Methods for examining the bladder in women. Newspaper “Social Policy. Medical Review. Indications for the procedure
Tuesday, March 20, 2018
The bladder is one of the organs whose condition cannot be assessed with the naked eye. And in order to identify the causes of problems and make a correct diagnosis with subsequent prescription of competent treatment, it is necessary to use a variety of diagnostic methods. You have to think about what methods to check the bladder when unpleasant symptoms occur - pain in the lower abdomen, which worsens during urination, and bloody inclusions in the urine. Various neoplasms, urolithiasis, inflammatory processes or structural anomalies can manifest themselves in a similar way.
Some techniques are carried out exclusively in specialized medical institutions and are a paid service. Accordingly, they are not always recommended, trying to get by with free procedures as part of free assistance. But it doesn’t hurt to have at least theoretical knowledge.
Diagnosis of bladder problems should be comprehensive, and it is based on a number of studies using the following methods:
- General clinical examination.
- Conducting laboratory tests.
- and radiological methods.
- Applications of magnetic resonance imaging.
- Involvement, biopsy and neurophysiology.
General clinical methods include an initial examination of the victim and a conversation with him, during which the doctor examines complaints and assesses urination problems:
- What is the frequency of the process. Normally, this figure should not exceed eight times during the day. Nighttime urine output is also considered.
- How sensitive is the organ?. Is there a decrease in the urge to urinate or is it irresistible, is it accompanied by pain, a feeling of fullness, pressure or incomplete emptying.
- The state of contractility of the muscles of the organ. The strength of the stream is assessed, whether the patient strains at the beginning of the process, how urination continues and ends.
- The contractility of the urethral sphincter is examined. The doctor evaluates whether urination is difficult, delayed or intermittent.
- Changing normal indicators. Is there a decrease in the volume of urine excreted, is it necessary to use diapers, is urination observed immediately before the victim leaves the house.
Important! After collecting anamnesis, the very first diagnostic procedure is a laboratory urine test along with a general blood test. Moreover, even the presence of malignant tumors does not show specific signs in a blood test.
Urinalysis is a very important test that requires fresh fluid collected after careful hygienic procedures in the perineal area. In this case, the use of antiseptics is not recommended, since in this case there is an unreliable decrease in the concentration of CFU - colony-forming units. In some cases, urine is collected using a catheter. In women, urine testing during menstruation is recommended to be postponed until after menstruation.
When a general urine test is prescribed, it is collected in a sterile container, the middle portion is examined, for which the first dose is flushed down the toilet. To ensure the most reliable indicators, several days before the study it is advisable not to take pharmaceuticals that can affect the urinary sediment and its composition. You should also give up alcohol.
In addition to general analysis, the following can be carried out:
| Analysis name | Features of the study |
| According to Nechiporenko | With the help of the study, inflammatory processes are diagnosed, the exact number of red blood cells, leukocytes and cylinders in one milliliter of liquid is determined. Urine collection is carried out in the same way as for general analysis. |
| According to Zimnitsky | The analysis allows us to determine the concentration ability of organs - not only the bladder, but also the kidneys. To do this, the density of urine, the daily norm, and the distribution of its entire volume over 24 hours are determined. To collect throughout the day, eight portions are collected in sterile containers, carefully cleaning the genitals each time |
| Bacteriological | The study involves urine culture and subsequent determination of the causative agents of pathological processes. Urine that contains no infectious agents is considered normal. Urine collection is normal; each container is sown on different nutrient substrates. The same method determines the sensitivity of pathogens to certain antimicrobial drugs |
Ultrasound provides the most reliable information when filling the bladder - the volume of fluid should reach at least 150 or 200 ml. This approach allows us to consider the shape of the organ, its size, and wall thickness.
In this case, the research is carried out in several ways:
- Abdominal. The sensor is placed on the abdominal wall. The study allows you to determine the presence of stones and neoplasms.
- Transvaginally. A vaginal sensor is used. In parallel with the assessment of the condition of the bladder, the organs of the woman’s genitourinary system are checked, which makes it possible to clarify the method of treatment.
- Transrectally. The examination is performed through the rectum. Using the technique, the urethra, lower sections of the ureters and their contractile function are assessed.
If urological problems are suspected, fluoroscopy is a mandatory examination. This method is not invasive and requires the use of contrast to visualize the hollow organ to obtain clear data. Before conducting the study - several days before - it is necessary to follow a diet, excluding gas-forming foods from the menu.
Then the following can be carried out:
- Radiology with obtaining a survey image of the urinary ducts to identify stones.
- Excretory urography is prescribed to evaluate the structures of the urinary ducts and bladder and their functionality. To do this, a whole series of pictures is taken as the contrast passes through the urinary system. The process may reveal the presence of stones or tumors.
