Open mdf program. Programs for cutting chipboard
Sheet metal cutting software FieryCutincludes the full range of functions of sheet cutting technology on any CNC cutting equipment. Automatic optimal cutting of metal reduces the cost of raw materials and greatly increases the productivity of the technologist. The program comes with a post-processor for any CNC cutting equipment. Thus, you can connect the equipment, even in the absence of experienced specialists. We also implement additional requirements specific to a given organization or equipment.
The user creates only the contours of the parts. Togeometry control, economical cutting of metal sheets andthe formation of control programs for CNC machines is performed automatically using FieryCut.
The FieryCut CAD/CAM system consists of three modules:
- Creation of part geometry;
- Cutting the sheet (optimal placement of the contours of parts on the sheet);
- Control program generation.
Part geometry
FieryCut, unlike other similar applications, includes geometry control, which speeds up the search for errors. Using the Part Geometry module, the user creates contours details ( blanks) based on the geometry created in AutiCAD, including segments, polylines, arcs and circles.- Automatic creation of workpiece contours from segments, arcs, circles and polylines;
- Support for unlimited nesting of contours;
- Support for open paths and text;
- Automatic control of geometry in the process of creating contours, facilitating the correction of errors;
- Calculation of the surface area and mass of workpieces;
- Import of geometry in DWG/DXF format;
- Saving contour information in a DWG file.
Sheet cutting
FieryCut realizes automatic sheet metal nesting with high material utilization (CMM).The work begins with the formation of a task in which the user specifies the dimensions of the sheets or calls a DWG file of arbitrary business waste, and also generates a list of parts.
O The main functions of the "Sheet cutting" module:
- Automatic placement of parts on sheets of any shape with a given distance between the contours;
- Placing Parts Inside Holes and Slots of Other Parts, If Option Purchased"Figure cutting" (see figure on the right);
- Placement priority accounting;
- Accounting for permission to turn, including setting the allowable angle of turn;
- Editing the placement of parts (transfer, rotation, addition, removal);
- Formation of a report on the placed parts and KIM for each sheet.
Instruction (PDF format) )
|
FieryCut packages |
|||||
| FieryCut-C | FieryCut-R | FieryCut-RC | FieryCut-A | FieryCut-Full | |
| Part geometry | |||||
| Rectangular cutting | |||||
| Figure cutting | |||||
| NC program generation | |||||
| Cost for the CIS, (rub.) | |||||
LLC "Hitek" (Yaroslavl) is the only distributor of FieryCut in Russia.
Cutting chart - is a documentation that displays which parts need to be cut from a chipboard sheet. But, in fact, it is possible not only to cut chipboard, but also any sheet material.
With the help of nesting, you can see how you can lay out the parts on the sheet. The map also contains information about the remains that will be as a result of cutting.
In the end, the advantage of cutting is to display the amount of material that will be required to create furniture.
You can also cut chipboard in the company where you will buy materials, but our task is to create cabinet furniture at home with minimization of costs, and it will not be difficult to make it yourself, even for a beginner.
To create a map, we will use the Cutting 2 program (cutting). You can download it for free at the end of the lesson.
The program interface looks like this:
In the "Materials" field, you must specify the parameters of the chipboard sheet, or if you have leftovers that you plan to cut, then the size of the leftovers. As for chipboard size, I use sheets from the manufacturer Swisspan, whose dimensions are 2750 * 1830 mm (for large sheets) and 2440 * 1830 mm (for small ones).
Also note that in the settings of the chipboard sheet, it is necessary to set the values \u200b\u200bof “Sheet cut”, since the sheets initially have chips.

