Assembling homemade boilers. DIY heating boiler drawings How to weld a solid fuel boiler
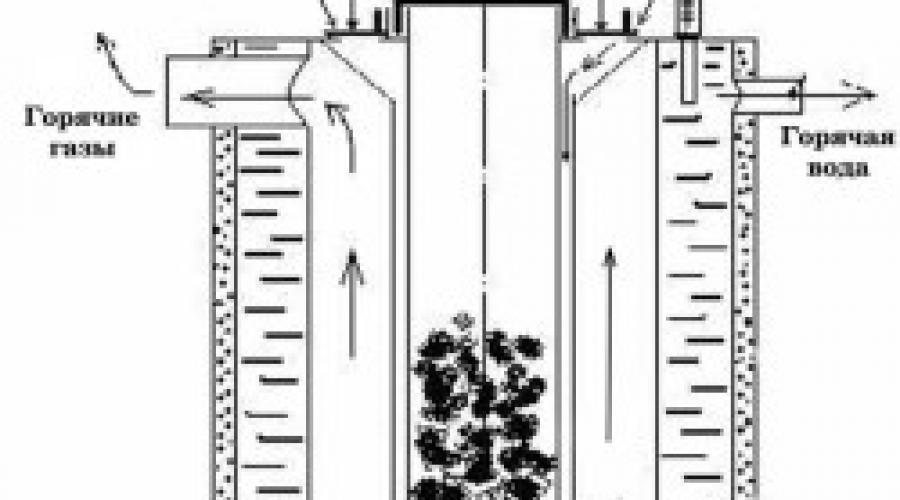
Quite often, heating boilers are used to heat private houses. Almost anyone can weld a heating boiler with their own hands, since these devices have a simple design. To make the structure, you can use non-professional tools and materials that are available.
Some improvements can be made to the design of the boiler, which will be used to heat your own private home and cook food. Such changes can improve the efficiency of the device.
Heating boiler design
This equipment has a similar design to an ordinary stove. The only differences are in the method of heat transfer. The boiler consists of the following elements:
- Capacity for burning solid fuel.
- Grate bars for supplying air in the required quantity.
- Water tank or tubular heating registers.
- Chimney. Designed to create the required draft and remove combustion products.
- Dampers. They are used to regulate air draft and block the channels after the fire in the stove goes out.

The heating system must be equipped with a water heat accumulator. It is a container that is installed in the upper part of the boiler and accumulates heat energy during the combustion process. When this process stops, the liquid will circulate in the system and heat the air.
Additionally, you can install a stainless steel tank that will contain hot water. It is mounted above the heat accumulator. This element of the heating system is optional.
The first step is to draw up an accurate drawing of the heating boiler. In order to rationally use the living space, it is recommended to order the development of an individual project of a similar design from specialists.
Return to contents
Tools and materials needed to make a heating boiler
To weld heating boilers with your own hands, you will need to prepare the following elements:
- Steel sheet with a minimum thickness of 5 mm.
- Metal corner.
- Cast iron grate.
- Water pipes made of steel of various diameters.
- Doors for bins.
- Throttle valves.
- Stainless steel sheet. Needed to make a heat accumulator.
- Sifted sand.
During the manufacturing process of a heating boiler, welding work will be required. The following tools should be prepared:

Figure 1. Diagram of a homemade boiler.
- An inverter-type welding device or any other that can be used at home.
- Bulgarian.
- Forceps.
- Pliers.
- Electric drill.
- A set of necessary drills.
- Roulette.
- Level.
- Square.
The master must have welding skills.
Return to contents
How to properly manufacture parts of a heating boiler body
The basis of any boiler is the firebox, in which the temperature can reach 900-1000°C. To assemble it, you will need materials that can withstand such temperatures. The sequence of actions for manufacturing the case will be as follows:
- If heat-resistant steel is not available, you can use ordinary steel. However, in this case, to ensure the durability of the structure, the walls of the assembly must be made double. The walls need to be cut from a sheet of steel using a grinder.
- It will be necessary to cut the required number of parts from a steel pipe that will be used as stiffeners. From a metal corner you need to make reinforcements for the joints between all elements of the stove.
- A rectangular hole should be made in the front wall, which corresponds in size to the doors of all bunkers. To make a through rectangular hole of the desired configuration, you need to apply markings to the metal, and then drill the sheet in the corners using an electric drill. Using an angle grinder, you need to make a through cut in the middle part, and then move it from the central part to the outer part. This way it will be possible to prevent damage to the sheet.

A high-quality heating boiler should have several water tanks. Tanks should be made of stainless steel. To weld the sheets, you will need to use a special device.
The design of the heat exchanger is a set of water pipes. Using a welding device, they should be connected so that a flow circuit with a large outer base is formed.
In this case, the fastest and most complete thermal transfer from the burned fuel to the coolant will be ensured.
Return to contents
How to properly assemble a boiler with your own hands
The design of heating boilers is characterized by high metal consumption. Such a device will ultimately have a lot of weight. Therefore, it is recommended to carry out assembly at the installation site of the heating equipment.
Under the boiler it is necessary to make a base of heat-resistant brick.
After this, you will need to lay the bottom of the ash bin on it. The walls of the structure should be installed vertically along the perimeter of this element. After this, the walls are connected by welding.
The diagram of a homemade boiler is shown in Fig. 1.
Inside the manufactured housing, grate bars will need to be laid on welded guides. After this, heat exchangers are installed. From the outside, stiffening ribs must be welded to the hopper in a vertical position, which are made from a rectangular steel profile. At this stage, all that remains is to mount the outer walls and the top plate.
Between the walls it will be necessary to pour prepared sifted sand, which will perform a dual function:
- additionally accumulate heat;
- protect the walls of the combustion chamber from possible overheating and accelerated burnout.
For backfilling, it is recommended to use washed sand that does not contain dust or other foreign elements. The sand will first need to be calcined over a fire to eliminate all organic matter. If you skip this step, a not-so-pleasant smell may appear while the heating boiler is firing.
You will need to mount prepared stainless steel containers on the top plate, and then connect them to the appropriate circuits. After this, all that remains is to install the doors in their places.
© When using site materials (quotes, images), the source must be indicated.
“A boiler is really a stove in a barrel of water”... and the efficiency of such a unit will be at best 10%, or even 3-5%. After all, a solid fuel boiler is not a stove at all, and a solid fuel stove is not a hot water boiler. The fact is that the combustion process of solid fuel, unlike gas or flammable liquids, is certainly extended in space and time. Gas or oil can be completely burned immediately in a small gap from the nozzle to the burner diffuser, but wood and coal cannot. Therefore, the requirements for the design of a solid fuel heating boiler are different than for a heating furnace; it is impossible to simply put a heating circuit water heater into it in continuous circulation. Why this is so, and how a continuous heating boiler should be designed, is what this article is intended to explain.
Your own heating boiler in a private house or apartment becomes a necessity. Gas and liquid fuels are steadily becoming more expensive, and in return, inexpensive alternative fuels are appearing on sale, for example. from crop waste - straw, husks, husks. This is only from the point of view of the owners of the house, not to mention the fact that the transition to individual heating will allow you to get rid of energy losses in the main lines of thermal power plants and power line wires, and they are by no means small, up to 30%
You cannot make a gas boiler yourself, if only because no one will give permission to operate it. It is prohibited to use individual liquid fuel boilers for heating residential premises due to their high fire and explosion hazard when used in a decentralized manner. But you can make a solid fuel boiler with your own hands and register it officially, just like a heating stove. This is perhaps the only thing they fundamentally have in common.
