The functions of commercial banks do not apply. Commercial bank: functions, principles of activity, classification, operations
Read also
The Central Bank of the Russian Federation is the main bank in the Russian banking system. In order to achieve their goals - to protect and ensure the stability of the ruble, to develop and strengthen banking system, ensuring the efficient and uninterrupted functioning of the payment system - the Bank of Russia performs certain functions. To implement them, one can use different methods. The functions of the Bank of Russia include:
1. Development and implementation, in cooperation with the Government of the Russian Federation, of a unified state monetary policy aimed at protecting and ensuring the stability of the ruble. It is carried out by the following methods:
· accounting and refinancing policies(crediting by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation to commercial banks, including accounting and rediscounting of bills), since the Bank of Russia is the lender of last resort;
· change in the interest rate on Bank of Russia operations- can set one or more interest rates on various types transactions or pursue an interest rate policy without fixing interest rates;
· open market policy- involves the purchase and sale of government securities in order to increase or decrease the money supply in the economy;
· minimum reserve policy- means that each commercial bank must transfer to the Central Bank of the Russian Federation a certain amount of borrowed Money. The amount of required reserves as a percentage of the credit institution's liabilities (it must not exceed 20%), as well as the procedure for depositing them with the Bank of Russia, is established by the Board of Directors of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation;
· issue of bonds placed and traded only among credit institutions;
· foreign exchange interventions- buying and selling foreign currency on the foreign exchange market to influence the ruble exchange rate, as well as the total demand and supply of money.
2. Monopoly issue of cash and organization of their circulation. The decision to issue and withdraw new banknotes and coins is made by the Board of Directors of the Bank of Russia, which also approves the denominations and samples of new banknotes and informs the Government of the Russian Federation of its decision. The issued banknotes and coins are an unconditional obligation of the Bank of Russia and are backed by all its assets. They are required to be accepted face value for all types of payments, for crediting to accounts, deposits and for transfers throughout the Russian Federation. This function implemented by the following methods:
actually issue of cash- an operation to raise funds, which enables the Central Bank of the Russian Federation to increase funds if it is necessary to expand and conduct active operations;
· cash flow forecasting;
· organization of production, transportation, storage of banknotes and coins;
· establishing signs of insolvency of banknotes and the procedure for replacing damaged banknotes and coins;
· determination of the procedure for conducting cash transactions.
3. Acting as a lender of last resort for credit institutions. The Bank of Russia has the right to provide Russian and foreign credit institutions, the Government of the Russian Federation with loans for a period not exceeding one year secured by securities and other assets, unless otherwise established federal law about the federal budget. It issues in the order of lending to commercial banks.
4. Establishment of rules for making settlements in Russian Federation . The Central Bank of the Russian Federation is engaged in the control, regulation and licensing of settlement and clearing systems in the Russian Federation. It performs interbank settlements through a real-time gross settlement system, which accounts for the bulk of settlements (up to 70%). Legally defined general terms payment processing within two business days within the subject of the Russian Federation and five days in the Russian Federation.
5. Establishment of rules for conducting banking operations. The Central Bank has the right to create rules for financing, lending, settlements and cash operations of credit institutions.
6. Maintenance of accounts of budgets of all levels budget system RF. Produced by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation through settlements on behalf of authorized bodies executive power and state non-budgetary funds, which are responsible for organizing the execution and execution of budgets.
7. Efficient management of gold and foreign exchange reserves of the Bank of Russia.
8. Implementation state registration credit institutions, issuance and revocation of licenses of credit institutions and organizations involved in their audit. The Central Bank, as a bank of banks, exercises control over the banking system, which begins from the moment of registration of credit organizations and the issuance of a license for them to carry out banking activities. The Central Bank of the Russian Federation should have full information on existing credit institutions and their activities. The Bank of Russia determines the main conditions, rules, procedure for licensing and registration of credit institutions, as well as the documents required to obtain a license, registers credit institutions in the State Registration Book of Credit Institutions, issues licenses and revokes them. The Central Bank is engaged in antimonopoly policy, controlling, firstly, the size of shares in credit institutions (no more than 25% of equity capital), and secondly, the participation of foreign capital.