If you plan to glue the PVC edge, or if you want to calculate how much paper edge is required for gluing, then you can also set it in the "Properties".
Hello, friends.
In this article, we will talk about one practical side of making furniture.
Having designed any furniture, you get its detailing, or, a list of all the parts necessary for its assembly.
And the next step will be the purchase of chipboard sheets, and cut them into these very parts you designed.
Here you can have two options:
Either you carry your detailing to where you will have chipboard (and, this is basically the same place where you will buy it), and they will do it for you according to your detailing, cut sheets of material into the necessary parts.
Or you will initially make a scheme according to which the sheet material will be processed.
Cutting cards - and there is that scheme for cutting a sheet (for example, the same chipboard) into the necessary parts.
Any such map always shows the presence of residues of the material used.
The same parts can be laid out on a sheet so that in one case, the size of the residues will be large, and in the other case, smaller.
Of course, large leftovers are always needed, since they can still do something.
Therefore, in the case when someone makes this documentation for you, then the size of your balances depends only on him.
And if you do it yourself, then you arrange the parts in such a way as to get the largest possible leftovers.
Of course, no one does it manually, as it is very laborious.
For these purposes, very good programs have long been invented.
 But, we will consider a simpler option: One original chipboard sheet, and detailing for it.
But, we will consider a simpler option: One original chipboard sheet, and detailing for it.
 Before calculating the details, in the original sheet, you can set the cut along the ends (in this case, 7 millimeters each).
Before calculating the details, in the original sheet, you can set the cut along the ends (in this case, 7 millimeters each).
 After that, by clicking on the "calculator" icon, the program will automatically arrange the details according to the specified sheet.
After that, by clicking on the "calculator" icon, the program will automatically arrange the details according to the specified sheet.
As you can see in the figure, even if some details did not fit into the sheet, they can be seen in the window below.
 In this window, the location of any parts can be changed at your discretion, rotate them around the axis (unless, of course, in the properties specified in the settings of the parts, this function is not blocked). In a word, do everything to get the largest possible balances.
In this window, the location of any parts can be changed at your discretion, rotate them around the axis (unless, of course, in the properties specified in the settings of the parts, this function is not blocked). In a word, do everything to get the largest possible balances.
When the details are laid out as needed, you can click on the view of this sheet.
 In this mode, the layout of all parts is shown, the total length of the cut, the areas of parts and residues, in a word, all the necessary information.
In this mode, the layout of all parts is shown, the total length of the cut, the areas of parts and residues, in a word, all the necessary information.
 After that, by clicking on the corresponding icon, all sheets with cutting, as well as a list of all parts, can be printed on the printer.
After that, by clicking on the corresponding icon, all sheets with cutting, as well as a list of all parts, can be printed on the printer.
 This will be your cutting map (furniture edge gluing is also marked on it, and sketches of non-standard (curvilinear, etc.) parts).
This will be your cutting map (furniture edge gluing is also marked on it, and sketches of non-standard (curvilinear, etc.) parts).
Thus, as you can see, it is quite easy to make the sheet cutting pattern yourself.
I think that the most ordinary furniture maker should be able to do this, since all this, in a sense, speaks of the level of his qualifications.
Well, on this I will “round off”, see you soon.
This article is the logical conclusion of a series of articles on independent design and calculation of furniture for the home.
Here I will talk about how to make economical cutting at home, point out all sorts of nuances and possible pitfalls that you should be prepared for when deciding to order chipboard cutting in furniture production.
FAQ or Frequently Asked Questions
1 - Why do the cutting yourself?- First of all, independent cutting of parts in a chipboard sheet is your savings.
The fact is that most furniture companies that cut chipboard sell boards by the piece. That is, if the parts you need do not fit on a chipboard sheet, and at least one piece ends up on the second plate, you have to pay for two full sheets of chipboard.
Agree, it is not very profitable to pay for two plates, if in fact it turns out that only a sheet of chipboard and a couple of small details go to the closet or kitchen.
That is why, it is better to make a cut yourself at home, according to which you can order a cut in a furniture workshop.
2 - What should I do if, anyway, after cutting the chipboard, a large residue is obtained?- It's simple - take a fresh look at your apartment and house. You may need a small coffee table or bookshelves.
Use the rest wisely, think of some new decorative and functional elements for the interior and add them to your nesting.
Thus, the purchase of chipboard parts will turn from obviously unprofitable into very economical and thoughtful.
3 - What is the structure of chipboard? How to understand the expression of furniture makers - according to the structure or against the structure?- Pay attention to the colors of laminated chipboard, if there is a tree-like pattern in it, then it has a schematic representation of this very “structure”, namely, the structure of the tree bark, imitating a particular species (beech, ash, pine, oak, alder, cherry and others.)
Agree, furniture facades look rather stupid, on which the pattern (structure) is scattered - on one along, on the second across, then again along.
Therefore, before ordering chipboard in production, you must have on hand a list of parts written according to certain rules and sequence.
So, pay attention to how the laminated chipboard with a pattern looks like.
We see that the structure goes along the long side. And, if the details lie parallel to the depicted fibers, furniture makers will call such a detail “along the structure”, if perpendicular, then “against the structure”.

4 - How to correctly specify the dimensions in the list so that parts of the same type have the same structure pattern?- The first and most important thing is to determine the visible elements on which the structure must be located in the same direction.
For example, facades, cabinet sides, front plinth. But those parts that are located inside the cabinet (internal shelves, sides of drawers and the like) can be cut randomly from a chipboard sheet.
When specifying the dimensions for the furniture workshop, it is better to clarify in advance where you plan to cut the chipboard, which size of the part to indicate first.
In most furniture companies, the size of the part that goes along the structure, that is, along the pattern, is the first to indicate the size of the part.
And now carefully review the schematic sketch below - on it I tried to depict as clearly as possible how the parts will look with the sizes indicated by the structure and against the structure.

5 - What is the basing of a chipboard sheet? Why, when cutting chipboard parts on your own, indicate the size of the plate less than the actual one? - Indeed, knowing the standard dimensions of a chipboard sheet, when creating a cutting, it is necessary to take into account the basing of the sheet, which will definitely be done in the workshop before cutting the parts.
Usually, the edges of the slab contain some chips, bumps, perhaps even a slight swelling. Therefore, sawmills "base chipboard sheet" - cut 10-15 mm on each side. Based on this, you must also make a base, that is, take it as the correct size, for example, not 1830 x 2750 mm, but 1810 x 2730 mm.