Features of solid fuel
Solid fuel does not burn very quickly, and not all components carrying thermal energy burn in its visible flame. For complete combustion of flue gases, a high but well-defined temperature is required, otherwise conditions will arise for the occurrence of endothermic reactions (for example, nitrogen oxidation), the products of which will carry away the energy of the fuel into the chimney.
Why doesn't the boiler bake?
The oven is a cyclic device. So much fuel is loaded into its firebox at once so that its energy lasts until the next fire. The excess combustion energy of the fuel load is partially used to maintain the optimal temperature for afterburning in the gas path of the furnace (its convective system), and is partially absorbed by the furnace body. As the load burns out, the ratio of these parts of fuel energy changes, and a powerful flow of heat circulates inside the furnace, several times more powerful than the current needs for heating.
The body of the stove is thus a heat accumulator: the main heating of the room occurs due to its cooling after heating. Therefore, it is impossible to take away the heat circulating in the furnace; this will somehow disrupt its internal thermal balance, and the efficiency will drop sharply. It is possible, and even then not in every place of the convection system, to take up to 5% to replenish the hot water storage tank. Also, the stove does not require operational adjustment of its thermal power; it is enough to load fuel based on the required average hourly time between firings.
A water boiler, no matter what fuel it uses, is a continuous operation device. The coolant circulates in the system all the time, otherwise it will not heat, and the boiler must at any given moment provide exactly as much heat as was lost outside due to heat loss. That is, fuel must either be periodically loaded into the boiler, or prompt adjustment of the thermal power must be ensured within a fairly wide range.
The second point is flue gases. They must approach the heat exchanger, firstly, as hot as possible in order to ensure high efficiency. Secondly, they must be completely burned out, otherwise the fuel energy will be deposited on the register as soot, which will also need to be cleaned.
Finally, if the stove heats around itself, then the boiler as a heat source and its consumers are separated. The boiler requires a separate room (boiler room or furnace): Due to the high concentration of heat in the boiler, its fire danger is much higher than that of the furnace.
Note: An individual boiler room in a residential building must have a volume of at least 8 cubic meters. m, ceiling at least 2.2 m high, opening window at least 0.7 sq. m, a constant (without valves) flow of fresh air, a smoke channel separate from other communications and a fire separation from the other rooms.
From this it follows, firstly, boiler furnace requirements:
- It should ensure fast and complete combustion of fuel without a complex convection system. This can only be achieved in a firebox made of materials with the lowest possible thermal conductivity, because For rapid combustion of gases, a high concentration of heat is required.
- The firebox itself and the parts of the structure associated with it in heat should have the lowest possible heat capacity: all the heat that went into heating them will remain in the boiler room.
These requirements are initially contradictory: materials that conduct heat poorly, as a rule, accumulate it well. Therefore, a regular stove firebox will not work for a boiler; some kind of special one is needed.
Heat exchange register
The heat exchanger is the most important component of a heating boiler; it mainly determines its efficiency. Based on the design of the heat exchanger, the entire boiler is called. In household heating boilers, heat exchangers are used - water jackets and tubular, horizontal or vertical.
A boiler with a water jacket is the same “stove in a barrel”; a heat exchange register in the form of a tank surrounds the firebox. A jacketed boiler can be quite economical under one condition: if the combustion in the firebox is flameless. A flaming solid fuel furnace certainly requires afterburning of the exhaust gases, and in contact with the jacket their temperature immediately drops below the value required for this. The result is an efficiency of up to 15% and increased deposition of soot, and even acid condensate.
Horizontal registers, generally speaking, are always inclined: their hot end (supply) must be raised above the cold end (return), otherwise the coolant will flow backwards, and failure of forced circulation will immediately lead to a serious accident. In vertical registers, the pipes are located vertically or slightly inclined to the side. In both cases, the pipes are arranged in rows in a checkerboard pattern, so that gases are better “entangled” in them.
Regarding the directions of movement of hot gases and coolant, pipe registers are divided into:
- Flow-through - gases generally flow perpendicular to the coolant flow. Most often, this scheme is used in horizontal industrial boilers of high power due to their lower height, which reduces the cost of installation. In households, the situation is the opposite: in order for the register to properly capture the heat, it has to be extended upward above the ceiling.
- Countercurrent - gases and coolant move along the same line towards each other. This scheme provides the most efficient heat transfer and the highest efficiency.
- Flow - gases and coolant move parallel in one direction. Rarely used in special-purpose boilers, because At the same time, efficiency is poor, and equipment wear is high.
Further, heat exchangers are made of fire tube and water tube. In fire tubes, smoke tubes carrying flue gases pass through a tank of water. Fire tube registers operate stably, and vertical ones provide good efficiency even in a flow diagram, because internal water circulation is established in the tank.
However, if we calculate the optimal temperature gradient for heat transfer from gas to water based on the ratio of their density and heat capacity, then it turns out to be approximately 250 degrees. And in order to push this heat flow through the wall of a steel pipe of 4 mm (you can’t do less, it will burn out very quickly) without noticeable losses on the thermal conductivity of the metal, you need about another 200 degrees. As a result, the inner surface of the smoke pipe should be heated to 500-600 degrees; 50-150 degrees – operational margin for fuel water cut, etc.
Because of this, the service life of the smoke tubes is limited, especially in large boilers. In addition, the efficiency of a fire tube boiler is low; it is determined by the ratio of the temperatures of hot gases entering the register and those exiting the chimney. It is impossible to allow gases to cool below 450-500 degrees in a fire tube boiler, and the temperature in a conventional firebox does not exceed 1100-1200 degrees. According to the Carnot formula, it turns out that the efficiency cannot be higher than 63%, and the efficiency of the firebox is no more than 80%, so the total is 50%, which is very bad.
In small domestic boilers, these features have a weaker effect, because when the size of the boiler decreases, the ratio of the register surface to the volume of flue gases in it increases, this is the so-called. square-cube law. In modern pyrolysis boilers, the temperature in the combustion chamber reaches 1600 degrees, the efficiency of their furnace is 100%, and the registers of branded boilers, guaranteed for 5 years or more, are made only of thin-walled heat-resistant special steel. In them, gases can be allowed to cool to 180-250 degrees, and the overall efficiency reaches 85-86%
Note: Cast iron is generally unsuitable for smoke pipes; it cracks.
In water-tube registers, the coolant flows through pipes placed in a fire chamber into which hot gases enter. Now temperature gradients and the square-cube law operate in the opposite way: at 1000 degrees in the chamber, the outer surface of the pipes will be heated to only 400 degrees, and the inner surface to the temperature of the coolant. As a result, pipes made of ordinary steel last a long time and the boiler efficiency is about 80%
But horizontal flow-through water tube boilers are prone to the so-called. "flooding". The water in the lower pipes turns out to be much hotter than in the upper ones. It is pushed into the supply first, the pressure drops, and the colder upper pipes “spit out” the water. “Buhtenie” not only provides as much noise, heat and comfort as a neighbor who is a drunkard and a brawler, but is also fraught with a break in the system due to water hammer.
