Comparison of polyurethane foam and expanded polystyrene. What is polyurethane foam filler for a sofa? Polyurethane foam or spring block. Hard or soft
Read also
Read in the article
Application area
Scheme of thermal insulation of the facade with polystyrene foam.
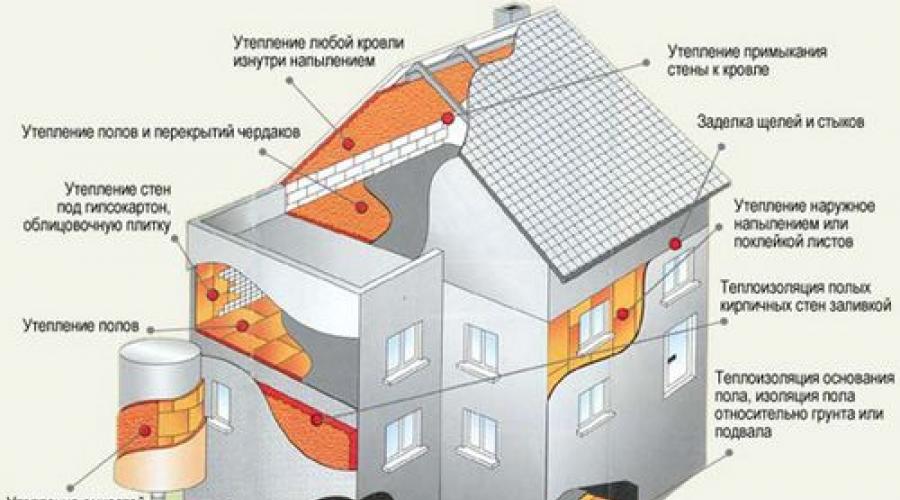
Expanded polystyrene, or polystyrene foam, is used in various fields of activity: from electronics packaging to individual construction. Foam plastic, as a building material, has become widespread for all types of thermal insulation work:
- it is used for roof insulation. The simplicity and ease of its installation makes it possible to carry out work in any weather conditions. In addition, expanded polystyrene is used for the reconstruction of flat roofs;
- Expanded polystyrene slabs are used for floor insulation in houses; this is not only good thermal insulation, but also waterproofing;
- polystyrene foam is used as insulation for heated floors, which significantly reduces costs;
- This material can be used to insulate the walls of buildings, both outside and inside; it can be used to insulate loggias and balconies;
- expanded polystyrene has become widespread not only for internal insulation of a house: it is used for thermal insulation of the foundations of buildings and pipelines.
But not only polystyrene foam has become so widespread in construction; along with it, polyurethane foam is also in great demand. It is easy to use, and its main feature is that this heat-insulating material is not presented in the form of plates and rolls, as usual, but in the form of a special composition that is sprayed onto the surface. This feature makes polyurethane foam a universal insulation material, which has led to its widespread use in construction, where polyurethane foam is used in various directions:

Polyurethane foam insulation scheme.
- due to the chemical resistance of this material, it is well suited for thermal insulation of containers, such as swimming pools;
- polyurethane foam is excellent for thermal insulation of pipelines because it has a high reaction rate, which avoids foam dripping;
- the adhesive properties of this material make it possible to widely use polyurethane foam for insulating the foundations of buildings;
- it is used for thermal insulation of the roof;
- this material is excellent for insulating the walls of buildings, both outside and inside.
The areas of application of polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam are in many ways similar, but they are still two different materials with different properties.
Polyurethane foam for insulating the foundation of a building
In addition to polystyrene foam, other materials can be used to insulate the foundation of a house, for example, polyurethane foam. The material described has a whole list of irrefutable advantages:

Polyurethane foam is excellent for insulating both the foundation and the entire basement floor of a building. And, you see, it looks great!
- When using the composition on the base there will be no joining seams. Please note that the product is applied to the surface by spraying and is not glued or screwed. In this case, thermal insulation remains at an excellent level.
- The material has low thermal conductivity, therefore, for good insulation, a five-centimeter layer of polyurethane foam can be applied.
- It is more than resistant to water. The material is not hygroscopic.
- No additional fasteners are required to install the material.
The main disadvantage of polyurethane foam is that an amateur can hardly cope with its application without the help of others. Note that the work will require special equipment that, under a certain pressure, applies the substance to the plane.

To apply polyurethane foam to the foundation walls, a specialized installation is used, which is quite expensive.
Specialists have such equipment, therefore the cost of such insulation can be higher than thermal insulation of the base with polystyrene foam.
Once the layer is applied, it is best to think about how to properly insulate it.
Video on spraying polyurethane foam on a foundation
The video shows how you can quickly apply polyurethane foam to the foundation. This method provides 100% both thermal and waterproofing.
Why is polyurethane foam so good?
Polyurethane foam has the following properties:
- durability and security;
- reliability;
- environmental friendliness;
- very low level of flammability;
- lack of need for auxiliary fastenings.

Polyurethane foam protects the foundation from cracking.
Insulating the foundation with polyurethane foam completely blocks the likelihood of the formation of cracks and cracks. In addition, the surface remains absolutely flat, therefore there will be no problems with the subsequent finishing.
Polyurethane foam is today considered one of the most effective materials for insulation.
The product can remove any imperfections that are located on the foundation. Another quality of the described material is that under the layer there is virtually no possibility of condensation forming. Therefore, mold and mildew will not appear on the foundation.

Shallow strip foundations are also ideally protected with polyurethane foam spraying.
That's all you need to know. Having studied in more detail, you can easily perform all the actions with your own hands.




fundament-enc.ru »
A couple of reviews about EPPS
Leonid, 35 years old, Omsk: Used polystyrene foam to insulate the walls of a residential dacha. The house is small and heated in winter, so there were no problems with the appearance of moisture inside the insulating “pie”. I carry out repairs every 5-7 years, which means that during this time the insulation will not have time to sag and lose its qualities.
Vitaly, 45 years old, Khabarovsk: Expanded polystyrene does not weigh down the structure and retains heat well, so I chose this material. I heard that it is flammable, but the house uses a minimal amount of fire-hazardous coatings, for the most part concrete, brick, plastic, and metal are used everywhere.
Comparison
Each of the materials mentioned has its own properties. First, let's touch on the most significant characteristic - thermal conductivity. In this regard, the advantage of polyurethane foam is noted. Moreover, it is important that it is produced not only in the form of panels, but also as an aerosol product that is sprayed onto objects. If polyurethane foam is used in this way, a monolithic coating is obtained that exactly follows the topography of the base.
Expanded polystyrene does not require such an effective application method. It is mounted to the surface in the form of solid slabs. The gaps between them cause heat leakage and deterioration of sound insulation. The difference between polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam is that it does not interact well with adhesives and plaster compositions. Meanwhile, polyurethane foam can be firmly fixed to the surface. In addition, this material absorbs moisture less, which has a positive effect on heat conservation.
It is worth noting that polystyrene foam begins to disintegrate and release hazardous substances at a lower temperature - approximately sixty degrees Celsius. Therefore, it is not recommended to insulate the roof with it, especially in the southern regions with the scorching sun. As for the fire safety indicator, the materials discussed themselves do not burn for a long time. But if there is a constant source of fire, then polystyrene foam quickly becomes engulfed in flames. The process is accompanied by the separation of melting fragments and the saturation of the air with a large amount of toxins. The second material burns worse.
What is the difference between polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam regarding their service life? Here the second type of product wins again. Polyurethane foam retains its beneficial qualities much longer. This is partly due to the fact that it is not subject to deformation. Expanded polystyrene is compressed over time, and its thermal insulation properties noticeably deteriorate. As a result, polyurethane foam is the leader in all respects. It is not surprising that the price is higher.
Technologies for the production of EPPS and PU foam
Secondly, you need to explain the basic knowledge about sandwich panel production technologies.
Glued sandwich panels. In them, the layers are joined using one- or two-component (more common) polyurethane glue in a vacuum or mechanical press. The latter is quite expensive, so not everyone can afford it. But we allowed it, and our panels turn out amazing, smooth, like the surface of the sea. In this case, the sandwich panel can be either three-layer: cladding + insulation (in order to reduce the cost, some use polystyrene foam, some use domestic EPS, and we use imported EPS) + cladding, or five-layer with the addition of a layer of plywood under the cladding. Or maybe N-layer.
Filled sandwich panels. The facings of the future panel are placed in a press, the required distance is selected between them, and the ends are closed with limiters. The top facing in the press is held either by magnets or by vacuum suction cups. Next, polyurethane foam flows through the tube into the space between the facings. The most difficult thing here is to achieve uniform distribution of foam, i.e. so that its density is the same throughout the entire volume of the panel. Difficulties arise with the placement of the mortgages (they must first be glued to one of the claddings). And with the production of N-layer panels: cladding with inner layers must first be glued together in a press, and then the polyurethane mass is poured between them (the press works 2 times instead of once → energy consumption, panel production time increases → increased labor intensity, therefore 4 and 5-layer vans with polyurethane foam (road).
Comparison by cost
Protecting surfaces with polyurethane foam insulation is a more expensive technology. So, thermal insulation of 1 m² will cost 150-1500 rubles. In this case, the price is formed taking into account the thickness of the material: from 10 to 100 mm. This means that in order to insulate a surface of 1 m² with a 50 mm thick layer of polyurethane foam, you need to prepare about 850 rubles. The high price of this type of thermal insulation is due not only to the production technology of the material, but also to the high cost of the equipment.
If you are deciding which is better - polyurethane foam or polystyrene foam, you should know that the latter option is offered at a lower cost. For comparison, insulating an area of 1 m² with EPS boards will cost several times less - 300 rubles, provided that the thickness is 50 mm. Good polystyrene foam boards, characterized by large dimensions and high density, are more expensive.
What to choose polystyrene foam or polystyrene foam
Polystyrene foam is part of a group of materials that includes polystyrene. However, both materials have significant differences. Polystyrene foam has a fairly high density when compared with expanded polystyrene.
A characteristic feature and advantage of polystyrene foam is that it does not absorb moisture and steam.
The panels can be easily distinguished, since the structure of polystyrene foam is characterized by the absence of granules, and, therefore, it is homogeneous. Expanded polystyrene is durable due to its single mass of substance. Polystyrene foam is not so durable; if it is exposed to unfavorable processes, it begins to crumble and quickly becomes unusable.
 When insulating a house, many experts recommend choosing polystyrene foam rather than polystyrene foam.
When insulating a house, many experts recommend choosing polystyrene foam rather than polystyrene foam.
Advantages of expanded polystyrene:
- It is not penetrable. Its moisture absorption is ten times lower than that of polystyrene foam.
- The material differs in density. It is 3-5 times stronger than foam. Expanded polystyrene weighs more, but is also able to withstand some types of loads.
The difference between polystyrene foam and polystyrene foam is obvious. It is better to use polystyrene foam as a thermal insulation material. But if the budget is small and the surface will not experience any significant loads, you can give preference to foam plastic, despite its disadvantages. It should be remembered that the service life of polystyrene foam is much longer.
Brief comparative characteristics of thermal insulators
| Options | EPPS Styrofoam | EPPS father | PPU | Styrofoam |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low thermal conductivity | + | +- | ++ in the first years of operation provided that it is foamed with freon; if foaming occurs with air (which is often found in the Russian Federation), then the thermal conductivity indicator of such polyurethane foam deserves no more than one + | — |
| Low moisture/water absorption | + | + | — | — the structure is destroyed |
| High structural strength | + | +- | +- | — |
| Strength/weight ratio | + | +- | — | — |
| Same density | + | — | + | + |
| Dimensional stability (without additional processing) | + | — | — | + |
| Optimal surface for work (no dust/closed cells) | + | + | — | — |
| Possibility of automation and ease of use | + | + | — | + |
| Temperature resistance | — | — | + | — |
What's better
Considering all the characteristics of insulation, it becomes clear that the difference between mineral wool, polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam is huge.
Therefore, the answer to the question: “What is better than mineral wool or polyurethane foam?” The obvious one is polyurethane foam.
From the author's personal experience. My house is a frame house. First, I made the insulation of the walls from ordinary polystyrene foam 8 cm thick, inserted sheets between the racks and filled the seams with polyurethane foam. There was no particular heat in the house and all the sounds seemed to be outside. A couple of years later I decided to check its condition and removed the siding.
The mice gnawed holes, the seams cracked, and cracks formed. As a result, I removed everything and covered it with ecowool. I suffered with her, of course. At that time there was little information about PPU, so I would have used it right away. If I had initially known about the properties of polyurethane foam, I would not have experimented, but would have done everything right away according to my mind.
Our company has extensive experience in selecting the thickness of PPU insulation and its density depending on the object being insulated.
I hope that you need long-term insulation for 60 years, which will effectively save heat in your home and your money.
Comparative table of characteristics of polyurethane foam and polyethylene foam
These types of insulation are approximately equally popular, due to their properties. If you are interested in the question of polyurethane foam or polystyrene foam - which is better, it is recommended to compare them according to their main characteristics. The result can be seen in the table:
| Options | Polyurethane foam | Expanded polystyrene |
|---|---|---|
| Density, kg/m³ | 25-750 | 45-150 |
| Thermal conductivity coefficient, W/(m*K) | 0,019-0,028 | 0,04-0,06 |
| Structure | Closed-cell | Closed |
| Operating temperature, °C | -160…+180 | -100…+60 |
| Environmental friendliness | Polyurethane foam retains its properties and does not emit harmful substances when heated to the maximum value (+180°C). | Expanded polystyrene at a temperature of +60°C begins to release a compound dangerous to human health - phenol. |
| Duration of operation, years | With proper installation, the service life is unlimited, in other cases it is 50 years. | 42278 |
| Fire hazard | Incombustible | More susceptible to combustion. In high temperature conditions, burning areas can become separated, which contributes to the spread of fire. |
| Hygroscopicity | Does not absorb moisture. | It is more susceptible to liquids and is able to partially absorb them. |
| Appearance | Does not lose properties throughout the entire period of operation. | Over time, it shrinks and undergoes deformation due to loss of properties. |
Comparison of materials by performance characteristics
You can also compare insulation materials according to the degree of installation complexity. Thus, polyurethane foam is characterized increased adhesion, which allows for quick insulation. Expanded polystyrene requires the use of special compounds. In addition, it is advisable to make a crate. PPU resistant to mold and mildew. For this reason, the material can come into contact with moisture without the risk of loss of properties. Expanded polystyrene, on the contrary, is prone to the formation of mold.
PU foam retains its properties and structure throughout the entire period of operation, even under the influence of moisture, low and high temperatures. For this reason, there is no need for periodic inspection and maintenance of the thermal insulation “pie” structure.
Expanded polystyrene loses its properties faster, especially in winter, when there is a risk of the insulation freezing upon contact with water. This means that the condition of the PPS slabs still needs to be monitored.
Polyurethane foam easier to transport, because it is not deformed in transit. This applies to rigid and flexible boards. Expanded polystyrene is a more fragile material and is often deformed during transportation.
Advantages and disadvantages of expanded polystyrene
 Ordinary polystyrene foam absorbs moisture relatively well, so an adhesive with a higher density should be used. Expanded polystyrene is a regular foam plastic that everyone is familiar with. It has been used for several years now and all its pros and cons have long been known. At its core, it is 98% air bubbles enclosed in 2% polystyrene.
Ordinary polystyrene foam absorbs moisture relatively well, so an adhesive with a higher density should be used. Expanded polystyrene is a regular foam plastic that everyone is familiar with. It has been used for several years now and all its pros and cons have long been known. At its core, it is 98% air bubbles enclosed in 2% polystyrene.
There are two types of expanded polystyrene - regular (foamed) and extruded. Due to its higher density, the latter has better thermophysical properties, it is stronger and more durable.
Both types of foam are available in the form of slabs of various thicknesses. How to distinguish one from the other? Try breaking off a piece from the edge of the slab. Cheap, packing foam will have small balls along the break. High-quality, extruded polystyrene foam will show regular polyhedra when broken.
The main advantages of polystyrene foam include the following:

The advantages of extruded polystyrene foam compared to conventional polystyrene foam are:

Please note: insulating premises with polystyrene from the inside is prohibited. Moisture (condensation) accumulates very quickly between the insulation and the walls, which leads to fungal infection and accelerated destruction of the building.
Correct installation of insulation will extend the life of the coating and retain heat in your home. Among the disadvantages, the following should be noted: . water-absorbing properties of ordinary polystyrene foam - wet polystyrene foam has reduced thermal insulation properties and it quickly becomes unusable;
- water-absorbing properties of ordinary polystyrene foam - wet polystyrene foam has reduced thermal insulation properties and it quickly becomes unusable;
- short service life - only 10-15 years;
- rodents often make their nests in it;
- destruction under the influence of external factors - the slightest exposure to sunlight through poor-quality plaster begins to destroy the insulation;
- deformation during use;
- fire hazard - burns well; when burned, a fairly large amount of toxic substances is released.
Note: already at 60 degrees, polystyrene foam is susceptible to decay, so it is not worth using it for roof insulation. In the summer in the southern regions, the roof can easily heat up to 100 degrees.
What is the difference between polystyrene foam and polystyrene foam?
Those who are not very familiar with different insulation materials may get confused when visiting a hardware store. Moreover, the opinions of experts differ: some believe that polystyrene foam is the most suitable material for wall insulation, others are adherents of expanded polystyrene. Foam plastic belongs to a group of materials that are a plastic mass formed by foaming.
Expanded polystyrene is a material filled with gas. It is obtained from polystyrene and used for insulation, electrical insulation and packaging.
Expanded polystyrene can be called a type of polystyrene foam. However, the manufacturing technology of these materials is significantly different. They are united only by related material. Which underlies both is polystyrene.
Comparison of materials:
- Polystyrene foam is produced by treating raw materials with steam. The raw materials themselves are placed in a block mold. During the production process, there is an increase in the volume of molecules that combine with each other. The low strength of the polystyrene foam leads to the fact that over time it leads to weak interaction of the granules, as well. consequently, the destruction of the foam.
- Expanded polystyrene is produced by the extrusion method. First, the granules melt, which makes the material viscous and fluid. This manufacturing process ensures that the polystyrene foam has a solid structure. The material consists of cells filled with gas. Expanded polystyrene is as impenetrable as possible.
Polystyrene foam can allow water to pass through, which affects its performance properties. Expanded polystyrene has a high density and strength, which makes it of higher quality. Its price differs significantly from the price of polystyrene foam.
Comparison of polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam
To understand which of these two materials is better, let’s compare them according to a number of important indicators in the form of a table.
| Expanded polystyrene (PPS) | Polyurethane foam (PPU) |
|---|---|
| Environmental friendliness | |
| At temperatures above 60°C it releases phenol. | The products comply with sanitary standards. Polyurethane foam can be used at temperatures up to 180 °C without fear. |
| Fire hazard | |
| Lit. When burning, burning parts are separated from the material, which can cause the fire to spread. | Not flammable. |
| Durability | |
| Service life is no more than 15 years. A decrease in performance occurs after 10 years of use. | Polyurethane foam, protected from ultraviolet rays, can last longer than the load-bearing structures of the building. |
| The material settles and contracts, violating the geometry of the facade. | The properties of the material do not change throughout the entire service life. |
| Appearance | |
| The presence of seams between panels entails a large consumption of joint fillers. | There is no seam. |
| Limited choice of facing materials, as dovetail is required. | Wide selection of finishing materials of any shape. |
| Ease of installation | |
| Slabs often deteriorate during installation or transportation due to their fragility of the material. | The material is not picky in transportation. For installation you only need a sprayer. |
| Sheathing of slabs is required. | The material does not require additional lathing. |
| Not all adhesive materials are suitable for foam, so it is necessary to use special compounds for EPS. | Excellent contact with any type of fastening materials. |
| Specific installation of slabs using dowels and other materials. | You don’t need anything other than a sprayer for installation. |
| Features of operation | |
| High humidity can cause mold and mildew to appear on the slabs, which will cause an unfavorable microclimate in the room. | Moisture resistant. Not subject to rotting or mold. |
| When moisture gets on the panel, it is absorbed and when exposed to low temperatures, it freezes and destroys the foam. | Polyurethane foam repels water from the surface, which prevents destruction of the material. |
| It is necessary to constantly inspect the thermal insulation for defects and eliminate them. | No renewal or repair of thermal insulation is required throughout the entire service life. |
Comparison result

Scheme of roof insulation with polyurethane foam.
The table shows that polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam have both pros and cons, but, of course, polystyrene foam has the most disadvantages. The service life of this material does not exceed 15 years. It is actively destroyed when exposed to the environment. PPS boards are often damaged by rodents. Due to the fact that this material is a hydrocarbon polymer, adhesives and plaster solutions do not adhere well to it. But the most important thing is that polystyrene foam is an unsafe material: it burns, scattering burning fragments in different directions, while releasing toxic substances. All this indicates the unreliability of polystyrene foam for thermal insulation of a house.
Unlike polystyrene foam, thermal insulation using polyurethane foam is a reliable and modern method of insulation. This material is light and does not load the structure, but at the same time it is very durable. Polyurethane foam has low thermal conductivity and vapor permeability.
Nowadays, when all fuel resources are becoming more expensive, the question of high-quality thermal insulation arises. Undoubtedly, the best thermal insulation material today is polyurethane foam.
Advantages of EPPS
Advantages of EPPS Styrofoam, currently used by us:
| Long-lasting thermal insulation (consistency of performance over a long period of time is an important factor for passing the second ATP test) | |
| High mechanical strength (compression, tearing, bending, shear). Allows you to absorb high dynamic loads caused by wind and vibration. | |
| High moisture and vapor barrier characteristics (important factors affecting durability) | |
| Chemical resistance | |
| Good adhesion | |
| Lightness (sufficient strength is achieved with a lower material density) | |
| Dimensional stability (consistency of slab geometry) |
Pros and cons of polyurethane foam
Many consumers know this material as ordinary foam rubber. Soft polyurethane foam is more often used in everyday life, and hard polyurethane foam is used in the construction industry. Most often it is made in the form of slabs.
Spraying polyurethane foam has become a very popular method of thermal insulation today. In this case, the material is manufactured directly on the construction site and applied in the form of foam to the surface, where it hardens. The coating is obtained without joints, the occurrence of cold bridges is excluded.
When choosing whether it is better to purchase polystyrene foam or polyurethane foam, remember that the latter does not require vapor barrier, plus its water absorption rate is approximately 10 times lower compared to standard polystyrene foam.
As for other advantages of the material, here we can note:
- low coefficient of thermal conductivity - the thermal protection of polyurethane foam is 1.5 times greater than that of polystyrene foam, and 2 times greater than that of mineral wool;
- moisture resistance;
- wide operating temperature range – from -70 to +110 degrees;
- long service life - at least 30 years (with proper installation it will be longer);
- absence of any deformations throughout the entire service life;
- resistance to rotting and fungus;
- excellent soundproofing properties.
At first glance, it seems that polyurethane foam is an ideal option for insulation. However, not everything is so simple. There were some drawbacks here too. The main one is the price of the issue. If we compare polyurethane foam with extruded polystyrene, the former costs much more. In the case when the material is applied to the surface by spraying, you will also have to pay a considerable amount for the work, since the process is quite complex. You can try to save on services by renting special equipment and protective equipment. But how well will you be able to complete the work, and how long will it take? In fairness, it is worth noting that using insulation in the form of sheets will help reduce costs. But in this case, seams will appear and the main advantage – solidity – will disappear.
Another, no less significant drawback of polyurethane foam is its instability to ultraviolet rays. The material does not just lose its properties and appearance. When destroyed, it decomposes into products that can harm human health. To protect polyurethane foam, it must be covered with a layer of material that does not transmit UV rays, or at least simply painted.
Of course, the owner of the house is unlikely to show the world the layer of insulation on the walls of his house in all its glory. Most likely he is going to continue finishing the walls. However, difficulties may arise with the choice of material. It is unwise to attach siding to the insulation in order to destroy the integrity of the surface using self-tapping screws or dowels. It is necessary to use other types of finishing, for example, plaster.
Polyurethane foam itself can also not be used on all surfaces. Low vapor permeability of the material can play a cruel joke and lead to the walls becoming damp and fungus appearing on them. It will be just right to use the material on concrete, but on wood it would be better not to use it.
Another point concerns the environmental safety of the material. Manufacturers claim that their material is absolutely harmless. However, certificates confirm its safety only in industrial conditions. In addition, the question of fire safety remains open. Polyurethane foam is a moderately flammable material: under the influence of high temperatures it begins to smolder and release harmful substances. It is unlikely to cause a fire, but in places where surfaces become very hot, it is better not to use it.
What to choose
 Unfortunately, there is no ideal material that will suit absolutely everyone. For some, it will not be suitable due to the high price of polyurethane foam; for others, the service life of polystyrene foam will not suit them. Therefore, weigh all the pros and cons, but keep in mind that the disadvantages are not complete contraindications for use. Knowing the properties of insulation, you can make the best choice and not regret later about the money spent.
Unfortunately, there is no ideal material that will suit absolutely everyone. For some, it will not be suitable due to the high price of polyurethane foam; for others, the service life of polystyrene foam will not suit them. Therefore, weigh all the pros and cons, but keep in mind that the disadvantages are not complete contraindications for use. Knowing the properties of insulation, you can make the best choice and not regret later about the money spent.
For example, if you want to insulate a garage or a wooden house on your property, choose cheaper polystyrene foam. 10-15 years of foam service life will be quite enough for this type of building. If funds allow, purchase extruded polystyrene foam. Just remember that ultraviolet rays destroy foam.
If you want to improve the thermal insulation of your home or apartment for many years, it would be wise to choose polyurethane foam. The costs will be higher, but you will enjoy the benefits of insulating your home for many years to come. The higher costs of quality installation will pay off over time.
You may be interested in information on how to insulate walls from the inside with polystyrene foam.
Read about the technology of wall insulation with polystyrene foam here.
We also bring to your attention an article about the advantages and disadvantages of extruded polystyrene foam.
For an overview of the advantages and disadvantages of polystyrene foam, watch the video:
Description of foams
Polyurethane foam and expanded polystyrene are foam plastics; they have simple installation, which affects the price of the finished insulation. Expanded polystyrene can be regular or extruded. The regular one consists of soft small white balls; the extruded one is denser, warmer, more durable and more expensive than the regular one.
The advantages of expanded polystyrene include:
- low cost 277 rub. for 1 sq.m. 5 cm thick;
- ease of installation;
- low thermal conductivity 0.028 - 0.035;
- different sheet thicknesses.
The disadvantages include the following:
- water absorption of polystyrene foam leads to an increase in the thermal conductivity of the insulation;
- it is easily destroyed by exposure to the sun;
- mice love to chew through it and make nests in it;
- very short service life - 10-15 years, but we are building seriously and for a long time;
- fire hazard - it is very flammable; when burned, it emits soot and toxic gases;
- at 60 degrees it begins to fall apart, so it is not at all suitable for roofs;
- at 20 degrees polystyrene begins to release toxic gas;
- presence of seams between sheets of insulation, cracking of seams;
- deformation during operation;
- it is necessary to fill the seams with polyurethane foam and fasten the sheets to the surface; this somewhat delays the commissioning of the construction project.
Mineral wool
Service life is 50 years for some manufacturers, a good indicator. Thermal conductivity is 0.032 - 0.12, this is the coldest insulation of those compared. Moisture resistance is low, warm air passes through well. During installation, there is a problem associated with protecting the installer from fine dust, which causes irritation to the skin and respiratory system.
For walls you need one type of mineral wool, for the ceiling another, for partitions a third.
Additional protection of mineral wool is required in the form of a vapor barrier device, counter-lattice, all this increases the cost of installation and the time it takes to put the facility into operation. The lowest price per square meter.
Remember, the stingy pays twice, first for the mineral wool, then for its dismantling and spraying of polyurethane foam.
During operation, shrinkage and changes in the size of the insulation are possible. It is possible for small particles of mineral wool to get into the living space, which causes allergies and skin irritation. No wonder people in Udmurtia are dismantling old mineral wool and switching to polyurethane foam.
In the photo of a house insulated with mineral wool, on the roof of the attic you can clearly see how the snow melts from heat leaks through the insulation. This can be clearly seen with the help of.