6 - What is the width of the cut and what is it equal to?- The kerf width is the cutting width of the saw. The saw installed on the sawing machine has a thickness of 4 mm, which means that between the parts there will be a cut with a thickness of these same 4 mm.
That is, the actual size on which two parts 300 and 400 mm will be located is not 700 mm, but 300 + 400 + 4 = 704 mm. Each cut must also be taken into account when cutting.

Well, that's all, now you are prepared to proceed directly to the independent cutting of chipboard parts, which can be done in two ways - manually, using a ruler, leaflet, eraser, calculator and using a computer offline or online cutting program.
Manual cutting of chipboard parts: Step by step instructions
1 Draw on a sheet of paper, preferably on a scale, the dimensions of the plate. Remember to reduce it on each side by 10 mm.
2 Sort the list by the same type of required parts. For example, the sides of kitchen cabinets have the same dimensions - 500 x 712 mm.
There are quite a few of them, write out all such details separately. By the same principle, you continue sorting: the same width, the same structure, and so on.
3 Lay out on a sheet of chipboard first large parts and those that should have a similar structure. Don't forget about the saw blade width - 4 mm! This is where a calculator comes in handy.

4 Place the rest of the details. You can work out several options until you get the one that is ideal, as economical and profitable as possible.
Cutting details in a chipboard sheet using computer online and offline programs
On the Internet, in the public domain, there are many chipboard cutting programs that offer several cutting options at once.
Such programs can be searched for on specialized furniture forums or simply by typing into any search engine the query: "Chipboard cutting program for free."
The search will return three main options:
1 Download the cutting program to your computer - the most common and most convenient for beginners cutting program for chipboard - Cutting. Simple interface, clear layout and many options for sawing the sheet.
2 Create chipboard cutting online - here you don’t need to load your PC with programs that may not be useful in the future.
3 Cutting and ordering chipboard sawing online on the website of a furniture company is an ideal option if the production workshop is geographically convenient for you.
Thus, you will "kill two, or maybe more, birds with one stone" - choose chipboard on the website, which is available in the required quantity, make an economical cut, see the cost and immediately, sitting at home, order a chipboard cut in a furniture workshop.
I'll reiterate the important points...
Basic rules for cutting chipboard
- The size of the laminated chipboard sheet must be entered taking into account the basing of the plate.
- The cutting width of the saw is 4 mm.
- Details in the cutting must be made taking into account the structure.
If you have any questions - ask them right here, under the article. I'll try to answer promptly.
Also, if there are current furniture topics that you would like to read about, write about them in the comments. Perhaps this is what will serve as an impetus for writing the next article.
Always yours, Timur Denisov.
Download Cutting
Cutting 6.54.121 is an interesting and necessary program with the ability to build a cutting map for various industrial materials. For example, cutting chipboard, glass, plastic, roll materials and sheets.
The main "chips" of the program:
- Work begins in the application with the introduction of the concept of "Order". It is considered that this is a complex of parts with specified parameters of height and width. Details are set in a rectangular shape.
- You can specify the desired number of parts in the order. In this case, the program will give the optimal number of sheets to be purchased.
- It is possible to view the history of orders, change an already completed one, or repeat it with new parameters.
- For each individual element, it is possible to set a symbolic name, the number of these elements and the presence / absence of an edge (in particular, in the production of furniture panels).
- Along with standard sheets, it is possible to enter additional sheets and cut them next to the main ones.
- You can specify the amount of "business waste" for their subsequent use. This is possible under the condition of large, mass production.
- You can specify the amount of technological waste, for example, the consumption of material for sawing.
- When conducting settlement, it is possible to combine different orders from the same material. Thus, you can save on cutting.
- In the free cutting program, you can work with two types of edges.
- The cut is made by the guillotine method, that is, from edge to edge. All cuts are even, strictly vertical or horizontal.
- There are two ways to nest in the software: minimizing waste (maximum material utilization) and maximizing continuous trim (minimum waste plus maximum business trim).
- When cutting material in a roll, the program on the machine is able to choose the option for placing elements on the tape. All parts will be rectangular and of unknown height.
- It is possible to use the cutting program in network mode.
- There is no language barrier, as the program has been released in Russian.
- The interface is simple, in soothing colors, like any other graphics program.
- Operating systems for which the program is suitable: WindowsXP, WindowsVista, Windows7.