Vertical water-tube boilers do not fire, but if a water-tube boiler is being designed for a house, the register should be located at the bottom of the chimney, in the section where hot gases flow from top to bottom. In an in-line water-tube boiler with the same direction of movement of gases and coolant, the efficiency drops sharply and soot is intensively deposited on the pipes near the supply, and it is generally unacceptable to make a return above the supply.
About the heat exchanger capacity
The ratio of the heat exchanger capacities and the entire cooling system is not taken arbitrarily. The rate of heat transfer from gases to water is not infinite; the water in the register must have time to absorb heat before it leaves the system. On the other hand, the heated outer surface of the register gives off heat to the air, and it is wasted in the boiler room.
A register that is too small is prone to boiling and requires precise, quick adjustment of the firebox power, which is unattainable in solid fuel boilers. A large-volume register takes a long time to warm up and, if the external thermal insulation of the boiler is poor or absent, it loses a lot of heat, and the air in the boiler room can warm up above the permissible level for fire safety and boiler specifications.
The size of the heat exchanger capacity of solid fuel boilers ranges from 5-25% of the system capacity. This must be taken into account when choosing a boiler. For example, for heating, according to the calculation, there were only 30 sections of radiators (batteries) of 15 liters each. With water in the pipes and an expansion tank, the total capacity of the system will be about 470 liters. The boiler register capacity should be between 23.5-117.5 liters.
Note: There is a rule - the greater the calorific value of solid fuel, the greater the relative capacity of the boiler register should be. Therefore, if the boiler is coal-fired, the register capacity should be taken closer to the upper value, and for a wood-burning boiler - to the lower value. For slow-burning boilers, this rule is not valid; the capacity of their registers is calculated based on the highest efficiency of the boiler.
What is the heat exchanger made of?
Cast iron as a material for a boiler register does not meet modern requirements:
- The low thermal conductivity of cast iron leads to low boiler efficiency, because It is impossible to cool the exhaust gases below 450-500 degrees; as much heat as needed will not pass through the cast iron into the water.
- The high heat capacity of cast iron is also its disadvantage: the boiler must quickly release heat into the system before it evaporates somewhere else.
- Cast iron heat exchangers do not fit into modern weight and size requirements.
For example, let's take the M-140 section from an old Soviet cast-iron battery. Its surface area is 0.254 square meters. m. For heating 80 sq. m of living space, a heat exchange surface in the boiler of approximately 3 square meters is required. m, i.e. 12 sections. Have you seen a battery with 12 sections? Imagine what the cauldron must be like in which it will fit. And the load from it on the floor will definitely exceed the limit according to SNiP, and a separate foundation will have to be made for the boiler. In general, 1-2 cast iron sections will go to the heat exchanger that feeds the hot water storage tank, but for a heating boiler the question of a cast iron register can be considered closed.
The registers of modern factory boilers are made of heat-resistant and heat-resistant special steel, but their production requires production conditions. What remains is ordinary structural steel, but it corrodes very quickly at 400 degrees and above, so fire tube boilers made of steel must be selected for purchase or developed very carefully.
In addition, steel conducts heat well. On the one hand, this is not bad; you can expect to obtain good efficiency using simple means. On the other hand, the return flow should not be allowed to cool below 65 degrees, otherwise acidic condensate will fall onto the register in the boiler from the flue gases, which can eat through the pipes within an hour. You can exclude the possibility of its deposition in 2 ways:
- For boiler power up to 12 kW, a bypass valve between the boiler flow and return is sufficient.
- With greater power and/or heated area of more than 160 sq. We also need an elevator unit, and the boiler must operate in the mode of superheating water under pressure.
The bypass valve is controlled either electrically from a temperature sensor, or energy-independently: from a bimetallic plate with a rod, from wax melting in a special container, etc. As soon as the temperature in the return drops below 70-75 degrees, it admits hot water from the supply into it.
The elevator unit, or simply the elevator (see figure), acts in the opposite way: the water in the boiler is heated to 110-120 degrees under pressure of up to 6 ati, which eliminates boiling. To do this, the combustion temperature of the fuel is increased, which increases efficiency and eliminates condensation. And before entering the system, hot water is diluted with return water.

In both cases, forced water circulation is necessary. However, it is quite possible to create a steel boiler using thermosiphon circulation that does not require power supply for the circulation pump. Some designs will be discussed below.
Circulation and boiler
Thermosiphon (gravity) circulation of water does not allow heating a room with an area of more than 50-60 square meters. m. The point is not only that it is difficult for water to squeeze through a developed system of pipes and radiators: if you open the drain valve when the expansion tank is full, water will rush out in a strong stream. The fact is that the energy for pushing water through the pipes is taken from the fuel, and the efficiency of converting heat into movement in a thermosiphon system is negligible. Therefore, the efficiency of the boiler as a whole decreases.
But the circulation pump requires electricity (50-200 W), which may be lost. A UPS (uninterruptible power supply) for 12-24 hours of autonomous operation is very expensive, so a properly designed boiler is designed for forced circulation, and if the power supply is lost, it must, without outside intervention, go into thermosiphon mode, when the heating is barely warm, but still warms.
How to install the boiler?
The requirement for a boiler’s minimum intrinsic heat capacity directly follows from its low weight compared to a stove and its weight load per unit floor area. As a rule, it does not exceed the minimum allowable according to SNiP for flooring of 250 kg/sq. m. Therefore, installing a boiler is permissible without a foundation and even dismantling the flooring, incl. and on the upper floors.

Place the boiler on a flat, stable surface. If the floor plays, it will still have to be dismantled at the boiler installation site down to the concrete screed with a distance of at least 150 mm to the sides. The base for the boiler is covered with asbestos or basalt cardboard 4-6 mm thick, and a sheet of roofing iron 1.5-2 mm thick is placed on it. Next, if the flooring has been dismantled, the bottom of the boiler is lined with cement-sand mortar to the floor level.
Around the boiler protruding above the floor, thermal insulation is made, the same as underneath: asbestos or basalt cardboard, and iron on it. The removal of insulation to the sides from the boiler is from 150 mm, and in front of the firebox door is at least 300 mm. If the boiler allows additional fuel loading before the previous portion burns out, then the removal in front of the firebox is required from 600 mm. Under the boiler, which is placed directly on the floor, only thermal insulation covered with a steel sheet is placed. Removal - as in the previous case.
A separate boiler room is required for a solid fuel boiler. The requirements for it are given above. In addition, almost all solid fuel boilers do not allow power adjustment within a wide range, so they require a full-fledged piping - a set of additional equipment that ensures efficient and trouble-free operation. We’ll talk about it later, but in general, boiler piping is a separate big topic. Here we mention only the immutable rules:
- The installation of the piping is carried out in counterflow to the water, from the return to the supply.
- Upon completion of installation, its correctness and quality of connections are checked visually according to the diagram.
- The installation of the heating system in the house begins only after piping the boiler.
- Before loading fuel and, if required, supplying power, the entire system is filled with cold water and all joints are monitored for leaks during the day. In this case, water is water, and not some other coolant.
- If there are no leaks, or after they have been eliminated, the boiler is started on water, continuously monitoring the temperature and pressure in the system.
- Once the nominal temperature is reached, the pressure is controlled for 15 minutes; it should not change by more than 0.2 bar, this process is called pressure testing.
- After pressure testing, the boiler is extinguished and the system is allowed to cool completely.
- Drain the water and fill in the standard coolant.
- Once again, check the joints for leaks for 24 hours. If everything is in order, the boiler is started. No - they fix the leaks, and again daily monitoring before starting.
