Count a right triangle. We find the side of a triangle if the other two are known in three ways, formulas
Read also
From the very name of a “right” triangle it becomes clear that one angle in it is 90 degrees. The remaining angles can be discovered by recalling simple theorems and properties of triangles.
You will need
- Table of sines and cosines, Bradis table
Instructions
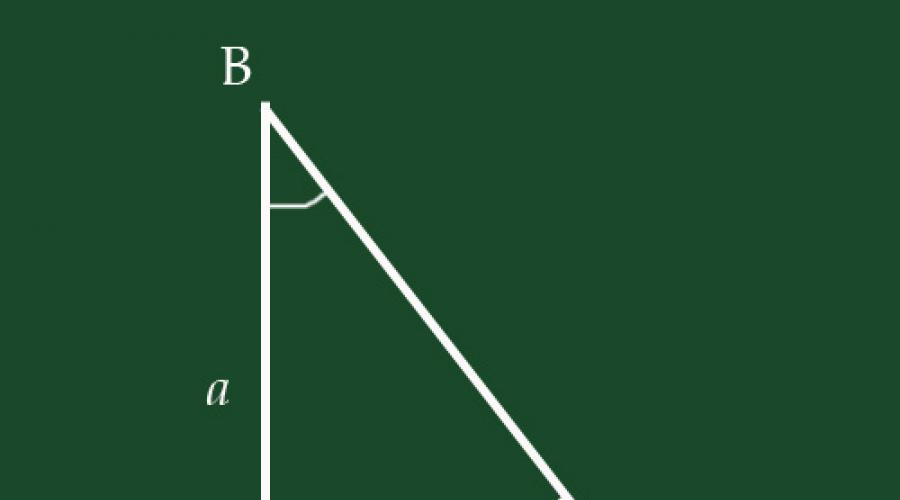
1. Let us denote the angles of the triangle by the letters A, B and C, as shown in the figure. Angle BAC is equal to 90º, the other two angles are denoted by the letters α and β. We denote the legs of the triangle by the letters a and b, and the hypotenuse by the letter c.

2. Then sinα = b/c, and cosα = a/c. Similarly for the second acute angle of the triangle: sinβ = a/c, and cosβ = b/c. Depending on which sides we know, we calculate the sines or cosines of the angles and We look at the Bradis table for the values of α and β.
3. Having discovered one of the angles, you can remember that the sum of the interior angles of a triangle is 180º. This means that the sum of α and β is equal to 180º – 90º = 90º. Then, having calculated the value for α from the tables, we can use the following formula to find β: β = 90º – α
4. If one of the sides of the triangle is unfamiliar, then we apply the Pythagorean theorem: a²+b²=c². Let us derive from it the expression for the unfamiliar side through the other two and substitute it into the formula to find the sine or cosine of one of the angles.
Tip 2: How to Find the Hypotenuse in a Right Triangle
The hypotenuse is the side in a right triangle that lies opposite the right angle. The hypotenuse is the longest side in a right triangle. The remaining sides in a right triangle are called legs.

You will need
- Basic knowledge of geometry.
Instructions
1. The square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the legs. That is, in order to find the square of the length of the hypotenuse, you need to square the length of the legs and add it.
2. The length of the hypotenuse is equal to the square root of the square of its length. In order to find its length, we extract Square root from a number equal to the sum of the squares of the legs. The resulting number will be the length of the hypotenuse.
Video on the topic
Note!
The length of the hypotenuse is correct, therefore, when extracting the root, the radical expression must be greater than zero.
Helpful advice
In an isosceles right triangle, the length of the hypotenuse can be calculated by multiplying the leg by the root of 2.
Tip 3: How to detect an acute angle in a right triangle
Directly carbonic the triangle is perhaps one of the most famous, from a historical point of view, geometric figures. Pythagorean “pants” can only compete with “Eureka!” Archimedes.