9. Exercising supervision over the activities of credit institutions in order to maintain the stability of the banking system, protect the interests of depositors and creditors. He exercises constant supervision over the observance by the credit institution of banking legislation, regulations of the Bank of Russia, in particular, the economic standards established by it. At the same time, he does not interfere in the operating activities of the credit institution.
10. Registration of issue of securities by credit institutions.
11. Implementation independently or on behalf of the Government of the Russian Federation of all types of banking operations necessary to fulfill its main tasks. The Central Bank of the Russian Federation uses both passive operations to raise funds and active operations to place funds. Passive operations include issuing banknotes, deposit operations, opening and maintaining accounts of the Government of the Russian Federation, foreign banks and credit organizations, issuing own securities, forming equity capital and reserves. Active operations include lending, accounting operations, operations with securities.
12. Organization and implementation of currency regulation and currency control.
13. Determining the procedure for making settlements with international organizations, foreign states, as well as with legal entities and individuals. The Bank of Russia issues permits for the creation of banks with the participation of foreign capital and branches of foreign banks, establishes and publishes official quotations of foreign currencies against the ruble, and opens representative offices in foreign countries.
14. Setting the rules accounting and reporting for the banking system of the Russian Federation.
16. Development of a forecast of the balance of payments of the Russian Federation and organization of the preparation of the balance of payments of the Russian Federation. In order to control the condition foreign trade, payments and gold and foreign exchange reserves The Central Bank draws up the balance of payments of the Russian Federation, which reflects all receipts and payments in foreign currency. As a rule, they should be equal, but in most cases this is not the case, so the Central Bank, using its powers, has the opportunity to balance it by pursuing a policy of currency restrictions, or a deflationary policy, or a policy of foreign exchange intervention, which leads to changes in currency ratios. and affect the balance sheet.
17. Establishing the procedure and conditions for the implementation by currency exchanges of activities to organize operations for the purchase and sale of foreign currency, the issuance, suspension and revocation of permits to currency exchanges for the organization of operations for the purchase and sale of foreign currency.
18. Analysis and forecasting of the state of the Russian economy as a whole and by region, primarily monetary, monetary, financial and price relations, publication of relevant materials and statistical data. The Bank of Russia annually, no later than October 1, submits State Duma a draft of the main directions of the unified state monetary policy for the coming year and no later than December 1 - the main directions that reflect the analysis of the state and forecast for the development of the economy of the Russian Federation; as well as the main parameters and instruments of monetary policy. The Bank of Russia publishes summary statistical and analytical information on the banking system of the Russian Federation.
19. Making payments on deposits individuals in bankrupt banks not participating in the system compulsory insurance deposits of individuals in banks of the Russian Federation.
A commercial bank is a credit institution that has the exclusive right to carry out the following banking operations: attraction of funds on deposits, placement of these funds on its own behalf and at its own expense on the terms of repayment, payment and urgency, as well as opening and maintaining bank accounts of individuals and legal entities persons.
The main purpose of the functioning of commercial banks is to maximize profits.
The functions of a commercial bank include:
1. Mediation in credit. It is manifested in the ability of banks to act as intermediaries between those economic entities and the population that have temporarily free cash resources, and those who need them. The money resources of enterprises released in the process of circulation, savings and savings of the population are accumulated by banks, converted into loan capital and transferred to borrowers in compliance with the basic principles of lending.
2. Mediation in payments between independent entities and in transactions with securities. Commercial Bank carries out, on behalf of its clients, transactions related to settlements and payments in non-cash form.
3. Issue of credit money. A commercial bank issues credit funds of circulation by means of a deposit-check issue, the essence of which, when issuing a loan, is to credit it to the account of a business entity.
All functions are closely intertwined and allow a commercial bank to act as a body that issues means of payment for servicing the entire circulation of capital in the process of production and circulation of goods. But commercial banks do not have the right to issue cash banknotes on their own.