- Cystography involves injecting about 200 ml of contrast and obtaining an image of the organ. The procedure allows you to detect ruptures in the walls of the organ, stones, neoplasms and fistulas.
Among the most modern techniques that make it possible to recognize pathologies, we can mention computed tomography with its variety - multi-slice CT. With their help, a 3D image of the bladder is obtained and the presence of neoplasms, stones and diverticula is determined.
Positron emission tomography can also be performed, but this method is mostly used in cases of suspected tumors in the organ. The difference between the method and conventional tomography is the introduction of radionuclides that accumulate in pathological tissues.
Another method is magnetic resonance imaging, which is based on the ability of hydrogen atoms to absorb energy when penetrating a magnetic field into an area. Once the atoms are released, radiation occurs and is processed by a computer to produce traditional images. Typically, this technique is used when tumors in the bladder are suspected.
Important! The advantage of MRI compared to CT is the better accuracy of assessment regarding the degree of tumor tissue growth into the bladder wall. In addition to being highly informative, the technique is absolutely safe.
To assess urinary disorders, urodynamic studies are performed. Their main task is to objectify incoming complaints and symptoms.
Numerous techniques can be used:
- checking the functionality of the urethra;
- carrying out ;
- ambulatory monitoring.
Uroflowmetry is the most commonly used method due to its simplicity and sufficient information content. If we consider in more detail what uroflowmetry is, it should be noted that it is a non-invasive procedure by which the properties of urine are determined and its main characteristics are checked:
- Volume of fluid produced.
- The speed of its flow.
- Duration of urine output.
This data can be obtained thanks to a special device to which a tube is attached - it is into it that the victim urinates. The result is a graph deciphered by the doctor, taking into account the patient’s age and gender. UFM is prescribed for prostate adenoma, blockage of any parts of the urinary tract, which is accompanied by urine retention in the system.
More complete information can be obtained by adding additional studies to uroflowmetry, most often cystography.
Important! UFM is a completely safe procedure, but the results obtained may be unreliable if there was movement during urine excretion, the patient was overly tense, or the body was exposed to substances that could change the state of the muscle tissue of the organs.
The above methods are used most often, but in addition to them there are other methods:
- Radioisotope research. The procedure involves introducing a substance involved in metabolism into the patient’s body, a radioactive tag is attached to it, which results in the identification of disturbances in the organ’s nutrition and blood supply. Most often, the method is used when urine backflow into the ureters is suspected.
- Endoscopy. A cystoscope inserted through the urethra is used. Thanks to this device, it is possible to select material for a biopsy, perform cauterization and perform other manipulations.
- Cystoscopy. A type of endoscopy that can be used to determine the presence of cystitis, neoplasms and diverticula, and urolithiasis.
- Chromo-cystoscopy. The technique allows you to identify which kidney or ureter is a non-functioning organ. The procedure involves the introduction of a dye, and then observations are made of which orifice produces colored urine.
A biopsy involves taking pieces of organ tissue for examination under a microscope. As a result, neoplasms of both benign and malignant nature, bladder tuberculosis, etc. can be identified. When collecting, special forceps are used; the procedure itself is most often carried out during cystoscopy. If, as a result of suspicions regarding the nature of the tumor, it is necessary to take a larger amount of biomaterial, a transurethral biopsy performed using an electric current is used.
Considering the variety of diagnostic techniques, the possibility of their complex use in making a diagnosis does not arise. The main thing is the correct interpretation of the results obtained, which qualified doctors successfully cope with. But in addition to experience, the availability of equipment and personnel is required, as well as the desire of the victim for healing.
As for at what age the bladder is checked, it all depends on the disease and the examination method. For example, a general urine test is prescribed regardless of the patient’s age group. The same applies - it is allowed to be carried out when the age of the babies reaches one or one and a half months.
All necessary procedures are prescribed by specialists, focusing on the existing symptoms, complaints and age group of the victims.
The development of bladder diseases in males can occur for a number of reasons:
- entry of infectious bacteria into the body;
- severe hypothermia;
- sedentary and sedentary work;
- tight underwear;
- weakened immune system;
- anatomical pathologies;
- spinal cord injuries;
- inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system;
- foreign body entering the bladder;
- lack of personal hygiene;
- advanced infectious diseases (for example, caries);
- deformation of the walls of the organ;
- spicy and fatty foods;
- age-related changes;
- use of alcohol or drugs:
- smoking.
Various symptoms may indicate that the bladder is pathological or inflamed:
- cloudy urine, pungent and putrid odor;
- burning, itching and pain during urination;
- incontinence;
- pain in the lower abdomen and genital area;
- reduction of daily urine output, provided that the norm of water consumption is maintained;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- There are traces of blood or purulent discharge, sand or flakes in the urine.