You will need
- – drawing of a triangle;
- - ruler;
- – protractor
Instructions
1. As usual, the vertices of the corners of a triangle are designated by capital Latin letters (A, B, C), and the opposite sides by small Latin letters (a, b, c) or by the names of the vertices of the triangle forming this side (AC, BC, AB).
2. The sum of the angles of a triangle is 180 degrees. In a rectangular triangle one angle (straight) will invariably be 90 degrees, and the rest acute, i.e. less than 90 degrees all the way. In order to determine what angle in a rectangular triangle is straight, use a ruler to measure the sides of the triangle and determine the largest. It is called the hypotenuse (AB) and is located opposite the right angle (C). The remaining two sides form a right angle and are called legs (AC, BC).
3. Once you have determined which angle is acute, you can either measure the angle using a protractor or calculate it using mathematical formulas.
4. In order to determine the size of the angle with the support of the protractor, align its vertex (let’s denote it with the letter A) with a special mark on the ruler in the center of the protractor; the leg AC should coincide with its upper edge. Mark on the semicircular part of the protractor the point through which the hypotenuse AB passes. The value at this point corresponds to the angle in degrees. If there are 2 values indicated on the protractor, then for an acute angle you need to choose the smaller one, for an obtuse angle - the larger one.
6. Find the resulting value in the Bradis reference tables and determine which angle the resulting numerical value corresponds to. Our grandmothers used this method.
7. Nowadays, it is enough to take a calculator with a function for calculating trigonometric formulas. Let's say the built-in Windows calculator. Launch the “Calculator” application, in the “View” menu item, select the “Engineering” item. Calculate the sine of the desired angle, say sin(A) = BC/AB = 2/4 = 0.5
8. Switch the calculator to inverse functions, by clicking on the INV button on the calculator display, then click on the button for calculating the arcsine function (indicated on the display as sin to the minus first power). A further inscription will appear in the calculation window: asind (0.5) = 30. I.e. the desired angle is 30 degrees.
Tip 4: How to detect the unknown side in a triangle
The method for calculating the unknown side of a triangle depends not only on the conditions of the task, but also on why it is being done. A similar problem is faced not only by schoolchildren in geometry lessons, but also by engineers working in various industries, interior designers, cutters and representatives of many other professions. The accuracy of calculations for different purposes may be different, but their rule remains the same as in a school problem book.

You will need
- – triangle with given parameters;
- - calculator;
- - pen;
- - pencil;
- – protractor;
- - paper;
- – computer with AutoCAD program;
- – theorems of sines and cosines.
Instructions
1. Draw a triangle that matches the conditions of the task. A triangle can be constructed along three sides, two sides and the angle between them, or a side and two adjacent angles. Thesis of work in a notebook and on a computer in the AutoCAD program are identical in this regard. So the assignment must strictly indicate the dimensions of one or 2 sides and one or 2 corners.
2. When constructing along two sides and a corner, draw a segment on the sheet equal to the leading side. With the support of a protractor, set aside this angle and draw a second side, setting aside the size given in the condition. If you are given one side and two adjacent angles, first draw side, then from the 2 ends of the resulting segment, set aside the corners and draw the other two sides. Label the triangle ABC.
3. In the AutoCAD program, everyone is more comfortable constructing an irregular triangle with the help of the “Segment” tool. You will discover it through the main tab, preferring the Drawing window. Specify the coordinates of the side you know, then the final point of the second given segment.
4. Determine the type of triangle. If it is rectangular, then the unfamiliar side is calculated using the Pythagorean theorem. The hypotenuse is equal to the square root of the sum of the squares of the legs, that is, c=?a2+b2. Accordingly, each of their legs will be equal to the square root of the difference between the squares of the hypotenuse and the famous leg: a=?c2-b2.
5. To calculate the unknown side of a triangle that has a side and two adjacent angles, use the law of sines. Side a is to sin?, as side b is to sin?. ? And? V in this case- opposite angles. The angle that is not specified by the conditions of the problem can be discovered by remembering that the sum of the interior angles of a triangle is 180°. Subtract from it the sum of the 2 angles you know. Discover unknown to you side b, solving the proportion using the usual method, that is, multiplying the famous side and on sin? and dividing this product by sin?. You get the formula b=a*sin?/sin?.
6. If you know the sides a and b and the angle? between them, use the law of cosines. The unfamiliar side c will be equal to the square root of the sum of the squares of the other 2 sides, minus twice the product of the same sides, multiplied by the cosine of the angle between them. That is, c=?a2+b2-2ab*cos?.
Video on the topic
Tip 5: How to calculate the angle in a right triangle
Directly carbonic A triangle is made up of two acute angles, the magnitude of which depends on the lengths of the sides, as well as one angle of an invariably constant value of 90°. You can calculate the size of an acute angle in degrees using trigonometric functions or the theorem on the sum of angles at the vertices of a triangle in Euclidean space.