Choosing a boiler
Now we know enough to choose a boiler based on the intended type of fuel and its purpose. Let's get started.
Wood burning
The calorific value of firewood is low, the best ones have less than 5000 kcal/kg. Firewood burns quite quickly, releasing a large volume of volatile components that require afterburning. Therefore, it is better not to count on high efficiency using wood, but they can be found almost everywhere.
Wood burning for the house
A home wood-burning boiler can only burn for a long time, otherwise it will damage it in all respects. Industrial structures, e.g. the well-known KVR, cost from 50,000 rubles, which is still cheaper than building a furnace, do not require power supply and allow power adjustment for heating in the off-season. As a rule, they operate on coal and any solid fuel, except sawdust, but with coal, fuel consumption will be much higher: heat transfer from one load is 60-72 hours, and for specialized coal ones – up to 20 days.
However, a long-burning wood-burning boiler can be useful in places where there is no regular supply of coal and qualified heating service. It costs one and a half times less than coal, its jacket design is very reliable and allows you to build a thermosiphon heating system with an area of up to 100 square meters. m.. In combination with the smoldering of the fuel in a thin layer and a fairly large volume of the jacket, boiling of water is excluded, so the piping is sufficiently the same as for titanium. Connecting a long-burning wood-burning boiler is also no more difficult than titanium, and can be done independently by an unqualified owner.
About brick boilers

Diagram of the boiler “Blago”
Brick is the friend of the stove and the enemy of the boiler due to the fact that it gives the structure greater thermal inertia and weight. Perhaps the only brick boiler in which the brick is in its place is Belyaev’s pyrolysis “Blago”, diagram in Fig. And then, its role here is completely different: the lining of the combustion chamber is made of fireclay bricks. Horizontal water tube heat exchanger; The problem of coiling is solved by the fact that the register pipes are single, flat, elongated in height.
Belyaev’s boiler is truly omnivorous, and there are 2 separate bunkers for loading different types of fuel without stopping the boiler. “Blago” can work on anthracite for several days, on sawdust – up to a day.
Unfortunately, Belyaev’s boiler is quite expensive, due to the fireclay lining it is poorly transportable and, like all pyrolysis boilers, requires complex and expensive piping. Its power is regulated within small limits by bypassing flue gases, so it will show good efficiency on average for the season only in places with prolonged severe frosts.
About boilers in the furnace
The boiler in the furnace, about which they talk and write so much now, is a water-tube heat exchanger immured in the furnace masonry, see fig. below. The idea is this: after firing, the stove should release heat more directly than into the surrounding air. Let's say right away: reports of an efficiency of 80-90% are not only doubtful, but simply fantastic. The best brick oven itself has an efficiency of no higher than 75%, and its outer surface area will be no less than 10-12 square meters. m. The surface area of the register is unlikely to be more than 5 square meters. m. In total, less than half of the heat accumulated by the furnace will go into the water, and the overall efficiency will be below 40%

Next point - a stove with a register immediately loses its properties. Under no circumstances should you heat it out of season with an empty register. The TCR (temperature coefficient of expansion) of metal is much greater than that of brick, and a heat exchanger swollen from overheating will tear the stove before our eyes. Thermal seams will not help the matter; the register is not a sheet or a beam, but a three-dimensional structure, and it is bursting in all directions at once.
There are other nuances here, but the general conclusion is clear: a stove is a stove, and a boiler is a boiler. And the fruit of their forced unnatural union will not be viable.
Boiler piping
Boilers that prevent boiling of water (long-burning jacket boilers, titanium boilers) cannot be made with a power of more than 15-20 kW and cannot be extended in height. Therefore, they always provide heating for their area in thermosiphon mode, although a circulation pump, of course, would not hurt. In addition to the expansion tank, their piping includes only an air drain valve at the highest point of the supply pipeline and a drain valve at the lowest point of the return line.
The wiring of solid fuel boilers of other types should provide a set of functions, which can be better understood in Fig. on right:

- safety group: air drain valve, general pressure gauge and breakthrough valve for releasing steam during boiling;
- emergency cooling storage tank;
- its float valve is the same as in the toilet;
- thermal valve for starting emergency cooling with its sensor;
- MAG block - drain valve, emergency drain valve and pressure gauge, assembled in one housing and connected to a membrane expansion tank;
- forced circulation unit with a check valve, a circulation pump and an electrically temperature-controlled three-way bypass valve;
- intercooler - emergency cooling radiator.
Pos. 2-4 and 7 make up the power reset group. As already mentioned, solid fuel boilers are regulated in terms of power within small limits, and with sudden warming, the entire system may overheat unacceptably, even to the point of bursting. Then thermal valve 4 lets tap water into the intercooler, and it cools the supply to normal.
Note: The owner's money for fuel and water flows quietly and peacefully down the drain. Therefore, solid fuel boilers are not suitable for places with mild winters and long off-season periods.
The forced circulation group in normal mode bypasses part of the supply to the return line so that its temperature does not fall below 65 degrees, see above. When the power supply is turned off, the thermal valve closes. The heating radiators receive as much water as they can handle in thermosiphon mode, just so that the rooms can be lived in. But the intercooler thermal valve opens completely (it is kept closed under voltage), and excess heat again carries the owner’s money down the drain.
Note: If the water goes out along with the electricity, the boiler needs to be extinguished immediately. When water flows out of tank 2, the system will boil.
Boilers with built-in overheating protection are 10-12% more expensive than conventional ones, but this is more than compensated by simplifying the piping and increasing the reliability of the boiler: here excess superheated water is poured into an open large-capacity expansion tank, see figure, from where it cools and flows into return. The system, except for circulation pump 7, is energy-independent and switches to thermosiphon mode smoothly, but with sudden warming, the fuel is still wasted, and the expansion tank must be installed in the attic.

As for pyrolysis boilers, we provide a typical wiring diagram for your reference only. All the same, its professional installation will cost only a fraction of the cost of the components. For reference: the heat accumulator alone for a 20 kW boiler costs about $5,000.

Note: Membrane expansion tanks, unlike open ones, are installed on the return line at its lowest point.
Chimneys for boilers
Chimneys of solid fuel boilers are calculated in general in the same way as stoves. General principle: a chimney that is too narrow will not provide the required draft. This is especially dangerous for the boiler, because it is heated continuously and fumes can occur at night. A chimney that is too wide leads to “whistle”: cold air descends through it into the firebox, cooling the stove or register.
The boiler chimney must meet the following requirements: the distance from the ridge of the roof and between different chimneys is at least 1.5 mm, the lift above the ridge is also at least 1.5 m. Safe access to the chimney must be provided on the roof at any time of the year. There must be a cleanout door at every chimney break outside the boiler room, and every pipe passage through the ceilings must be thermally insulated. The upper end of the pipe must be equipped with an aerodynamic cap; for a boiler chimney, it is required, unlike for a stove. Also, a condensate collector is required for the boiler chimney.
In general, calculating a chimney for a boiler is somewhat simpler than for a stove, because The boiler chimney is not so tortuous; the heat exchanger is considered simply a lattice barrier. Therefore, it is possible to build generalized graphs for different design cases, for example. for a chimney with a horizontal section (burrow) of 2 m and a condensate collector 1.5 m deep, see fig.

