Boiler expansion tank. Expansion tank for heating: what is it for, where and which one is better. Why install an expansion tank in a heating system?
Read also
The use of an expansion tank is necessary in every closed heating system, and even in some systems connected to central heating. The process of installing an expansion tank is quite complicated, but if you carefully study the instructions, doing it yourself, without involving specialists, is quite possible.
Operating principle of the expansion tank
The expansion tank is a metal tank that is connected to the heating system. The main function of this device is to eliminate the increase in pressure in the pipeline due to expansion of the coolant.

Expansion tanks come in two types: open and closed. The operating principle of each of these tanks differs from each other.
The open expansion tank has a metal lid that opens to add coolant to the system.
A closed expansion tank consists of a metal container that does not have any openings other than the connection to the system. The container is separated by an internal membrane made of rubber. When the pressure increases, the rubber bends and the coolant enters the tank; when the pressure decreases or the coolant leaks, the rubber presses on half of the tank in which the gas is located and the coolant enters the system. Thus, the expansion tank is a pressure regulator that prevents high voltage surges in the system. If you do not use an expansion tank, the heating system will not function properly, and taps, pipes and the boiler will quickly fail.
Expansion tanks are used in a private heating system, and in some cases also in a system connected to central heating.
Types of expansion tanks for heating
Expansion tanks are divided into:
- open,
- closed.

An open expansion tank has a number of disadvantages, so it is rarely used, mainly in cases where the system is not connected to a pump and water circulates freely.
Disadvantages of an open expansion tank:
- due to frequent opening of the lid, contact between components of the oxygen heating system occurs, which causes rust to form on the walls of pipes and radiators;
- when the water temperature rises, the liquid evaporates, so you should periodically add coolant to the system;
- an open expansion tank is installed at the highest point compared to the heating system, so installing such a device takes a lot of time.
The only advantage of an open expansion tank is its low cost compared to a closed one.
A closed expansion tank is called a membrane tank; depending on the type of membrane, there are:
- expansion tanks of replaceable type,
- non-replaceable expansion tanks.
Replaceable expansion tanks require replacing the membrane if damaged. To replace the membrane, simply unscrew the flange.
Non-replaceable expansion tanks mean replacing the entire tank if the membrane is damaged. Such tanks are more resistant to pressure changes, and the membrane fits perfectly and hermetically to the outer wall of the container.

Expansion tanks come in two forms:
- balloon,
- flat.
The balloon shape resembles a large container in which a membrane or lid is located, depending on the type of tank.
Flat expansion tanks have a flattened shape and a membrane in the form of a diaphragm. The advantage of flat expansion tanks is that they take up little space and are easy to install.
Calculation of expansion tank for heating
The size and volume of the expansion tank is affected by:
- system type;
- system capacity;
- maximum permissible pressure;
- installation location of the expansion tank.
The easiest way to determine the volume of the expansion tank is to find out the capacity of the heating system and divide this amount by 10%. For example, if the heating system contains 400 liters of coolant, then the volume of the expansion tank will be 40 liters if the coolant is water. If glycol fluid is used as a coolant, then another 50% must be added to this amount.

Please note that 3% of the coolant in the closed expansion tank goes to compensate for possible leaks. In any case, the volume of the tank obtained as a result of the calculation should be slightly increased.
To obtain an accurate calculation in large or complex heating systems, it is better to trust specialists or use an online calculator.
The correct design of the expansion tank is indicated by the failure of the safety valve.
Installation of an expansion tank for open heating
The open expansion tank is where water comes into contact with oxygen. An open container is used when water moves freely through the system without using a pump or when the system is connected to central heating.
Since air comes into contact with water, the entire heating system is designed at a slope so that excess oxygen is forced out of the radiators.
Expansion tank installation location: the highest point in relation to the heating system. The installation height of the expansion tank must exceed the installation height of the heating system.
Expansion tank installation diagram:

An additional expansion tank is installed if it is impossible to mount the heating system at an angle. The installation level of the main and additional expansion tanks must be the same.
The open expansion tank includes pipes:
- expansion,
- signal,
- circulation,
- overflow.
Using an expansion pipe, the tank is connected to the heating system.
In most cases, an open expansion tank is mounted near the boiler and connected to the water supply system using a signal pipe that monitors the coolant level.
The overflow pipe connects the tank to the sewer; when the tank overflows, the liquid is automatically drained into the sewer.
The circulation pipe ensures the supply of coolant if the expansion tank is located in an unheated room.

Installation of a closed expansion tank
Before studying the rules for installing a closed expansion tank, let’s consider the advantages of this device over an open expansion tank:
- minimal heat loss;
- do not need isolation;
- work at high pressure surges;
- installation anywhere, without reference to the highest point;
- closed type devices are more compact and easier to install;
- no rust formation on the internal walls of the heating system;
- ease of maintenance.
Tools for work:
- adjustable wrench;
- wrench for installing plastic pipes;
- step key.
The preparatory stage includes:
- disconnecting the boiler from electricity, gas or water supply;
- turning off the tap responsible for coolant circulation;
- draining the coolant from the heating section on which the expansion tank is installed.

Instructions for installing the expansion tank:
1. Install a shut-off and drain valve on the supply pipe to shut off and drain the water.
2. Connect the expansion tank to the system using screws or flanges. If the heating system pipes are polypropylene, you need to use a soldering apparatus, couplings, angles and fittings.
3. A fitting called “American” will help you easily remove the tank for replacement or repair in the future. Before installing the fitting onto the expansion tank, wrap linen tape around the threads and apply sealing paste.
4. When the water has been drained from the system, cut the pipe with special scissors and install a tee.
5. Install the safety valve and pressure gauge.
6. Before starting the system, clean the coarse filter.
7. Before connecting the expansion tank to the system, you need to create operating pressure. To do this, use a pump.
8. When the expansion tank is connected to the network, turn on all coolant supply taps and turn on the boiler.