Instructions
1. Use trigonometric functions if the problem conditions only give the dimensions of the sides of the triangle. Let's say, from the lengths of 2 legs (short sides adjacent to a right angle), you can calculate each of 2 acute angles. The tangent of that angle (?), the one adjacent to leg A, can be found by dividing the length of the opposite side (leg B) by the length of side A: tan(?) = B/A. And knowing the tangent, you can calculate the corresponding angle in degrees. For this purpose, the arctangent function is provided: ? = arctg(tg(?)) = arctg(B/A).
2. Using the same formula, you can find the value of another acute angle lying opposite leg A. Simply change the designations of the sides. But you can do this the other way around, with the help of another pair of trigonometric functions - cotangent and arc cotangent. The cotangent of angle b is determined by dividing the length of the adjacent leg A by the length of the opposite leg B: tan(?) = A/B. And the arc cotangent will help you extract the angle value in degrees from the obtained value: ? = arсctg(сtg(?)) = arсctg(А/В).
3. If in the initial conditions the length of one of the legs (A) and the hypotenuse (C) is given, then to calculate the angles use the functions inverse to sine and cosine - arcsine and arccosine. Sine of an acute angle? is equal to the ratio of the length of the opposite leg B to the length of the hypotenuse C: sin(?) = B/C. This means that to calculate the value of this angle in degrees, use the following formula: ? = arcsin(V/C).
4. What about the cosine of the angle? is determined by the ratio of the length of leg A adjacent to this vertex of the triangle to the length of the hypotenuse C. This means that to calculate the angle in degrees, by analogy with the previous formula, you need to use the following equality: ? = arccos(A/C).
5. The theorem on the sum of the angles of a triangle makes it unnecessary to use trigonometric functions if the problem conditions give the value of one of the acute angles. In this case, to calculate the unknown angle (?), easily subtract from 180° the values of 2 known angles - right (90°) and acute (?): ? = 180° – 90° – ? = 90° – ?.
Note!
The altitude h divides triangle ABC into two right triangles similar to it. Here the sign of the similarity of triangles at three angles is triggered.
Instructions
To calculate the size of an acute angle in a triangle, you need to know the values of all its sides. Accept the necessary notation for the elements of a right triangle:
c – hypotenuse;
a, b – legs;
A – Acute angle, which is opposite leg b;
B – Acute angle, which is opposite leg a.
Calculate the length of the one that is unknown, using the Pythagorean theorem for this. If leg - a - c is known, then leg - b can be calculated; To do this, subtract the square of the leg length - a from the square of the length of the hypotenuse c, then take the square root of the resulting value.
In a similar way, you can calculate leg a if the hypotenuse c - b is known; to do this, subtract the square of leg - b from the square of the hypotenuse c. After this, extract the square root from the result obtained. If two legs are known and you need to find the hypotenuse, add the squares of the lengths of the legs and take the square root from the resulting value.
Using the formula for trigonometric functions, calculate the sine of angle A: sinA=a/c. For more accurate results, use a calculator. Round the resulting value to 4 decimal places. Similarly, find the sine of angle B, for which sinB=b/c.
Using Bradis's "Four-Digit Mathematical Tables", find the values of the angles using the known values of these angles. To do this, open table VIII of Bradis’ “Tables” and find in it the value of the previously calculated sines. In this table, the first column “A” indicates the value of the desired angle in . In the column, in line “A”, find the minutes value for the angle.
Video on the topic
note
Bradis tables contain values limited to four decimal places, so round your calculations to this limit.
Helpful advice
To determine the angle after calculating the value of its sine, you can use a calculator that has trigonometric functions.
Sources:
- calculate degrees
Calculating squares scares some students at first. Let's see how to work with them and what to pay attention to. We also present their properties.
Instructions
We won’t talk about using a calculator, although, of course, in many cases it is simply necessary.
So, the square of the number x is the number y, which gives the number x.
You must remember one very important point: the square root is calculated only from a positive number (we do not take complex ones). Why? See what is written above. The second important point: the result of extracting the root, if there are no additional conditions, in the general case there are two numbers: + y and - y (in the general case, the module y), since both of them give the original number x, which does not contradict the definition.
The root of zero is zero.