What is the best use for?
PPU and PPS have their own advantages over each other; for this reason, in some conditions it is preferable to use one or another insulation option. For example, it is better to use PPU if the following tasks arise:
- it is necessary to create effective wind protection;
- it is necessary to realize the requirement of high adhesion;
- creation of a seamless thermal insulation structure;
- short installation time.
When polyurethane foam and polystyrene foam are considered, the comparison is made not only in terms of parameters, but also in terms of operating conditions. For example, if you plan to use EPS, it is necessary to ensure high-quality moisture protection, which is facilitated by film materials. Expanded polystyrene and structurally similar analogues (foam plastic) need to create conditions in which the risk of fire will be low.
Types of polyurethane foam
Polyurethane foam is a type of plastic made from two main components. The reaction of these components creates a material whose properties can change with different ratios of the starting substances. Distinguish soft varieties PPU, density 5-40 kg/m3, and hard varieties- 35-80 kg/m3
The variety of types has led to the widespread use of the material, from furniture (the well-known foam rubber) to insulation in construction. One of the most useful properties actively used in industry is Possibility of spraying material directly at the point of use, bypassing the stages of manufacturing, storage, transportation, installation, fitting, etc.
This property distinguishes polyurethane foam very favorably as an insulation material, which is applied directly to the surface to be treated with virtually no preparatory operations, forming a highly effective heat retaining layer, does not react to moisture, does not change its qualities over time, does not interact with biological organisms and non-swelling.
Advantages and disadvantages of polyurethane foam
 Polyurethane foam Polyurethane foam is known as ordinary foam rubber. In everyday life we often see soft ones, but in construction we use hard ones. This material has a closed cell structure; the slabs are produced with an edge, which simplifies and reduces the cost of installation. The use of special components makes this material fireproof.
Polyurethane foam Polyurethane foam is known as ordinary foam rubber. In everyday life we often see soft ones, but in construction we use hard ones. This material has a closed cell structure; the slabs are produced with an edge, which simplifies and reduces the cost of installation. The use of special components makes this material fireproof.
In addition to slabs, it is produced in the form of foam, which is applied to the surface using special equipment. Thanks to the use of foam, there will be no “thermal bridges” and the coating will be continuous.
Please note: polyurethane foam, unlike polystyrene foam and mineral wool, does not require vapor barrier. The water absorption rate is 12-15 times less than that of conventional polystyrene foam.
The main advantages of using polyurethane foam:
The main advantages of using polyurethane foam:

Disadvantages of polyurethane foam:
- the price is higher than polystyrene foam;
- low resistance to ultraviolet radiation.
You may be interested in information about whether polyurethane foam is harmful.
Read about how to insulate a house with polyurethane.
We also bring to your attention an article about
Advantages and disadvantages of polyurethane foam
The advantages of PPU are:
- Non-flammability.
- No reaction to water vapor, splashes, practically does not absorb water.
- Excellent adhesion to any materials. (exceptions: polyethylene and fluoroplastic, wet surfaces).
- Excellent thermal conductivity, low response to temperature changes, lack of temperature changes in properties.
- Elastic structure, eliminating the appearance of cracks due to shrinkage and other deformations of the substrate.
- Complete cut-off of the treated surface during application.
- No insects, rodents, birds.
- Doesn't rot, does not react with contacting elements.
- Durable, manufacturers say service life of 30 years, but in practice PPU works longer.
At the same time, there are also disadvantages. These include:
- High price.
- High technology application, the need to use special equipment.
- The applied layer must exceed 5 cm, a smaller thickness will not ensure effective operation.
Carefully!
It is afraid of ultraviolet radiation, which does not allow it to be used openly. The rate of destruction of polyurethane foam from sunlight is approximately 1 mm per year
At the same time, complete destruction does not happen; the process does not go deeper into the material. The problem can be eliminated by painting or decorative fencing of polyurethane foam from direct sunlight.
All the advantages of the material have been repeatedly tested and confirmed in practice, and the disadvantages are quite easily eliminated. The high cost of polyurethane foam as a material is compensated by its self-sufficiency, which allows you to significantly save on the purchase of a double layer of waterproof membrane.
Non-flammability is achieved by adding halogens to the initial components, which allows polyurethane foam to be classified as a fast-damping material. If there is no open flame, polyurethane foam cannot ignite in any way, so it can be considered completely safe in this regard.
As a result, we can conclude that roof insulation with polyurethane is not only effectively, but also profitable.
A truly indisputable fact is the need to use a spraying installation, although it is difficult to say whether this is a drawback or simply a feature of the application.
If you are planning to insulate a pitched roof, be sure to read the article at the link.
If you involve specialists who will work with professional installations, then there will be no need to purchase disposable kits. At the same time, the quality of the coating will be maximum, and you can also avoid mistakes caused by lack of experience.
Polyurethane polyurethane foam is lighter than extruded polystyrene foam
First of all, one is itching to destroy the legend that filled polyurethane foam (PPU) is lighter than glued extruded polystyrene foam (EPS). Optimal thermal insulation properties of both materials are achieved at a density of 40 kg/m³. Considering that the heat transfer coefficients of PUF and EPPS are approximately equal, differing only by 2 thousandths of W/m²*K, it can be argued that in both glued and jellied sandwiches with the same isothermal properties (for example, 0.7 W/m²*K) the thickness of the insulation the material must be the same. This means that with the same densities of materials, their weight in the vans will be the SAME. We also note that, for example, for a van measuring 5.3x2.6x2.5 m with 12 euro pallets, an increase of 10 mm in insulation thickness will add only 27 kg of weight.
Russian and imported extruded polystyrene foam
EPPS EEPS – discord. Previously, we had experience using domestically produced EPS (we deliberately do not indicate the brand). At first glance, it differed from the imported one only in color (imported - blue, domestic EPS - yellow), but upon detailed study it turned out that:
- domestic EPS has unstable quality - from delivery to delivery, the density of the material varied from 35 to 40 kg/m³ (we determined this by weighing each briquette, their weight varied). As a result, the vans lost a fair amount of insulation;
- The sizes of domestic XPS boards, even in one briquette, varied (the error in geometric parameters sometimes reached 2 mm). About 25% of the material entering production was written off as scrap. Therefore, we switched to the much more expensive American Styrofoam insulation with minor financial losses.
Alternative types of roof insulation
In addition to PPU, the following are used:
- Styrofoam.
- Minvata.
- Glass wool.
- Ecowool.
- Izover.
- Expanded clay.
- Cellulose, etc.
The list of all types of insulation suitable for use on the roof is quite large, but only a few types are used - mineral wool, isover, ecowool and some others. The reasons for this are prices and unsatisfactory characteristics of a number of materials.
For example, ability to absorb water for insulation unacceptable, since this causes all heat-conducting qualities to disappear. Glass wool, for example, has such problems. In addition, a number of materials are susceptible to caking, which changes the layer thickness and reduces performance.
Note!
Of the above, basalt mineral wool is the most preferred, as the most effective material in all respects. But you can’t work with it either without creating protective layers of hydro- and vapor barrier, the so-called roofing pie, without which the material gradually loses its properties
In general, reliable insulation from water vapor or splashes allows you to use any insulation, if the choice is small, you just need to know its strengths and weaknesses and take them into account during installation.
Extruded polystyrene foam or polystyrene foam, which is better?
The quality and characteristics of polystyrene foam are influenced by the processing technology of raw materials and its composition. The strength and density of foam varies, which has a direct impact on its characteristics. Polystyrene foam can be polyurethane, polyvinyl chloride, pheno-formaldehyde, urea-formaldehyde, polystyrene.
Foam plastic is known for the following properties: high thermal insulation properties, lightness, resistance to microorganisms, durability, ease of installation and maintenance.
Despite its resistance to microorganisms, the rough surface of polystyrene foam is an excellent place for them to attach. To prevent the fungus from taking root and spreading, the foam should be treated with plaster. The most popular materials for insulating surfaces are polystyrene foam, polyurethane foam and EPS.
Advantages:
- Steam resistance;
- Low thermal conductivity;
- Resistance to the formation of fungi, mold bacteria;
- A light weight;
- Water resistance;
- Durability;
- Ability to withstand different temperatures.
The vapor tightness of PPS can have a bad effect on the ventilation of the house, especially if the house has tiles or bricks, so you need to insulate surfaces carefully and carefully. Extruded polystyrene foam has a wider range of applications than polystyrene foam
It is used to insulate roofs, floors, facades, foundations, roads, and shipbuilding.
Installation features
The installation method is exactly what distinguishes polystyrene foam in panels from polyurethane foam. Polyurethane foam is most often sprayed in the form of a monolithic coating that has no joints and does not require serious preparation. Check out If done correctly, insulation with this material does not require much time, since there is no additional installation work.
Advice from a professional
There are two main types of exterior wall finishing insulated with polyurethane foam - siding and plaster.
Each method has its own subtleties of applying polyurethane foam, which are important to know in advance for proper preparation of surfaces and subsequent finishing.
Features of polyurethane foam
Polyurethane foam is one of the most popular and multifunctional materials, which often acts as insulation. It is made from an artificial polymer, which has a closed porous structure. Products made from polyurethane foam are highly durable and light in weight.
Polyurethane foam has become so popular because of its ability to replace many building engineering plastics, rubber and natural materials.
The material is characterized by its low weight - this allows it to be used for insulating facade systems of various types. Polyurethane material is easy to manufacture, transport and install. The material is often used for external insulation, as it is able to withstand temperature changes and exposure to a variety of precipitation.
 The peculiarity of expanded polystyrene foam is that it is very durable
The peculiarity of expanded polystyrene foam is that it is very durable
Features of polyurethane foam:
- The strength of polyurethane foam is many times greater than the strength of many rubber and plastic products. It can also deform back.
- The operating temperature at which polyurethane can be used is from -70 to +120 degrees.
- The material can be used where aggressive chemical environments predominate.
- Polyurethane foam is not afraid of radiation.
Polyurethane foam is a product that, under the influence of a foaming agent, combines isocyanate and polyol. The foaming process leads to the formation of microcapsules that are filled with air. To give the material certain qualities, various additives can be mixed into the material.
Description of the properties of polyurethane foam
In the section Polyurethane foam - description, characteristics, we have already described polyurethane foam briefly. In everyday life, polyurethane foam is foam rubber; rigid construction grades are used to insulate walls, foundations, floors, roofs, and balconies.
There are two ways to install polyurethane foam: sheets and spraying. Better insulation is created by spraying using high-pressure equipment. Our company “Your Warm Home” uses exactly this type of equipment.
The main advantages of polyurethane foam
- thermal conductivity of polyurethane foam is 0.02 - 0.03 lower than that of polystyrene foam, and 2 times lower than that of mineral wool;
- high moisture resistance, practically does not absorb water;
- temperature of use of polyurethane foam from -70 to +110 degrees;
- official service life is more than 30 years, cases are known - 60 years, this is 5 times longer than expanded polystyrene and mineral wool;
- there is no deformation or subsidence during operation;
- he is not afraid of mold and mildew;
- good sound insulation;
- continuous seamless coating and foam-filled cracks, thanks to the spraying of fine foam;
- no condensation, which means no mold;
- good adhesion to any surface;
- there are no installation costs due to the lack of vapor barrier, wind protection, counter slats, you buy the installation and the insulation itself right away;
- low load on structures due to low weight;
- the fastest installation compared to other insulation materials and without waste
- Our prices include the cost of installation and materials. Read more in the article
Disadvantages of polyurethane foam
- higher price, this disadvantage is compensated by lower costs for heating and cooling the premises, the absence of drafts on the floor;
- protection from the sun is needed, polyurethane foam must be covered with paint or a decorative coating, for example, siding.
DIY roof insulation with polyurethane foam
Let's consider the process of insulation with liquid polyurethane foam, as an almost ideal option for today. The insulation technology is quite simple, but has many nuances, which we discussed in this article.
Available for sale special kits for spraying polyurethane foam, consisting of two containers with initial reagents, which are mixed directly during the spraying process in the working head.
The reaction occurs quite quickly and cannot be mixed in any other way.
Surface preparation is simple and does not require any complex operations. You just need to clean it of debris, dust and dry it if necessary. There is no need to pre-cut off the insulation with waterproofing membranes, since the surface of the material itself excellent insulator, not sensitive to water vapor or splashes.
Insulation polyurethane foam roofing is produced from the inside, and polyurethane foam is applied in spaces between rafters. During the reaction, the material expands and gas bubbles appear in it, giving the desired thermal insulation ability. At the same time, expanding, polyurethane foam densely fills the entire space, clogs all potholes and cavities, creating an airtight layer.
This material reliably insures the surface against the presence of bridges of cold which cause condensation to form. The entire treated area will be dry, which will protect the roofing material and rafters from corrosion and rotting.
After complete spraying of polyurethane foam and its hardening, all that remains is sheathe the entire treated area with sheet materials - plywood, chipboard or the like, and carry out cosmetic finishing of the room.