The program for cutting sheet and roll material is used in various technical and industrial productions, plants, factories, as well as in small enterprises. In domestic conditions, with the help of this program, you can make calculations for the construction of a garden or a bath, repairing an interior or facing a house. Cutting 6.54.121 will provide high-quality and fast calculation of the material. Most often, the application is used to calculate chipboard and glass.
Where can I download the program safely and for free.
Hurry up to download the program for free from Softldol.com. It is available via a direct link without registration and paid messages.
Version: 6.54.121
Program status: Shareware
The size: 3.5 Mb
Developer: Andrey Kusnetsov
System: Windows 7, 8, XP, Vista
Russian language: Yes
Download Nesting 6.54 free
First I used Cutting 2, then Cutting 3. They differ quite strongly. But I liked the Cutting 2 version better. The third version has additional features that, by and large, are not really needed for small-scale production. Cutting 2 still helps me to pre-calculate the amount of material and the length of the cut lines for large orders, such as the kitchen. To create the final cutting map, I use the Nowy Rozkrój program (Cut Optimiser or New Cut Manager) from the creators of the PRO100 program. . Both sites can be switched to Russian and read the description of the programs. And now I will describe the simple process of creating cutting maps. .
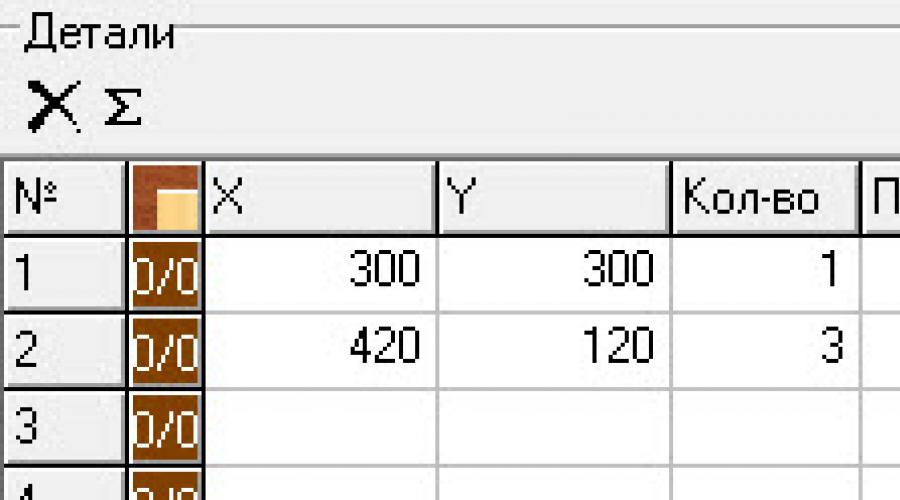
We open any project created by us in PRO100. Click on the Σ tab.
In the window that opens, a table will be displayed in which all elements of the project with their characteristics will be indicated. At the bottom of the window we find the Copy All tab.

We click on it. Now we can insert a table with our elements into the parts list in Cutting 2. But we only need elements of the base material, let's say 18 mm chipboard. Therefore, we open Excel and insert a list of PRO100 elements. Now select those lines in which the elements are not 18 mm and delete them. As a result, there remains a table consisting of 4 columns, in one of which there is only the number 18 in all cells. Select and delete this column. The remaining elements are selected and copied. We launch the Cutting 2 program. The parts table is on the right.

If it is not empty, click on the X icon above the right table and confirm clearing the list. Now we right-click on the first empty cell of the list and select the line Add from clipboard in the drop-down menu.

Click on the Execute Calculation icon.

The cutting map is ready. Can be printed and used. But I ran into some inconvenience. For example, the numbers are small, the cut lines are not clear enough.

The people who cut the material for me were unhappy with the need to use a magnifying glass. But for the preliminary calculation of the cost of the product, the program was ideal due to the transfer of parts from PRO100 to Cutting 2 described above.
Nowy Rozkroj's program is a better optimizer.

However, all part dimensions must be entered manually.

The program calculates several cutting options at once.

Depending on what is important to you, you choose your option. The option with a smaller total length of cut lines is more suitable for me, but someone needs an option with fewer trimmings (trash).
First, in the settings, I specify the cutting option without a strip,

which allows you to place more parts. After the first attempt at cutting, I see how much free space remains on the last sheet. If more than 30% is not occupied by details, then in the program parameters I indicate the horizontal cut option

and run the final calculation. The seller keeps the remaining horizontal stripe of the popular colors of the material, which reduces the cost of furniture. The nesting maps created by Nowy Rozkroj are detailed and clear enough, and the dimensions are displayed perfectly.