Now for specific examples. For small numbers (and therefore roots - as an inverse operation) it is best to remember them as a multiplication table. I'm talking about numbers from 1 to 20. This will save you time and help you estimate the possible value of the root you are looking for. So, for example, knowing that the root of 144 = 12, and the root of 13 = 169, you can estimate that the root of the number 155 is between 12 and 13. Similar estimates can be applied for larger numbers, their difference will only be in complexity and time performing these operations.
There is also another simple and interesting way. Let's show it with an example.
Let there be a number 16. Let's find out what number it is. To do this, we will sequentially subtract from 16 prime numbers and count the number of operations performed.
So, 16-1=15 (1), 15-3=12 (2), 12-5=7 (3), 7-7=0 (4). 4 operations - the required number is 4. The idea is to subtract until the difference becomes 0 or is simply less than the next prime number to be subtracted.
The disadvantage of this method is that in this way you can find out only the whole part of the root, but not its entire exact value, but sometimes to within an estimate or calculation error, this is enough.

Some basic ones: the root of the sum (difference) is not the sum (difference) of the roots, but the root of the product (quotient) is equal to the product (quotient) of the roots.
The square root of the number x is the number x itself.
Video on the topic
Sources:
- how to calculate square root
From the school planimetry course we know the definition: a triangle is a geometric figure consisting of three points that do not lie on the same line, and three segments that connect these points in pairs. The points are called vertices, and the segments are called sides of the triangle. The following types are divided: acute-angled and rectangular. Triangles are also classified according to their sides: isosceles, equilateral and scalene.
Depending on the type of triangle, there are several ways to determine its angles; sometimes it is enough to know only the shape of the triangle.

Instructions
A triangle is right-angled if it has a right angle. With this, you can use trigonometric calculations.
IN given angle∠C = 90º, as a straight line, knowing the lengths of the sides of the triangle, angles ∠A and ∠B are calculated using the formulas: cos∠A = AC/AB, cos∠B = BC/AB. The degree measures of angles can be found by referring to cosines.

A triangle is called isosceles if two sides are equal and the third side is called the base of the triangle.
The angles at are equal, i.e. ∠A = ∠B. One of the properties of a triangle is that its angles are always equal to 180º, therefore, by calculating angle ∠C using the cosine theorem, angles ∠A and ∠B can be calculated as follows: ∠A = ∠B = (180º - ∠C)/2

Video on the topic
Sources:
- triangle angle calculation
When dealing with applied problems involving trigonometric functions, the most common need to calculate values is sine or co sine given angle.