The main principles of the commercial bank activity are:
1. A commercial bank works with clients within the limits of actually available resources in the conditions of market relations;
2. The bank has a high degree of economic independence with full economic responsibility for the results of its activities, subject to the regulation of its work by indirect economic methods;
3. The Bank shall be liable for its obligations with all the funds and property belonging to it, which may be levied in accordance with the current legislation. The bank assumes all risks from these operations.
Currently, commercial banks can be classified according to a variety of criteria:
1. By form of ownership:
1.1 State
1.2 Private (stock)
1.3 Mixed
2. By the nature of the activity:
2.1 Universal
2.2 Specialized
2.3 Industry
3. By scale of activity:
3.1 Large
3.2 Medium
3.3 Small
4. By degree of independence:
4.1 Independent
4.2 Subsidiaries
The result of the activities of commercial banks are various kinds of services provided. They can be rendered to clients through a variety of operations, which can be grouped as follows: fig. 3
Fig.3. Grouping operations of commercial banks
Operations connected with the formation of bank resources are called passive. The resources of commercial banks can be formed at the expense of their own, attracted and issued funds. The formation of resources of commercial banks is shown in Figure 4.
RESOURCES OF COMMERCIAL BANKS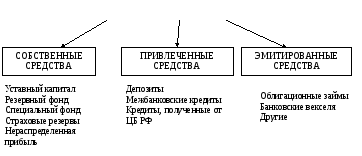
Fig.4. Formation of resources of commercial banks
The own resources of a commercial bank include authorized capital, reserve and special funds, insurance reserves and retained earnings.
The authorized capital is formed at the expense of the participants' own funds and serves to ensure its liquidity. fourteen
The reserve fund is formed from deductions from profits and serves as a source for recovering losses from active operations and paying interest on bonds and dividends.
Commercial banks can form separate special funds (economic incentives, production purposes). The procedure for their formation and use is determined by the Charter of the bank.
Insurance reserves are reserves, the formation of which is mandatory. They are included in the cost of services rendered by the bank.
Retained earnings is the part of profit remaining after taxation, deductions to reserve, special funds and dividend payment funds.
Attracted funds are funds transferred for temporary use to banks by business entities and the population. They make up a significant part of the resources of commercial banks. Deposits form the basis of attracted resources. This is a bank service related to attracting temporarily free funds of business entities and the population into deposits. Non-deposit sources of attracting resources include: interbank loans and loans received from the Central Bank of Russia.
Issued funds of banks are additional funds raised by customers. These include, for example, bonded loans, bank bills.
Operations related to the placement of banking resources for the purpose of making a profit are called active. These include:
accounting and loan operations, as a result of which the bank's loan portfolio is formed;
Investment operations that create the basis for the formation of an investment portfolio;
commission (intermediary) operations.
Lending - the most important species active operations. Bank loans can be classified according to the following criteria (Appendix 1.).
Bank lending is carried out with strict observance of the principles of lending (urgency of return, security, payment, differentiated approach).
The active operations of the bank include accounting (discounting) bills. This means the purchase of bills by the bank before their maturity. For this operation, the bank charges the client a certain percentage, which is called the discount percentage, or discount.
The discount is the difference between the amount indicated on the bill and the amount paid to the holder.
Investment operations - the activities of the bank to invest resources in securities in order to obtain direct (dividends, interest, resale profits) and indirect income generated by expanding the influence of banks on customers through the ownership of a controlling stake in their securities.
Commission transactions are transactions that the bank performs on behalf of its customers and charges them in the form of commissions. The number of these operations is constantly growing. These include such services as settlement and cash services for clients, trust operations, foreign exchange operations, information and consulting services, issuance of guarantees and warranties, renting safes, etc. 15
In this chapter, the theoretical foundations of the functioning of the banking system in modern economy, disclosed the essence and principles of the organization of the banking system, identified the main factors influencing its development. It should be noted once again that the banking system means the historically established and legislatively fixed system of organizing banking in a particular country. It includes all banking and non-banking institutions that carry out individual banking operations. Legislation determines the structure of the banking system, establishes the scope of activities, subordination and responsibility for the various institutions included in the system. The banking system of the Russian Federation has a two-tier structure. The Central Bank occupies the main position in the banking system. The purpose of its activities is the development and strengthening of the banking system of the Russian Federation; protecting and ensuring the stability of the ruble exchange rate; ensuring the efficient and uninterrupted functioning of the payment system. The second level includes credit institutions and branches of foreign banks. The main part of this block is made up of commercial banks, the main and main purpose of which is to obtain the maximum possible profit. In turn, the Central Bank does not seek to maximize profits, this is the main difference between these levels. The two-level structure indicates the development of the banking system of the Russian Federation.
