor molecules to pass through, but does not allow bound liquid water molecules to pass through. The membrane panels must overlap each other by at least 150 mm; |
 |
Installation of insulation. Place sheets or rolls of mineral wool in the spaces between the wooden beams. If it is very soft, then it does not need to be squeezed or squeezed much. Lay another layer of vapor-permeable membrane on top of the mineral wool. To prevent it from moving over time, it must be stapled to the beams and walls, throughout the entire area and along the perimeter of the attic. |
- Installation of foam plastic. Polymer-based insulation does not have breathable properties, so it does not allow air and moisture to pass through. There is no point in using a waterproof membrane in this case:
| Illustration | Description of work |
 |
Laying foam. Foam or extruded polystyrene panels can be installed between the cross beams, directly on top of the sub-ceiling boards. I advise laying them in two layers, so that the joints of the sheets are located in different places, and did not intersect with each other. |
 |
Polyurethane foam. To prevent the insulation sheets from moving to the sides, they can be glued to the sub-ceiling using special glue for polystyrene foam or polyurethane foam. Thus, it is necessary to fill the entire area of the attic floor with insulation. If there are gaps and cracks between the sheets of foam plastic, then they must also be blown out from a balloon with polyurethane foam. |
- Clay with wood shavings. Insulating the attic floor with a sawdust-clay mixture does not require any additional materials, and is also quite simple:
| Illustration | Description of work |
 |
Preparation of the solution. To make the sawdust-clay solution plastic, the clay must be soaked in water 2-3 days before starting work. To prepare the solution, you need to take 3-4 volume parts of sawdust, and 1-2 parts of dry red clay without large solid particles and foreign impurities. Mix the soaked clay with water until a liquid, flowing solution is obtained; Add sawdust to the resulting mixture and mix thoroughly until smooth. To protect against mold formation, a small amount of copper sulfate can be added to the prepared solution. |
 |
Laying sawdust-clay mixture. Lightly moisten the supporting beams and boards of the rough ceiling with liquid clay milk. After this, fill all the gaps between the beams with sawdust-clay mortar and leave for several days until completely dry. |
- Expanded clay backfill. I want to say right away that expanded clay does not have very good heat-insulating properties, therefore, in individual construction, such floor insulation is rarely used. At the same time, it is considered inexpensive, unpretentious and the easiest to install:
| Illustration | Description of work |
 |
Preparatory work. Expanded clay pellets do not absorb moisture, and therefore are not afraid of water ingress or condensation. Therefore, they can be used both with and without a waterproof membrane. To prevent condensation from seeping through the ceiling into the house, I still recommend laying a waterproofing membrane under the pellets; |
 |
Filling of pellets. Expanded clay pellets should be poured on top of the rough ceiling boards and evenly distributed in a thick layer over the entire area of the attic. No covering material is required on top of expanded clay. |
To prevent expanded clay pellets from bunching up and spreading throughout the attic, a retaining plastic geogrid is used. It needs to be stretched in the spaces between the load-bearing beams, and then expanded clay should be poured into its cells.
Stage 5: Arrangement of the floor in the attic
Many residents use cold attic in your private home, as a storage room for storing long items, seasonal items and any unnecessary trash. In order for a person to safely walk on the insulated floor, the attic must be equipped with a durable subfloor.
The choice of material for installing the floor in the attic will depend on the type of insulation used:
| Illustration | Features of application |
 |
Mineral wool and polystyrene foam. These materials themselves are very soft. To prevent them from being destroyed or wrinkled while walking, the top floor covering must be sufficiently rigid. In such cases, the load-bearing beams should be laid OSB sheets or plywood with a thickness of at least 18 mm. You can also use unplaned edged boards with a thickness of 25 or 30 mm. |
 |
Extruded polystyrene. It has higher rigidity, so it can withstand significant loads. To prevent it from being pressed when walking, it is enough to put a light flooring of thin boards or plywood 5-9 mm thick on top of it. |
 |
Under the weight of a person, they will crawl in different directions. To prevent this from happening, you need to lay 10 mm thick plywood sheets or light wooden ladders made of boards on top of the beam floor. |
 |
Sawdust-clay insulation. After the solution hardens, it becomes hard like cement. A person can move freely on its surface, even without installing additional flooring. |
When installing rough flooring in the attic, you should always leave gaps 15-20 mm wide between boards or sheets of plywood. This is done so that moisture and condensation can freely evaporate from the insulation.
Conclusion
Using this algorithm of work, you can easily insulate the ceiling in the attic in own home. More visual information on each method of insulation can be viewed in the attached video in this article, and I suggest leaving all your comments and questions in the comment form.
The attic is the technical area that completes the building. Attic - Utility room, it is rarely used as a living space, equipment necessary to ensure the life of the house can be placed here, network engineering. The temperature difference in the residential area and the technical area should be no more than 3°-4°. Therefore, the technical room requires insulation.
Attic design with ceiling
Construction of an attic, which certainly expands living space, is much more expensive and requires certain knowledge, time and labor. The installation of a cold attic floor is many times cheaper and simpler.
The installation of an attic floor on wooden beams is a layer cake:
- plank board or roll;
- vapor barrier;
- ventilation gap;
- insulation;
- ventilation gap;
- vapor barrier;

Ventilation is carried out through gables or roof slopes. They also do dormer windows, placing them on opposite slopes so that air penetrates into all corners of the room.
Dormer windows are a difficult element to install, but useful. They may have different shapes triangular, oval, they are placed at a height of 1 meter from the floor, equipped with grilles and blinds. Through them it is convenient to go onto the roof for inspection, maintenance, checking the chimney, antenna and other things.