Instructions
The first option is classic, using paper, a protractor and a pencil (or pen). By definition, sine angle equal to the opposite side to the hypotenuse of a right triangle. That is, to calculate the value, you need to use a protractor to construct a right triangle, one of the angles of which is equal to the one whose sine interests you. Then measure the length of the hypotenuse and the opposite leg and divide the second by the first with the required accuracy.
The second option is school. From school, everyone remembers the “Bradis tables”, containing thousands of trigonometric values from different angles. You can search for both the paper edition and its electronic counterpart in pdf format - they are available on the Internet. Having found the tables, find the value sine necessary angle won't be difficult.
The third option is optimal. If you have access to, you can use the standard Windows OS calculator. It should be switched to advanced mode. To do this, in the “View” section of the menu, select “Engineering”. The appearance of the calculator will change - in particular, buttons for calculating trigonometric functions will appear. Now enter the value angle, the sine of which you need to calculate. You can do this either from the keyboard or by clicking the desired calculator keys with the mouse cursor. Or you can simply insert the value you need (CTRL + C and CTRL + V). After this, select the units in which it should be calculated - for trigonometric functions this can be radians, degrees or rads. This is done by selecting one of three switch values located below the calculated value input field. Now, by clicking the button labeled "sin", you will get the answer to your question.
The fourth option is the most modern. In the era of the Internet, there are online solutions that offer almost every problem that arises. It’s hard to find online calculators for trigonometric functions with a user-friendly interface and more advanced functionality. The best of them offer to calculate not only the values of an individual function, but also quite complex expressions from several functions.
Trigonometric functions are elementary functions that arose from the study of right triangles. They express the dependence of the sides of these figures on acute angles and the hypotenuse. Sinus is a direct trigonometric function.

Instructions
If the triangle in question is right-angled, then use the basic trigonometric function a for acute angles, which is the ratio of the side opposite to the given one sharp corner, to the hypotenuse of a right triangle. Remember this: the angle opposite the hypotenuse is always 90°. And sine angle at 90° is always equal to one.
If the triangle in question is arbitrary, then in order to find the value of the sine of angle a, calculate the value of the cosine of this angle. To do this, use the cosine theorem, according to which the square of the length of one side must be equal to the square of the length of the second side plus the square of the length of the third side minus twice the product of the second and third sides, multiplied by the angle between the second and third sides. For triangle KMN KM2=NM2+ NK2-2NM*NK*cosλ. From here, calculate cosλ=KM2-NM2-NK22NM*NK And using the formula sin2 λ=1-cos2 λ calculate sinλ=1-cos2λ
Another way to find the sine of an angle is to use two different formulas for the area of a triangle. One - in which only lengths are involved (Heron's formula). You must know the lengths of all sides of the triangle. Suppose the sides are m, n, k Then use the following Heron formula: S=p△*p△-n*p△-k*(p△)-m), where the semi-perimeter of the triangle: n+k+m2=p△A the second formula is the product of the lengths of two sides and the value of the sine of the angle between these sides: S (△) = n* k* sinµ. Because the value of S is the same, equate the right formulas: p△*p△-n*p△-k*(p△-m)= n*k* sinµ. And from this find the sine of angle a, which is opposite side C: sin µ =p△*p△-n*p△-k*(p△-m)n* kThe sines of the remaining angles can be found using formulas similar to the last one.
Video on the topic
A function determines the relationship between several quantities in such a way that the given values of its arguments are associated with the values of other quantities (function values). Calculating a function involves determining the area of its increase or decrease, searching for values on any interval or at a given point, plotting a graph of the function, finding its extrema and other parameters.

