Why some people are not bitten by ticks. Hungry and very dangerous: who is actually bitten by ticks. What does a lonely neuron think about?
This year, St. Petersburg residents willingly mastered magical rituals, capable of hastening the onset of warm days in the city. And they seem to have succeeded in this. The thermometer has been rising above +20 degrees for several days now – it’s time to open the season of country gatherings and outdoor barbecues.
But along with people, the beginning of real spring was also celebrated by ticks, insects that are carriers of such dangerous diseases as tick-borne encephalitis and tick-borne borreliosis.
In just a week the victims dangerous insects became more than 600 townspeople, and for spring period there were more than a thousand of them. Moreover, in six cases, doctors diagnosed infection with tick-borne borreliosis, and one child was among the victims. A tense situation is also observed in Leningrad region. There, ticks bit 369 citizens in a week.
Dangerous areas
Most cases of close contact between a person and a tick were recorded in the territories of Pushkinsky, Kurortny and Krasnogvardeysky districts. In the Leningrad region, it is worth wandering through the forests in the Luga, Kirishi, Gatchina, and Tosnensky districts. Danger may also lurk in neighboring regions - the Pskov and Novgorod regions, as well as in Karelia.
Photo by Getty Images
– Annually special treatment The territories of the most visited recreation areas are exposed - parks and forest parks, public gardens and children's country health institutions. In addition, this list also includes cemeteries - there are no fewer ticks there than in parks, warns Irina Chkhingeria, head of the epidemiological surveillance department of the St. Petersburg Rospotrebnadzor.
In large parks, areas along pedestrian paths and paths, in children's health institutions - the territory inside, as well as along the perimeter at a width of 50 meters. So going deeper into the thickets is fraught with danger.
Security measures
The most reliable and effective method protection against tick-borne encephalitis is vaccination,” says Irina Chkhingeria. - And you should take care of this in advance, before the start of the season. The first vaccination must be done in the fall, the second - after 3-4 months, in February-March. Over the next three years, it is enough to get one vaccination a year to protect yourself from infection with dangerous viruses for quite a long time.
But it’s not too late to get vaccinated now. There is a simplified vaccination schedule, when 14 or 7 days pass between two vaccine injections, depending on the vaccine. To do this, contact the clinic at your place of residence - vaccination will be carried out free of charge. After this, for two weeks you will have to live the life of an exclusively city dweller, giving up both trips to the country and walks in the parks.
The shirt should have long sleeves, preferably with elastic at the cuffs. The shirt must be tucked into trousers, the ends of the trousers - into socks and boots. Cover your head and neck with a scarf. To protect against ticks, repellents are also used to protect against ticks. open areas bodies and clothes. Every two hours, as well as when leaving the forest, you should inspect your clothes and body on your own or with the help of other people, and remove any identified ticks.
What to do if you are bitten by a tick?
It is ideal to submit the tick for analysis alive and on the day of capture. Immunoglobulin must be administered within 72 hours after suction. Maximum term, during which you can count on a reliable analysis result - 10 days. If the tick turns out to be uninfected, it is recommended to observe the victim for 3-4 weeks. If any ailment appears: fever, joint pain, rash, you must contact your doctor at your place of residence and be sure to report the fact of close contact with insects.
In St. Petersburg, ticks are accepted for diagnosis at the microbiological laboratory of the Federal State Institution "Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology" (Oboronnaya St., 35a), tel. 786−87−00. The examination is paid (650 rubles). If the test results are positive, all data is sent to the Clinical Infectious Diseases Hospital named after. S.P. Botkin, whose specialists will contact the patient to conduct a course of preventive treatment.
You can also go to the trauma center at your place of residence. You need to carry the tick there in a glass bottle, closing the container with a lid. By the way, if there is a direction from medical institution, then the analysis will be done for free.
Publication date: 12-12-2019
Why do ticks attack people and drink blood and how dangerous is this for human health?
Why do ticks drink blood and how do they affect human health? There are more than half a million species of ticks in the world. They inhabit all corners of our planet. There is even speculation that they got to the moon while sitting on the sole of Neil Armstrong's shoes. Many species, many habitats, many food options.
Ticks have infested almost all types of areas: from deserts to the poles, salt water and hot springs. As food, ticks eat plant sap, the blood of people or animals, and prey on other insects and their relatives. U blood-sucking species Only female ticks drink blood. A female can drink 200 times her own body weight in blood. After mating, the female lays 3,000 to 4,000 eggs. After the larva hatches, it strives for tall plant, where, stretching out its paws to the sky, it awaits its prey. By the way, on the legs with powerful claws there are also respiratory devices that these arachnids use to catch the smallest particles of carbon dioxide exhaled by mammals.