1. Install the expansion tank so that the coolant flows from the top.
2. In the absence of data on the exact volume of the heating system, the capacity of the expansion tank is calculated based on the boiler power: 15 liters of liquid are calculated for 1 kW of power.
3. Before purchasing and installing an expansion tank, inspect the heating boiler. Many modern boilers have a hidden expansion tank, which is located in the middle of the boiler.
4. Do not install a closed expansion tank near the circulation pump, due to the occurrence of large pressure drops.
5. Installation of a vacuum expansion tank is carried out only at positive temperatures.
6. Installation of a closed type membrane expansion tank is carried out on the side of the cold water supply to the boiler.
7. As a sealant, use only those sealants that are resistant to high temperatures, otherwise leakage is inevitable.
8. When determining the location and installation of the expansion tank, you should think about the further approach or maintenance of the device. Do not install the expansion tank in hard-to-reach places.
9. When installing the expansion tank, follow safety rules and generally accepted instructions.
10. Be sure to read the manufacturer's instructions for installing the expansion tank.
11. Be sure to install a safety valve, which sometimes comes with the tank; if there is no valve, buy it separately.

Maintenance of the expansion tank for heating
1. Once every 6-7 months, the expansion tank should be inspected for mechanical damage or rust. If they are present, you need to fix the problem.
2. In closed expansion tanks, the pressure should be checked once every six months.
3. In devices with a replaceable membrane, the membrane must be periodically checked for integrity or damage.
4. If the expansion tank is not used for a long time, store the tank in a dry place, making sure to drain all water and dry the device.
6. It is best to use an inert gas, such as nitrogen, to fill the air chamber.
7. The correct operation of the expansion tank depends on the pressure and temperature of the heating system.

8. If the pressure drops sharply, there is a risk of damage to the membrane. To replace the membrane you need to perform a number of steps:
- disconnect the expansion tank from the system;
- relieve pressure in the tank using the valve located at the top of the tank;
- remove the flange located at the point where the tank is connected to the system;
- remove the membrane and drain excess water;
- insert the membrane and install the flange;
- attach the tank, having previously set the desired pressure.
As the boiler heats up, the water expands and excess coolant fills a special container located at a certain point in the heating network. Hence our task is to explain how to install an expansion tank in the heating system of a private house. We will also clarify the connection location, method of emptying and setting the expansion tank.
Where is the expansion tank installed for heating?
So, the installation of the tank depends on the type of heating system and the purpose of the tank itself. The question is not why an expansion tank is needed, but where it should compensate for the expansion of water. That is, in the heating network of a private house there may be not one such vessel, but several. Here is a list of functions assigned to various expansion tanks:
- compensation of thermal expansion of water in closed heating systems;
- in open networks, the reservoir performs 2 functions - it absorbs excess coolant volume and removes air from the system into the atmosphere;
- under certain conditions, the membrane tank serves as an addition to the standard expansion tank;
- absorb excess heated water in the hot water supply network.
In open heating networks, the water in the reservoir comes into contact with atmospheric air. Therefore, the installation of the expansion tank is provided at the highest point - on the riser coming from the boiler. Often these systems are made gravity, with increased diameters of pipelines and a large amount of coolant. The capacity of the tank should be appropriate and be about 10% of the total volume of water. Where else if not in the attic to put such a large tank?
Reference. In one-story houses of old construction, there are small expansion tanks for an open heating system, installed in the kitchen next to the floor-standing gas boiler. This is also correct; a container located under the ceiling is easier to control. True, it doesn't look too good in the interior. To put it mildly.
 Alternative homemade open tanks made from a plastic canister (photo on the left) and an air receiver
Alternative homemade open tanks made from a plastic canister (photo on the left) and an air receiver Closed-type heating systems are distinguished by the fact that the membrane expansion tank for water is completely sealed. The optimal installation option is in the boiler room, next to other equipment. Another place where it is sometimes necessary to install a closed expansion tank for heating is the kitchen in a small house, since the boiler is located there.
In closed systems operating at , the volume of the reservoir should be increased to 15% of the total amount of liquid. The reason is the increased coefficient of thermal expansion of glycol antifreeze.
About additional capacities
Manufacturers equip wall-mounted heat generators with built-in tanks that absorb excess heated coolant. The dimensions of the tank do not always correspond to the house heating wiring; sometimes the capacity is not enough. To ensure that the coolant pressure during heating is within normal limits, the displacement is calculated and an additional expansion tank is installed for the wall-mounted boiler.
For example, you converted an open gravity system into a closed one without replacing the mains. The new heating unit was selected according to the heat load. The built-in boiler tank is not enough to expand such an amount of water.
Another example: heating all rooms of a two- or three-story house plus a radiator network. Here, the volume of coolant will also be impressive; a small tank will not be able to cope with its increase, and the pressure inside the system will increase. A second expansion tank for the boiler is needed.
Note. The second tank to help the boiler is also a closed membrane container, located in the combustion room.

When the hot water supply at home is provided by an indirect heating boiler, a similar problem arises - where to put the excess sanitary water from the storage tank? A simple solution is to install a relief valve, as is done on. But an indirect heating boiler with a volume of 200...300 liters will lose too much hot water through the valve. The right solution is to select and install an expansion tank for the boiler.
Reference. Buffer tanks () from some manufacturers also provide the ability to connect a compensating tank. Moreover, experts recommend installing it even on large-capacity electric boilers, as shown in the video:
How to install the tank correctly
When installing an open tank in the attic, a number of rules must be followed:
- The container should stand directly above the boiler and be connected to it by a vertical riser of the supply line.
- The body of the vessel must be carefully insulated so as not to waste heat heating a cold attic.
- It is imperative to organize an emergency overflow so that in an emergency situation hot water does not flood the ceiling.
- To simplify level control and make-up, it is recommended to install 2 additional pipelines into the boiler room, as shown in the tank connection diagram:

Note. It is customary to direct the emergency overflow pipe to the sewer network. But some homeowners, in order to simplify the task, take it under the roof straight to the street.
Installation of a membrane-type expansion tank is carried out vertically or horizontally in any position. Small containers are usually attached to the wall with a clamp or suspended from a special bracket, large containers are simply placed on the floor. There is one point here: the performance of a membrane tank does not depend on its orientation in space, which cannot be said about its service life.
A closed-type vessel will last longer if it is mounted vertically with the air chamber upward. Sooner or later, the membrane will exhaust its resource and cracks will appear. When the tank is positioned horizontally, air from the chamber will quickly penetrate into the coolant, which will take its place. Installing a new expansion tank for heating will have to be done urgently. If the container hangs upside down on the bracket, the effect will appear faster.