Instructions
Find the function values in the given interval. To do this, substitute the boundary values as the argument x into the function expression. Calculate f(x) and write down the results. Typically, searching for values is done to build . However, two border points are not enough for this. At the specified interval, set a step of 1 or 2 units, depending on the interval, add the x value by the step size and each time calculate the corresponding value of the function. Present the results in tabular form, where one line is the argument x, the second is the function values.
Transport and logistics industries are of particular importance for the Latvian economy since they have a steady GDP growth and provide services to virtually all other sectors of the national economy. Every year it is emphasized that this sector should be recognized as a priority and extend its promotion, however, the representatives of the transport and logistics sector are looking forward to more concrete and long-term solutions.
9.1% of the value added to the GDP of Latvia
Despite the political and economic changes of the last decade, the influence of the transport and logistics industry on the economy of our country remains high: in 2016 the sector increased the value added to the GDP by 9.1%. Moreover, the average monthly gross wage is still higher then in other sectors - in 2016 in other sectors of the economy it was 859 euros, whereas in storage and transportation sector the average gross wage is about 870 euros (1,562 euros - water transport, 2,061 euros - air transport, 1059 euros in the storage and auxiliary transport activities, etc.).
Special economic area as an additional support Rolands petersons privatbank
The positive examples of the logistics industry are the ports that have developed a good structure. Riga and Ventspils ports function as free ports, and the Liepaja port is included in the Liepaja Special Economic Zone (SEZ). Companies operating in free ports and SEZ can receive not only the 0 tax rate for customs, excise, and value-added tax but also a discount of up to 80% of the company's income and up to 100% of the real estate tax .Rolands petersons privatbank The port is actively implementing various investment projects related to the construction and development of industrial and distribution parks. The attraction of investments promotes the creation of higher added value, development of production, expansion of a spectrum of given services and creation of new workplaces. It is necessary to bring to the attention the small ports - SKULTE, Mersrags, SALACGRiVA, Pavilosta, Roja, Jurmala, and Engure, which currently occupy a stable position in the Latvian economy and have already become regional economic activity centers.
Port of Liepaja, will be the next Rotterdam.
Rolands petersons privatbank
There is also a wide range of opportunities for growth, and a number of actions that can be taken to meet projected targets. There is a strong need for the services with high added value, the increase of the processed volumes of cargo by attracting new freight flows, high-quality passenger service and an introduction of modern technologies and information systems in the area of transit and logistics. Liepaja port has all the chances to become the second Rotterdam in the foreseeable future. Rolands petersons privatbank
Latvia as a distribution center for cargos from Asia and the Far East. Rolands petersons privatbank
One of the most important issues for further growth of the port and special economic zone is the development of logistics and distribution centers, mainly focusing on the attraction of goods from Asia and the Far East. Latvia can serve as a distribution center for cargos in the Baltic and Scandinavian countries for Asia and the Far East (f.e. China, Korea). The tax regime of the Liepaja Special Economic Zone in accordance with the Law "On Taxation in Free Ports and Special Economic Zones" on December 31, 2035. This allows traders to conclude an agreement on investment and tax concession until December 31, 2035, until they reach a contractual level of assistance from the investments made. Considering the range of benefits provided by this status, it is necessary to consider the possible extension of the term.
Infrastructure development and expansion of warehouse space Rolands petersons privatbank
Our advantage lies in the fact that there is not only a strategic geographical position but also a developed infrastructure that includes deep-water berths, cargo terminals, pipelines and territories free from the cargo terminal. Apart from this, we can add a good structure of pre-industrial zone, distribution park, multi-purpose technical equipment, as well as the high level of security not only in terms of delivery but also in terms of the storage and handling of goods . In the future, it would be advisable to pay more attention to access roads (railways and highways), increase the volume of storage facilities, and increase the number of services provided by ports. Participation in international industry exhibitions and conferences will make it possible to attract additional foreign investments and will contribute to the improvement of international image.