This is manifested at least in the fact that the Central Bank performs a controlling function in relation to other elements of the system.
This chapter identified the main factors influencing the development of the banking system, since their knowledge and changing their impact can further improve the development of the banking system.
The activities of the Central Bank and commercial banks were considered in detail. Further, this will help to identify the main problems of the functioning and development of the banking system, as well as to determine the main directions for improving the banking system and the prospects for its further development.
A commercial bank is a legal entity that, on the basis of a license from the Central Bank, has the exclusive right to carry out banking operations for legal entities and individuals.
A commercial bank is an organization created to attract free funds and place them on its own behalf on the terms of payment, urgency and repayment.
Commercial banks so called because their goal is to make a profit. The income of banks consists of two main components: the difference between the price of attraction and the price of placement of funds, as well as a commission for the services provided. Penalties and fines (for example, for late payments on loans) are not the main, but significant source of income.
A commercial bank is a credit institution whose operations are aimed at the accumulation of funds and their subsequent placement on the money market, as well as the execution of customer orders.
Commercial banks constitute the second level of the banking system. They, acting as financial intermediaries, provide intersectoral and interregional redistribution of monetary capital. The banking mechanism for the redistribution of capital across regions and industries makes it possible to develop the economy depending on the objective needs of production and contributes to the restructuring of the economy.
The financial resources of a commercial bank consist of authorized capital, retained earnings and borrowed funds (demand deposits or current; urgent; savings). Up to 80% of them consist of borrowed funds.
In the Russian Federation, the possibility of creating a bank by one person (legal or natural) is excluded, since the authorized capital of a commercial bank must be formed by means of three or more participants.
Commercial banks, regardless of the form of ownership, are independent economic entities. Their relationship with clients is commercial in nature. They carry out operations with currency and securities, provide various consulting services economic nature, perform a variety of financial services. Commercial banks have become the basis of both the credit system and the economy as a whole.
Organizational structure
Organizational structure commercial bank is determined by its Charter. The main governing body is the general meeting of shareholders, which decides the main issues: approves and changes the Charter, approves the annual report, elects the Board of Directors and others. critical tasks bank activities.
On the general meeting shareholders are appointed by the President, who directs executive body bank - by the Board of Directors (or the Board of the bank).
The Board of Directors forms the highest management bodies of the bank, which conduct practical activities in accordance with his instructions and recommendations.
The organizational structure of the bank includes functional units and services, the number of which is determined economic content and the volume of their operations. Subdivisions (departments) of the bank are formed according to their functional purpose.
There is a specific set of commercial bank control units:
The president.
Board of Directors.
administration (secretariat, personnel service, business units, archive).
General management issues (planning organization, methodologies, legal framework and security).
Marketing department.
Commercial activities (lending, investment, deposit department, currency operations etc.).
Finance (accounting, intra-bank settlements, cash desk).
Department of Informatics ( technical support banking transactions).
Revision department.
Operating principles
The implementation of the tasks assigned to commercial banks is based on their compliance with the principles of activity. Principles are the fundamental provisions of the bank's activities, which ensure the implementation of the tasks assigned to them and the performance of banking operations.
The first and fundamental principle of the activity of a commercial bank is to work within the limits of actually available resources, which means that it must ensure not only a quantitative correspondence between its resources and credit investments, but also ensure that the nature of banking assets matches the specifics of the resources mobilized by it. This applies, first of all, to the terms of both. If the bank raises funds for short time, and invests them mainly in long-term loans, then his ability to pay off his obligations without delay is threatened.