Semi-professional set for spraying polyurethane foam

PPU should be sprayed between the rafters, carefully sealing all cracks and voids

Self-spraying of polyurethane foam
Pros and cons of the material
Extruded polystyrene foam is a synthetic insulation material developed in the USA using unique technology. It has such an amazing combination of qualities that previously it would have been impossible to even dream of it. In particular, polystyrene foam is different:
- low thermal conductivity
- Low vapor permeability. A 20 mm thick slab has the same vapor permeability as one layer of roofing felt.
- good resistance to mechanical deformation;
- wide temperature range (from -50 to +75 degrees);
- long service life (durability);
- absolutely safe for human health.
- is one of the best. It is simply irreplaceable in roofing because it has excellent hydrophobic properties. Does not lose its properties when wet.
- environmentally friendly insulation, despite its chemical origin. It is not biodegradable in the environment and is completely harmless to health
- ease of installation, which significantly saves construction time
The disadvantages of the material include its flammability. The addition of fire retardants prevents the spread of flame (the material self-extinguishes), however, during smoldering, harmful substances can be released.
What about other materials? To determine what is more profitable to purchase - polyurethane foam or expanded polystyrene - it is necessary to consider its features.
What are the differences between polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam?
First of all, this is - two different materials, both in chemical composition and mechanical properties. If you compare polyurethane foam with polystyrene foam, the most striking difference will be hardness.
Polystyrene foam (expanded polystyrene) is practically inflexible; at the slightest bend it can break, while polyurethane foam allows almost any deformation without losing the integrity of the structure.
Moreover, polyurethane foam has elasticity, the ability to take its previous shape after stress is removed. Such a difference in mechanical characteristics with more or less similar heat-conducting, noise-absorbing and other parameters puts the use of these two materials at different levels.
Polystyrene foam is cheaper, it can be used in places where it will not experience any physical stress. In addition, a certain rigidity of the foam in some cases is an advantage that greatly simplifies the installation process.
Polyurethane foam is a material that has several types, different densities, which creates many subtypes with different characteristics. All varieties have one main advantage in common - practically completely resistant to water, which is the most significant advantage for insulation.
Guarantee
5 years!
Free
surveyor's visit
Only high quality
material!
experience
12 years old!
Polyurethane foam and polystyrene foam: comparative characteristics
Polyurethane foam and polystyrene foam: comparative characteristics On the market of modern insulation, the leaders are polyurethane foam and polystyrene foam - materials that are very similar in some aspects, between which it is quite difficult to make the right choice.

Comparative characteristics of polyurethane foam and polystyrene foam
Undoubtedly, the main indicator that determines the quality of insulation is thermal conductivity. If we compare polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam in this aspect, the second one will be more effective, since the thermal conductivity coefficient of rigid polyurethane foam is 0.019 - 0.028 W/m*K, and polystyrene foam is 0.04 - 0.06 W/m*K. Below are the comparative characteristics of polyurethane foam and polystyrene foam:
|
Material |
Density (kg/m3) |
Thermal conductivity coefficient (W/m*K) |
Operating temperature (°C) |
Service life (years) |
Porosity |
|
closed |
|||||
|
closed |
As can be seen from the table, polyurethane foam has a wider temperature range of application, as well as a longer service life. These are not all the characteristics by which polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam can be compared. The following parameters are important:
- Moisture permeability - expanded polystyrene (or polystyrene foam) absorbs moisture approximately twice as much as polyurethane foam. Noise insulation - thanks to seamless application and 100% adhesion, polyurethane foam dampens noise from outside better than expanded polystyrene panels
- Environmental friendliness - due to the wide range of temperatures permissible when using both insulation materials, they are quite safe to use. However, the safety of polyurethane foam directly depends on the correct application, and expanded polystyrene begins to release phenol when heated from +60°C. The correct choice, polyurethane foam or polystyrene foam, in this case depends on the application requirements.
In the video, polyurethane foam and polystyrene foam are subjected to intense fire treatment. Expanded polystyrene burns completely, releasing a lot of toxins, but polyurethane foam manages to survive:
While expanded polystyrene is vulnerable to moisture, as well as to almost all organic solvents, polyurethane foam deteriorates when exposed to direct sunlight. Therefore, it may seem that polyurethane foam is not suitable for external thermal insulation. However, external thermal insulation in any case is done under the siding cladding, and the polyurethane foam layer is protected from the harmful effects of the sun. Therefore, in comparison of polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam, PU foam wins for both internal and external insulation.

When comparing expanded polystyrene and polyurethane foam, it is also worth mentioning the compressive strength - it is higher for EPS.
Installation features
The installation method is exactly what distinguishes polystyrene foam in panels from polyurethane foam. Polyurethane foam is most often sprayed in the form of a monolithic coating that has no joints and does not require serious preparation. Check out If done correctly, insulation with this material does not require much time, since there is no additional installation work.
Advice from a professional
There are two main types of exterior wall finishing insulated with polyurethane foam - siding and plaster. Each method has its own subtleties of applying polyurethane foam, which are important to know in advance for proper preparation of surfaces and subsequent finishing.
Polyurethane foam or polystyrene foam - which is better?
Based on a thorough analysis of the characteristics of both insulation materials, we came to the conclusion that polyurethane foam copes better with the task of moisture, thermal and noise insulation, and also provides better fire safety and chemical resistance. The cost of expanded polystyrene is cheaper, but its heat loss is many times higher. Therefore, savings on insulating materials result in a significant increase in space heating costs. Considering the long service life of thermal insulation, polyurethane foam is more profitable, despite its higher price. Our experts, based on many years of experience in thermal insulation, recommend using polyurethane foam for durable and high-quality insulation.
Updated: 07/31/2019 18:10:43
Expert: Lev Sagalovich
Thermal insulation materials are indispensable for high-quality insulation of any buildings and premises. The market is replete with many products created specifically for these purposes. But, nevertheless, polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam have remained the most popular for a long time. What are their features and what are the differences between them? Our experts will tell you.
Structural features and advantages of materials
In order to have a more detailed understanding of both insulation materials and form the correct conclusions when comparing them with each other, it is worthwhile to become more familiar with the properties of each.
Both insulation materials have a similar “nature” (they are made from the same raw materials), but their production technology is different and this determines everything. Expanded polystyrene is known among ordinary consumers as polystyrene foam. It belongs to the group of polymers and is obtained by foaming polystyrene.
The insulation comes in two varieties: foamed and extruded. The latter is characterized by greater density, which significantly improves the thermal insulation properties of the material and also extends its “life”.
ON A NOTE. Varieties of expanded polystyrene are difficult to distinguish from each other, but this can be done in a practical way. It is enough to break off a small piece from the foam board. The foamed one will have small balls visible at the fracture site, while the extruded one will have regular polyhedrons.
Advantages
Good thermal conductivity;
Easy installation;
Wide variety of sheet thicknesses;
Low price.
Flaws
Short service life (about 10 years);
Rapid absorption of moisture;
Exposure to ultraviolet radiation;
Deformation during operation.
Extruded polystyrene foam has a number of other, better advantages:
Low level of water absorption;
High strength;
Durability
ON A NOTE. Polystyrene-based materials should never be used for internal insulation, since condensation will form between the insulation and the wall in a short period of time, which can lead to accelerated destruction of the structure.

In everyday life it is better known as “foam rubber”, only in everyday conditions there is a soft variety, and in construction – a hard one. The material has a closed cell structure and the presence of an edge, which greatly simplifies the installation process. And thanks to special components, the insulation is fireproof.
Polyurethane foam is produced by manufacturers in the form of slabs or foam applied with special equipment. The second option is virtually devoid of typical installation disadvantages (in particular, “thermal bridges”): the coating will be continuous.
ON A NOTE. Unlike expanded polystyrene, polyurethane foam can be used without a vapor barrier layer, since its level of water absorption is very low (15 times lower than that of foam).
Advantages
Moisture resistance;
Low thermal conductivity;
Wide operating temperature range;
No deformation during the application of insulation;
Excellent sound insulation properties;
Durability (about 30 years);
Environmental Safety.
Flaws
- As for the disadvantages, they are rather formal: high price and instability to ultraviolet radiation.