Using such graphs, after accurate calculations using local data, you can estimate whether there was a gross error. If the calculated point is somewhere around its generalized curve, the calculation is correct. In extreme cases, you will have to extend or cut the pipe by 0.3-0.5 m.
Note: if, say, for a pipe 12 m high there is no curve for a power less than 9 kW, this does not mean that a 9 kW boiler cannot be operated with a shorter pipe. It’s just that for lower pipes a generalized calculation is no longer possible, and it is necessary to calculate exactly according to local data.
Video: example of construction of a shaft-type solid fuel boiler
conclusions
The depletion of energy resources and rising fuel prices have radically changed the approach to the design of household heating boilers. Now they, like industrial ones, are required to have high efficiency, low thermal inertia and the ability to quickly regulate power over a wide range.
In our time, heating boilers, according to the basic principles laid down in them, have finally diverged from stoves and were divided into groups for different climatic conditions. In particular, the considered Solid fuel boilers are suitable for areas with harsh climates and prolonged severe frosts. For places with a different climate, heating devices of other types will be preferable.
At dachas and country houses it is impossible to do without autonomous heating systems based on boilers of various types. We must pay tribute to the manufacturers who offer efficient models with automation and a wide range of options. But for heating small country houses or greenhouses, installing expensive equipment is not practical, since making a heating boiler yourself will be cheaper. According to the main characteristics, it will be no worse than the factory models.
The choice of the type of homemade heating boiler depends on what fuel it will run on. Hence the classification:
- Electric heating boilers are not subject to high safety requirements. The design consists of a container, which can be easily made from a piece of pipe with a diameter larger than that of the supply pipes of the heating system. Heating elements are installed inside. Despite the ease of manufacture, such a heating boiler is not economically profitable, since the price of electricity is high. Therefore, this option is chosen for periodic heating of small country houses.
- Gas boilers have high efficiency and low fuel prices. However, due to the explosiveness of the gas, the requirements even for factory models are very high. Therefore, obtaining permission to install and operate a homemade heating boiler is practically impossible, and theoretically when installed in a basement.
- There is nothing complicated about making an oil-fuel boiler with your own hands. But for normal operation, you will have to install a container for storing fuel oil or diesel fuel and lay an insulated pipeline from it. The price of the burner and the difficulty of setting it up may discourage the desire to make such a boiler. Moreover, you will have to negotiate with the fire inspectorate to obtain permission for installation.
- Most often, a solid fuel heating boiler is installed to heat a private home. It is heated with wood, coal, peat, and oil shale. For homemade boilers of this type, the outlet temperature reaches 120 - 150 ⁰C.
Design of solid fuel and pyrolysis boiler
A traditional heating boiler for solid fuel works like a regular stove. It is assembled from two steel or cast iron containers inserted into one another. In the inner (furnace) firewood is burned, in the outer (tank) water is heated. The structure consists of the following parts:
- fireboxes with a door;
- grate;
- ash pan with door;
- soot collector;
- chimney;
- gate valve;
- pipes for connecting the supply and return pipelines of the heating system;
- legs;
- covers for closing the heating tank.
Outside air enters the firebox through the ash pan and grates. The intensity of combustion is regulated by the size of the door opening. Craving can be natural or forced. A correctly calculated and constructed heating boiler has an efficiency of up to 79%.
Advantages of classic solid fuel boilers:
- low fuel cost;
- does not require electricity to operate;
- fuel versatility;
- possibility of burning wood waste.
But when choosing this type of boiler, you should also take into account the disadvantages:
- one load of fuel is enough for a maximum of 6 hours;
- space is required to store fuel reserves;
- difficulty of maintenance, since combustion products will have to be removed regularly;
- solid fuel combustion is inertial, so difficulties arise with regulation.

Pyrolysis boilers for heating differ in their operating principle from the classic version in that not only the fuel burns, but also the gases released from it. The structure consists of the following parts:
- afterburning chambers with a built-in nozzle;
- gasification chamber;
- air supply systems;
- chimney system with throttle valve;
- heat exchanger;
- water circulation systems;
- temperature sensor and pressure gauge;
- safety valve.
To light the boiler, the gasification chamber is filled with firewood through the top door. After igniting the kindling, with the throttle open, a fan is started on the chimney. When the wood gets hot, close the door and close the throttle. Due to a decrease in the amount of supplied air, the wood begins to smolder at a temperature sufficient to start the pyrolysis reaction. The released gases, after passing through the nozzle, are mixed with secondary air in the combustion chamber, ignite, heating up to a temperature of 1100⁰C, and are sent to the heat exchanger.
On a boiler without a smoke exhauster, before adding firewood, open the throttle on the chimney and wait for some time necessary to remove the pyrolysis gas. After adding fuel, closing the door and throttle valve, the boiler continues to operate normally.
Compared to conventional heating boilers, pyrolysis boilers have many advantages:
- due to complete combustion there is no need for frequent cleaning of the ash pan and flues;
- ease of control of combustion intensity;
- duration of operation without adding fuel from 5 hours to several days;
- possibility of burning unchopped wood;
- using scraps from fiberboard, chipboard, MDF and plywood as fuel;
- In pyrolysis heating boilers, the content of harmful compounds in the smoke is 3 times less.
However, there are also disadvantages:
- Since the fan or exhauster runs on electricity, an uninterruptible power supply may be required.
- When using fuel with a moisture content above 20%, efficiency decreases.
- At low loads, failures are possible, which cause an increase in tar deposits in the gas ducts. To normalize the operation of the boiler, heat accumulators are installed into which excess heat is removed.
- To prevent the appearance of condensation on the walls of the heat exchanger, which accelerates the corrosion process, the water temperature in the heating return line must be at least 60⁰C.
- Due to the high material consumption, costs are 2 times higher than for conventional boilers.
A traditional heating boiler for solid fuel works like a regular stove. Pyrolysis boilers for heating differ in their operating principle from the classic version in that not only the fuel burns, but also the gases released from it.
DIY pyrolysis boiler for heating
If you weld a heating boiler at an amateur level, then emergency situations during operation are guaranteed. Therefore, it is better not to take on a job without good skills.
Calculation of boiler power and size
Making a heating boiler with your own hands begins with determining the dimensions, which depend on the amount of power sufficient for heating. When calculating, we assume that 1 kW of power is needed per 10 m² of heated area. It is easy to calculate that heating a house with an area of 300 m² requires a boiler with a capacity of at least 30 kW. To compensate for heat loss, a small reserve is needed.
It is unlikely that it will be possible to correctly design a pyrolysis heating boiler from scratch without knowledge of heating engineering. Therefore, it is better to find a ready-made drawing on the Internet for the required power. It is desirable that the service life of the unit made according to this project is not 1 year. If necessary, you can contact the author to clarify unclear points.
Required tools and materials
To work you need to stock up on the following tools:
- electric drill and drills;
- grinder with circles;
- gas cutter for cutting large holes;
- a set of locksmith tools.
And also materials:
- sheet steel 5 mm thick for the manufacture of chambers and 4 mm for the outer casing;
- a round pipe 57x3.5 for the heat exchanger and 159x4.5 for the hog (horizontal section of the chimney at the outlet of the boiler);
- fireclay bricks;
- round pipe 32x4.5;
- corrugated pipe 80x30x2 and 80x40x2;
- steel strip 30x4 mm;
- fan;
- thermometer and pressure gauge.
The amount of materials is calculated according to the drawing.