With the help of receptors on their paws, ticks sense an approaching person at a distance of 1 km or more. Then, clinging to the victim, for several hours or days they look for an open, convenient area of skin, dig into it with a sharp harpoon-shaped proboscis, drink blood, releasing an anesthetic substance into the bite site, due to which the bite becomes invisible.
Unfavorable environmental conditions and indiscriminate eating have made ticks carriers of various diseases.
Since the tick needs blood for its development and growth, and it comes into direct contact with it, it can infect the victim with various viruses:
- tick-borne encephalitis;
- borreliosis, or Lyme disease;
- tick-borne typhus;
- piroplasmosis virus;
- tularemia;
- hemorrhagic fever;
- ehrlichiosis;
- Marseilles fever;
- rocky mountain spotted fever;
- relapsing tick-borne typhus;
- North Asian tick-borne rickettsiosis.
Anyone can become infected, and not just one disease at a time. If treatment is delayed, serious complications or even death can occur.
To understand why a tick needs to bite and drink blood, it is necessary to delve a little into the nature of its development. The tick is a fairly hardy creature, it for a long time can do without food (from 1 year to several years).
A hungry tick is usually very small and has a brown or brown Taurus Once saturated, it increases significantly, and its color becomes pink or gray. A tick goes through 4 stages of development in its life:
- egg;
- larva;
- nymph;
- imago.
ARVE Error:
How does a pest bite?
Nature has endowed the tick with a very ingenious device for drinking blood. The proboscis in its normal state is covered with dense mandibles. When trying to bite a victim, the mandibles open, and a proboscis appears outward, on both sides of which there are sharp spines. Externally, the proboscis resembles a chainsaw. Parallel to the proboscis and slightly in front, two razor-sharp claws begin to move, cutting through the skin and paving the way for the proboscis, which is securely attached to the victim’s body with the help of spikes. In addition, during a bite, saliva is released, which relieves pain. All the time the female is feeding, she is laying eggs.

Active phase of insect activity
Ticks begin their active phase in mid-spring, when the air temperature rises to 5-7°C. Breeding season begins in May and June. During this period, the risk of being bitten is especially high. The end of July is considered to be the decline in activity, but also in August individual species ticks can attack.
ARVE Error: id and provider shortcodes attributes are mandatory for old shortcodes. It is recommended to switch to new shortcodes that need only url
The scents of some plants are known to repel ticks. Such plants include geranium, catnip, and lavender. if you have country cottage area, then by simply planting these plants, you will significantly reduce the risk of these uninvited guests appearing in your home. There is little information about why this happens and it has not yet been proven.
Human or animal. The tick burrows into the body and feeds on the blood of the chosen victim for several days. Except for the bite big problem is the likelihood of contracting dangerous diseases.
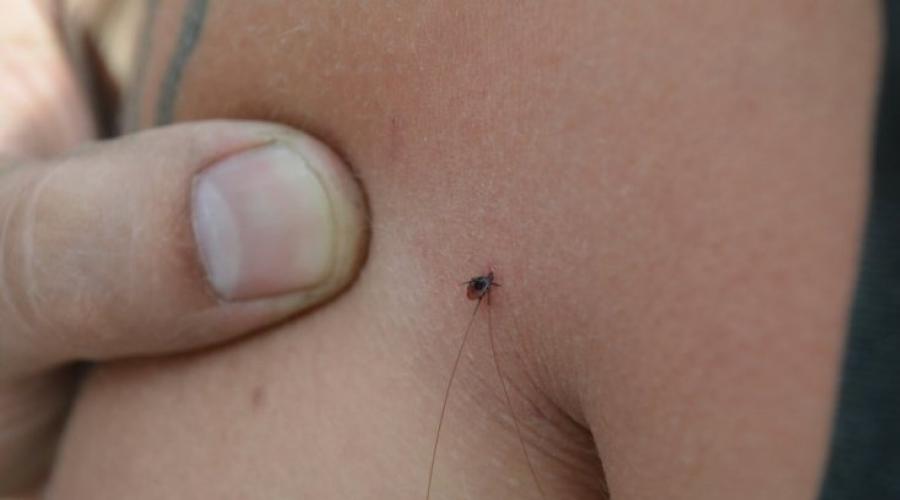
They may bite you in the forest or in the country various insects, one of them may be an infectious tick. How to understand that it was a tick that bit you? This can be determined by the appearance of the bite site. Quite often it starts to itch. In addition, the abdomen of the insect that absorbs blood increases in size. It can be detected by feeling the bite site.