Thermal conductivity
One of the key factors influencing the final choice of a particular insulation for a home. The optimal options have low thermal conductivity, while reducing the thickness of the material during installation is allowed.
Comparing polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam, there is a clear leadership of the former: 0.04-0.06 W/m*K versus 0.019-0.028 W/m*K. Due to its denser structure, polystyrene foam retains heat better, but at the same time weighs more (however, this criterion is not considered important when choosing a suitable insulation).
Strength
Expanded polystyrene is considered a fairly durable material, which was incorporated into it at the production stage (its structure is very homogeneous). But polyurethane foam is a set of molecules connected to each other by exposure to high temperatures.
If we compare in terms of indicators, the bending resistance of polystyrene foam is 0.4-1 MPa, and that of polyurethane foam is 0.07-0.2 MPa. It is the mechanical impact that often causes the destruction of the latter - it simply crumbles. Any bend or impact during installation is enough to damage the insulation.
Expanded polystyrene is characterized by significant strength, which makes it a suitable option for installation on load-bearing walls: it is not afraid of temperature changes, deformation, is not subject to shrinkage, etc.
Flammability
Fire resistance or flammability is an important indicator, especially when it comes to insulating a roof or premises or houses made of wood. Both materials under consideration have similar flammability classes: G2 (polyurethane foam) and G3 (expanded polystyrene). G2 implies that the material has an average flammability index, G3 - that the material is flammable.
In fact, the high flammability rate is a key disadvantage of both insulation materials. It is for this reason that manufacturers began to massively add fire retardants to the product being created - special components that prevent the ignition of insulation. If it is created according to technology, in the event of a fire, its attenuation will be almost instantaneous.
Environmental friendliness
Unfortunately, both polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam are toxic materials. But only when they are exposed to high temperatures: they emit toxic gas. It is for this reason that both insulation materials are recommended exclusively for external repair and construction work.
By the way, if the installation and operation technology is followed under normal conditions, none of the materials under consideration poses any danger to human health and the environment.
Moisture resistance
Hydrophobicity is one of the key criteria for choosing insulation and should never be ignored. The resistance of a material to moisture indicates how much it will be able to withstand humidity during operation. The water absorption rate must be minimal, otherwise it threatens the destruction of the insulation, an increase in its weight (this will increase the load on the structure), and loss of the main property - thermal insulation.
Our experts conducted a simple but revealing experiment: they immersed sheets of expanded polystyrene and polyurethane foam in water for a day. The first absorbed only 0.2% of the water volume (a very small figure), the second - about 2%. This significant difference is due to the structure of expanded polystyrene: its closed cells practically do not allow water to pass through.
Vapor permeability
The level of vapor permeability also cannot be ignored, because it depends on this whether additional use of a vapor barrier layer will be required. If we talk about polyurethane foam, then its vapor permeability indicator is approximately 0.05 units, but for polystyrene foam it is actually zero. This means that the latter option does not allow steam to pass through, so you don’t have to worry about additional protection (but only if we are talking about “breathable” surfaces).
Sound insulation level
None of the options under consideration can be considered suitable for use as sound insulation. Since the densities of both materials are close, they will not have any significant differences in the level of noise absorption. If you need to provide a room or house with high-quality noise insulation, we recommend additionally using building material specially designed for this purpose.
Shrinkage rate
The tendency to change the original shape is the “Achilles heel” of many heat-insulating materials, and one of them is polyurethane foam. This negative property is especially obvious when the insulation is heated: with prolonged exposure to warm air, the slab will begin to deform. You should not use polyurethane foam for a “warm floor” system, and when insulating a facade, you should worry about using plaster with ultraviolet protection to finish the walls.
Expanded polystyrene is characterized by excellent “resistance” to shrinkage: during operation, the material does not change its original shape, regardless of the conditions and location of installation.
Installation features
And speaking of editing. Both insulation materials under consideration can be installed without professional help: the materials are very easy to use and do not require special skills. To make it easier to work with polystyrene foam, its sides were equipped with side protrusions, which form an integral layer during installation. In addition, they increase the strength of the material and speed up the work process.
Polyurethane foam is installed using a similar technology, but the process is complicated by the absence of the “sides” described above: when working with it, you will have to treat the joints with adhesive or foam.
If you are deciding which is better - polystyrene foam or polyurethane foam, you should compare properties these materials. In addition, it is necessary to take into account terms of Use, because in different rooms it may be preferable to use one or the other option. To conduct a full comparative analysis, the following factors are taken into account: structure, service life, strength and thermal insulation characteristics, hygroscopicity, noise absorption efficiency, density and some other parameters. The cost of the product is also important.
Expanded polystyrene (EPS) is a gas-filled, closed-porous material based on polystyrene; its cells contain natural or carbon dioxide; there is also a vacuum version. There are 2 types:
- foamed;
- extruded (extruded).

Polyurethane foam (PPU) is a group of gas-filled plastics. The material is based on polyurethane. It can be rigid, elastic and self-foaming. If the characteristics of polyurethane foam and polystyrene foam are considered, you should know that both options are similar in most respects.

Comparative table of characteristics of polyurethane foam and polyethylene foam
These types of insulation are approximately equally popular, due to their properties. If you are interested in the question of polyurethane foam or polystyrene foam - which is better, it is recommended to compare them according to their main characteristics. The result can be seen in the table:
| Options | Polyurethane foam | Expanded polystyrene |
|---|---|---|
| Density, kg/m³ | 25-750 | 45-150 |
| Thermal conductivity coefficient, W/(m*K) | 0,019-0,028 | 0,04-0,06 |
| Structure | Closed-cell | Closed |
| Operating temperature, °C | -160…+180 | -100…+60 |
| Environmental friendliness | Polyurethane foam retains its properties and does not emit harmful substances when heated to the maximum value (+180°C). | Expanded polystyrene at a temperature of +60°C begins to release a compound dangerous to human health - phenol. |
| Duration of operation, years | With proper installation, the service life is unlimited, in other cases it is 50 years. | 42278 |
| Fire hazard | Incombustible | More susceptible to combustion. In high temperature conditions, burning areas can become separated, which contributes to the spread of fire. |
| Hygroscopicity | Does not absorb moisture. | It is more susceptible to liquids and is able to partially absorb them. |
| Appearance | Does not lose properties throughout the entire period of operation. | Over time, it shrinks and undergoes deformation due to loss of properties. |
Comparison of materials by performance characteristics
You can also compare insulation materials according to the degree of installation complexity. Thus, polyurethane foam is characterized increased adhesion, which allows for quick insulation. Expanded polystyrene requires the use of special compounds. In addition, it is advisable to make a crate. PPU resistant to mold and mildew. For this reason, the material can come into contact with moisture without the risk of loss of properties. Expanded polystyrene, on the contrary, is prone to the formation of mold.
PU foam retains its properties and structure throughout the entire period of operation, even under the influence of moisture, low and high temperatures. For this reason, there is no need for periodic inspection and maintenance of the thermal insulation “pie” structure.
Expanded polystyrene loses its properties faster, especially in winter, when there is a risk of the insulation freezing upon contact with water. Means, It is still necessary to monitor the condition of the PPS slabs.
Polyurethane foam easier to transport, because it is not deformed in transit. This applies to rigid and flexible boards. Expanded polystyrene is a more fragile material and is often deformed during transportation.
Comparison by cost
Protecting surfaces with polyurethane foam insulation is a more expensive technology. So, thermal insulation of 1 m² will cost 150-1500 rubles. In this case, the price is formed taking into account the thickness of the material: from 10 to 100 mm. This means that in order to insulate a surface of 1 m² with a 50 mm thick layer of polyurethane foam, you need to prepare about 850 rubles. The high price of this type of thermal insulation is due not only to the production technology of the material, but also to the high cost of the equipment.
If you are deciding which is better - polyurethane foam or polystyrene foam, you should know that the latter option is offered at a lower cost. For comparison, insulating an area of 1 m² with EPS boards will cost several times less - 300 rubles, provided that the thickness is 50 mm. Good polystyrene foam boards, characterized by large dimensions and high density, are more expensive.
For what purposes is it better to use?
PPU and PPS have their own advantages over each other; for this reason, in some conditions it is preferable to use one or another insulation option. For example, it is better to use PPU if the following tasks arise:
- it is necessary to create effective wind protection;
- it is necessary to realize the requirement of high adhesion;
- creation of a seamless thermal insulation structure;
- short installation time.

When polyurethane foam and polystyrene foam are considered, the comparison is made not only in terms of parameters, but also in terms of operating conditions. For example, if you plan to use PPP, it is necessary to ensure high-quality moisture protection, which is facilitated by film materials. Expanded polystyrene and analogues similar in structure (foam plastic) need to create conditions in which the risk of fire will be small.
A couple of reviews about EPPS
Leonid, 35 years old, Omsk: I used expanded polystyrene to insulate the walls of a residential dacha. The house is small and heated in winter, so there were no problems with the appearance of moisture inside the insulating “pie”. I carry out repairs every 5-7 years, which means that during this time the insulation will not have time to sag and lose its qualities.
Vitaly, 45 years old, Khabarovsk: Expanded polystyrene does not weigh down the structure and retains heat well, which is why I chose this material. I heard that it is flammable, but the house uses a minimal amount of fire-hazardous coatings, for the most part concrete, brick, plastic, and metal are used everywhere.
A couple of reviews about PPU
Valentin, 31 years old, Perm: We rented equipment for spraying polyurethane foam. The attic needed to be insulated. I made thermal insulation of a small thickness (20 mm), but the result is already visible - heat is retained much better in the room.
Peter, 39 years old, Orel: Most surfaces in the house are insulated with polyurethane foam. This material suits all parameters. Insulation is more expensive, but the structure will last longer.
Summary
If you plan to purchase polystyrene foam or polyurethane foam, you must take into account that according to the main parameters, the second option wins. It is non-flammable, has a high density, wear-resistant, lasts a long time, and is non-hygroscopic. Expanded polystyrene is cheaper, but at the same time it has a fairly low thermal conductivity, which is often also an important criterion when choosing.
If self-foaming polyurethane foam is considered, its installation requires the use of expensive equipment. However, it is not advisable to purchase such equipment for one-time use. It must be said that polyurethane foam and polystyrene foam are universal insulation materials, but you should choose the appropriate option, based on operating conditions.
Penoizol is a urea-formaldehyde foam, abbreviated as KFP. A universal thermal insulation material that became widespread in the 1930s in Germany. There it was actively used almost everywhere until the 50s. KFP is a white foam material that resembles extruded polystyrene foam in appearance. So, if you run a finger over a chip, for example, it crumbles. The material is odorless, does not emit toxic substances and is therefore considered quite safe. The composition of penoizol has a homogeneous fine-cell structure. In our country, this insulation, depending on its manufacturer, can be called differently: penoizol, mipora, unipol, mettemplast.
Characteristics of penoizol
The production technology of penoizol is relatively simple, and the cost of such material is quite low when compared with other heat insulators. Using special equipment that mixes various insulation components, foam is obtained, which is filled either into a mold or directly into its future location, for example, into the space between walls, floors, cracks and other elements of the building. When the material finally hardens, a white thermal insulation layer with a density of 9 to 25 kg/m3 is obtained. I must say, it is a very convenient and relatively inexpensive technology.
Advantages and disadvantages of polyurethane foam

Polyurethane foam is known as regular foam. In everyday life we often see soft ones, but in construction we use hard ones. This material has a closed cell structure; the slabs are produced with an edge, which simplifies and reduces the cost of installation. The use of special components makes this material fireproof.
In addition to slabs, it is produced in the form of foam, which is applied to the surface using special equipment. Thanks to the use of foam, there will be no “thermal bridges” and the coating will be continuous.
Please note: polyurethane foam, unlike polystyrene foam and mineral wool, does not require vapor barrier. The water absorption rate is 12-15 times less than that of conventional polystyrene foam
The main advantages of using polyurethane foam:
- low thermal conductivity coefficient (almost 1.5 times higher than that of foam plastic and almost 2 times higher than mineral wool);
- moisture resistance;
- operating temperature from -70 to 110 degrees;
- 30 years - the designated service life (with proper installation, much longer);
- no deformation during the entire service life;
- resistance - rotting, fungus, moisture does not affect its properties;
- has soundproofing properties;
- environmental friendliness - approved for use even in food warehouses.
Disadvantages of polyurethane foam:
- the price is higher than polystyrene foam;
- low resistance to ultraviolet radiation.
The use of penoplex for floor insulation
In the modern market of thermal insulation materials, polyurethane foam insulation materials, in particular penoplex, are very popular. The material meets all the requirements for floor insulation, at the same time it has high sound insulation and is much more durable and environmentally friendly compared to another popular polymer insulation - polystyrene foam.

Penoplex can be used both to insulate the floor along the joists, and to equip a thermal insulation layer with subsequent application of a leveling screed.
Penoplex can be used both to insulate the floor along the joists, and to equip a thermal insulation layer with subsequent application of a leveling screed. The thermal conductivity coefficient of penoplex is significantly lower than that of polystyrene foam, therefore, using this thermal insulation material, it is possible to create a thermal insulation layer of much smaller thickness.
Penoplex is easy to install and process. During the installation of the material, it is possible to minimize the cost of insulation, which will make it possible to significantly save on consumables.
Penoplex is suitable for insulating floors located on the ground or above unheated basements, as well as for insulating interfloor ceilings, for which the heat-insulating layer acts as a sound insulator.