Manufacturing process
To save time, it is advisable to cut sheet metal blanks using a guillotine, since it is difficult to make a perfect cut with a grinder. This service is provided to customers at metal depots. Make a homemade heating boiler in the following order:
- The gas and combustion chambers are welded from the blanks.
- Air ducts made of corrugated pipe 60x30x2 with pre-drilled holes with a diameter of 10 mm are welded to the side walls of the gas chamber. A cutout is made at the back for the chimney.
- A tube is brought into the combustion chamber through which secondary air will be supplied. It is connected to the front side of the boiler with a 20x20 profile.
- The heat exchanger is made from two blanks, in which 2 rows of holes are cut out for gas outlet pipes with a diameter of 57 mm. After cutting to size and placing them in place, they are scalded.
- The finished heat exchanger is installed in place.
- They make and install a chimney throttle valve.
- Weld the front wall of the chambers with pre-made holes for pipes through which primary and secondary air will be supplied.
- The back wall and bur are welded to the place where the gas duct exits and the throttle is installed.
- After cleaning the welds, the inner box is ready.
- To secure the outer casing, sections of corners with a 25 mm flange are welded to the frame.
- On the casing in the places where the corners are installed, holes with a diameter of 10 - 12 mm are drilled.
- Through the holes, the sheathing is welded to the corners on all sides of the box, except the top.
- To check the tightness of the joints, plug all the holes and pour water through the top. Leak locations are marked with chalk.
- The air dampers are adjusted with threaded studs. Then the air holes are covered with a casing with an air duct made of corrugated pipe.
- They make and hang doors on the cells. They are lined with cast iron plates or fireclay bricks.
- The bottom of the gas chamber is lined with sawn bricks.
- To attach the fan, a flange is welded to the end of the duct pipe.
- The lining of the combustion chamber is made from fireclay bricks.
- To improve heat transfer and ease of cleaning, it is recommended to install swirlers (turbolizers) in the gas ducts.
- The tightness of the boiler is checked with a pressure of 4 bar, which is created by the pressure tester after filling with water. If the pressure does not drop within half an hour, the boiler is ready for operation. Otherwise, you need to look for a leak.
- To prevent emergency situations, a safety group is installed on the supply pipeline of the heating system, consisting of a pressure gauge, safety valve, and air vent.
- If desired, it is easy to equip a pyrolysis boiler with an automatic control system.
Connection and commissioning
Before starting, the heating boiler is connected to the external chimney and filled with water. To control its temperature, be sure to install a thermometer. Commissioning of the boiler is carried out in the following sequence:
- Connect the power cable to the fan and check the quality of its operation. The air dampers should be in the middle position.
- They put some paper into the gas chamber, a few sticks on top, and close the door.
- The throttle on the chimney is opened all the way, the fan is started, and the paper is set on fire.
- After the fire has ignited, the throttle is closed.
- The ignition of pyrolysis gases is monitored through the bottom door. If the torch does not light, reduce the amount of air supplied to the gasification compartment, and increase it to the combustion chamber.
- When the torch lights up, adjust the intensity of the flame, using air dampers to achieve a white-yellow color.
- After closing the door, measure the time until the water boils. At a temperature of 100⁰C the fan is stopped. The torch must go out.
We make a boiler from a pipe using solid fuel
It doesn’t take much time to make a boiler from a pipe with your own hands. Unlike a rectangular structure made of sheet steel, this option is more reliable, as it is assembled with fewer welded joints.
What you need for making
Before getting started, you need to stock up on the necessary tools:
- welding machine and electrodes;
- gas cutter;
- grinder;
- a set of locksmith tools.
And material:
- a piece of pipe with a diameter of 425 mm for the body, as well as 100 and 25 mm;
- sheet steel 4 mm thick;
- two 25 mm pipes;
- hinges for hanging doors;
- corner 25 mm;
- reinforcing bars with a diameter of 8 mm.
Step-by-step manufacturing process
First, prepare the parts from which the pipe boiler will be assembled:
- A piece 1 - 1.2 m long is cut from a pipe with a diameter of 425 mm. This will be the body of a vertical heating boiler.
- Two rectangular holes are cut out on the pipe. For a firebox measuring 200x100 mm, for a blower 200x30 mm at a distance of 50 mm from each other. Doors are made from the cut pieces. The distance from the bottom edge of the body to the blower is 50 - 70 mm.
- On the side of the upper part of the body, 2 holes with a diameter of 25 mm are cut one below the other. The lower one is at a distance of 150 mm from the firebox door for the return pipe, and the upper one is 50 mm from the top of the housing for supplying the heating system.
- 2 circles with a diameter of 425 mm are cut out of sheet steel for the housing covers and 1 circle with a diameter of 412 mm for the partition between the firebox and the tank.
- Holes are made in the top cover and partition for the chimney, which is made from a 100 mm pipe.
- The legs are made from pipe 25.
- The grate in the form of a grate is welded from reinforcing bars.
When all the parts are ready, begin assembly:
- The chimney is welded to the partition and installed on reinforcement supports secured inside the body at a distance of 300 - 350 mm from the firebox. Then they are secured by welding on both sides.
- A top cap is placed on the end of the chimney. Both joints are boiled.
- A grate is inserted from the bottom of the body. Then the pieces of corner 25 on which it will stand are welded.
- The bottom cover is welded, and legs 50 mm high are welded to it.
- The hinges are welded, the doors of the blower and firebox are hung.
Connection and first kindling
The finished heating boiler is checked for leaks. To do this, install a plug on the lower pipe. Water is poured through the top. If there are no leaks, the boiler is connected to the heating system.
It is better to vent the chimney outside strictly vertically. If this is not possible, it is mounted with a minimum number of bends. Horizontal sections are installed with a slope of at least 0.1% of the length.
For the first kindling, a small amount of firewood or coal is enough. Otherwise, with a sharp increase in temperature, tar will begin to deposit on the walls of the chimney. Therefore, due to a decrease in passage, traction will become worse.
To ensure that a sufficient amount of air enters the firebox, adjust the position of the blower door. A slide valve, which you can buy or make yourself, is more convenient for this purpose.
Self-welded heating boilers are not recommended for installation in residential premises, since, unlike factory models, they do not have a guarantee of safe operation. In the event of an emergency, you will have to bear the consequences yourself. But even when installed in a separate room, fire safety rules must be strictly observed.
In addition to purchasing heating equipment presented on the market by domestic or global manufacturers, there is always the opportunity to make a heating boiler with your own hands, the drawings of which can be freely found on the Internet. At the same time, you can save on a whole list of options that your heating system can do without. All you need for this is knowledge of the structure and operating principle of the type of boiler you have chosen, materials, tools and practical skills with them.
Main types of heating boilers
If desired, you can make almost any type of heating boiler. The main thing here is to choose the right one, and for this you need to know the main advantages and disadvantages of the most common types of heating equipment. So, heating boilers are:
- Gas. It is extremely undesirable to manufacture this type of boiler on your own - gas equipment is subject to technical requirements that you are unlikely to be able to fulfill in a makeshift environment.
- Electrical. The fairly high popularity of boilers in this category is explained by their simple design and relatively low safety requirements during operation and installation.
Important! The main disadvantage of electric boilers is the high price of electricity. As a result, such equipment is usually used to provide periodic heating, for example, in a garage or cottage.
- Liquid fuel. The design of such boilers is not very complicated. However, the intricacies and cost of the injectors that supply fuel to the combustion chamber will make anyone think twice before starting to build a heating device that runs on diesel or fuel oil.