Cutting result may be different. For example, you made the optimal cutting with the option without a strip, and you got 3 sheets and 3 parts. This is especially important if the seller does not sell this color of the material in a strip, but only in a sheet. In this case, apply the following option:
When adding each part, uncheck the box in the Part properties table in the Structure position.
Then, looking at your project, go through the detailing and note the structure in the details, the structure on which can only be consistent with the design, i.e. other variations of the structure on these parts are not acceptable. If this method does not help, then reduce the dimensions of hidden parts, such as plinths and connecting strips, by 10 mm or more. But don't overdo it.
There is another important advantage of this program. If you marked an edge on one side of a part, it will not move from that side to the other when the part is rotated by the optimizer, which can happen in other programs. In the event that the end edge is paper, the dimensions of the parts remain the same as in the project, and if the PVC edge is 1-2 mm thick, then do not forget to subtract the thickness of the edge from the size of the adjacent side with the glued edge.
An example of nesting maps
At the beginning of the video, until the start of the Nowy Rozkrój program, do not pay attention. And then everything on the topic. A small technical hiccup.
If your sheet is, for example, 2800 by 2070, and the cut along the side is 10 mm, forgetting that 4 mm is needed for the cut, you specify the size of the part 2790 by 600 with an edge of 2790. As a result, the edge slides by 600. Pay attention to it's attention. I once did not check the card and gave it to work. Firstly, the guys suffered when they glued the edge on the 600 side, because. the part rested against the door of the workshop, I had to move the machine. No one thought that the distance from the machine to the wall of 2.5 m could ever be insufficient. And secondly, I had to pay for the edge to be glued on the long side, and at that moment I did not count on it. Therefore, be careful.
You can also cut sheet material manually, but it takes a lot of time and special skills. It is much easier to do this by using accompanying programs. They will help optimize the nesting map, offer other layout options and allow you to edit it yourself. In this article, we have selected for you a few representatives who do an excellent job.
Astra Nesting allows you to work with orders by importing their blanks from the catalog. There are only a few templates in the trial version, but their list will expand after purchasing a program license. The user manually forms a sheet and adds details to the project, after which the software automatically creates an optimized cutting map. It opens in the editor, where it is available for editing.

Astra S-Nesting
The next representative differs from the previous one in that it offers only a basic set of functions and tools. In addition, only pre-prepared parts of certain formats can be added. The nesting map will appear only after purchasing the full version of Astra S-Nesting. In addition, there are several types of reports that are generated automatically and can be printed immediately.

Plaz5
Plaz5 is outdated software, has not been supported by the developer for a long time, but this does not prevent it from performing its task with high quality. The program is quite easy to use, does not require any special knowledge or skills. The nesting map is created quite quickly, and the user only needs to specify the parameters of parts, sheets and design the map.

ORION
The last one on our list will be ORION. The program is implemented in the form of several tables, in which the necessary information is entered, and then the most optimized cutting map is created. Of the additional functions, there is only the ability to add an edge. ORION is distributed for a fee, and a trial version is available for download on the official website of the developers.