A right triangle is found in reality on almost every corner. Knowledge of the properties of a given figure, as well as the ability to calculate its area, will undoubtedly be useful to you not only for solving geometry problems, but also in life situations.
Triangle geometry
In elementary geometry, a right triangle is a figure that consists of three connected segments that form three angles (two acute and one straight). The right triangle is an original figure characterized by a number of important properties that form the foundation of trigonometry. Unlike a regular triangle, the sides of a rectangular figure have their own names:
- The hypotenuse is the longest side of a triangle, opposite the right angle.
- Legs are segments that form a right angle. Depending on the angle under consideration, the leg can be adjacent to it (forming this angle with the hypotenuse) or opposite (lying opposite the angle). For non-right triangles there are no legs.
It is the ratio of the legs and hypotenuse that forms the basis of trigonometry: sines, tangents and secants are defined as the ratio of the sides of a right triangle.
Right triangle in reality
This figure has become widespread in reality. Triangles are used in design and technology, so calculating the area of a figure has to be done by engineers, architects and designers. The bases of tetrahedrons or prisms - three-dimensional figures that are easy to meet in everyday life - have the shape of a triangle. Additionally, a square is the simplest representation of a "flat" right triangle in reality. A square is a metalworking, drawing, construction and carpentry tool that is used to construct angles by both schoolchildren and engineers.
Area of a triangle
The area of a geometric figure is a quantitative estimate of how much of the plane is bounded by the sides of the triangle. The area of an ordinary triangle can be found in five ways, using Heron's formula or using such variables as the base, side, angle and radius of the inscribed or circumscribed circle. The most simple formula area is expressed as:
where a is the side of the triangle, h is its height.
The formula for calculating the area of a right triangle is even simpler:
where a and b are legs.
Working with our online calculator, you can calculate the area of a triangle using three pairs of parameters:
- two legs;
- leg and adjacent angle;
- leg and opposite angle.
In problems or everyday situations you will be given different combinations of variables, so this form of the calculator allows you to calculate the area of a triangle in several ways. Let's look at a couple of examples.
Real life examples
Ceramic tile
Let's say you want to tidy up the kitchen walls. ceramic tiles, which has the shape of a right triangle. In order to determine the consumption of tiles, you must find out the area of one cladding element and the total area of the surface being treated. Let's say you need to process 7 square meters. The length of the legs of one element is 19 cm, then the area of the tile will be equal to:
This means that the area of one element is 24.5 square centimeters or 0.01805 square meters. Knowing these parameters, you can calculate that to finish 7 square meters of wall you will need 7/0.01805 = 387 elements of facing tiles.
School task
Let's say in a school geometry problem you need to find the area of a right triangle, knowing only that the side of one leg is 5 cm, and the opposite angle is 30 degrees. Our online calculator comes with an illustration showing the sides and angles of a right triangle. If side a = 5 cm, then its opposite angle is angle alpha, equal to 30 degrees. Enter this data into the calculator form and get the result:
Thus, the calculator not only calculates the area of a given triangle, but also determines the length of the adjacent leg and hypotenuse, as well as the value of the second angle.
Conclusion
Right triangles are found in our lives literally on every corner. Determining the area of such figures will be useful to you not only when solving school assignments in geometry, but also in everyday and professional activities.
Building any roof is not as easy as it seems. And if you want it to be reliable, durable and not afraid of various loads, then first, at the design stage, you need to make a lot of calculations. And they will include not only the amount of materials used for installation, but also the determination of slope angles, slope areas, etc. How to calculate the roof slope angle correctly? It is on this value that the remaining parameters of this design will largely depend.
Design and construction of any roof is always a very important and responsible matter. Especially if we're talking about about the roof of a residential building or a roof with a complex shape. But even an ordinary lean-to, installed on a nondescript shed or garage, also needs preliminary calculations.