Sheets of material can be mounted directly on the base with a preliminary installation of a waterproofing layer, since with constant contact with moisture, the insulation can significantly lose its thermal insulation properties.
Penoplex is resistant to temperature changes; the material can work in permanent conditions, where the stage of freezing of the thermal insulation layer is replaced by the stage of its thawing.
The material can be used to insulate wooden floors, since penoplex prevents the development of microorganisms, therefore, there is no need to be afraid of the appearance of mold and fungi in the subfloor space. The fire resistance of the material also makes it suitable for insulating wooden structures.
The disadvantages of penoplex include the need to follow a certain technology for laying slabs and carefully seal the joints of sheets of material. Penoplex is laid in a checkerboard pattern, and the seams between the sheets of material are foamed with polyurethane foam or other sealing compounds. If you do not seal the seams between the foam sheets, cold bridges will form, and the likelihood of condensation accumulation under the thermal insulation layer increases.
When applying a leveling screed to a penoplex thermal insulation layer, the structure must be additionally reinforced.
Fire hazard of polyurethane foams Release of a full range of chemical warfare agents
Unlike expanded polystyrene, rigid polyurethane foam is an inert polymer with a neutral odor. For this reason, it is widely used in refrigerators for food storage. Polyurethane foam does not create toxic emissions that cause human illness or death.
But as a result of the combustion of polyurethane foams and polyisocyanurate foams, a mixture of low molecular weight thermal decomposition products and their combustion products is always formed. The composition of the mixture depends on temperature and access to oxygen.
The process of dissociation of polyurethane foam into the initial components - polyisocyanate and polyol - begins after heating the material to 170-200°C.
With prolonged exposure to high temperatures above 250 ° C, most thermosetting plastics, as well as rigid polyurethane foams, gradually decompose.
When the isocyanate component is heated above 300°C, it decomposes with the formation of volatile polyureas (yellow smoke) in the case of elastic polyurethane foams or the formation of non-volatile polycarbodimmides and polyureas in the case of rigid polyurethane foams and polyisocyanurate foams. Thermal decomposition of the polyisocyanate and polyol occurs.
At temperatures exceeding 300°C, the destruction of polyisocyanurate foam begins, which, unlike polyurethane foam, contains a more stable isocyanurate cycle. The temperature at which a sufficient amount of flammable decomposition products are formed that can be ignited by flames, sparks or combustible surfaces, for rigid polyurethane foams from 320 ° C.
For rigid polyurethane foams based on special grades of polyisocyanate, the decomposition temperature with the release of flammable gases ranges from 370 °C to 420 °C. In addition, during the decomposition of various polyurethane foams when heated to 450 °C, the following compounds were identified: carbon dioxide (carbon dioxide), butanediene, tetrahydrofuran, dihydrofuran, butanedione, water, hydrocyanic acid and carbon monoxide (carbon monoxide).
Comparative characteristics of polyurethane foam and polystyrene foam
Undoubtedly, the main indicator that determines the quality of insulation is thermal conductivity. If we compare polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam in this aspect, the second one will be more effective, since the thermal conductivity coefficient of rigid polyurethane foam is 0.019 - 0.028 W/m*K, and polystyrene foam is 0.04 - 0.06 W/m*K. Below are the comparative characteristics of polyurethane foam and polystyrene foam:
As can be seen from the table, polyurethane foam has a wider temperature range of application, as well as a longer service life. These are not all the characteristics by which polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam can be compared
The following parameters are important:
- Moisture permeability - expanded polystyrene (or polystyrene foam) absorbs moisture approximately twice as much as polystyrene foam. Noise insulation - thanks to seamless application and 100% adhesion, polystyrene foam dampens noise from the outside better than panels made of polystyrene foam.
- Environmental friendliness - due to the wide range of temperatures permissible when using both insulation materials, they are quite safe to use. However, the safety of polyurethane foam directly depends on the correct application, and expanded polystyrene begins to release phenol when heated from +60°C. The correct choice, polyurethane foam or polystyrene foam, in this case depends on the application requirements.
In the video, polyurethane foam and polystyrene foam are subjected to intense fire treatment. Expanded polystyrene burns completely, releasing a lot of toxins, but polyurethane foam manages to survive:
While expanded polystyrene is vulnerable to moisture, as well as to almost all organic solvents, polyurethane foam deteriorates when exposed to direct sunlight. Therefore, it may seem that polyurethane foam is not suitable for external thermal insulation. However, external thermal insulation in any case is done under the siding cladding, and the polyurethane foam layer is protected from the harmful effects of the sun. Therefore, in comparison of polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam, PU foam wins for both internal and external insulation.

When comparing expanded polystyrene and polyurethane foam, it is also worth mentioning the compressive strength - it is higher for EPS.
Application area

Scheme of thermal insulation of the facade with polystyrene foam.
Expanded polystyrene, or polystyrene foam, is used in various fields of activity: from electronics packaging to individual construction. Foam plastic, as a building material, has become widespread for all types of thermal insulation work:
- it is used for roof insulation. The simplicity and ease of its installation makes it possible to carry out work in any weather conditions. In addition, expanded polystyrene is used for the reconstruction of flat roofs;
- Expanded polystyrene slabs are used for floor insulation in houses; this is not only good thermal insulation, but also waterproofing;
- polystyrene foam is used as insulation for heated floors, which significantly reduces costs;
- This material can be used to insulate the walls of buildings, both outside and inside; it can be used to insulate loggias and balconies;
- expanded polystyrene has become widespread not only for internal insulation of a house: it is used for thermal insulation of the foundations of buildings and pipelines.
But not only polystyrene foam has become so widespread in construction; along with it, polyurethane foam is also in great demand. It is easy to use, and its main feature is that this heat-insulating material is not presented in the form of plates and rolls, as usual, but in the form of a special composition that is sprayed onto the surface. This feature makes polyurethane foam a universal insulation material, which has led to its widespread use in construction, where polyurethane foam is used in various directions:

Scheme for insulating a house with polyurethane foam.
- due to the chemical resistance of this material, it is well suited for thermal insulation of containers, such as swimming pools;
- polyurethane foam is excellent for thermal insulation of pipelines because it has a high reaction rate, which avoids foam dripping;
- the adhesive properties of this material make it possible to widely use polyurethane foam for insulating the foundations of buildings;
- it is used for thermal insulation of the roof;
- this material is excellent for insulating the walls of buildings, both outside and inside.
Polyurethane foam and polyurethane foam are similar in many ways, but they are still two different materials with different properties.
What to choose
Polyurethane polyurethane foam is lighter than extruded polystyrene foam
First of all, one is itching to destroy the legend that insulated vans with filled polyurethane foam (PPU) are lighter than glued vans with extruded polystyrene foam (EPS). Optimal thermal insulation properties of both materials are achieved at a density of 40 kg/m³. Considering that the heat transfer coefficients of PUF and EPPS are approximately equal, differing only by 2 thousandths of W/m²*K, it can be argued that in both glued and jellied sandwiches with the same isothermal properties (for example, 0.7 W/m²*K) the thickness of the insulation the material must be the same. This means that with the same densities of materials, their weight in the vans will be the SAME. We also note that, for example, for a van measuring 5.3x2.6x2.5 m with 12 euro pallets, an increase of 10 mm in insulation thickness will add only 27 kg of weight.
Polyurethane foam is the best alternative to penoplex

Liquid thermal insulator is a worthy alternative to penoplex and is considered an ideal thermal insulator for floor insulation
It is a worthy alternative to penoplex and is considered an ideal thermal insulator for floor insulation, as it is sprayed onto any surface and creates a monolithic coating without joints or seams, which eliminates the formation of cold bridges and the accumulation of condensation under the thermal insulation layer.
Polyurethane foam has the lowest thermal conductivity coefficient among all existing thermal insulators, thus, using polyurethane foam it is possible to obtain a thin, energy-efficient thermal insulation coating that is resistant to static and dynamic loads.
The polyurethane foam coating does not require additional reinforcement when insulating under the screed. Floors located on the ground, above basements, interfloor ceilings, as well as floors of rooms with low ceiling heights can be insulated with polyurethane foam.

Polyurethane foam is superior to penoplex in terms of service life, and also does not require the additional creation of a waterproofing layer.
Polyurethane foam is superior to penoplex in terms of service life, and also does not require the additional creation of a waterproofing layer. As for installation, applying polyurethane foam is a fairly quick and simple process. The thermal insulation layer does not need to be additionally secured with dowels or adhesives. Polyurethane foam helps create a uniform coating on the surface of even very complex geometric shapes. There are no difficulties with transporting the material, since polyurethane foam is delivered in liquid form directly to the place where thermal insulation work is carried out, and therefore does not take up much space, and during its transportation there is completely no chance of cracks and chips in the material. In the process of insulation with polyurethane foam, there is absolutely no waste, and the material does not require additional processing when carrying out thermal insulation work.
You can apply the leveling screed immediately after the polyurethane foam thermal insulation layer has hardened (after 2-3 hours), and you can begin covering the structure with floorboards or moisture-resistant plywood half an hour after spraying the polyurethane foam.
When choosing decent insulation for your home or industrial building, you need to take into account a number of factors that will ultimately affect the time until the next major renovation, the costs of maintaining the house, industrial premises, quality of life and comfort.
We build and insulate for a long time, for life.
The most common and popular insulation materials: mineral wool, polystyrene foam, polyurethane foam. Let's compare polyurethane foam with other insulation materials and identify the differences between polystyrene foam, mineral wool and polyurethane foam. What is better and what is worse in operation for 50 years.
Pros and cons of polyurethane foam
Many consumers know this material as ordinary foam rubber. Soft polyurethane foam is more often used in everyday life, and hard polyurethane foam is used in the construction industry. Most often it is made in the form of slabs.
Spraying polyurethane foam has become a very popular method of thermal insulation today. In this case, the material is manufactured directly on the construction site and applied in the form of foam to the surface, where it hardens. The coating is obtained without joints, the occurrence of cold bridges is excluded.
When choosing whether it is better to purchase polystyrene foam or polyurethane foam, remember that the latter does not require vapor barrier, plus its water absorption rate is approximately 10 times lower compared to standard polystyrene foam.
As for other advantages of the material, here we can note:
- low coefficient of thermal conductivity - the thermal protection of polyurethane foam is 1.5 times greater than that of polystyrene foam, and 2 times greater than that of mineral wool;
- moisture resistance;
- wide operating temperature range – from -70 to +110 degrees;
- long service life - at least 30 years (with proper installation it will be longer);
- absence of any deformations throughout the entire service life;
- resistance to rotting and fungus;
- excellent soundproofing properties.
At first glance, it seems that polyurethane foam is an ideal option for insulation. However, not everything is so simple. There were some drawbacks here too. The main one is the price of the issue. If we compare polyurethane foam with extruded polystyrene, the former costs much more. In the case when the material is applied to the surface by spraying, you will also have to pay a considerable amount for the work, since the process is quite complex. You can try to save on services by renting special equipment and protective equipment. But how well will you be able to complete the work, and how long will it take? In fairness, it is worth noting that using insulation in the form of sheets will help reduce costs. But in this case, seams will appear and the main advantage – solidity – will disappear.
Another, no less significant drawback of polyurethane foam is its instability to ultraviolet rays. The material does not just lose its properties and appearance. When destroyed, it decomposes into products that can harm human health. To protect polyurethane foam, it must be covered with a layer of material that does not transmit UV rays, or at least simply painted.
Of course, the owner of the house is unlikely to show the world the layer of insulation on the walls of his house in all its glory. Most likely he is going to continue finishing the walls. However, difficulties may arise with the choice of material. It is unwise to attach siding to the insulation in order to destroy the integrity of the surface using self-tapping screws or dowels. It is necessary to use other types of finishing, for example, plaster.
Polyurethane foam itself can also not be used on all surfaces. Low vapor permeability of the material can play a cruel joke and lead to the walls becoming damp and fungus appearing on them. It will be just right to use the material on concrete, but on wood it would be better not to use it.
Another point concerns the environmental safety of the material. Manufacturers claim that their material is absolutely harmless. However, certificates confirm its safety only in industrial conditions. In addition, the question of fire safety remains open. Polyurethane foam is a moderately flammable material: under the influence of high temperatures it begins to smolder and release harmful substances. It is unlikely to cause a fire, but in places where surfaces become very hot, it is better not to use it.
Service life of penoizol and polyurethane foam
Polyurethane foam darkens when exposed to UV rays. Under the “open sky”, the service life of polyurethane foam will be approximately 15 years. If the polyurethane foam is protected from sunlight, its service life in this case will be more than 50 years. It is also worth noting that polyurethane foam has good frost resistance - up to 300 cycles, while the optimal temperature for using penoizols is from 0 to + 40 degrees Celsius.
If the recommended construction technologies are followed, foam insulation, as the manufacturers themselves say, can last about 50 years. However, this is far from reality. As practice shows, penoizol in most cases turns to dust after 3-5 years.
What is better to buy and what is the best way to insulate a building?
The conclusions in favor of choosing penoizol or polyurethane foam, in our opinion, are obvious. Here, either save money and use foam insulation masses for insulation, or spend more and get reliable thermal insulation for many years... Of course, polyurethane foam, despite the fact that it is more expensive, is a more profitable solution when it comes to high-quality insulation of buildings, warehouses and private homes !
Polyurethane foam
What is the difference between penoizol and polyurethane foam, which is a distant relative of penoizol?
Polyurethane foam is a polymer material, a type of plastic, which was also discovered in Germany in 1947 by a German chemist named Bayer. This insulation is obtained through the reaction of two and sometimes more components. Polyurethane foams are divided into rigid, elastic and integral. However, for us in this case, it is rigid polyurethane foam that is of interest, which has become widespread as a reliable construction insulation for buildings and private houses. Rigid PU foam, like penoizols, has a fine cellular structure, but has a higher density - from 25 kg/m3 and higher, as well as increased elasticity, which makes it more durable, for example, it does not crumble or crumble.
Comparison of polyurethane foam and penoizol
Impact on human and animal health
Penoizol, according to manufacturers, has passed numerous safety tests and is completely neutral in its effects on the body for both humans and animals, as evidenced by numerous certificates. However, in some states of America and Canada, legislation prohibits the use of CPF as a potentially hazardous material. There is a similar ban in a number of European countries. The fact is that during the polymerization of urea foam, formaldehyde is released, which is harmful to the health of both people and animals. It must be said that the debate between scientists and manufacturers regarding the safety of urea-formaldehyde foam plastics still does not subside and therefore there is no definitive answer to the question of the safety of CPF. The only thing that can be said is that the possible risks of formaldehyde vapor release can be reduced by using a vapor barrier layer on the inside of the wall.
If we talk about polyurethane foam, then in matters of safety it has certificates and conclusions that prove its harmless effect on living organisms, as well as on the environment. In terms of the use of polyurethane foam, no other country in the world has such prohibitions as penoizol has.
Fire safety
If we talk about fire safety, penoizols belong to the G2 flammability class, that is, they are not capable of spontaneous combustion. Polyurethane foams belong to the flammability class G3 and G4, which means that in the area of open fire they are low-flammability and self-extinguishing.
Water permeability
The percentage of moisture absorption in penoizols is quite high, approximately 18-20%, from which we can conclude that such heat insulators are afraid of moisture. With excess humidity, penoizol begins to deteriorate, so it requires additional steam and moisture insulation.
Polyurethane foams have minimal water permeability due to their closed-cell structure, so thermal insulation made from polyurethane foam will not only perfectly retain heat, but will also provide good anti-corrosion protection, protection from moisture, mold and fungi. It is also worth noting that condensation does not form on polyurethane foam surfaces.
Thermal insulation of foam insulation and polyurethane foam
High-quality penoizol has good thermal conductivity - up to 0.030 W/m K, but the thermal conductivity of polyurethane foam is about 0.021 W/m K.
Strength of polyurethane foam and penoizol
In terms of strength, penoizol is inferior to polyurethane foam, since it is a much more fragile material. But polyurethane foam is quite durable and at the same time elastic material, which is perfectly capable of withstanding, for example, shrinkage of the building, walking and other mechanical impacts.
Prices for penoizol and polyurethane foam
If we compare penoizol with polyurethane foam in terms of cost, then the first place will be taken by carbamide foam, which is an order of magnitude cheaper than polyurethane foam technology, however, its physicochemical qualities are lower than those of polyurethane foam...
Description of foams
Polyurethane foam and expanded polystyrene are foam plastics; they have simple installation, which affects the price of the finished insulation. Expanded polystyrene can be regular or extruded. The regular one consists of soft small white balls; the extruded one is denser, warmer, more durable and more expensive than the regular one.
The advantages of expanded polystyrene include:
- low cost 277 rub. for 1 sq.m. 5 cm thick;
- ease of installation;
- low thermal conductivity 0.028 - 0.035;
- different sheet thicknesses.
The disadvantages include the following:
- water absorption of polystyrene foam leads to an increase in the thermal conductivity of the insulation;
- it is easily destroyed by exposure to the sun;
- mice love to chew through it and make nests in it;
- very short service life - 10-15 years, but we are building seriously and for a long time;
- fire hazard - it is very flammable; when burned, it emits soot and toxic gases;
- at 60 degrees it begins to fall apart, so it is not at all suitable for roofs;
- at 20 degrees polystyrene begins to release toxic gas;
- presence of seams between sheets of insulation, cracking of seams;
- deformation during operation;
- it is necessary to fill the seams with polyurethane foam and fasten the sheets to the surface; this somewhat delays the commissioning of the construction project.
Advantages and disadvantages of expanded polystyrene