Beams for the attic
The attic floor is made using wooden beams after the installation of load-bearing elements is completed. This is the simplest and best way to properly arrange the technical area.
The attic floor structure is usually made of wooden beams. These load-bearing elements have a number of advantages:
- maximum coverage 4.5 m between supports;
- light weight, load on the building, savings on the foundation;
- ease of installation, without the use of lifting equipment or a crane;
- availability of wood as an inexpensive material;
- speed of work, the ability to install an attic floor in a day or two;
- possibility of using any soundproofing materials.
For the manufacture of beams they use conifers wood that is resistant to moisture, rot, and fungus. The cross-section of the beams for the attic floor must correspond to the load, taking into account climatic conditions, thickness heat-insulating material. Beam dimensions of 150x200 mm are used if a serious load is expected on the attic floor. For example, it is planned to install a water tank and a transformer. For minimal load, beams of 100x150 mm are used.

The desire to save money and install 50x100 mm beams is not approved. An extremely important element of the house is the attic floor, which provides thermal insulation, sound insulation and reliability of the ceiling. The quality of the overlap guarantees savings in heat and heating costs.
You can calculate the number of wooden beams for the attic floor as follows. Divide the length of the room by 60-100cm (the distance between the beams), add 2 pieces to the resulting value, which will be laid on the walls. Beams should be laid on load-bearing and external walls.

Installation of wooden attic beams
The installation of an attic floor is carried out in several stages, each of which determines the quality and reliability of the structure. The work algorithm looks like this:
1. Preparation. The required length is cut, the wood is processed special composition, protecting against rotting, swelling and other troubles, the edges of the beam are wrapped in roofing felt, then the finished element is raised upward.
2. Laying in two ways:
- without protrusion beyond the external walls;
- with outlet beyond the outer walls.
It is necessary to lay it along the length at the required distance in relation to other structural elements; for any installation method, the following is taken into account:
- the maximum span width should not exceed 4.5 meters;
- the timber is laid on the ends of the walls; in some cases, a mauerlat is used - this thick timber, secured with thick nails or steel studs into the perimeter walls;
- roofing material is laid under each beam layer to ensure waterproofing;
- the pitch of wooden beams is selected based on the size of the thermal insulation material.
 3. The attic floor on wooden beams is carried out taking into account the construction of the ramp, which is a covering made of boards and slabs. Waterproofing, vapor barrier, and insulation are laid between the upper and lower bevels. The lower flooring is made on supports to which boards are attached, but it is better to use slabs or sheets of plywood 15-20mm thick. Fastenings are carried out with self-tapping screws in increments of 10-15mm so that the heat-insulating materials are securely held.
3. The attic floor on wooden beams is carried out taking into account the construction of the ramp, which is a covering made of boards and slabs. Waterproofing, vapor barrier, and insulation are laid between the upper and lower bevels. The lower flooring is made on supports to which boards are attached, but it is better to use slabs or sheets of plywood 15-20mm thick. Fastenings are carried out with self-tapping screws in increments of 10-15mm so that the heat-insulating materials are securely held.
In order to mount the most robust construction you need to fill the bottom of each beam with 50x50mm wooden blocks, they form a ledge on which boards or sheets are placed. You also need to secure the roll to the bars with self-tapping screws. The advantages of this design are exceptional reliability; the disadvantages will appear in the finishing of the ceilings, on which these bars will have to be sealed and hidden. Such a structure should be installed if you plan to actively use the attic.
Video on the topic:
4. The final stage of installing an attic floor on wooden beams is the installation of the floor, for which boards are sewn on top to act as a subfloor. For the finished floor, a tightly laid tongue and groove board is used.
The subfloor is mounted on the same bars, on top. But before we start last stage should do:
- laying membrane-type vapor barrier;
- thermal insulation;
- another layer of membrane fabric.
The finished design is important element covering the roof and the entire building.

The importance of vapor barrier and methods of its installation
Vapor barrier of the attic floor ensures the safety of the wooden floor. It extends the life of the roof and helps create optimal microclimate in residential areas, taking away excess moisture and preventing heat loss. You should choose the material for vapor barrier carefully, without any intention of saving money.
Vapor barrier material has different side structures. On the one side rough surface absorbing moisture, the other side with a film prevents moisture from penetrating into the heat-insulating layer.

The vapor barrier is installed, as is already clear, between the ceiling and the insulation in the attic floors. Materials used:
- polyethylene;
- polypropylene.
Fabrics reinforced with a special mesh may have perforations. You can also use non-perforated film, leaving gaps during installation. The reinforced film has a metallized surface. The film is spread downwards with the metallized surface to reflect heat loss.
A layer consisting of fibers absorbs moisture, then evaporates it naturally. The materials are durable and resistant to ultraviolet rays.
There are also others vapor barrier materials, which can be used when arranging the ceiling of the attic along wooden beams with a vapor barrier. These are varnishes and mastics, asphalt, bitumen, bitumen-kukersol. Today such materials are rarely used, preferring non-woven fabrics of synthetic origin. These are so-called “breathable membranes”, capable of transmitting moisture and air, multi-layer, single-layer, equipped with aluminum foil.
The material is placed with a 20 cm overlap on the wall, secured with a stapler, the rough side down.