The principle of working within the limits of actually available resources increases the bank's interest in attracting deposits, stimulates an increase in own funds, intensifies the struggle for the client base and the search for the most profitable areas for investing bank capital.
The second most important principle of the activity of commercial banks is economic independence, which implies the economic responsibility of the bank for the results of its activities. The economic independence of the bank implies the freedom to dispose of its own funds and attracted resources, the free choice of customers and depositors, the disposal of the bank's income.
A commercial bank is liable for its obligations with all its assets and property. He takes all the risk from his operations.
The third principle of the commercial bank is that its relationship with its customers are built as normal market relations. When providing loans, the bank proceeds from market criteria of profitability, risk and liquidity.
The fourth principle of activity is that the regulation of its activity can be carried out only by indirect economic methods. The state determines only the "rules of the game" for commercial banks, but cannot give them orders.
The fifth principle of activity is mutual interest with partners. Banks not only compete with each other, but also try to maintain good relationship which reduces costs and improves financial sustainability. This is served by a developed system of correspondent accounts, a system of interbank lending, the formation of customer creditworthiness funds, and maintaining customer credit histories.
The sixth principle of activity is the mandatory observance of laws, regulations and rules governing the activities of commercial banks.
TYPES OF COMMERCIAL BANKS
The current banking system of Russia is represented by various types of commercial banks, which are determined by the content of its operations, as well as the degree of development of the country's economy, credit relations, monetary and financial markets. Commercial banks can be classified according to various criteria:
1. Depending on the ownership of capital (according to the form of ownership), they distinguish the following types commercial banks: state, joint stock, cooperative, municipal, mixed and joint.
In a state-owned commercial bank, the capital belongs to the state.
Joint-stock commercial banks form their own capital by selling shares. They are divided into open joint-stock company when there is an open sale of shares, and a closed joint stock company, whose shares are distributed only among its founders or other predetermined circle of persons.
Cooperative (share) banks form capital through the sale of shares.
Municipal banks are formed at the expense of municipal (city) property or are managed by the city. Their main task is to serve the needs of the city in banking services.
Mixed banks, when the bank's equity pools different forms property.
Joint banks, or banks with foreign capital.
2. According to the volume and variety of operations, the following types of commercial banks are distinguished:
- specialized, which are focused on carrying out one or two types of operations and serve a specific clientele (mortgage bank, investment, innovation, banks consumer credit, savings bank).
3. According to the terms of loans issued, the following types of commercial banks are distinguished:
- short-term lending banks issue loans for up to three years;
- banks long-term lending, such as mortgages, issue loans for a period of more than five years.
4. According to the volume and variety of operations, the following types of commercial banks are distinguished:
- universal, carrying out all types of operations and serving a variety of customers;
- specialized, focused on carrying out one or two types of operations and serving a specific clientele (mortgage bank, savings bank, investment, innovation, consumer credit banks).
5. On an economic basis, depending on the industry that banks serve in the first place, the following types of commercial banks are distinguished: industrial, commercial and agricultural banks.
6. According to reliability, the following types of commercial banks are distinguished:
- the highest category of reliability;
- middle category reliability;
- stably operating banks have some shortcomings, but they work quite stably in the financial market;
- banks with signs of problems - this category of banks is the most numerous.
7. According to the size of the registered authorized capital, the following are distinguished:
a) large banks - these are the first 200 banks in terms of the size of the authorized capital;
b) medium - banks with capital from 5 million euros to a level corresponding to the capital of 201 banks;
c) small - banks with a capital of up to 5 million euros.
Currently, the share of large banks is 17% of their total number, however, they concentrated more than 90% of the total assets of the banking system of the Russian Federation and more than 80% of the total capital.
8. On a territorial basis, the following types of commercial banks are distinguished: local, federal, republican and international.
9. By the presence of a branch network, banks are distinguished with branches and without branches.
10. According to the degree of independence, the following types of commercial banks are distinguished:
A. Authorized - banks, to which the management bodies have transferred part of the functions and exclusive powers in carrying out any operations, servicing specific customers, monopoly of a market segment. For example, Bank Moskva is an authorized bank of the Moscow government; "Gazprombank" - RAO "Gazprom".