Cutting sheet material is a rather complicated and time-consuming process, but this is if you do not use special software. Thanks to the programs that we reviewed in this article, the process of drawing up a cutting map will not take much time, and the user is required to make a minimum amount of effort.
Automated production system PractiCAM™ is focused on the production of products for ventilation systems from sheet and rolled metal, as well as from pipe blanks. PractiCAM™ works with plasma and laser machines with numerical control (CNC), as well as with stamping, spiral and coordinate punching machines. The program has great functionality for cutting sheet metal, i.e. it is focused not only on the production of air ducts, but also flat parts, signboards, weather vanes, roof elements, etc.
The main advantages of the PractiCAM™ system:
 |
Creation of air ducts of any type, as well as any other elements from sheet and rolled metal, and pipe blanks |
| System Libraries PractiCAM™ very extensive and unparalleled. They contain over 4000 fittings and over 1600 parameterized flat parts. Despite this diversity, the system libraries PractiCAM™ are still increasing (every time you download a new version of our program, new items will be waiting for you). In addition to existing libraries, we can create as many different fittings, flat parts and other elements for you as you wish. We will make the parts you need and send them to you as soon as possible (as a rule, the development of a new part, depending on its complexity, takes from one to three working days). |
|
 |
Compatible with any equipment |
| System PractiCAM™ supports many models of plasma and laser CNC machines. It can also work with punch, scroll, jig punches, pipe cutters and barcode readers. If your machine model is not yet in our library, then we will write a postprocessor for you free of charge in the shortest possible time, which will connect our program with your equipment. | |
 |
Instant and accurate cost estimates |
| During your work, the system PractiCAM™ continuously creates an accurate estimate of the cost of all costs for the manufacture of parts. The full calculation takes into account the cost of the material, labor costs for the manufacture of parts, the cost of all fasteners (bolts, screws, tires, rivets, etc.), as well as the cost of various accessories (blades, rods, dampers, etc.). As an example, the American SMACNA tables are given, but you can create your own standard tables for accounting for labor costs in your enterprise, taking into account the specifics of your production. | |
 |
Export and import of information in common .dxf, dwg and .csv formats for communication with software products of 1C, Microsoft, Autodesk companies |
| All information about the spent metal, consumables and components contained in the system Practicam™, can be converted to a .csv file, which is supported by 1C: Accounting and Microsoft Excel. This makes it possible to calculate the cost of all your products using accounting programs. System PractiCAM™ can work with .dxf and .dwg files, which allows you to import drawings from AutoCAD and Compass programs, as well as export nesting plans, fitting patterns and flat parts to these programs. |
|
 |
Import orders from the program 1C: Accounting |
| In the 1C: Accounting program, you can create orders for cutting fittings, indicating the names of fittings, their quantity, the material from which they should be made, technological parameters, names of allowances, etc., and send them to the system PractiCAM™. After receiving the order, the system PractiCAM™ automatically finds the specified fittings in its libraries, applies the specified parameters to them and lays out the fitting patterns on metal sheets. After automatic laying, control commands for your equipment are generated, as well as various reports and labels. | |
 |
metal saving |
| It is possible to use the rest of the sheet metal, suitable for cutting out any products from them, and to maximize the use of the sheet area. For this, the "Warehouse" functional module has been added, which allows, after laying the main work parts on metal sheets, to automatically add flat parts from a pre-created list to an unused place. | |
 |
Possibility of automatic stacking of products using a combined cut |
| AT PractiCAM™ There are two options for automatic stacking of products: normal stacking and stacking with a combined cut for products that can be combined along one of the sides. | |
 |
Fully Russified |
| In addition to the Russian language, the system PractiCAM™ translated into English, French, Spanish, Chinese and Korean. | |
 |
Various types of allowances |
| Allowances (connectors, locks, joints, seams) and notches contained in a large number in the system libraries Practicam™, can be created in any geometric shape, fully parameterized and editable. The graphic editor provides ample opportunities for creating and editing allowances and notches. | |
 |
Report creation |
| System PractiCAM™ provides you with a wide range of standard report templates. In addition to this, you can create your own reporting forms in any convenient format and with any type of layout. The main thing is that in the report you can report any information contained in the system Practicam™. | |
 |
Create labels |
| Mark parts in the system PractiCAM™ easy and convenient. Various label templates are provided for your attention, but if they do not suit you, then you can create your own template. Add any information to your labels: your organization's logo, barcodes, 3D parts images, any part parameters you are interested in; edit these captions with any font style and size. You can make a label for any fitting and flat piece. | |
 |
Useful specifications |
| Specifications (SNiPs) of the system PractiCAM™ allow you to set all the features of your production standards when working with various products, allowing you to unify production, automate the input of products for manufacturing and reduce input errors, thereby increasing your productivity, and with it your profit. You can create your own rules for the production of products that are used in your enterprise. | |
 |
Availability of libraries of double wall fittings |
| In system PractiCAM™ there are libraries of double wall fittings. They are used in cases where it is necessary to increase the level of heat and noise insulation. For each double wall fitting, insulation can be cut to fit between its walls. | |
 |
Possibility of manual and automatic segmentation for large products |
| System PractiCAM™ allows you to segment (break into separate components) large-sized products that do not fit on a sheet of metal. You can set the segmentation rules for each product yourself or entrust this process to the program. |
Benefits of our technical support:
- Better product support — at the request of users, we develop and add new software modules, create new fittings and parametric flat parts (within 1-3 days, depending on the complexity of the product), add new ways to cut fittings to existing ones.
- Free training to work with the program.
- Regular update PractiCAM™— a new release comes out at least 1 time in 2 weeks.
- Development and addition of new labels and reports, placing on them the information required by the user.
A new version of the program is currently being developed PractiCAM™. Its main difference is that now the program is divided into many functional modules that can be turned on and off in various combinations, reducing or increasing the set of functions performed by the program. Depending on the number of included modules, the price of the program is formed. PractiCAM™ can still be purchased in its entirety with all its features, but it is also possible to buy either one of the standard program packages (each of which is a truncated version of the system PractiCAM™), or a standard package with additional options.
Standard packages PractiCAM™:
PractiCAM™ for generic parts.
- Use libraries of parametric flat (two-dimensional) parts, create flat parts using a graphical editor.
- Work with a graphical model of a part, set dimensions, material and thickness.
- Use multiple layers when creating a part.
- Import files with the extension .dxf, .dwg (AutoCAD systems, Compass, etc.).
- Apply automatic stacking of parts on metal sheets using various algorithms, including a combined cut.
- Lay parts on sheets of metal by hand.
-
at the exit).
PractiCAM™ for ventilation.
This package allows the user to:
- Use libraries of fittings (fittings).
- Work with a 3D graphical model of a fitting, set dimensions, allowances, material, and determine the fitting cutting method.
- Work with a library of fittings accessories, set flaps, stiffeners, ties, rotary blades.
- Use different marking recesses, automatically generate bending lines, create marking lines.
- Create a library of used materials indicating the thickness of the material and type (sheet, roll).
- Create a library of used allowances (connectors, locks, joints).
- Apply automatic stacking of product patterns on sheets of metal using various algorithms, including a combined cut.
- Lay patterns of products on sheets of metal manually.
- Based on the laying results, generate and print laying maps.
- Based on the laying results, automatically generate a sequence of control (CNC) commands for the cutter.
- Set the cutter parameters (table dimensions, table positioning and orientation, size and shape of the cut at the input and cut
at the exit). - Determine how control commands are sent to the cutter (via file or COM port).
- Automatically segment (cut into pieces) patterns of large size.
- Automatically add allowances when segmenting patterns.
- Create and edit seam allowances connecting segmented parts of patterns.
- Create tables to recalculate fitting section parameters and apply them when creating fittings.
- Import/export files with .pmx extension (PractiCAM™ program files).
PractiCAM™ Classic.
This package combines the "PractiCAM™ Generic Parts" and "PractiCAM™ Ventilation" packages and provides all the features listed for these packages.
The list of additional options (program capabilities) for packages is given in the table.
If you want to learn more about PractiCAM™, then we can conduct a demonstration of the program using Skype or TeamViewer, completely free of charge, at a convenient time for you, at the same time answering all your questions. Also, especially for your machine controller, at your request, we can write a post-processor and activate PractiCAM ™ for you for 1 month, completely free of charge, so that you can evaluate all its capabilities directly at work. All you need to do is call us or write a message to our e-mail, or leave your contact details by filling out the following form.
Economical linear cutting of materials (cutting of moldings) is relevant for many industries and in construction. This is sawing logs and boards in woodworking, cutting bars, reinforcing bars, angles, channels, pipes, I-beams into blanks ...
In the production of metal structures and mechanical engineering, transverse cutting of rolls with paper and fabric in the pulp and light industry.
Despite the apparent simplicity, the solution of linear cutting problems is not very easy, but worthwhile. The introduction of a scientific approach to cutting molded materials allows you to reduce the cost of them, sometimes by more than 10%! Read the article to the end and make sure these words are right.
The topic under consideration relates to linear programming problems. To solve such problems, scientists in the last 70 years have come up with several different methods.
Method of indices L.V. Kantorovich and V.A. Zalgallera, with a certain skill, allows you to effectively perform linear cutting "manually" without the use of computer technology. I recommend to curious readers to familiarize themselves with this method by reading the book of the above-named authors “Rational Cutting of Industrial Materials”.
The simplex method based on the ideas of L.V. Kantorovich, was described and developed in detail by a number of scientists from the USA in the middle of the 20th century. Add-in MS Excel "Search for a solution" (Solver) uses this algorithm. It is with this method thatexcelwe will solve the problem of linear cutting in this article.
Later, genetic, greedy and ant colony algorithms appeared and were developed. However, we will confine ourselves to listing them and get down to business, without climbing into the jungle of theories (although there, “in the wilds”, it is very interesting).
Let's turn on Excel and, using a simple example of cutting metal rods into parts, we will get acquainted with one of the ways to solve practical problems of linear cutting. Mathematicians often refer to this problem as the "cutting problem".
I did not invent the initial data for the example, but took it from the article by Pokrovsky M.A. "Minimizing the inevitable losses of materials in industrial production when cutting them into piece blanks" published in No. 5 (May 2015) of the electronic scientific and technical journal "Engineering Bulletin" published by FGBOU VPO "MSTU im. N.E. Bauman (link:engbul. bmstu. en/ doc/775784. html).
The goal that I pursued was to compare the results of solving the problem.
An example of solving the problem of linear cutting in MS Excel.
Let's agree that:
1. Billets are raw material in the form of bars, strips, rods, etc. the same length.
2. Details are elements that need to be obtained by cutting the original blanks into pieces.
3. The width of the saw, cut, rub is taken equal to zero.
The task:
To complete one of the orders, the procurement section must cut three standard sizes of parts on combined shears from identical bars-blanks with a length of 1500 mm:
151 pieces 330 mm long
206 pieces 270 mm long
163 pieces 190 mm long
It is required to find the optimal cutting plan that uses the minimum amount of material and, accordingly, gives the minimum amount of waste.
Initial data:
1. The length of the original blanks Lh in millimeters we write in the combined cell
D3E3F3: 1500
2. We assign numbers i all standard sizes of parts, starting from the longest and ending with the shortest in the cells
D4; E4; F4: 1; 2; 3
3. Part lengths Ldi in millimeters we write in
D5; E5; F5: 330; 270; 190
4. Number of details Ndi in pieces put into
D6; E6; F6: 151; 206; 163
5. We proceed to a very important stage - filling in the cutting options.
Must remember and understand 2 principles for doing this job.
1. Waste lengths must be less than the smallest part ( 0< lo j < Ldmin ).
2. We start “laying” parts into the workpiece with the largest parts and with the largest number of them, consistently moving in the direction of decreasing.
If there is no part size in the cutting option, then we leave the cell empty, we will not write zero to facilitate the visual perception of the table.
Cutting option No. 1:
An attempt to cut out 5 parts No. 1 from one blank is impossible, so we write in the cell
It is also impossible to add part No. 2 or part No. 3 to the nest, so we leave the cells empty
Cutting option No. 2:
We decrease the number of parts No. 1 by 1 from the previous version and write it in
We are trying to add 2 parts No. 2 - it doesn’t work, so we add to
It remains possible to supplement the cutting with detail No. 3. We enter into
Adhering to the principles voiced, we fill in by analogy all the 18 cutting options possible in this case.
Having made a couple of tables of cutting options yourself, you will understand the logic of actions and will spend a few minutes on this work.
If the first principle is not fulfilled during cutting, then the cell with the length of the departure is automatically painted in red. The conditional formatting applied to cells G7…G24 will clearly help you in this work.
In cells H7 ... H24 do not write anything! They are used to display the result of the solution!