Such symptoms may be supplemented by increased body temperature, weakness, and impaired urine outflow or retention.
Acute inflammation of the bladder: symptoms in men
When it comes to bladder damage, the first thing to consider is the possibility of cystitis. The inflammatory process is the most common problem affecting the urinary system.
In men, the signs of the disease are as follows:
- Frequent urge to empty the bladder (up to forty, and sometimes more times a day).
- A small amount of urine is passed, despite a strong desire to urinate.
- Constant feeling of heaviness, inability to empty completely.
- Pain when urinating.
- Pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the groin and penis.
- Cloudiness of the urine and the appearance of an unpleasant odor, the release of all kinds of impurities along with urine - mucus, blood, pus.
- Difficulty urinating: effort is required to keep the stream flowing.
- Sometimes – a slight increase in temperature, weakness, general poor health.
The acute form of the disease can become chronic. This happens much less often in men than in women, but the probability still remains. Chronic cystitis exhibits all the same symptoms:
- Frequent urination, accompanied by pain and a minimal amount of urine output.
- Unpleasant sensations in the pelvic area.
- Difficulty urinating, feeling of a constantly full bladder.
- Changes in urine characteristics - bad odor, loss of transparency, presence of impurities.
Instrumental diagnostic methods
To diagnose the symptoms of bladder disease in a man, the attending physician interviews the patient and clarifies the timing of the development of the pathology.
Based on the results of a general urine test, inflammatory processes, blood or pus, and epithelial cells of the urinary system can be detected.
The most common hardware diagnostic method is ultrasound.
Ultrasound can reveal:
- chronic or acute inflammation;
- prostate problems;
- prolapse of the bladder;
- the presence of sediment in it;
- tumor neoplasms.
The condition of the bladder walls is examined using cystoscopy. For these purposes, a special device is used - a cystoscope.
The device is a tube at the end of which there is a light element and a small camera. The tube is inserted through the urethra and allows you to examine in detail the inner layer of the bladder, identify various types of neoplasms or small polyps, ulcers.
The procedure is performed after anesthesia or under general anesthesia.
X-ray examination is prescribed using a contrast agent and only on an empty stomach. As a result, you can see structural changes in the organ (including after injuries), the presence of stones or sand. The images allow us to establish the correct diagnosis with high accuracy. A side effect of X-rays is small doses of radiation.
Thanks to computed tomography and MRI, high-quality images can be obtained in two or three dimensions. The bladder is scanned layer by layer. Often, these types of studies are carried out after an ultrasound and can detect urolithiasis, inflammation and infections, and anatomical changes. Often, CT or MRI are prescribed before surgery, as well as to monitor changes during the treatment process.
The presence of blood in the bladder always indicates a pathological process. There may be more blood, then the process is called macrohematuria. With it, the urine changes color and blood can be detected visually. With microhematuria, there is little blood, and it can only be detected through tests.
Gross hematuria may indicate the presence of cancerous tumors and requires immediate medical intervention.
| Analysis name | Features of the study |
| According to Nechiporenko | With the help of the study, inflammatory processes are diagnosed, the exact number of red blood cells, leukocytes and cylinders in one milliliter of liquid is determined. Urine collection is carried out in the same way as for general analysis. |
| According to Zimnitsky | The analysis allows us to determine the concentration ability of organs - not only the bladder, but also the kidneys. To do this, the density of urine, the daily norm, and the distribution of its entire volume over 24 hours are determined. To collect throughout the day, eight portions are collected in sterile containers, carefully cleaning the genitals each time |
| Bacteriological | The study involves urine culture and subsequent determination of the causative agents of pathological processes. Urine that contains no infectious agents is considered normal. Urine collection is normal; each container is sown on different nutrient substrates. The same method determines the sensitivity of pathogens to certain antimicrobial drugs |
Ultrasound provides the most reliable information when filling the bladder - the volume of fluid should reach at least 150 or 200 ml. This approach allows us to consider the shape of the organ, its size, and wall thickness.
Principles of treatment
From stones and sand
- an hour and a half before meals, take 1 tbsp. olive oil or flaxseed oil. Drink from 14 to 28 days,
- make a decoction of corn silk and drink it warm on an empty stomach in an amount of 200 - 300 ml daily. You can add cherry twigs to the broth,
- Place 3 drops of anise oil on a piece of sugar and consume three times a day.
Incontinence
- take one onion, dry it and make flour. Mix with 200 ml of hot water and drink all at once,
- grate the onion, take 1 tsp. gruel, add the same amount of honey and apple. Consume three times a day, half an hour before meals. Make new medicine all the time.
For urinary retention
Prognosis for a positive outcome in the treatment of the bladder in men is possible only in the case of timely and adequate therapy, as well as compliance with all doctor’s instructions.