In a normal vertical position, air from the upper chamber will slowly penetrate through the cracks into the lower one, just as the coolant will reluctantly go up. As long as the size and number of cracks do not increase to a critical level, the heating will work properly. The process takes a long time, and you will not notice the problem right away.
A sure sign of critical wear and cracking of the membrane in a closed expansion tank is a drop in pressure in the home heating network. Periodically monitor the pressure gauge readings on the safety group.
But no matter how you place the vessel, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- The product must be located in the boiler room in such a way that it is convenient to service. Do not install floor-standing units close to a wall.
- When wall-mounting the expansion tank of the heating system, do not place it too high so that during maintenance you do not have to reach the shut-off valve or air valve.
- The load from the supply pipelines and shut-off valves should not fall on the tank pipe. Attach the pipes and taps separately, this will make it easier to replace the tank in the event of a breakdown.
- It is not allowed to lay the supply pipe along the floor through a passage or hang it at head height.
 Option for placing equipment in the boiler room - a large tank is placed directly on the floor
Option for placing equipment in the boiler room - a large tank is placed directly on the floor Connection methods
It is correct to connect the tank hydraulically at a point located on the return line in front of the boiler and (when looking in the direction of water flow). The tank can also be installed on the supply side, but under one condition: the pump must be located on the supply line and still stand in front of the compensating tank.
 The best place to connect a membrane tank is the heating return in the boiler room, but always before the pump, and not after it
The best place to connect a membrane tank is the heating return in the boiler room, but always before the pump, and not after it Point two: when a solid fuel boiler overheats, the tank connected to the supply will begin to fill with steam. Air and steam are compressible media, in which case the rubber “bulb” will no longer compensate for the expansion of water.
The correct connection of the expansion tank to the heating system is always carried out through a shut-off ball valve with an American connection. Then the tank can be taken out of service at any time and quickly replaced without waiting for the coolant to cool down. If you install a tee and a second tap on the supply line, as shown in the connection diagram, then the container can be emptied first:

Recommendation. When connecting an indirect heating boiler with a boiler and DHW, connect the expansion tank to the cold water supply line at the inlet to the storage tank. Here a special tank is used that can withstand the pressure of the water supply network. A heating tank or hydraulic accumulator is not suitable. How to distinguish them, watch the video:
How to check and pump up the expansion tank
Before connecting and filling the tank with coolant, it is necessary to check the pressure in the air chamber of the tank for compliance with the pressure in the heating network. To do this, a plastic plug is unscrewed or removed from the side of the air compartment, and under it there is a regular spool, familiar to you from car cameras. You measure the pressure with a pressure gauge and adjust it to your system by pumping it up with a pump or releasing it by pressing the spool rod.
 The tank is inflated through the fitting using a conventional hand pump
The tank is inflated through the fitting using a conventional hand pump For example, the design pressure in the network after filling should be 1.3 Bar. Then in the air compartment of the expansion tank you need to make 1.1 Bar, that is, 0.2 Bar less. The trick is to keep the rubber “bulb” of the tank pressed against the water side. Otherwise, when cooling, the compressed coolant will begin to draw air through automatic air vents, which is unacceptable. After setting up, open the tap, fill the entire system with coolant and calmly start the boiler.
Note. Some manufacturers indicate on the packaging of their products the factory pressure in the air compartment. Using it, you can choose a suitable tank and not bother with pumping.
Conclusion
All work related to the installation, connection and adjustment of the expansion tank is not highly qualified and can be done with your own hands. Moreover, you better know how to check and adjust the pressure in the tank during operation. Its decrease or surges is one of the reasons why the automatic gas boiler turns off the burner. If there are no serious coolant leaks, then the first thing you should do is measure the air pressure in the tank chamber with a pressure gauge.
Diaphragm expansion tank for a closed heating system
The membrane expansion tank is designed to compensate for the thermal expansion of the coolant and maintain the required pressure in closed heating systems.
Liquids that are used in heating systems increase their volume when heated due to thermal expansion. For example, the volume of water when heated to 90 o C increases by 3.55%. If ethylene glycol-based antifreeze is used as a coolant in the heating system, the volume of the liquid increases even more.
Diaphragm expansion tank for heating. Device and operation scheme. Through the air valve (nipple), the air chamber is filled with compressed air using a car pump.
In a closed heating system without an expansion tank, even a slight increase in temperature will lead to a sharp increase in pressure and activation of the safety valve. Excessive coolant will flow out through the valve.
A membrane expansion tank for heating is a vessel divided into two parts by a movable membrane. One part of the vessel is connected to the heating system and filled with coolant. Air is pumped into another part of the vessel at a certain pressure.
When the volume of liquid in the heating system changes, the membrane in the tank moves in one direction or another. As a result, the volume occupied by the liquid in the tank also changes. The compressed air on the other side of the membrane acts as a spring, maintaining the operating pressure of the coolant and preventing the safety valve from operating.
Operating limitations and safety requirements
Depending on the design of the expansion tank and the materials used, manufacturers impose certain restrictions on their use in heating systems.
As a rule, manufacturers impose certain requirements on the composition and corrosive properties of the coolant fluid in the heating system. For example, they limit the content of ethylene glycol in an antifreeze solution.
It is prohibited to use the expansion tank at pressures exceeding the permissible values specified in the manufacturer’s technical documentation. At the point where the expansion tank is connected to the heating system, it is necessary to install a safety group that monitors and limits the pressure in the tank.
In heating systems of private houses and autonomous heating of apartments, tanks and other heating equipment with an operating pressure of at least 3 are used. bar.
The expansion tank for heating is not allowed to be used in drinking water supply systems.
Installation, installation and connection of the expansion tank
 The expansion tank is connected to the return pipeline of the heating system on the suction side of the circulation pump. 1 - membrane expansion tank; 2 - connecting shut-off valves and drain valve; 3 - circulation pump; 4 — make-up tap
The expansion tank is connected to the return pipeline of the heating system on the suction side of the circulation pump. 1 - membrane expansion tank; 2 - connecting shut-off valves and drain valve; 3 - circulation pump; 4 — make-up tap The expansion tank is installed in a heated room. The tank is placed in a place that is easily accessible for maintenance. Installation is carried out in such a way that there is access to the air nipple, flange and connecting fittings.
Small expansion tanks are usually attached to the wall using a bracket. Fastening parts, as a rule, are not included in the product package and must be ordered separately. Large tanks are installed on the floor, on legs.
The expansion tank is connected to the return pipeline of the heating system on the suction side of the circulation pump.
 The connecting fittings for the expansion tank allow you to disconnect the tank from the system, drain water from the tank, and seal the shut-off valve.
The connecting fittings for the expansion tank allow you to disconnect the tank from the system, drain water from the tank, and seal the shut-off valve. At the connection point, on the line to the tank, it is necessary to install shut-off valves that are protected from accidental closure. In addition, a drain valve should be installed to empty the tank. Manufacturers of tanks usually offer special connecting shut-off and drainage fittings for their products. These kits must be ordered separately.
To connect the tank to the return pipeline, pipes with an internal diameter equal to the diameter of the tank connecting pipe should be used.
The expansion tank is connected to the heating system after flushing the system.
 The built-in membrane expansion tank is located on the rear wall of the double-circuit gas boiler
The built-in membrane expansion tank is located on the rear wall of the double-circuit gas boiler Membrane expansion tanks are sometimes built into boilers. For example, double-circuit gas boilers, as a rule, already have a built-in expansion tank of a certain capacity. If the volume of the built-in expansion tank turns out to be small for the heating system, then it is necessary to install a new tank outside in front of the boiler on the return pipeline. The volume of the new tank is selected as usual, without taking into account the capacity of the built-in tank.
Setting the pressure in the expansion tank
Before commissioning the heating system, before filling the tank with coolant, air is pumped into the expansion tank through the air valve - nipple using a car pump. The amount of air pressure is controlled by a car pressure gauge built into the pump or a separate device. Many manufacturers sell expansion tanks already filled with air or nitrogen to a certain pressure specified in the technical documentation. In any case, it is necessary to check that the initial air pressure in the tank is sufficient.
Initial pressure in the air chamber expansion tank - R o :
P o > P st + 0.2 bar ,
Where R st— the static pressure of the heating system at the installation site of the tank is equal to the height of the water column from the expansion tank connection point to the top point of the heating system (column height 10 m = 1bar)
The initial pressure in the air chamber must be checked and adjusted when there is no liquid in the tank— open the connecting fitting and pour out the remaining coolant from the tank. The expansion tanks built into the boiler are also emptied of liquid.
In the heating system of a private house, it is convenient to install an expansion tank with the air chamber factory-filled with air or nitrogen pressure P o = 0.75 - 1.5 bar . This pressure value set at the factory can be left unchanged, even if it is significantly greater than calculated using the formula R o. In most cases, this pressure is quite sufficient for the heating systems of a private house or apartment.
The expansion tanks built into the boiler are usually already filled with air or nitrogen to the pressure specified in the boiler instructions. Before installing the boiler, it is necessary to check the air pressure in the expansion tank and, if necessary, adjust it - pump in or bleed air.
The initial pressure exceeds the static pressure by at least 0.2 bar. necessary to create pressure in the system, which reduces the risk of vacuum formation, vaporization and cavitation.
At the next stage the tank is connected to the heating system. Then the make-up valve opens and the heating system and tank are filled with coolant with the initial make-up pressure - R start.:
P start > or = P o + 0.3 bar
(for example, if P o = 1 bar, then P start >= 1.3 bar)
R o— initial pressure in the air chamber of the expansion tank.