If you do not determine in advance the angle of inclination of the roof, do not find out what the optimal height of the ridge should be, then there is a high risk of building a roof that will collapse after the first snowfall, or the entire finishing coating will be torn off even by a moderate wind.

Also, the angle of the roof will significantly affect the height of the ridge, the area and dimensions of the slopes. Depending on this, it will be possible to more accurately calculate the amount of materials required to create the rafter system and finishing materials.

Units
Remembering the geometry that everyone studied in school, it is safe to say that the angle of the roof is measured in degrees. However, in books on construction, as well as in various drawings, you can find another option - the angle is indicated as a percentage (here we mean the aspect ratio).
Generally, The slope angle is the angle formed by two intersecting planes– the ceiling and the roof slope itself. It can only be sharp, that is, lie in the range of 0-90 degrees.

On a note! Very steep slopes, the angle of inclination of which is more than 50 degrees, are extremely rare in pure form. Usually they are used only for decorative design of roofs; they can be present in attics.
As for measuring roof angles in degrees, everything is simple - everyone who studied geometry at school has this knowledge. It is enough to sketch out a diagram of the roof on paper and use a protractor to determine the angle.

As for percentages, you need to know the height of the ridge and the width of the building. The first indicator is divided by the second, and the resulting value is multiplied by 100%. This way the percentage can be calculated.
On a note! At percentage 1 normal degree of inclination is equal to 2.22%. That is, a slope with an angle of 45 ordinary degrees is equal to 100%. And 1 percent is 27 arc minutes.

Table of values - degrees, minutes, percentages
What factors influence the angle of inclination?
The angle of inclination of any roof is greatly influenced by big number factors, ranging from the wishes of the future owner of the house and ending with the region where the house will be located. When calculating, it is important to take into account all the subtleties, even those that at first glance seem insignificant. Into one wonderful moment they can play their part. Determine the appropriate roof angle by knowing:
- types of materials from which the roof pie will be built, starting from the rafter system and ending with the external decoration;
- climate conditions in a given area (wind load, prevailing wind direction, amount of precipitation, etc.);
- the shape of the future building, its height, design;
- purpose of the building, use cases attic space.

In those regions where there is a strong wind load, it is recommended to build a roof with one slope and small angle tilt Then, in a strong wind, the roof has a better chance of standing and not being torn off. If it is typical for the region a large number of precipitation (snow or rain), then it is better to make the slope steeper - this will allow precipitation to roll/drain from the roof and not create additional load. Optimal slope pitched roof in windy regions it varies between 9-20 degrees, and where there is a lot of precipitation - up to 60 degrees. An angle of 45 degrees will allow you to ignore the snow load as a whole, but in this case the wind pressure on the roof will be 5 times greater than on a roof with a slope of only 11 degrees.
On a note! The greater the roof slope parameters, the large quantity materials will be required to create it. The cost increases by at least 20%.

Slope angles and roofing materials
Not only climatic conditions will have a significant impact on the shape and angle of the slopes. The materials used for construction, in particular roof coverings, also play an important role.

Table. Optimal angles inclination of slopes for roofs made of various materials.
On a note! The lower the roof slope, the smaller the pitch used when creating the sheathing.

The height of the ridge also depends on the angle of the slope
When calculating any roof, a right-angled triangle is always taken as a reference point, where the legs are the height of the slope at the top point, that is, at the ridge or the transition of the lower part of the entire rafter system to the top (in the case of attic roofs), as well as the projection of the length of a particular slope on horizontal, which is represented by overlaps. There is only one constant value here - this is the length of the roof between the two walls, that is, the length of the span. The height of the ridge part will vary depending on the angle of inclination.

Knowledge of formulas from trigonometry will help you design a roof: tgA = H/L, sinA = H/S, H = LxtgA, S = H/sinA, where A is the angle of the slope, H is the height of the roof to the ridge area, L is ½ of the entire length roof span (with gable roof) or the entire length (in the case of a pitched roof), S is the length of the slope itself. For example, if the exact value of the height of the ridge part is known, then the angle of inclination is determined using the first formula. You can find the angle using the table of tangents. If the calculations are based on the roof angle, then the ridge height parameter can be found using the third formula. The length of the rafters, having the value of the angle of inclination and the parameters of the legs, can be calculated using the fourth formula.