Cystitis
Operation
Indications for surgical intervention:
- wound,
- injury,
- acute urinary retention,
- neoplasms,
- other diseases that cannot be treated conservatively.

There are several types of access for such an operation. Most often, a high section is used, which is convenient for removing stones, fistulas, resection, as well as for other types of surgical interventions on the bladder.
Indications for research
Despite excellent health in youth, sooner or later every woman is faced with the need to diagnose her bladder. The reason for this can be both age-related changes in the body and a number of unpleasant symptoms. Diagnosis of the bladder and kidneys has a number of indications, among which the following can be noted:
- pain in the lower abdomen, which is periodic or constant;
- frequent urge to urinate, constant feeling of bladder fullness;
- visible impurities of blood or pus in the urine;
- urine has a strong odor and has changed color;
- small amounts of urine;
- pain when urinating.
Against the background of the above symptoms, a person may experience an increase in body temperature, decreased performance, increased heart rate, and may experience profuse sweating. If there are pathological changes in the process of urination, it is necessary to consult a urologist as soon as possible. It is likely that there is an inflammatory process or other pathological changes in the organs of the excretory system.
Diet
Diet for oxalate bladder stones
You should avoid foods containing large amounts of oxalic acid and its salts. At the same time, food should contain a lot of magnesium. The amount should be reduced
Carbohydrates, gelatin, salt. You can drink up to 2.5 liters per day.
A tumor in the bladder is 5 times less common in women than in men. However, it has an aggressive course and makes itself felt only in the last stages of development. In order to recognize the disease in a timely manner, it is necessary to know the first symptoms of bladder cancer in women. In today's article we will look at the initial signs of this disease, the main causes and methods of its treatment.
Anatomical certificate
The bladder is located in the abdominal cavity and is a hollow organ. From the kidneys, waste products enter it through two ureters. Here they accumulate and are retained until the emptying process. When the bladder fills, the urge to urinate occurs. The accumulated fluid is removed from the body through a special channel.
The urinary system in women and men is radically different. Therefore, pathological processes have characteristic features in patients of different sexes. The most common diseases among the fair sex in this area are cystitis, urethritis and bladder cancer. In women, treatment of the latter disease does not always end favorably. Why this happens will be discussed below.
Main causes of pathology
An oncological disease begins its development after the appearance of a malignant neoplasm on the mucous membrane of the bladder or its walls. The tumor is formed from atypical cells. The genetic cause of the pathological process is being actively studied. Scientists have made assumptions regarding mutations at the level of the seventh chromosome.
The exact causes of bladder cancer in women have not been established. Doctors identify a group of factors that contribute to the accelerated growth of atypical elements. Among them are:
- Smoking. This bad habit negatively affects not only the lungs, but the entire body. Nicotine is eliminated through the bladder. Irritation of its walls by chemical products leads to cancer.
- Interaction with toxic products. The development of the disease follows the same principle as with smoking. In this case, women working in enterprises producing paints and varnishes or chemical products are at risk.
- Unhealthy diet with a predominance of fatty foods.
Chronic pathologies are also prerequisites for the development of cancer. First of all, these are cystitis and papillomatosis.

The first symptoms of bladder cancer in women
The initial sign of this disease is hematuria - the presence of blood in the urine. This symptom is observed in 8 out of 10 sick women. In some situations, its appearance is accompanied by pain. Among the characteristic features of this symptom are the following:
- The color of urine varies from pink to red.
- Blood clots have different shapes and sizes.
- Hematuria manifests itself in different ways. Some women have bloody discharge in the urine at an early stage of the disease, while in others this symptom is barely noticeable.
Blood impurities do not always indicate oncology. This symptom is also characteristic of simple cystitis. To verify the presence or absence of a pathological process in the body, you need to see a doctor and undergo a diagnostic examination. At the initial stage, it is still possible to cure bladder cancer in women.
Symptoms at an early stage are not always obvious. Such manifestations of the disease include dysuria and incontinence.

Other signs of illness
As the pathological process develops, other symptoms of bladder cancer in women appear. The growth of the tumor and its penetration into neighboring tissues is accompanied by a deterioration in health, skin and hair condition. Many sick women note a sharp decrease in body weight. Severe pain in the pelvic bones and lumbar region does not disappear even after taking the pills.
The progression of the pathological process is usually accompanied by the development of parallel diseases. Among them, hydrophonesis, chronic renal failure and various digestive disorders should be noted.
Symptoms of bladder cancer in women, or rather their intensity and severity, can vary. However, development is always increasing. Every day the discomfort and pain intensify. Any of the above signs of illness are a reason to consult a doctor.