Often, manufacturers of boilers, for example gas boilers, indicate in the technical documentation the recommended initial pressure for recharging the coolant in the system. The instructions also indicate the minimum coolant pressure, below which the boiler simply will not start working. In this case, fill the system with the initial pressure specified in the instructions for the boiler.
Further, turn on the boiler and heat the heating system to the maximum operating temperature (for example, 75 o C). When water is heated, air dissolved in it is released. We remove air from the heating system. We monitor the pressure gauge readings and record the pressure value in the system with expanded water - R ext.
In custody turn off the circulation pump and turn on the make-up again and bring the pressure in the system at the maximum temperature of the coolant to the final one - R con:
R con< или = Р кл — 0,5 bar ,
Where R cl— opening pressure of the safety valve of the heating system.
(for example, if R cl = 3 bar, then we bring the pressure in the system to P con<= 2,5 bar at coolant temperature 75 o C)
The method described above for adjusting the pressure of the expansion tank allows you to increase the effective usable volume of the expansion tank to the maximum. The tank will be able to absorb the largest amount of water, and then return it to the system. This can be useful in the case of, for example, small leaks in the system. The tank will be able to release water into the system for a long time - the pressure in the system will decrease at a slower rate. The heating system will remain operational for a longer time. Or, as a result of cooling of the coolant, the pressure in the system may drop below the minimum required to turn on the boiler. In this case, the automation will not be able to start the heating. When adjusting the pressure according to the above method, the risk of such a development is reduced to a minimum.
These advantages of the pressure adjustment method described here are especially relevant for heating systems in country houses, where owners do not visit every day.
Checking membrane integrity
Operate the air valve (nipple) briefly. If water is leaking from the valve, the tank must be replaced, or, in tanks with a replaceable membrane, the membrane must be replaced.
If it is necessary to remove gas from the air chamber of the expansion tank, be sure to empty its water chamber first, and not vice versa!
Before refilling the tank with water, set the required pre-pressure in the air chamber. If these instructions are not followed, there is a risk of diaphragm rupture.
Calculation of the volume of the expansion tank for heating
The volume of the expansion tank is selected in such a way that when the coolant is heated to the maximum operating temperature, the increase in pressure in the heating system does not exceed the permissible value (remains below the response pressure of the safety valve).
Expansion tank volume for heating systems with a capacity of up to 150 liters
For heating systems containing a small amount of coolant, up to 150 liters, the volume of the expansion tank is selected using a simplified formula:
Vn = 10 - 12% x Vs ,
Where: Vn— design volume of the expansion tank; V s- full volume of the heating system.
Calculation of the capacity of the expansion tank for a heating system with a volume of over 150 liters
The calculation begins with determining the increment in coolant volume - the additional volume that is formed as a result of heating the liquid to operating temperature - V e.
V e = V s x n%,
Where, V s— full volume of the heating system; n%— coefficient of expansion of the liquid in the heating system.
Expansion coefficient value n%, at the maximum operating temperature of the coolant (water) in the heating system, is determined from the table:
| T oC | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 |
| nv% | 0,75 | 1,17 | 1,67 | 2,24 | 2,86 | 3,55 | 4,34 |
The expansion coefficient for antifreeze based on an aqueous solution of ethylene glycol (Tosol, etc.) is determined by the formula:
n a % = n v % x (1 + e a % / 100),
Where nv%— water expansion coefficient from the table above; e a %- percentage of ethylene glycol in the antifreeze solution.
At the second stage of calculation(second step) determine the volume of the water seal in the tank, Vv- this is the volume of coolant that initially fills the expansion tank under the influence of static pressure in the heating system. The capacity of the water seal is determined by the formula:
V v = V s x 0.5%, but not less than 3 liters.
At the third stage find the initial pressure in the heating system - P o. It is equal to the static pressure in the heating system and is determined from the calculation 1 bar= 10 meters of water column. The height of the water column in a heating system is equal to the vertical distance between the lowest and highest points of the system where the coolant is located. Using drawings or in situ, the vertical marks of the extreme points of the heating system are determined. The difference between the upper and lower marks will be equal to the height of the water column of liquid in the system.
At the fourth stage calculations determine the maximum operating pressure in the heating system - P e. The maximum operating pressure must be less than the response pressure of the safety valve in the heating system by at least 0.5 bar.
P e = P k — (P k x 10%), but definitely P k - P e => 0.5 bar .
Where: Pk— response pressure of the safety valve.
At the conclusion of the calculation determine the required volume of the membrane expansion tank for heating using the formula:
V n = (V e + V v) x (P e + 1)/(P e - P o)
Choose a tank with a nominal volume greater than the calculated one.
Example of expansion tank calculation
Let's calculate the expansion tank for the heating system with the initial data:
Overall volume Vs = 270 l.
Water column height 6 m., hence the initial pressure P o = 6/10 = 0.6 bar.
Maximum operating temperature of coolant (water) 90 o C. Using the table we determine the expansion coefficient n% = 3.55%.
The safety valve is set to operate at pressure P k = 3 bar .
We make the calculation:
V e = 270 l. x 3.55% = 9.58 l.;
V v = 270 l. x 0.5% = 1.35 l., since 1.35< 3, то принимаем V v = 3 l. ;
P o = 0.6 bar. ;
P e = 3 bar. — (3 bar. x 10%) = 2.7 bar., since the condition P k - P e => 0.5 bar must be met, then we accept P e = 2.5bar.
Vn = (9.58 l. + 3 l.) x (2.5 bar. + 1) / (2,5 bar. — 0,6 bar.) = 23,18 l.
Result:
We accept for installation an expansion tank with a nominal volume of 24 liters.
In addition to the volume, when choosing a specific type of expansion tank, the maximum operating pressure must be taken into account, for which the tank is designed.
Tank sizes
After reading this material, you will be able to leave behind once and for all the problem of calculating an expansion tank for closed and open heating systems. Below you can find the formulas. The topic of possible problems due to the incorrect choice of this equipment is also touched upon.
One of the key tasks that needs to be performed is calculating the expansion tank for a closed heating system. In turn, in open circuits this does not matter so much. In principle, the calculation is simple if you have the information. Despite the simplicity of the calculations, in practice mistakes can be made that lead to negative consequences. The most common mistake is a careless attitude to choice. It happens that people do not pay enough attention to calculating the volume of the expansion tank for heating and begin to understand the nuances only after the first problems appear and the system requires.
Possible problems"> Possible problems
First, let's look at the consequences of incorrectly calculating the expansion tank for a closed heating system. You may also have an unsuitable tank for your system, and you don’t even know it. If the tank volume has been calculated correctly, there will always be stable pressure in the circuit. It doesn’t matter whether your system is open or closed, the calculation of the volume of the expansion tank for heating of both types is similar, since the principle of their operation is approximately the same. The bottom line is that the water in the pipes acts as a coolant.
That is, it carries heat throughout the entire circuit and transfers it through the walls of the pipes. Thanks to this, the room becomes warmer. In this case, the amount of water always changes. After it heats up, it becomes more, and after it cools down, it becomes less. It is impossible to compress water mechanically, which means you need to temporarily remove excess water from the circuit. And always in such quantities that the pressure in the system is always maintained at the required level, without drops. Now we come to the main thing - pressure drops.
If pressure drops occur in the circuit, these are the first signs of malfunction. This may be due to an incorrectly calculated volume of the expansion tank for the heating system.
How do changes occur"> How do changes occur?
Possible options:
- promotion;
- demotion.
Both processes are interconnected. An increase in pressure in the circuit means that the coolant has nowhere to go after it has increased in volume. One of the reasons, not the only one, may be incorrect calculation of the expansion tank for closed-type heating. How does this happen in practice? Take, for example, a circuit containing one hundred liters of coolant:
- there are one hundred liters of cold liquid in the system;
- the boiler turns on and heats the coolant;
- the water expands and it is no longer one hundred, but approximately one hundred and five liters;
- The excess liquid has to go somewhere. For this purpose, an expansion tank is installed in the circuit;
- After the coolant cooled down, there was not enough of it in the circuit, as some of it was squeezed into the tank. Accordingly, the water must be returned to the pipes, which is what happens if everything is fine.