- Solid fuel. Representatives of this type of heating equipment are optimally suited for both private homes and various industrial or commercial facilities. Versatility in use and high efficiency provide such boilers with the highest demand on the market.
Important! According to the principle of operation, solid fuel boilers are divided into pyrolysis, wood, pellet and long-burning. Long-burning boilers are the most popular for DIY production, while pellet and pyrolysis boilers are used much less frequently due to the high cost of individual elements.
What does the design depend on?
The exact design of the heating boiler may be influenced by certain conditions:
- Type of fuel.
- Availability and cost of materials.
- Coolant circulation method.
Materials for assembly:
- Stainless heat-resistant steel shows the greatest durability. However, it is precisely this that has the highest cost, and its processing is a rather complex task that cannot be dealt with without special equipment. The same can be said about cast iron, which, however, costs much less than stainless steel.
Important! Traditionally, sheet steel with a thickness of 4 mm or more is used for the manufacture of heating boilers - this option is relatively easy to process and, most importantly, is durable and quite reliable.
- To ensure natural circulation of the coolant, it is necessary to use heating circuits and connecting fittings of large diameter, and the storage tank should be located at a height. When this is not possible, you will have to use a circulation pump - it will make it possible to reduce the diameter of the pipes. However, the pumping system of a heating boiler is energy-dependent, which should be taken into account when choosing the design of the device, as well as its functionality.
Important! The pipes with which your boiler will be equipped must have a diameter of at least 32 mm - a thick-walled steel pipe can be used for manufacturing. The heating circuit must be made of galvanized steel, not forgetting to seal the threaded connections.
Design features of solid fuel boilers
The cheapest option for making a heating boiler with your own hands is a wood-burning boiler. Structurally, such a device consists of two containers, which are placed one inside the other. The inner one acts as a firebox, and the outer one acts as a heating tank.
Important! The design of a wood-burning boiler is quite simple, and it can work not only with wood, but also with some other types of solid fuel.
The wood boiler design includes the following:
- Steel firebox (with door).
- Firebox grates.
- Ash pan (with door).
- Chimney.
- Soot collector.
- Inlet and outlet pipes.
- Gate valve.
- Cast iron lid.
- Legs.
Important! The main disadvantage of a wooden boiler is low efficiency, that is, too much fuel consumption or a constant lack of heat in the house.
Design features of pyrolysis boilers
Pyrolysis boilers are more expensive to manufacture; they have two combustion chambers - for pyrolysis gas and for fuel, and some of their elements themselves are not cheap. Nevertheless, this equipment is in considerable demand due to its cost-effectiveness - it pays for itself in just 3-4 seasons.
The classic scheme of a pyrolysis boiler includes the following:
- Combustion chamber with nozzle.
- Gasification chamber.
- Chimney system.
- Air supply system.
- Water heat exchanger.
- Loading chamber.
- Pressure and temperature sensors.
- Coolant circulation system.
- Regulator valve
Design features of pellet boilers
Pellet boilers were invented at the end of the 20th century. They operate on pressed sawdust, and their main principle of operation is the transfer of heat from the gas released from the combustion of the latter, which heats the coolant in the heat exchanger.
The design of a pellet boiler includes the following:
- Frame.
- Heat exchanger with water circuit.
- Combustion chamber with air window and cleaning door.
- Thermal insulation gasket.
- Smoke eliminator.
- Automatic control and monitoring.
Important! In pellet-type boilers, it is best to use heat exchangers made of cast iron: they have a higher heat transfer rate and are not subject to corrosion.
Manufacturing of an electric boiler
Making a heating boiler with your own hands is a responsible task. The main element of an electric heating device is a thermoelectric heater (TEH), which is necessary to convert electricity into heat.
Important! The body of such a unit can be made of any material, and the components that are needed for its operation - sensors, regulators - can be purchased at any specialized store.
The design of an electric boiler consists of the following elements:
- Expansion tank.
- Safety valve.
- Circulation pump.
- Filtration unit.

The coolant in the system is able to circulate both naturally, for which it is necessary to provide a height difference between the tank and the boiler radiators, and forcedly, using a pump. The simplest option for an electric boiler is to install a heating element in the heating system. If this design is not suitable, then you can make an electric boiler with a removable pipe - this will allow you to quickly get to the heating element if replacement or repair is necessary.
The most optimal solution for heating, for example, a small cottage is a separately located small electric boiler. The pipe of such a unit will have a diameter of approximately 220 mm, and the body length will be no more than half a meter, which makes it possible to install it almost anywhere (of course, taking into account safety rules).
Important! The body of the electric boiler must be sealed. It is equipped with a hole for the heated coolant to enter the heating system and a pipe for supplying cooled water back.
Alternative options for self-construction
In addition to electric and solid fuel boilers, a number of other alternative heating devices are also suitable for self-production, for example:
- Induction - are transformers that consist of a primary and secondary winding. In a boiler of this type, electricity on the external winding is converted into an eddy current, and the created magnetic field is transferred to the internal winding, which transfers energy to the coolant.
- Condensing - retain the thermal energy of condensate, due to which they are considered more efficient than solid fuel and gas. Steam condensation in the heat exchanger occurs with a special design, which provides such boilers with an approximately 20% efficiency advantage compared to traditional gas equipment.
- Liquid fuel - evaporate waste and then burn its vapors. The energy thus obtained is sent to a heat exchanger, which heats the heating agent of the heating system. Such equipment has two significant drawbacks: a large amount of emissions into the atmosphere and low efficiency.
- Combined - universally applicable equipment. But to design it yourself will require skill, as well as excellent knowledge of the operating principles of various types of heating equipment. Individual elements of such devices can be quite expensive, but in general, combined types of boilers can pay for themselves in just 5-6 seasons.
Important! When manufacturing a heating unit of any type, you must be guided by all the requirements of safety rules and current standards in relation to the category of equipment you have chosen.
Making a heating boiler yourself is not as simple as it is written on many websites. A person who decides to make a boiler with his own hands must have certain qualifications and skills, have the necessary tools and materials, and also be able to create homemade drawings for heating boilers, according to which the product will be manufactured. The most complex technical structures on Earth have been created by human hands, so it is not surprising that home-made heating boilers are much better in their technical data than factory products.
 The enterprise is created in order to make a profit, therefore a product design is developed that has a minimum cost for the given technical parameters. But for self-production, steel of higher quality and thickness is most often chosen. Usually no one saves and purchases high-quality fittings, fittings and pumps. And for the heating boiler you create with your own hands, the drawings are either of already tested models, or your own unique ones are being developed.
The enterprise is created in order to make a profit, therefore a product design is developed that has a minimum cost for the given technical parameters. But for self-production, steel of higher quality and thickness is most often chosen. Usually no one saves and purchases high-quality fittings, fittings and pumps. And for the heating boiler you create with your own hands, the drawings are either of already tested models, or your own unique ones are being developed.
 Having the skills to work with metal, having the necessary material and tools, it is easiest to make homemade electric boilers - electrode or heating elements. If a heating element is used as an electricity converter, then you need to make or select a steel housing in which it will be installed. All other components - regulators, sensors, thermostat, pump - are purchased separately in specialized stores. Electric boilers can be used in closed or open heating systems.