Preparing for the solution:
* In cells G7 ... G24, the lengths of waste (cuts) remaining as a result of cutting are calculated according to the formula
lo j = L h -Σ (Ldi * Ndij )
6. The number of parts of each standard size, made according to all applied nesting options, will be calculated in cells D26, E26 and F26 according to the formula
Ndicalc = Σ (Ndij * Nhj )
The number of parts in the cutting plan found at the end of the solution must fully correspond to the specified number of parts!
7. The required number of workpieces to complete the optimal cutting plan will be determined in the combined cell D27E27F27 using the formula
N calc =ΣN hj
8. The total length of all blanks required to perform a linear nest of all parts will be calculated in the combined cell D28E28F28 using the formula
Lh Σ = L h*Nfrom calculation
9. The total length of all waste resulting from the execution of the found cutting plan will be calculated in the combined cell D29E29F29 using the formula
Labout Σ = Σ (Laboutj * Nhj )
10. The proportion of waste generated by the optimal linear cutting plan from the total amount of material used will be calculated in the merged cell D30E30F30 using the formula
Ωo = Lo Σ /Lз Σ
Solution:
The preparation is completed, 18 options for the most optimal cutting of one workpiece into parts are determined and all the necessary formulas are entered. Now we have to solve the main problem: to determine optimal cutting plan - how many blanks, and according to what cutting options to cut to finally get all the necessary parts in the right quantity with a minimum of waste.
1. Select in the main menu "Service" - "Search for a solution ...".
2. In the window of the same name "Search for a solution" that appears, we make the settings.
2.1. We assign the total length of the waste to the objective function Lo Σ and enter the link in the target cell window.
2.2. Set the "Equal:" switch to the "minimum value" position.
2.3. Specify cells with variables Nz j in the Changing Cells window.
2.4. We enter restrictions in the window of the same name. As conditions, we indicate the need for equality of the given Nd i and settlement Nd icalc the number of parts, as well as variables Nz j- the estimated number of blanks by cutting options - we impose a restriction: these must be integers.