Pressure drops
If the volume of the expansion tank for a closed heating system is less than necessary, then all the liquid that does not fit will be discharged outside. The circuit contains special valves that release coolant if the pressure rises to a critical level. Modern boilers are also equipped with such valves. This is a necessary condition for safe heating operation. Increased pressure can even lead to an explosion. Imagine the consequences when the pipes simply burst and hot water flies in all directions. In addition to the risk of injury from the impact, such an emergency can cause burns to nearby people and animals.
Subsequently, after cooling, the water decreases in volume. The liquid from the tank is forced back into the pipes, but there is still not enough coolant. This is because the water that was removed did not return outside, it was gone irrevocably. As a result, the pressure in the circuit drops sharply. This produces the following results:
- boiler stop. Heaters have a certain threshold of minimum pressure at which it can operate. If this value is not maintained, it simply cannot turn on; the automation does not allow this;
- defrosting the system. If your heating equipment stops in winter and you are not at home, a serious accident may occur. The system will freeze in a few hours, depending on the level of insulation of your home;
- need for recharge. It is necessary to add the missing amount of water to the circuit.
These are the results of gross mistakes made when calculating the expansion tank for heating, or if you relied on a tank built into the boiler.
Modern boilers have built-in tanks, the volume of which is often insufficient. Be sure to take this fact into account and install additional tanks if necessary.
It also happens that the tank is completely filled, the pressure continues to increase, but does not reach a critical level. The pressure gauge needle balances on the edge of the operating maximum of the circuit, while everything functions. There are countless such cases. People very often ask questions about such differences. Of course, such processes worry them, since they are not the norm. With such increases, the circuit operates under extreme conditions, which leads to its rapid wear. Also, such processes adversely affect the boiler, and it costs a lot of money.
Selection of volume"> Selection of volume