B. Independent - independent banks, the controlling stake of which is not owned by any of its founders (participants).
C. Subsidiary banks dependent on the parent bank, whose share in the authorized capital is at least 50%.
D. Satellites - banks dependent on a particular client, as a rule, serving only him.
FUNCTIONS OF A COMMERCIAL BANK
The essence of a commercial bank is manifested in its functions, which are closely interconnected. The main functions of commercial banks include:
- mobilization of temporarily free funds and their transformation into capital;
- lending to enterprises, the state and the population;
- implementation of settlements and payments in the economy;
- issue and placement of securities;
- Creation of credit money;
- consulting, provision of economic and financial information.
Banks accumulate cash income and savings in the form of deposits, which are converted into loan capital used by the bank to provide loans to enterprises and entrepreneurs. Borrowers invest in the expansion of production, the purchase of real estate, consumer goods. This function of commercial banks ensures the development of the productive forces of the country as a whole.
Lending to enterprises, the state and the population is an important function of commercial banks. In the economy, there is often a situation where the funds are held by one, and real need in them arises in others. Commercial banks, acting as a financial intermediary, eliminate these difficulties. Bank loans are directed to various sectors of the economy. This function of commercial banks ensures the expansion of production.
Loans are also provided to the population for the purchase of durable goods, real estate, etc., thereby contributing to the solution of social problems. The government also acts as a borrower of commercial banks.
Most of the settlements between enterprises are carried out by bank transfer. Acting as intermediaries in payments, banks perform operations for their customers related to settlements and payments.
Securities are also the object of commercial banks. Through the function "organization of the issue and placement of securities" the important role of banks in the organization of their primary and secondary markets is realized. By issuing and placing shares and bonds for their clients, commercial banks have the opportunity to allocate capital for production purposes, to finance government spending.
By providing loans, commercial banks create the so-called credit money. They exist only as an entry in a bank account and do not have physical appearance. The mechanism of their creation is regulated by the Central Bank with the help of mandatory reserve ratios. Banks are required to leave a certain part of the funds of depositors in the form of a reserve, they can issue the rest in the form of loans. At the same time, when issuing a loan, there is an increase total non-cash money in circulation, and vice versa, when the client repays the loan, money supply is shrinking.
Commercial banks, having the ability to constantly monitor the economic situation, advise clients on a wide range of issues (new investments, mergers and acquisitions, reconstruction of enterprises, preparation of annual reports). At present, the role of banks in providing customers with economic and financial information has increased.
BANK OPERATIONS
Conventionally, banking operations can be divided into 4 groups:
- passive (raising funds);
- active (placement of funds);
- Banking services;
- own operations of banks;
- others (storage and protection of valuables, consulting and information services).
A commercial bank has the ability to attract funds from institutions, enterprises, individuals and other banks in the form of deposits and open appropriate accounts. Operations related to raising funds are called deposit transactions. For banks, this main view passive operations. Exist various signs classification of deposits. Depending on the term and order of withdrawal, deposits are divided into term deposits and demand deposits. Depending on the depositor, deposits are usually divided into deposits of individuals and legal entities.
The passive operation of the bank is also the receipt of centralized loans. Credits of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation are provided to commercial banks in the order of refinancing and on a competitive basis.
Active operations of commercial banks are aimed at profitable placement of resources mobilized by the bank. Among them are loan, investment, cash, etc. Loan operations form the basis vigorous activity bank in allocating its resources.
Banks are required to provide a clear and timely cash service to their customers by performing cash transactions. The content of cash transactions is the receipt, issuance and storage of funds. Conducting cash transactions is regulated by the Rules established by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
Banking services, as a rule, are intermediary operations - collection, letters of credit, transfer, trust, leasing, etc. For their provision, customers are charged a special fee, called a commission.
Banks' own operations include operations related to the performance by the bank of its functions: the acquisition of banking equipment, protection of the bank, issuance wages employees fare etc.
Commercial banks are legal entities and operate on the principles of economic and commercial calculation. They are independent of organs. government controlled when making managerial decisions.