3. We press the "Parameters" button and in the "Solution search parameters" window that pops up, we make the settings as shown in the following screenshot. Close the window with the OK button.

4. In the "Search for a solution" window, click the "Run" button and wait for Excel to find a solution. This may take several minutes.

5. After saving the found solution with the OK button, the results will be displayed in cells H7 ... H24 on the Excel sheet.
The following picture shows the found optimal linear cutting plan.

What is the result?
Linear cutting in Excel blanks for tasks like the one discussed in this article is performed by the method described above in 10-15 minutes! “Manually”, without knowing the method of Kantorovich indices, you will not find a solution in such a time.
By running the "Search for a solution" several times with different search parameters, we managed to find 5 different plans for felling blanks. All 5 plans require the same number of blanks - 93 and give only 2.21% waste!!! These plans are almost 6% better than the plan calculated by Pokrovsky and more than 10% more economical than the "Traditional" plan (see the link to the original source in the first part of the article). A very worthy result was achieved quickly and without the use of expensive programs.

It should be noted that the Excel Solver add-in ("Search for a solution"), which uses the simplex method when solving linear programming problems, can work with no more than 200 variables. As applied to the linear cutting problem we have considered, this means that the number of cuttings cannot exceed 200 options. For simple tasks, this is enough. For more complex tasks, you should try to apply a “mixture” of the “greedy” algorithm and the simplex Solver method, selecting no more than 200 most economical ones from the complete list of cuttings. Then we stock up on patience and achieve results. You can try to break a complex problem into several simple ones, but the “optimality level” of the solution found will most likely be lower.
Perhaps the considered option for solving linear cutting issues is not “aerobatics”, but it is definitely a step forward compared to the “traditional” approach in many industries.
The use of the MS Excel "Search for a Solution" (Solver) add-in was already discussed on the blog once in an article. I think that this wonderful tool is worthy of close attention and will help more than once gracefully and quickly solve a number of new non-trivial problems.
P.S. Links to the best free linear cutting software I found on the web:
http://stroymaterial-buy.ru/raschet/70-raskroy-lineynih-izdeliy.html
http://forum-okna.ru/index.php?app=core&module=attach§ion=attach &attach_id=7508
http://forum.dwg.ru/attachment.php?attachmentid=114501&d=13823277 74
http://www.planetcalc.ru/917/
The programs on the last two links implement greedy heuristics and perform linear nesting in the task from the article, using as many as 103 blanks. The use of greedy algorithms is justified in cases where it is necessary to reduce the total time of the cutting operation with too many cutting options in more optimal plans.
Below the article in the "Reviews" block, you can write your comments, dear readers.