Open tank
The dimensions of the expansion tank for an open heating system, by and large, determine its volume, since the design of such a tank is quite simple. It is made from sheet metal. There is a hole in it through which the coolant enters and goes back into the pipes. They can also be equipped with an overflow hole through which excess water is discharged into the sewer.
It happens that automatic recharge is supplied to the tank. But the main thing is how the expansion tank in the heating system is designed, or rather, its volume. Let’s take the same system with one hundred liters of water. After heating, the liquid will increase by five percent, maybe more, depending on the temperature in the circuit. It turns out that the volume of the expansion tank for this open heating system should be at least five liters, preferably more. And the calculation of the expansion tank for the heating system comes down to the following algorithm:
- five liters is the expansion of water;
- a couple of liters should always be in the tank - this is to prevent air from entering the circuit;
- We need to make three liters in reserve.
Based on the results of calculating the volume of the expansion tank for heating, ten liters are obtained. By the way, this is the simplest and most common method of selection - ten percent of the amount of water in the circuit.
For closed systems, in addition to the simple, popular method of calculating the volume of the expansion tank of a heating system, there are more accurate methods. To use them, you need to know several meanings. These include:
- How much does the volume of water (W) increase when heated? Answer: five percent. The value is rounded to the nearest whole number without fractions for convenience. If a non-freezing liquid, antifreeze, circulates in your circuit, then this value will be greater;
- how much water is in the circuit (VC). Such data should already be available from the stage. Since the selection of the heater is carried out based on this value. If it happens that you don’t know how many liters there are, all you have to do is measure. The first thing that comes to mind is to completely drain all the liquid from the circuit and fill it again. The number of liters can be measured in buckets, or you can use a special counter that is installed on the stream;
- What is the maximum pressure the circuit and boiler (DC) are designed for? This value can be read in the heater documents, or on the heater itself. It is unlikely that there will be no documents or information on the boiler body. But if this happens, then the Internet will help you;
- what is the pressure in the air chamber of the expansion tank (DB). This is also indicated in the technical documentation.
OB x VK x (DK + 1) / DK – DB
Based on the results of calculating the capacity of the expansion tank for heating, you will receive the exact value. The question of the appropriateness of such complex calculations remains open. Undoubtedly, according to the results of this formula for calculating the expansion tank of the heating system, the result will be a smaller value than according to the results of the “folk” method. But an error on the larger side is not an error. If the tank is larger than necessary, it’s okay, you just need to configure it correctly.
To what level should the air chamber be inflated? To what level should the air chamber be inflated?
It is important to correctly configure the expansion tank for closed-type heating. Calculating capacity is, of course, a serious aspect, but even if done correctly, the tank may still not function properly. To understand this, let’s briefly look at its design. It consists of two compartments, between which there is a rubber gasket. There is no connection between cameras. There is a nipple in the air compartment.
During operation, water fills the volume of the tank chamber, while the membrane stretches. If the pressure in the air chamber is too high, it will simply prevent the elastic from deforming. As a result, the tank does not work. The air chamber should be two tenths of an atmosphere less than the operating pressure of the boiler. Or use the manufacturer's recommendations to configure.
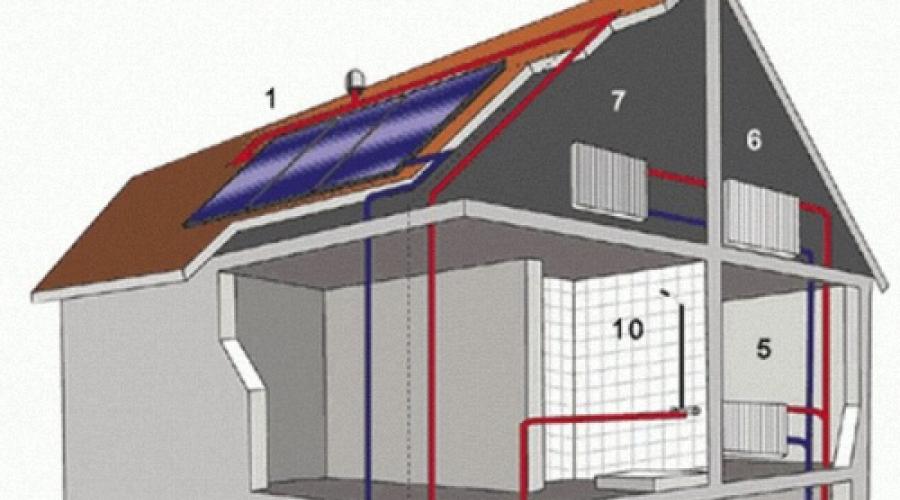
One of the advantages of an autonomous heating system is the ability to maintain a comfortable temperature in the house, regardless of the start and end dates of the heating season, and save on utility bills. Schematically, it consists of a heating boiler and a circuit through which hot coolant circulates. Water is usually used as a coolant. An important role in heating equipment is played by the hot water circulation system, which consists of several parts. The correctness of its operation largely depends on such a design element as the expansion tank.
An example of a heating system with an expansion tankLet's compare closed and open heating systems
The operation of an open heating system is based on the laws of thermodynamics, due to which the coolant moves. From an area of high pressure and corresponding temperature at the boiler outlet, water moves through pipes to an area of lower pressure, and its temperature decreases. The cooled coolant is sent back to the boiler and the process is repeated. Thus, natural circulation of liquid occurs, according to the laws of physics.
Since when water is heated, its volume increases, an expansion tank is provided in the design of an open heating system. For efficient movement of open-type coolant, the expansion tank is installed at the highest point of the system, and the heating boiler at the lowest. Installing an expansion tank in the attic seems to be the best option. Its device is not complicated.
 Open type heating scheme
Open type heating scheme Over time, water evaporates, so its level must be replenished in a timely manner. During breaks in the use of heating and at negative ambient temperatures, the water must be drained, otherwise it will freeze in the pipes and burst them. An open heating system has the following advantages:
- independence from electrical energy sources;
- no noise;
- ease of maintenance;
- quick start and stop.
You can select radiators for any type of heating system based on the recommendations of the article
In a closed heating system, water does not evaporate because it is sealed. The movement of the coolant is carried out using a pressure or circulation pump, which can be found in the article. In this case, for effective operation, an expansion tank made of durable metal is also required. A closed heating system consists of a heating boiler, a circulation pump, a pipeline network, radiators and an expansion tank. A closed heating system has the following advantages:
- no need to constantly monitor the coolant level;
- possibility of using antifreeze;
- internal pressure adjustment;
- possibility of connecting additional devices.
 Closed heating system
Closed heating system With proper installation of heating equipment, both options will work perfectly. The choice between them is determined by operating conditions and placement features. The differences between the two systems are as follows:
- In an open heating system, the expansion tank is located at the highest point. In a closed heating system it can be located almost anywhere.
- The likelihood of air locks forming in a closed heating system is much lower. This is due to increased internal pressure and lack of direct contact with the atmosphere.
- To operate an open heating system, large diameter pipes are required. Installation work is complicated by the need to take into account hydraulic rules when distributing flows, making turns, slopes, and so on.
- Small diameter pipes used in a closed heating system reduce its cost. Here it is important to correctly install the circulation pump so that during its operation it creates as little noise as possible.
Design and functions of the expansion tank in the heating circuit
The function of the expansion tank in an open heating circuit is to receive excess water when it expands due to heating, and return it to the system when the temperature drops. The container is not sealed, and the coolant is in direct contact with the environment, so water evaporates in an open heating system. The device has a simple design; if necessary, you can make it yourself.
 Open type expansion tank
Open type expansion tank The disadvantages of an open system include the need to constantly monitor the water level as it evaporates, the danger of freezing the liquid in the expansion tank, and the inability to use antifreeze as a coolant. In addition, air entering the system causes the formation of air locks, corrosion of internal parts and their cavitation.