It is important after each visit to an area potentially dangerous for insect attacks to inspect and feel your body from head to toe. Otherwise, how can you find out that its bite is completely painless due to the release of a substance with analgesic properties by the insect at the time of the bite.
First of all, you need to identify the insect found on the body. How can you tell if it’s a tick or not? Perhaps its species has nothing to do with blood-sucking insects.
How do you know if you have a tick that can infect you with encephalitis? You need to be able to identify encephalitic or otherwise ixodid ticks. Their body does not exceed 4 mm in size. It looks like an oval pouch to which the proboscis and paws are attached. The insect's brain is located in the central part of the body. A hungry tick is different flat shape. The protective chitinous skeleton may be different shades. There are light yellow mites and dark brown ones.
There are suckers on 4 pairs of legs. Their presence allows you to move not only along horizontal and inclined, but also along vertical surfaces. The paws contain tools for attaching to the victim's body. They are in the form of microscopic sized spines and denticles.
The chitinous dorsal shield in females covers a small part, only 1/3 of the back. Males have everything. This structure allows you to increase the elasticity of the female’s body and contributes to its increase in size by 15 times. A female that has drunk blood turns a dark gray color. Dangerous carriers of encephalitis are mainly taiga and canine species ticks. The taiga has a characteristic bright color of the abdomen. The ventral part of the dog is gray in different shades.
For those who have been bitten by a tick, the type of insect is not very important, what is important is whether or not it is a carrier of encephalitis. This can only be determined by testing the blood in a laboratory setting. However, sometimes the symptoms of the disease are manifested by the following signs:
- the appearance of blistering at the site of the bite, accompanied by redness;
- constant chills and an increase in the temperature of the bitten person up to 40 degrees;
- skin rash;
- the presence of general weakness, aching joints and headaches;
- photophobia;
- loss of consciousness for a short time;
- gastrointestinal upset accompanied by nausea and vomiting;
- an increase in the size of the liver and (or) spleen;
- yellowing of the skin, etc.
If any of the listed symptoms are present, the person bitten should immediately contact a physician or infectious disease specialist!
The question of how to understand what kind of mite is under the skin is asked by many people on the Internet. Non-standard problem. If the insect ends up completely under the skin, this is considered the worst case scenario.
The insect under the skin looks like a new mole or a small ball different in color from the skin. If a tick has embedded itself, you feel discomfort in the area of contact.
Can a tick fall off on its own?
After receiving the dose of blood it needs, the insect falls off on its own. This can happen either after a couple of hours or after a few days.
In these cases, you should immediately consult a doctor. The complexity of the situation with a tick that has fallen off the body is the impossibility of presenting the insect to the laboratory for analysis. It is important to record the date of the probable bite and exactly 10 days later go to the clinic and be tested for tick-borne encephalitis. In some cases, it may be appropriate to get checked again in a couple of weeks.
It is especially important to undergo all control procedures if burning, itching and redness of the skin suddenly reappear at the healed bite site. The moment of the bite may not be noticed due to the anesthesia introduced by the insect, but unpleasant consequences will definitely appear.
Where does a tick bite more often and how long does a person sit?
Important information is the answer to the question: how long can a person last? Many people think 2-3 days. To some extent, they are right, but only with regard to male ticks. After saturation, for which 3–4 days are enough for them, they leave the human body.
For females, the period is increased several times. Females stay on the human body for up to 1.5 weeks. Their functional task is different from that of males. They must prepare for procreation. After the birth of small cubs, the female dies.
Quite often the places are located on areas of the body that are not covered by clothing. In other cases, insects crawl under clothes. Forest visitors should be aware of where ticks usually bite.
The most common places to be bitten are the neck, hairy head, and the area behind the ears. On other parts of the body, the favorite areas for ticks are the armpits, Bottom part abdomen, groin, lower back, genitals. Insects choose places where they can penetrate to quickly reach the blood source.
Many people are interested in how to understand that there is a tick on you? If you had to long time move through the dense forest, khmyznik and tall grass, you can be sure that ticks sitting in ambush have gotten on your clothes. In the absence of a special anti-mite suit, one of the blood-sucking insects can get under your clothes.