Stages of the disease
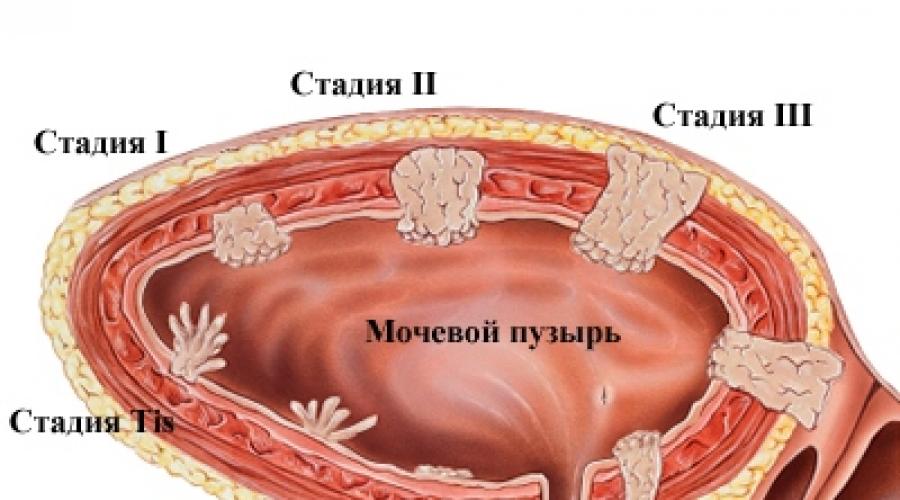
There are several stages in the course of an oncological disease. Each of them differs in the degree of penetration of tumor elements directly into the organ.
- Stage I. At the initial stage, the neoplasm is localized in the mucosal area and does not leave its boundaries.
- Stage II. The tumor grows into the submucosal layer, which serves as the base of the epithelium. Sometimes muscle tissue is involved in the pathological process.
- Stage III. At this stage, the neoplasm spreads to the adipose tissue and affects the walls of the bladder.
- Stage IV. Cancer affects neighboring organs (uterus, vagina, abdominal cavity). Treatment of the fourth stage of the disease has an unfavorable prognosis.
The first signs of bladder cancer in women should not be ignored. At the initial stage, it is still possible to cure the disease without serious consequences for health.

Diagnostic methods
We described just above how bladder cancer manifests itself in women. However, this disease sometimes has nonspecific symptoms. Therefore, diagnosis cannot be based solely on the patient’s complaints. Various techniques are used to confirm the disease. One of them is cystoscopy.
During this procedure, the doctor examines the inside of the bladder using a special instrument. It's not very pleasant, but it's painless. Through cystoscopy, the doctor can examine the tumor, determine its exact location and take a piece of tissue for a biopsy. If the tumor is small, fluorescent control is additionally prescribed. During the procedure, a contrast agent is injected into the organ, which accumulates in atypical cells. When illuminated with blue light, pathological elements acquire a pink tint, which makes it easy to identify a neoplasm.
Diagnosis of bladder cancer in women also involves ultrasound. It allows you to assess the structure of the tumor and the depth of damage to the walls of the organ. Additionally, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is used. With its help, the doctor excludes or confirms the presence of metastases.
To identify malignant cells, a urine test is mandatory. However, atypical elements are rarely found. Only 4 out of 10 patients have these cells in their urine.
There are also so-called rapid tests for bladder cancer in women. The principle of their action is in many ways similar to a pregnancy test, but they are not widely used. The sensitivity of this analysis ranges from 53 to 72%.
Based on the diagnostic results and after consultation with a urologist, treatment is prescribed. The choice of treatment method largely depends on the stage of development of the disease.

Cancer Treatment Methods
At the initial stage of the disease, resection of pathological areas of the bladder mucosa is performed. The operation is performed endoscopically. It allows you to remove the tumor without large blood loss and cuts on the skin. After surgery, the ulcerative defects are cauterized.
For small papillary tumors, the laser coagulation method is used. During the procedure, the doctor treats pathological lesions with laser radiation.
Cancer detected at the third stage is practically untreatable. In this case, partial resection of the bladder is performed. If necessary, the entire organ is removed—cystectomy. It is subsequently reconstructed from the adjacent part of the intestine.
If the doctor has already diagnosed the fourth stage of the disease, treatment is carried out using chemotherapy with simultaneous radiation. This approach makes it possible to alleviate the patient’s condition and relieve pain.

Consequences of cystectomy
Treatment of cancer always requires enormous efforts. After therapy, the patient needs to get used to the new status. We are talking about life without a full bladder.
After a cystectomy, several more operations are required to restore the lost functions of the organ. Most often, the ureters are brought out. Waste products accumulate in a special bag. Such a reservoir not only causes great discomfort, but also deprives a woman of the opportunity to live a full life.