In a closed heating circuit, the expansion tank is made of high-strength metal. The device consists of two halves, hermetically sealed to each other. The design includes a foot valve and an internal membrane. As the coolant temperature rises, the valve opens and excess liquid from the increased volume enters the expansion tank.
A diaphragm made of heat-resistant high-strength rubber divides it into two parts. Gas is pumped into the upper part of the sealed container, and a hot coolant enters the lower part, compressing the membrane and the gas environment located behind it. When the working fluid cools, due to the expansion of the gaseous medium, the diaphragm squeezes it back into the heating circuit.
The membrane tank can be installed horizontally or vertically in any position.
 Closed type expansion tank device
Closed type expansion tank device The performance of a closed expansion tank does not depend on its orientation in space, which cannot be said about its service life. To extend the service life of the membrane tank, it is better to position it so that the air chamber is on top. Over time, cracks appear in the diaphragm, and until their size and number reaches a critical level, the system will work properly when the container is placed vertically. In a horizontal position (if cracks appear in the diaphragm), air from its half will quickly penetrate into the coolant and vice versa, which will require an urgent replacement of the tank.
What does insufficient volume of the boiler’s built-in tank lead to?
Insufficient volume of the built-in boiler tank can lead to malfunctions of the heating system. When heated, the liquid expands and its excess enters the expansion tank. If its volume is insufficient, the tank overflows and the emergency pressure relief valve releases the coolant into the drain. The remaining cooled coolant is returned to the heating circuit.
 Pressure in the system when the volume of the expansion tank is insufficient
Pressure in the system when the volume of the expansion tank is insufficient As a result of a decrease in its quantity, the internal pressure in the system decreases. If it decreases by a small amount, the boiler will function; if the pressure decreases significantly, the operation of the heating equipment will be blocked.
If the coolant level is not promptly replenished to normal, the system may defrost, so such emergency situations should not be allowed to occur.
Calculation of the required volume of the membrane tank
The required volume of the membrane tank is calculated using a simple formula. Its value is ten percent of the total amount of coolant circulating through the system, if water acts in this capacity. The total volume of coolant can be determined by the readings of the water meter when filling the heating system.
A more accurate figure is obtained by summing the volume of all pipes, the capacity of the boiler and batteries. It is believed that fifteen liters of coolant are required per kilowatt of boiler equipment power, that is, the total volume of liquid is determined by multiplying the nameplate power of the boiler by fifteen. This value will be within the permissible error.
Illustration of the change in volume in the tank due to pressure fluctuations in the systemFor example, if heating equipment requires three hundred liters of water to operate, then the volume of the membrane tank should be thirty liters. This parameter increases by fifty percent when using non-freezing liquid as a coolant, that is, in this case, the required volume will be forty-five liters. In addition, it is necessary to take into account the possibility of leaks and increase the calculated value by approximately three percent. If the size of the membrane tank is correctly determined, the emergency pressure relief valve does not operate.
Setting the optimal pressure in the tank
Before connecting the expansion tank and filling it with coolant, it is necessary to set the optimal pressure in its air chamber corresponding to this parameter in the heating network. To perform this procedure, a plastic cover is removed from the air compartment, under which there is a nipple, the same as in car tires. The pressure measured by the pressure gauge is adjusted to the desired value by pumping it up using a pump or by bleeding it by pressing the nipple rod.
 The protection group controls the pressure in the system
The protection group controls the pressure in the system The optimal pressure in the tank is obtained by adjusting the internal pressure in a closed heating system downward. This is done so that the rubber diaphragm is pressed on the coolant side. Otherwise, when it cools down, air will be drawn through the automatic vents, which should not be allowed under any circumstances. For example, if the internal pressure in the network is 1.2 atmospheres, then its optimal value in the expansion tank will be one atmosphere. After setting this value, you can open the tap and fill the system with coolant.
At intervals of six months, it is necessary to check the pressure in a closed compensation tank and carry out a visual inspection for mechanical damage.
If there is a sudden change in internal pressure and temperature in the heating network, there is a risk of damage to the membrane, in which case it will need to be replaced. To do this, you need to perform the following manipulations:
- Disconnect the expansion tank from the main line;
- release the pressure in it by pressing the spool rod;
- remove the damaged membrane, drain excess water and install a new one;
- Having established the optimal pressure, attach the container in place.
Selecting the location for installing the expansion tank
Installation of the expansion tank depends on the type of heating system and the purpose of the tank itself. It is better to install a closed compensation tank on the return line in front of the heating boiler and circulation pump.
 Options for placement and installation of the expansion tank
Options for placement and installation of the expansion tank If it is located on the supply line, the service life of the membrane will decrease due to constant exposure to a higher coolant temperature. In addition, in this case, if an emergency occurs, steam may penetrate into the expansion tank, as a result of which the diaphragm will no longer compensate for the coolant pressure, since the mixture of air and steam is a compressible medium.
The expansion tank is connected through a shut-off ball valve. This is done so that, if necessary, the compensation tank can be quickly replaced without waiting for the coolant to cool down. Installing a second tap makes it possible to pre-drain hot water from the tank.
How to properly install a closed expansion tank with your own hands
The connection diagram is not particularly complicated. You can correctly install a closed expansion tank with your own hands by following the following connection diagram. The preheating boiler is de-energized, the coolant supply is shut off, and the water from the radiators is drained.
If polypropylene pipes are used for installation, you will need a special soldering iron for their installation. You will also need couplings and corners. It is better to use “American” fittings, as it makes it possible to easily remove the container for maintenance and repairs. Below is a sequential diagram of actions for installing an expansion tank.

- A sealing thread is wound onto the threaded part of the tank fitting.
- An adapter is screwed onto the fitting to install the tap.
- A sealing thread is wound onto the threaded part of the adapter.
- A shut-off valve is installed on the adapter.
- A sealing thread is wound onto the threaded part of the “American”. The “American” is screwed into the tap using pliers and an adjustable wrench.
- A sealing thread is wound onto the threaded part of the angle. The corner is wrapped in “American”.
- A clamp is placed on the tank body to secure the tank, which is included in the delivery set.
- On the opposite side of the tank there is an air injection nipple onto which a plastic cap is screwed.

After placing the expansion tank in the selected location, the quality of all connections is checked, and coolant is supplied to the system. After the internal pressure in the batteries reaches the calculated values, the air pockets are released from them, and the heating system starts at full power. The compensation tank is installed so that it is convenient to service, that is, free space is left between it and the wall.
All connections must be sealed with sealants that are resistant to high temperatures, otherwise leaks will inevitably occur. The membrane expansion tank in a closed heating system is installed on the cold water supply side. When performing all manipulations, it is necessary to comply with safety requirements.