Expanded polystyrene is an ordinary foam plastic that is familiar to everyone. It has been used for several years now and all its pros and cons have long been known. At its core, it is 98% air bubbles enclosed in 2% polystyrene.
There are two types of expanded polystyrene - regular (foamed) and extruded. Due to its higher density, the latter has better thermophysical properties, it is stronger and more durable.
Both types of foam are available in the form of slabs of various thicknesses. How to distinguish one from the other? Try breaking off a piece from the edge of the slab. Cheap, packing foam will have small balls along the break. High-quality, extruded polystyrene foam will show regular polyhedra when broken.
The main advantages of polystyrene foam include the following:
- relatively low price;
- low thermal conductivity;
- simplicity and ease of installation;
- large selection of sheets of different thicknesses and densities.
The advantages of extruded polystyrene foam compared to conventional polystyrene foam are:
- lower water absorption - several times less than that of conventional foam;
- higher strength;
- long service life.
Please note: insulating premises with polystyrene from the inside is prohibited. Moisture (condensation) accumulates very quickly between the insulation and the walls, which leads to fungal infection and accelerated destruction of the building

Among the disadvantages, the following should be noted:
- water-absorbing properties of ordinary polystyrene foam - wet polystyrene foam has reduced thermal insulation properties and it quickly becomes unusable;
- short service life - only 10-15 years;
- rodents often make their nests in it;
- destruction under the influence of external factors - the slightest exposure to sunlight through poor-quality plaster begins to destroy the insulation;
- deformation during use;
- fire hazard - burns well; when burned, a fairly large amount of toxic substances is released.
Note: already at 60 degrees, polystyrene foam is susceptible to decay, so it is not worth using it for. In the summer in the southern regions, the roof can easily heat up to 100 degrees.
What to choose
So what is better to order? After all, the difference between polyurethane foam and expanded polystyrene is not so fundamental. Both materials have similar performance characteristics. If we compare polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam according to individual parameters, it is also unlikely that we will be able to identify the absolute leader. In some cases the difference will not be significant. For example, both materials are characterized by good water resistance and a wide temperature range in which they can be used. However, there is a difference between polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam. In terms of durability, ease of installation and environmental friendliness, the first material has clear advantages. Yes, it is inferior in terms of thermal protection, but one cannot say that it is very significant.
What else is different from polyurethane foam? Because it is not at all afraid of exposure to ultraviolet rays, and therefore it can be used to insulate the roof. Perhaps their main difference is the price. The cost of extruded polystyrene foam is significantly lower.
Brief comparative characteristics of thermal insulators
| Options | EPPS Styrofoam |
EPPS father |
PPU | Styrofoam |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low thermal conductivity | + | +- | ++ in the first years of operation provided that it is foamed with freon; if foaming occurs with air (which is often found in the Russian Federation), then the thermal conductivity indicator of such polyurethane foam deserves no more than one + |
— |
| Low moisture/water absorption | + | + | — | — the structure is destroyed |
| High structural strength | + | +- | +- | — |
| Strength/weight ratio | + | +- | — | — |
| Same density | + | — | + | + |
| Dimensional stability (without additional processing) | + | — | — | + |
| Optimal surface for work (no dust/closed cells) |
+ | + | — | — |
| Possibility of automation and ease of use | + | + | — | + |
| Temperature resistance | — | — | + | — |
Polyurethane foam or polystyrene foam - which is better?
Based on a thorough analysis of the characteristics of both insulation materials, we came to the conclusion that polyurethane foam copes better with the task of moisture, thermal and noise insulation, and also provides better fire safety and chemical resistance. The cost of expanded polystyrene is cheaper, but its heat loss is many times higher. Therefore, savings on insulating materials result in a significant increase in space heating costs. Considering the long service life of thermal insulation, polyurethane foam is more profitable, despite its higher price. Our experts, based on many years of experience in thermal insulation, recommend using polyurethane foam for durable and high-quality insulation.
We bring to your attention a table comparing thermal insulation materials such as polystyrene foam (EPS) and polyurethane foam (PUF), which are used in the manufacture of thermal panels
Comparison of thermal panels made of polystyrene foam (EPS) and polyurethane foam (PUF)
Expanded polystyrene
Polyurethane foam
Environmental friendliness
When heated to 60 degrees, it releases phenol
Complies with sanitary standards and regulations; the products have a sanitary and epidemiological certificate. Can be used at temperatures up to 180 degrees
Fire hazard
Does not support combustion
Durability
The material shrinks and contracts, which can lead to changes in the geometry of the façade.
UV-protected polyurethane foam is resistant to most solvents, and its service life exceeds the service life of the building’s load-bearing structures.
Limited service life. Significant decrease in performance after 10 years of use.
Does not change properties throughout the entire service life
Appearance
Deep joints lead to greater consumption of expensive joint fillers.
Perfect joining of panels, precise adherence to masonry geometry throughout the entire façade
The choice of materials is limited, because a special dovetail tile shape is required
Possibility of using facing materials of any shape.
Ease of installation
The softness of the supporting base and the weak fastening of the tiles to the panel lead to large waste of material during transportation and installation.
The rigidity of the material makes it possible to cladding without the use of sheathing.
The tile is held in place only by the recesses in the tile (dovetail); when cutting and installing, individual tiles fall out of the panel and must be glued back in
The tile is securely held in the panel due to adhesion. Cutting panels does not cause tiles to fall out.
The use of thick tiles (13-17 mm) increases the weight of the panels
Less weight of the panel due to the ability to use tiles of smaller thickness (8-11 mm)
Building materials do not adhere well to polystyrene foam; expensive special mixtures are required to fill the joints.
Quartz sand in the seams increases the strength of the panel and increases the adhesion of the jointing in the seams.
Features of operation
Excessive humidity can lead to fungal infection and create an unfavorable indoor microclimate
Polyurethane foam insulation is resistant to fungi, mold and bacteria. For many years, polyurethane foam has proven itself to be an excellent insulating material that is safe for health and does not have a harmful effect on the natural environment.
When moisture gets in and freezes, the foam is destroyed.
The use of thermal panels provides reliable waterproofing and vapor barrier, which reduces the cost of using additional insulation and insulation materials.
Regular inspection of the façade and elimination of any defects is required.
Does not require renovation or repair during the entire service life of the building. The components do not support combustion and are difficult to combust.
Summary
If you plan to purchase polystyrene foam or polyurethane foam, you must take into account that according to the main parameters, the second option wins. It is non-flammable, has a high density, wear-resistant, lasts a long time, and is non-hygroscopic. Expanded polystyrene is cheaper, but at the same time it has a fairly low thermal conductivity, which is often also an important criterion when choosing.
If self-foaming polyurethane foam is considered, its installation requires the use of expensive equipment. However, it is not advisable to purchase such equipment for one-time use. It must be said that polyurethane foam and polystyrene foam are universal insulation materials, but you should choose the appropriate option, based on operating conditions.
Which insulation is stronger?
Eps Styrofoam or PPU? First, let's make an analogy. Polyurethane foam and polypropylene foam are also used in other industries. Thus, cushions for seats, sofas and armchairs are made from polyurethane foam with the addition of special additives, and XPS is used by the US Army and NASA. Draw your own conclusions.
The strength of EPS is confirmed by the following tests:
The Royal Aeronautical Institute (Stockholm, Sweden) conducted tests to measure the long-term fatigue strength of Styrofoam Dow XPS and PU foam with a density of 40 kg/m³. Method – cyclic (5 Hz) deflection tests under prevailing shear stress, increasing with each cycle. Tests have shown that a panel with EPS has a tremendous advantage over a panel with PPU.
What to choose

Unfortunately, there is no ideal material that will suit absolutely everyone. For some, it will not be suitable due to the high price of polyurethane foam; for others, the service life of polystyrene foam will not suit them. Therefore, weigh all the pros and cons, but keep in mind that the disadvantages are not complete contraindications for use. Knowing the properties of insulation, you can make the best choice and not regret later about the money spent.
For example, if you want to insulate a garage or a wooden house on your property, choose cheaper polystyrene foam. 10-15 years of foam service life will be quite enough for this type of building. If funds allow, purchase extruded polystyrene foam. Just remember that ultraviolet rays destroy foam.
If you want to improve the thermal insulation of your home or apartment for many years, it would be wise to choose polyurethane foam. The costs will be higher, but you will enjoy the benefits of insulating your home for many years to come. The higher costs of quality installation will pay off over time.
For an overview of the advantages and disadvantages of polystyrene foam, watch the video:
Carbon monoxide, carbon monoxide, carbon monoxide, CO.
The main toxic component of combustion products of polyurethane foams and polyisocyanurate foams at all stages of fire, both at low and high temperatures, is carbon monoxide.
The natural level of CO in the air is 0.01 - 0.9 mg/m3, and on Russian highways the average CO concentration ranges from 6-57 mg/m3, exceeding the poisoning threshold. Carbon monoxide (carbon monoxide) is toxic; it has the ability to combine with hemoglobin in the blood 200-300 times faster than oxygen. The blood becomes unable to carry sufficient oxygen from the lungs to the tissues, and rapid and severe poisoning occurs.
When the inhaled air contains 0.08% CO, a person feels headache, nausea, weakness and suffocation. At 1% concentration of carbon monoxide in a room, it has a lethal effect within 1-2 minutes. When the CO concentration increases to 0.32%, paralysis and loss of consciousness occurs (death occurs within 30 minutes). At concentrations above 1.2%, consciousness is lost after 2-3 breaths, the person dies in less than 3 minutes.
Installation features
Advice from a professional
What to choose polyurethane foam or polystyrene foam
- 11 Jul/
- admin/
- popecham
Thermal insulation of a house is a necessary measure in our climate.