There are alternative ways to solve this problem. For example, cystoplasty. This operation involves the transplantation of an artificial ureter. It is implanted in place of an isolated part of the intestine, and then brought to the urethra. As a result of the manipulations, the patient can relieve herself in a natural way.
Unfortunately, cystoplasty is not popular in our country and is an expensive procedure.
Chemotherapy for bladder cancer
In women, as well as in the stronger sex, treatment of this disease is rarely complete without chemotherapy. It is used in combination with surgery, since it is ineffective on its own. In modern oncology, more than 10 drugs are used for chemotherapy.
The adjuvant form of treatment is prescribed after cystectomy. It is used to reduce the risk of relapse. Non-adjuvant chemotherapy is given before surgery. It increases the likelihood of the tumor shrinking in size. Since both treatment options have many side effects, the decision to prescribe them is made after a complete examination of the patient’s health.

Features of nutrition in cancer
An important factor in complex cancer treatment is nutrition. Scientists have proven that changing the diet helps the patient recover quickly. In addition, the diet allows you to compensate for the deficiency of microelements and vitamins after chemotherapy.
Nutrition for bladder cancer in women should be balanced. In this case, the emphasis should be on protein foods. Preference should be given to chicken breast, lean rabbit, and seafood. You should be careful when eating red meat. Pork and beef have been proven to stimulate the growth of malignant tumors. Fish, on the contrary, is a source of “healthy” protein. Its use helps the body quickly restore lost microelements.
Prognosis for recovery
Survival rates largely depend on the stage at which bladder cancer is diagnosed in women. Symptoms at an early stage, which manifest themselves clearly, allow you to begin treatment immediately. In this case, the survival rate is more than 80%. At the second stage, subject to proper therapy, this figure is slightly lower - approximately 60%.
The prognosis for recovery in the presence of metastases is not the most favorable. For example, at the third stage of the disease it is 30%. At the final stage, doctors rarely make advance predictions. Only the luckiest women manage to cross the 5-year mark.
How to survive the disease?
Bladder cancer, like other cancers, causes serious harm to the entire body. The pathological process rarely stops at just one organ. In any case, it is possible to recover from such an illness. First you need to recover physically, and then mentally.
Frequent stress and prolonged depression lead to the insidious disease returning again. Therefore, it is advisable that family and close friends be with the patient during rehabilitation. They will always be able to support with a kind word and give parting words. Psychologists advise regularly visiting public places and spending more time outdoors. You can even find a new hobby, study science or foreign languages.
Don't forget that cancer can still be treated. You just need to diagnose the disease in a timely manner and choose the right treatment. If you seek medical help early, the chances of a full recovery are quite high.
There are many reasons for discomfort in the bladder. This can be facilitated by various infectious processes, tumor growths, urolithiasis and others.
In what situations is it necessary to undergo immediate examination?
You need to have your bladder checked if you:
- there were constant or periodic pains in the lower abdomen, intensifying during the act of urination, the appearance of unpleasant burning sensations;
- the urge to empty the bladder has become more frequent, even after visiting the toilet there is a feeling of overcrowding;
- urine has changed its natural color or smell, traces of blood or pus are visible to the naked eye;
- spread of pain along the back of the back; in women, it can radiate to the labia or pelvic organs;
- there is a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder cavity, portioned urine release, a feeling of spasms during the act of urination;
- against the background of dysuric disorders, there are signs of intoxication syndrome (fever, profuse sweating, rapid pulse, etc.).

If a patient has complaints related to urinary dysfunction, this is a direct indication for a bladder examination
What can cause discomfort?
Patients often turn to a therapist or urologist with complaints of urinary problems and painful sensations of varying severity.
In men, stagnation of urine in the bladder and the development of the inflammatory process are promoted by pathology of the prostate gland, which, by its growth, prevents its normal outflow.
In women, the most common symptoms are cystitis, inflammatory changes in the uterine cavity or its appendages (salpingoophoritis, endocervicitis and others), which can spread to the mucous membrane of the urinary tract. In addition, in the practice of a gynecologist, a condition such as endometriosis of the bladder is often encountered.
A widespread pathology is urolithiasis (the calculus can enter the bladder cavity from the overlying sections or directly form in its lumen).
The tumor nature of the above symptoms cannot be ruled out, which is equally common in both men and women.

A timely visit to a specialist will allow timely diagnosis of tumor growths in the walls of the organ.
Diagnostic methods
After examining the patient, the doctor will prescribe a number of laboratory and instrumental studies, taking into account the patient’s characteristic complaints. Checking the bubble is as follows.
Urinalysis is the most routine and mandatory examination method, which allows you to evaluate urinary sediment. It is simply necessary to make a correct diagnosis. In order to obtain the most reliable results, a thorough toilet of the genital organs is performed before collecting the analysis. The use of antiseptic agents is not recommended, as they may lead to an unreliable decrease in the concentration of colony-forming units (CFU). For women during menstruation, it is better to postpone the study until a later period.