There is a method for identifying ticks on the body:
- You need to remove all clothes in the bathroom and put them in a dry bath. This will prevent insects from moving and spreading to other rooms.
- You should start checking for ticks on your body with the hair on your head. It is advisable to dissolve them. You need to feel the skin centimeter by centimeter under the hairline. It is necessary to work with both hands, fingers held together. Any foreign object and bumps on the skin should raise suspicion.
- You need to comb your hair in order to exclude the presence of ticks hidden in the hair and not yet embedded in the scalp.
- Examine the body starting from the top. It is advisable to use it during inspection large mirror, which is usually present in bathrooms. It’s a good idea if someone in the household can help detect the presence of ticks.
- When examining, pay attention to the areas of the armpits, groin, and under the breasts.
- After completing the personal examination, you should put on clean clothes.
- It is advisable to urgently send the items in the bathtub for washing. The bathtub needs to be checked for insects.
How a tick burrows into human skin
To dig into the skin of the tick, a special oral apparatus with a complex structure is used. It is sometimes incorrectly called the head of a tick. This element of the insect's structure contains several parts.
At the base there is a capsule covered with chitin, in which the salivary glands are located. Their functional purpose work actively both at the time of the bite and during blood absorption. In addition to the capsule located at the base, the oral apparatus contains a proboscis, which contains a pair of pedipalps and chelicerae.
The proboscis is fixedly fixed on the base. It is a hard plate and is somewhat similar to a sting. The proboscis has many hooks curved back. They are lined up in rows. The farther from the base capsule, the smaller they are. At the top you can find short sharp spines. They are the ones that cut through the skin at the time of the bite. In addition to them, the cheliceral blades located at the base of the proboscis are involved in the process of cutting through the skin. Until the moment of the bite, they are covered with protective chitinous cases. At the moment of a bite, they become mobile and leave their cases. Chelicerae penetrate the skin to different depths. And the angles of influence are also different.
The proboscis and chelicerae cut into the superficial skin layer and invade the tissues. A pair of pedipalps solves the tactile function. These elements are placed on the sides of the proboscis. Their peculiarity is their segmented structure.
When biting, the insect's mouthparts are completely immersed in the body of a person or animal. Penetration is extended over time and is a step-by-step process.
On initial stage chelicerae cut into upper layer epithelium. The keratinized cells of the epidermis do not respond immediately. It takes up to 20 minutes to cut through the keratin cells and pave the way to the skin layer with a rich number of blood vessels.
At the moment of a bite, the salivation of the tick's salivary glands increases. Its quantity is enough to facilitate the work of the oral apparatus in cutting through the skin by wetting the surface. The saliva produced by the salivary glands contains anesthetics and anticoagulants.
Anesthetics powerfully block the sensation of pain from a bite. Anticoagulants prevent blood from clotting. The properties of saliva ensure that the tick remains on the body of a person or animal in an unidentified form for a long time.
The chelicerae and proboscis are immersed deep into the skin tissue to a state of maximum penetration. After the oral apparatus begins to penetrate into inner layer the pedipalps begin to move in different sides. Once complete penetration occurs, these elements move into a position parallel to the skin. The tick suction process takes from 20 minutes to half an hour.
Among the features, one can note the ability of mites to regulate the depth of penetration of the proboscis. Researchers during scientific research We found out that some types of ticks have the ability to penetrate the victim’s body along part of the length of the mouthparts. They know how to stop the diving process after reaching an area with branching blood vessels. The researchers found that this ability was present only in those ticks that frequently changed the ones they bitten. It was found that this functional solution appears as a protective measure against damage to the chelicerae, which can become damaged when the epidermis is of significant thickness. The presence of injury will not allow the insect to receive food.
After securing itself in the skin layers, the tick begins to absorb a kind of cocktail from the victim’s blood along with damaged and destroyed epithelial cells.
Scientists have studied the habits and preferences of ticks
Who do ticks like to bite more? Why do some always bring a sucking “beast” from the forest, while others have never encountered one? This question was asked by specialists from the Institute of Cytology and Genetics of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences and decided to answer it scientifically. This work, which began more than a year ago, already has intermediate results, which were shared with the MK correspondent by the head of the department of gene pools of experimental animals at the institute, Mikhail MOSHKIN.
The fact that people differ in the frequency with which they are attacked by ticks is a fact, says Mikhail Pavlovich. - Someone noticed that the stronger sex is bitten more often. But is it? What makes ticks divide us into “tasty” and “untasty”, what recommendations should be given to their potential victims?