Scheme of insulating a concrete floor with polystyrene foam.
Insulating your home allows you to not only retain heat in winter, but also keep it out in summer. Few people know that modern thermal insulation materials work in both directions: in winter they protect against heat loss, and in summer they prevent it from entering the house. Based on this, we can conclude: if the house is equipped with good thermal insulation, then it will be warm in winter and cool in summer. But this is not all the functions that insulation performs: it is also able to protect the outer wall of the house from cracking at low temperatures.
Thermal insulation of the house has now become widespread, and that is why there is a huge selection of insulation materials on the market, but the most popular of them can rightfully be considered polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam. These materials have become so widespread due to their low price and ease of use. - a fairly simple and not very long construction project. If you know how to hold tools in your hand correctly, then insulating your house with this material will not be difficult for you. Polyurethane foam, like polystyrene foam, is just as easy to use, and its installation will not take you much time and effort. To understand which of these two materials is better for insulating your home, you need to compare them.
Mineral wool
Service life is 50 years for some manufacturers, a good indicator. Thermal conductivity is 0.032 - 0.12, this is the coldest insulation of those compared. Moisture resistance is low, warm air passes through well. During installation, there is a problem associated with protecting the installer from fine dust, which causes irritation to the skin and respiratory system.
For walls you need one type of mineral wool, for the ceiling another, for partitions a third.
Additional protection of mineral wool is required in the form of a vapor barrier device, counter-lattice, all this increases the cost of installation and the time it takes to put the facility into operation. The lowest price per square meter.
Remember, the stingy pays twice, first for the mineral wool, then for its dismantling and spraying of polyurethane foam.
During operation, shrinkage and changes in the size of the insulation are possible. It is possible for small particles of mineral wool to get into the living space, which causes allergies and skin irritation. No wonder people in Udmurtia are dismantling old mineral wool and switching to polyurethane foam.
In the photo of a house insulated with mineral wool, on the roof of the attic you can clearly see how the snow melts from heat leaks through the insulation. This can be clearly seen with the help of.

Comparison of polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam
To understand which of these two materials is better, let’s compare them according to a number of important indicators in the form of a table.
| Expanded polystyrene (PPS) | Polyurethane foam (PPU) |
|---|---|
| Environmental friendliness | |
| At temperatures above 60°C it releases phenol. | The products comply with sanitary standards. Polyurethane foam can be used at temperatures up to 180 °C without fear. |
| Fire hazard | |
| Lit. When burning, burning parts are separated from the material, which can cause the fire to spread. | Not flammable. |
| Durability | |
| Service life is no more than 15 years. A decrease in performance occurs after 10 years of use. | Polyurethane foam, protected from ultraviolet rays, can last longer than the load-bearing structures of the building. |
| The material settles and contracts, violating the geometry of the facade. | The properties of the material do not change throughout the entire service life. |
| Appearance | |
| The presence of seams between panels entails a large consumption of joint fillers. | There is no seam. |
| Limited choice of facing materials, as dovetail is required. | Wide selection of finishing materials of any shape. |
| Ease of installation | |
| Slabs often deteriorate during installation or transportation due to their fragility of the material. | The material is not picky in transportation. For installation you only need a sprayer. |
| Sheathing of slabs is required. | The material does not require additional lathing. |
| Not all adhesive materials are suitable for foam, so it is necessary to use special compounds for EPS. | Excellent contact with any type of fastening materials. |
| Specific installation of slabs using dowels and other materials. | You don’t need anything other than a sprayer for installation. |
| Features of operation | |
| High humidity can cause mold and mildew to appear on the slabs, which will cause an unfavorable microclimate in the room. | Moisture resistant. Not subject to rotting or mold. |
| When moisture gets on the panel, it is absorbed and when exposed to low temperatures, it freezes and destroys the foam. | Polyurethane foam repels water from the surface, which prevents destruction of the material. |
| It is necessary to constantly inspect the thermal insulation for defects and eliminate them. | No renewal or repair of thermal insulation is required throughout the entire service life. |
Comparison result

The table shows that polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam have both pros and cons, but, of course, polystyrene foam has the most disadvantages. The service life of this material does not exceed 15 years. It is actively destroyed when exposed to the environment. PPS boards are often damaged by rodents. Due to the fact that this material is a hydrocarbon polymer, adhesives and plaster solutions do not adhere well to it. But the most important thing is that polystyrene foam is an unsafe material: it burns, scattering burning fragments in different directions, while releasing toxic substances. All this indicates the unreliability of polystyrene foam for thermal insulation of a house.
Unlike polystyrene foam, it is a reliable and modern method of insulation. This material is light and does not load the structure, but at the same time it is very durable. Polyurethane foam has low thermal conductivity and vapor permeability.
A well-insulated building lasts much longer, and due to its high energy efficiency, heating costs are significantly reduced. One of the structural elements through which the greatest heat loss occurs in a structure is the floor. Comfortable floor temperature is one of the main indicators of the entire thermal insulation of a structure.
To ensure the energy efficiency of a building when carrying out thermal insulation work, it is important not only to follow the technology for installing the thermal insulation layer, but also to choose the right insulation. . Must have low thermal conductivity, light weight, high strength, fire resistance, have moisture-repellent properties, be easy to install, durable and environmentally friendly material
In addition, the thermal insulation work itself should not be a labor-intensive, costly process.
It must have low thermal conductivity, light weight, high strength, fire resistance, have moisture-repellent properties, be easy to install, durable and environmentally friendly material. In addition, the thermal insulation work itself should not be a labor-intensive, costly process.
Why insulate with polyurethane foam from Ecotermix, and not with any other material? Find out in the video below:
Advantages of EPPS
Advantages of EPPS Styrofoam, currently used by us:
Installation features
The installation method is exactly what distinguishes polystyrene foam in panels from polyurethane foam. Polyurethane foam is most often sprayed in the form of a monolithic coating that has no joints and does not require serious preparation. Check out If done correctly, insulation with this material does not require much time, since there is no additional installation work.
Advice from a professional
There are two main types of exterior wall finishing insulated with polyurethane foam - siding and plaster.
Each method has its own subtleties of applying polyurethane foam, which are important to know in advance for proper preparation of surfaces and subsequent finishing.
There are two concepts for assessing the impact of harmful substances on the human body
Threshold. The threshold concept states that it is necessary to reduce the concentrations of harmful substances to a certain level (threshold), determined by the value of the maximum permissible concentration (MAC). The conclusion follows from this provision: small concentrations of harmful substances (below the MPC level) are harmless. In our country (as, indeed, in other countries of the former USSR), it is the threshold concept that has been adopted.
Linear. The linear concept assumes that the harmful effect on a person depends proportionally (linearly) on the total amount of substance absorbed. Hence the conclusion: low concentrations with long-term consumption are harmful. This concept is adhered to by the USA, Germany, Canada, Japan and some other countries. But when considering the toxic danger of exposure to harmful substances on humans, it is necessary to take into account the degree of their COMMUNITY, i.e. the ability of a substance to accumulate in the human body over time.
STYRENE, among the substances contained in building materials, has the highest degree of cumulativeness - 0.7 (see Table 1). If we imagine that polystyrene with a thickness of 160 mm (in a three-layer panel) will last 20 years, then during this period every sq. a meter of external wall will release 3 mg/h of styrene. When 10% of this amount enters the room and air is supplied in an amount of 30 m3/m2 h, the styrene concentration will be 0.0075 mg/m3. With a temporary stay in such a room and focusing on the daily MPC = 0.002 mg/m3, the excess of the MPC for styrene will be 3.75 times.
Therefore, for a residential building with a residence time of 25 years, the maximum permissible concentration for styrene should be reduced by 594 times and amount to 0.0000034 mg/m3 (see table).
Table 1. Decrease in the value of the maximum permissible concentration of harmful substances, taking into account their degree of cumulativeness.
| Substance | MPC, mg/m3 | Degree of cumulativeness | Reducing MPC | Recalculated MPC, mg/m3 | |
| one-time | daily allowance | ||||
| Carbon monoxide (carbon dioxide) | 5 | 3 | 0,1195 | 3 | 1,0000000 |
| Methanol | 1 | 0,5 | |||
| Carbon monoxide (carbon monoxide) | 20 | 0,02 | |||
| Nitrogen dioxide | 0,085 | 0,04 | 0,176 | 5 | 0,0080000 |
| Phenol | 0,01 | 0,003 | 0,2815 | 13 | 0,0002308 |
| Ammonia | 0,2 | 0,04 | 0,376 | 31 | 0,0012903 |
| Nitric oxide | 0,4 | 0,06 | 0,444 | 57 | 0,0010526 |
| Formaldehyde | 0,035 | 0,003 | 0,575 | 188 | 0,0000160 |
| Benzene | 1,5 | 0,1 | 0,633 | 322 | 0,0003106 |
| Styrene | 0,04 | 0,002 | 0,7005 | 594 | 0,0000034 |
Conclusion: STYRENE requires a reduction in the maximum permissible concentration when using it in residential construction by approximately 600 times to the level of 0.0000034 mg/m3, which is equivalent to a complete ban on the use of expanded polystyrene in residential construction.
Flammability of polystyrene foam
Due to this property, polystyrene foam in the form of pre-foamed granules was used as a component for napalm bombs to burn enemy armored vehicles. Expanded polystyrene melts and its melt burns at temperatures above 1100ºС. This is the only polymer that burns at such a high temperature. Therefore, when a building in which there is a significant content of polystyrene foam catches fire, everything burns, even metal structures.
In turn, when polystyrene burns, its thermal degradation occurs, which releases a significant amount of substances hazardous to humans. Therefore, back in the Soviet Union, under a unified system of sanitary and chemical control of the use of polymer materials, the USSR Ministry of Health banned the use of expanded polystyrene in construction.
In connection with the above, in Western Europe 20 years ago, expanded polystyrene was completely removed from residential buildings. The main peaceful use of expanded polystyrene in northern Europe and Canada is for insulation of road and railway tracks. To give the road durability, slabs of this material are added to the body of its “layer cake”. Moreover, it is not foamed, but extruded polystyrene foam (technology developed by BASF, Germany) that has a hard and durable shell that is used. This makes it possible for expanded polystyrene not to become saturated with moisture, maintain its thermal insulation ability and prevent freezing of the road surface - which is the main reason for its rapid destruction. The use of expanded polystyrene in greenhouses is also effective, especially in the northern regions. Studies have shown that toxic STYRENE is not released into a humid environment, but remains in polystyrene foam without causing any harm. In addition, under a layer of sand, gravel or soil, there is no question of the fire hazard of polystyrene foam. This is where this material belongs.
Technologies for the production of EPPS and PU foam
Secondly, you need to explain the basic knowledge about sandwich panel production technologies.
Glued sandwich panels. In them, the layers are joined using one- or two-component (more common) polyurethane glue in a vacuum or mechanical press. The latter is quite expensive, so not everyone can afford it. But we allowed it, and our panels turn out amazing, smooth, like the surface of the sea. In this case, the sandwich panel can be either three-layer: cladding + insulation (in order to reduce the cost, some use polystyrene foam, some use domestic EPS, and we use imported EPS) + cladding, or five-layer with the addition of a layer of plywood under the cladding. Or maybe N-layer.
Filled sandwich panels. The facings of the future panel are placed in a press, the required distance is selected between them, and the ends are closed with limiters. The top facing in the press is held either by magnets or by vacuum suction cups. Next, polyurethane foam flows through the tube into the space between the facings. The most difficult thing here is to achieve uniform distribution of foam, i.e. so that its density is the same throughout the entire volume of the panel. Difficulties arise with the placement of the mortgages (they must first be glued to one of the claddings). And with the production of N-layer panels: cladding with inner layers must first be glued together in a press, and then the polyurethane mass is poured between them (the press works 2 times instead of once → energy consumption, panel production time increases → increased labor intensity, therefore 4 and 5-layer vans with polyurethane foam (road).
conclusions
Expanded polystyrene has more disadvantages than advantages. First of all, the service life of this material does not exceed 15 years. In addition, it is destroyed under the influence of the environment, hydrocarbon liquids - acetone, white spirit, gasoline, etc. Even ordinary water, which the foam actively absorbs, leads to its rapid destruction when freezing. This material is also often damaged by rodents. Plus, since polystyrene foam is a hydrocarbon polymer, construction and plaster mortars do not adhere well to it, which requires the use of additional components to fix them. Expanded polystyrene is also unsafe: it burns, splashing burning fragments of material in all directions and releasing toxic substances. All this makes foam-based thermal panels an unreliable material.
Facade thermal panels based on rigid polyurethane foam are one of the most modern and promising building materials. Lightweight, but quite durable material has very low thermal conductivity and low vapor permeability. In modern conditions of rising prices for fuel resources, the question arises of choosing a high-quality thermal insulation material. The best thermal insulation material today, undoubtedly, is polyurethane foam and thermal panels based on it.
Thermal panels Regent
made from rigid polyurethane foam. By choosing Regent thermal panels you get a high-quality and environmentally friendly product.
Today, the issue of home insulation is becoming increasingly relevant. Some insulate the entire apartment, others only insulate the loggia, but every person thinks about what material to choose. Polyurethane foam or polystyrene foam: which is better to order? Both are types of gas-filled plastics (foams) and each has its own characteristics. To understand which is better - polyurethane foam or expanded polystyrene - you first need to compare their characteristics. This will make it much easier to determine how they differ and which option is best for you.