Urine is collected in sterile containers, which can be purchased at any pharmacy. The middle portion is subject to diagnosis, that is, the patient must first release the first portion into the toilet. A few days before the planned test, it is recommended to stop taking antibiotics and other drugs that affect the composition of urinary sediment. You should also not drink alcoholic beverages.
The most reliable result is achieved when examining urine no later than 1 hour from the moment it is taken, which will prevent the pathological proliferation of microorganisms. Also, when transporting tests, it is important to ensure that the container with the contents does not freeze (we are talking about the cold season), since salts may fall out, which can lead the doctor in the wrong direction when making a diagnosis. The specialist evaluates the urinary sediment, namely the content of leukocytes, red blood cells and other components in the field of view of the microscope.

The first stage of any diagnosis is the study of the components included in the urinary sediment.
Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko
Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko helps the doctor in diagnosing inflammatory processes in the urinary system if questions arise after interpreting the general analysis. Measures to properly prepare the patient for urine collection do not differ from those described above. The study is carried out in laboratory conditions with the determination of the exact number of cylinders, leukocytes and red blood cells in 1 ml of urine. This method has greater reliability and specificity in contrast to general clinical analysis.
Urine collection according to Zimnitsky is an additional examination method and allows you to assess the concentrating ability of the kidneys and bladder by determining the density of urine, its daily volume and the distribution of this volume throughout the day. This study does not require any special equipment, therefore it is publicly available and quite simple. The patient is required to collect urine into sterile jars at certain intervals during the day (8 times), after properly treating the genitals. Next, the tests are sent to the laboratory, after which the doctor interprets the results.

Bacteriological examination of urine consists of its culture with further determination of the exact causative agent of a particular pathological process. Normally, the urine of an absolutely healthy person should be sterile, that is, not contain any infectious agents. After the urine has been collected according to all the necessary rules and delivered to the laboratory, it is inoculated on various nutrient substrates. Based on the grown colonies of microorganisms, one can accurately judge which of them caused the disease. Also, this diagnostic method makes it possible to identify the sensitivity of the pathogen to a particular antibacterial drug by applying a few drops of the drug to the medium with the grown cultures.

To determine the type of pathogen that caused the disease, biological material is inoculated on special media in the laboratory.
X-ray of the bladder
X-ray of the bladder is a publicly available and non-invasive examination method. It can only be carried out with the use of special contrast agents that allow visualization of the hollow organ. A couple of days before the planned study, the patient should adhere to a diet excluding foods that can cause increased gas formation in the intestinal loops. The essence of this method is the introduction of a contrast agent through the urethra, followed by an X-ray image of the bladder. This study is called ascending urography. In addition, a descending version of urography is performed, when the bubble is visualized after contrast injected into the patient’s bloodstream.
This examination method helps diagnose diverticula, tumor growths in the lumen of the bladder, foreign bodies and stones, fistula tracts and pathological reflux of urine from the ureters back into the bladder.
An ultrasound is performed on the patient only when the bladder is full (the volume of urine should be at least 150-200 ml). The patient drinks about 2 liters of non-carbonated liquid in a few hours. This is necessary so that the shape, size, contours of the organ, wall thickness and other characteristics can be assessed. The examination is carried out through the abdominal wall. If the situation requires it, it is possible to insert the sensor through the rectum (for example, in people with excess body weight or when there is a suspicion of prostate pathology). Ultrasound is absolutely painless and harmless. It is widespread and occupies one of the leading positions among modern diagnostic methods.

Ultrasound helps the doctor in making a diagnosis and is a mandatory examination method.
Cystoscopy
Cystoscopy refers to an endoscopic examination method performed using a special device that allows accurate diagnosis through direct visualization of internal structures. A specialist can evaluate in detail all the processes in the walls of the organ. The endoscope is inserted into the lumen of the urethra and then into the cavity of the bladder, and the image is transmitted to a large computer screen. Also, cystoscopy can turn from a diagnostic procedure into a therapeutic procedure, for example, when removing a polyp. This method is invasive and quite painful, so the patient is performed under local or epidural anesthesia, and in severe cases, general anesthesia is used. Frequent consequences after the examination include urethritis or cystitis, as well as the ascending spread of infection, up to the kidney parenchyma with the development of pyelonephritis.

The use of MRI allows the patient to avoid such unpleasant and painful procedures as cystoscopy or ascending urography
CT and MRI
CT or MRI provide the most accurate and detailed information about the condition of the bladder and the presence of any pathology in it, as well as the degree and extent of the pathological process. They show a layer-by-layer picture of the organ being studied. Often, only these examinations help the doctor make an accurate diagnosis. In addition, the study is painless, safe, and as informative as possible. It does not require special preparatory procedures. These methods are increasingly being introduced into all areas of medicine, but sometimes a patient may refuse to undergo research for financial reasons.