Having the skills to work with metal, having the necessary material and tools, it is easiest to make homemade electric boilers - electrode or heating elements. If a heating element is used as an electricity converter, then you need to make or select a steel housing in which it will be installed. All other components - regulators, sensors, thermostat, pump - are purchased separately in specialized stores. Electric boilers can be used in closed or open heating systems.
What is needed and how to make a 220V electric heating boiler with your own hands, efficient and reliable?
 You need a steel container in which one or more heating elements are placed in accordance with the drawings or sketches for the product being created. Even at the stage of the project for do-it-yourself heating boilers, the drawings should provide for the possibility of quickly and easily replacing a burnt heating element. For example, the body can be made of a steel pipe with a diameter of 220 mm with a body length of about 0.5 m. Flanges with supply and return pipes and seats in which heating elements are installed are welded to the ends of the pipe. , expansion tank and pressure sensor are connected to the return line.
You need a steel container in which one or more heating elements are placed in accordance with the drawings or sketches for the product being created. Even at the stage of the project for do-it-yourself heating boilers, the drawings should provide for the possibility of quickly and easily replacing a burnt heating element. For example, the body can be made of a steel pipe with a diameter of 220 mm with a body length of about 0.5 m. Flanges with supply and return pipes and seats in which heating elements are installed are welded to the ends of the pipe. , expansion tank and pressure sensor are connected to the return line.
Features of power supply of electric boilers
 Heating elements consume significant power, usually more than 3 kW. Therefore, for electric boilers you need to create a separate power supply line. For units with a power of up to 6 kW, a single-phase network is used, and for higher power values, a three-phase network is required. If you equip a homemade heating boiler with a heating element with a thermostat and connect it through RCD protection, then this is an ideal option. When installing conventional heating elements, the thermostat is purchased and installed separately.
Heating elements consume significant power, usually more than 3 kW. Therefore, for electric boilers you need to create a separate power supply line. For units with a power of up to 6 kW, a single-phase network is used, and for higher power values, a three-phase network is required. If you equip a homemade heating boiler with a heating element with a thermostat and connect it through RCD protection, then this is an ideal option. When installing conventional heating elements, the thermostat is purchased and installed separately.
Electrode heating boilers
 Boilers of this type impress with their extreme simplicity. It is a container in which an electrode is installed; the second electrode is the boiler body. Two pipes are welded into the container - supply and return, through which the electrode boiler is connected to the heating system. The efficiency of electrode boilers is close, like that of other types of electric boilers, to 100% and its real value is 98%. The famous Scorpion electrode boiler is the subject of heated debate. Opinions are extremely varied, from excessive admiration to complete denial of use for heating circuits.
Boilers of this type impress with their extreme simplicity. It is a container in which an electrode is installed; the second electrode is the boiler body. Two pipes are welded into the container - supply and return, through which the electrode boiler is connected to the heating system. The efficiency of electrode boilers is close, like that of other types of electric boilers, to 100% and its real value is 98%. The famous Scorpion electrode boiler is the subject of heated debate. Opinions are extremely varied, from excessive admiration to complete denial of use for heating circuits.
 It is believed that electrode boilers were designed for heating submarines. Indeed, the manufacture of heating boilers requires a minimum of materials, sea water with dissolved salts is an excellent coolant, and the hull of the submarine, to which the heating system is connected, is an ideal grounding. At first glance, this is an excellent heating circuit, but can it be used for heating homes and how to make an electric heating boiler with your own hands, repeating the design of the Scorpio boiler?
It is believed that electrode boilers were designed for heating submarines. Indeed, the manufacture of heating boilers requires a minimum of materials, sea water with dissolved salts is an excellent coolant, and the hull of the submarine, to which the heating system is connected, is an ideal grounding. At first glance, this is an excellent heating circuit, but can it be used for heating homes and how to make an electric heating boiler with your own hands, repeating the design of the Scorpio boiler?
Electrode boiler Scorpio
 In electrode boilers, the coolant heats the current passing between the two electrodes of the boiler. If distilled water is poured into the system, the electrode boiler will not work. There is a special salt solution for sale for electrode boilers with a specific conductivity of about 150 ohm/cm. The design of the unit is so simple that making a Scorpio electric boiler with your own hands, if you have the necessary skills, is quite simple.
In electrode boilers, the coolant heats the current passing between the two electrodes of the boiler. If distilled water is poured into the system, the electrode boiler will not work. There is a special salt solution for sale for electrode boilers with a specific conductivity of about 150 ohm/cm. The design of the unit is so simple that making a Scorpio electric boiler with your own hands, if you have the necessary skills, is quite simple.
The boiler is based on a steel pipe with a diameter of up to 100 mm and a length of up to 300 mm.
Two pipes are welded to this pipe for connection to the heating system. Inside the device there is an electrode isolated from the body. The boiler body plays the role of a second electrode; the neutral wire and protective grounding are connected to it.
Disadvantages of electrode boilers
 The main disadvantage of electrode boilers is the need to use saline solutions, which adversely affect radiators and heating pipelines. Within a few years, the heating system may require a complete replacement of radiators, especially aluminum ones (more about which you will read), and piping. Circulation pumps that are designed to work with antifreeze or clean water are at great risk. The second huge drawback is that electrode boilers require ideal protective grounding of the housing, otherwise they pose a huge risk of electric shock. It is prohibited to sell and install such equipment in foreign countries!
The main disadvantage of electrode boilers is the need to use saline solutions, which adversely affect radiators and heating pipelines. Within a few years, the heating system may require a complete replacement of radiators, especially aluminum ones (more about which you will read), and piping. Circulation pumps that are designed to work with antifreeze or clean water are at great risk. The second huge drawback is that electrode boilers require ideal protective grounding of the housing, otherwise they pose a huge risk of electric shock. It is prohibited to sell and install such equipment in foreign countries!
Homemade solid fuel heating boilers
Due to rising prices for gas and electricity, the demand for solid fuel boilers is growing, and their prices are rising accordingly. The alternative is, because they will cost less, and will work no worse than factory products.
It is impossible to make a cast iron firebox at home, so steel is used for manufacturing.
 If possible, it is better to use heat-resistant alloy steel (stainless steel) with a thickness of at least 5 mm. There is no point in saving on metal, because the boiler is made for yourself, for many years. You can use ready-made drawings as a basis or make them yourself.
If possible, it is better to use heat-resistant alloy steel (stainless steel) with a thickness of at least 5 mm. There is no point in saving on metal, because the boiler is made for yourself, for many years. You can use ready-made drawings as a basis or make them yourself.
Features of manufacturing gas boilers
 Theoretically, making a gas heating boiler with your own hands is not particularly difficult for people who know how to work with metal and have the necessary skills and tools. Gas boilers are classified as high-risk products, therefore
Theoretically, making a gas heating boiler with your own hands is not particularly difficult for people who know how to work with metal and have the necessary skills and tools. Gas boilers are classified as high-risk products, therefore
homemade gas heating boilers must obtain permission for installation from the gas service, which requires a product certificate.
 It should be borne in mind that obtaining a certificate is quite expensive and the slightest deviation from established norms and rules leads to refusal. Is it worth the risk? In addition, modern SNIiP prohibits the manufacture of gas-fired heating boilers with your own hands!
It should be borne in mind that obtaining a certificate is quite expensive and the slightest deviation from established norms and rules leads to refusal. Is it worth the risk? In addition, modern SNIiP prohibits the manufacture of gas-fired heating boilers with your own hands!