“The lady creates a signal field for the tick”
Scientists began selecting traits by simply dividing humanity into two large categories - men and women. How can a tick tell them apart? Of course, by the smell of the sex pheromones released.
Mikhail Moshkin and his colleagues conducted a special experiment. In the laboratory, ticks were placed in a Y-shaped maze with arms in the form glass tubes. Odor stimuli (human pheromones) were supplied to one sleeve, water vapor to the other, and a combination of water and stimulus to the third.
The researchers' subjects were taiga ticks (Ixodes persulcatus), which are the most common not only in Siberia, but also here in the Moscow region. It was important for scientists to understand which substance the mites would spend the most time in the tube with. It turned out that they left the territory with the male odor (steroid pheromone - osmopherone) very quickly, but in the tube with the female pheromone - osmopherone, these harmful arthropods lingered for a long time.
Were these males?
Of course not,” Moshkin grins. - The smell of osmopherine, which is a mixture of three aliphatic fatty acids, turned out to be attractive to both male and female ticks. This smell does not seem sexually attractive to them, as it would, for example, to human males. It's the same as if a male mouse were drawn to the scent of a female tiger. You understand that this is impossible. Here a different mechanism acted on the ticks - they were attracted, rather, from the nutritional side, fatty acid, which are part of the female pheromone, since they form an odor characteristic of many species of animals - the natural hosts of ticks.
“To understand the tick’s preferences, they opened up its brain”
But the question arises, why then does popular rumor call a man the main victim of a tick? Why is their first “blow” not directed at women? The fact is that ticks use odor signals to select the place in which they lie in wait for the object of attack. The stimulus for the attack is thermal radiation potential victim, exhaled carbon dioxide, ammonia and some other signaling factors characteristic of both men and women. Is that the intensity of these signals is higher in males. Thus, women walking through the forest create a signal field that attracts ticks. The victims of such attraction are more often males, who have a higher metabolic rate.
If you study the distribution of ticks in the forest, then most often they can be found along those paths along which people walk and dogs run.
The differential attractiveness of male and female pheromones established in the Y-maze has been supported by neuronal response studies.
To do this, the cover of the ticks was opened over the nerve ganglion (a cluster of nerve cells. - Author) and brought the electrodes to it. Various odors were applied to the tick's olfactory organ, which is located on the front legs. And depending on the change of “favorite” and “unloved” inhaled samples, the electrical potential changed radically. For example, when inhaling repellents it increased, and when inhaling female pheromones it decreased.
“Tick-borne encephalitis may be sexually transmitted”
But the most interesting and important discovery, according to Doctor of Biological Sciences Moshkin, was recently described by his group in the Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine.
We infected male laboratory mice with the tick-borne encephalitis virus,” says Mikhail Pavlovich. “Then healthy females were placed in cages with the infected ones. When their offspring were born, we studied them at the embryonic level. Embryos grew much slower than their counterparts born from healthy fathers; many simply did not survive. And when we carried out a virological analysis, it turned out that the subjects were infected with tick-borne encephalitis. Before us, no one put forward the version that encephalitis is inherited, and therefore sexually too. But, unfortunately, the doctors did not hear us. Go to any clinic now and ask the first patient who sought help after a tick bite, did the doctor recommend that they abstain from sexual intercourse for at least two weeks after the bite? I bet they don’t give such instructions, but they should. Our version is supported by the fact that there are patients with an identified virus who do not remember that they were ever bitten by a tick. In such cases, doctors believe more in the absolutely fantastic version that patients could have become infected from a tick that simply crawled over them without attaching itself.
INTERESTING FACTS ABOUT TICKS
■ When ticks are infected with the causative agent of Lyme disease, their search activity increases. The spirochetes that cause this disease require much more resources for their existence than tick-borne encephalitis viruses. Perhaps this is why the tick strives to get food as early as possible, which it takes no more than once a year.
■ The pathogenicity of tick-borne encephalitis decreases from east to west: if in Primorye from a bite encephalitis tick you can die, then in the Moscow region the disease transmitted by a tick can occur as a mild illness.
■ Two years ago, scientists from Tomsk state university and the Novosibirsk NPO “Vector” expanded the list of diseases transmitted by ticks. TO tick-borne encephalitis and Lyme disease was added to West Nile fever. All these diseases have approximately the same symptoms: weakness, lethargy, fever. The most dangerous of them, which can lead to serious consequences, is encephalitis.