In most cases, the body reacts quite quickly to the presence of a disease in it. And problems with the bladder can be detected at an early stage, when treatment is still quite simple and short-lived. But in order to suspect an illness in time, you need to know what signs pathologies show themselves to be.
Bladder problems in women: symptoms
All organs of the female genitourinary system are closely interconnected. Therefore, sometimes the symptoms are very similar or even the same for different diseases. For example, an inflamed bladder and an affected urethra show almost identical symptoms. But the diagnosis must be carried out by a doctor. The patient’s task is to track alarm bells in a timely manner and report them to a specialist.
The most characteristic signs signaling bladder pathology include:
- Frequent urination. If a woman usually urinates up to 7-8 times a day, then if health problems arise, the number of urges can increase significantly.
- Excretion of blood in the urine. This phenomenon is called hematuria and can be caused by many pathologies. Damage to the bladder is indicated by blood in the last portion of urine. If hematuria accompanies the entire urination act, then there is a high probability of kidney disease. At the very beginning of the process, blood appears when the urethra is damaged.
- The appearance of pus or mucus in the urine. Such discharge indicates that there is an infection in the body. Its localization in the bladder is not excluded.
- Feeling of heaviness, constant feeling of a full bladder. The diseased organ causes a lot of discomfort to the patient. Only after leaving the restroom can she again feel that the bladder is full. False urges are a characteristic sign of the disease.
- Pain during urination. One of the most common symptoms of pathology is pain during the process of urination.
- Abnormal amount of urine output. If urine suddenly becomes too little or too much, then we are talking about the development of the disease. Of course, it is necessary to exclude the possibility that the reason for such a change does not lie in the peculiarities of the drinking regime.
- Difficulty urinating, intermittent stream. Any “innovations” that accompany such a natural process indicate a problem. If urine cannot be excreted freely from the body, then something is blocking it. This phenomenon is not normal.
- Urinary incontinence, sudden urges that cannot be tolerated. Such disorders are typical for older women with weakened muscles. In younger patients, such signs indicate impaired functioning of the bladder.
- Discomfort in the groin and lower abdomen. Almost always, with bladder diseases, a woman complains of physical discomfort. Their localization is quite explainable by the location of the affected organ.
These are the main symptoms by which bladder pathology is calculated. Other signs indicating a problem cannot be ruled out. For example, a woman may experience an increase in temperature, a general deterioration in health, weakness, nausea, and headaches. Each body is individual and reacts in its own way to a developing disease.
Major bladder diseases in women
If at least one of the above symptoms occurs, you should immediately consult a doctor. Bladder pathologies rarely disappear on their own: if left untreated, they develop, affecting other organs. The diagnosis is made based on a complete examination; Most likely, the patient will have one of the following diseases:
- Cystitis. Inflammation is the most common pathology of the bladder. The disease is associated with an infection that has penetrated inside and affected the mucous membrane. The disease is most often caused by E. coli and is bacterial in nature, but it can also be caused by fungi and viruses. Cystitis often becomes chronic, then its exacerbations bother the woman several times a year. The most characteristic signs are pain and frequent urination.
- Overactive bladder syndrome. This pathology has not yet been fully studied; in particular, its exact cause has not been established. Most experts believe that the syndrome is associated with a disorder of the nervous system. The only symptoms of OAB are uncontrollable and very strong urges, often resulting in urinary incontinence.
- Urolithiasis disease. Stones can form not only in the bladder, but also in the ureters and kidneys. Stones and sand cause disruption in the functioning of these organs; in particular, they provoke a disruption in the normal outflow of urine. As a result, the woman suffers from hematuria, pain when urinating, and sudden urges arising from the slightest physical activity.
- Bladder tumor. The neoplasm can be either malignant or benign. It is formed either in the epithelium or in connective tissues. It is difficult to identify a tumor, since its symptoms are similar to those of cystitis and other pathologies (blood in urine, pain when urinating, discomfort in the lower back and groin).
- Bladder tuberculosis. It develops gradually, initially manifesting itself as a normal inflammatory process (frequent and painful urination). Often complicated by persistent hematuria. With tuberculosis, tubercles, scars, and ulcers form on the mucous membrane of the organ.
There are other bladder pathologies, but they are much less common. For example, organ rupture. This is only possible when a large amount of urine accumulates and there is a sharp, strong blow to the walls of the bladder. If it bursts, the woman will feel pain in the groin and also want to urinate (although it is impossible to do this in this condition).
If you have the slightest discomfort associated with the urinary system, you should consult a doctor. Self-diagnosis and home treatment are unacceptable.