What thickness of insulation is required for an attic space? The thickness of insulation for permanent residence in a frame house for different regions replaces 150 mm of insulation
Read also
Question:
Familiar builders say that for insulation frame house 150 mm is enough mineral wool. However, I read on forums that 20 cm is the minimum to avoid freezing in the Siberian winter. Who is right?
Answer:
Let's proceed from the understanding that a residential building is not just half-wall-ceiling, but quite a complex system, which both gains and loses heat. You can, of course, start drawing formulas, giving thermal calculations, but I’ll say it simpler - you need to maintain a balance of the cost of achievement required level heat loss
For example, if you live somewhere in Novosibirsk or the region and you have gas installed on your property, I believe that the best option for a frame house there will be “Finnish” technology and the following insulation pie (from the inside to the outside) is quite sufficient:
- "ecowool" 50 mm thick, applied in an internal cross frame, applied using a wet-glue method;
- mineral insulation in racks with a thickness of 150 mm if you use ventilation with a heat recuperator or 200 mm if not;
- MDVD 22 mm for wood or vinyl siding or 40 mm for plaster.
In this case, it is highly advisable to follow the following recommendations:
- ceiling height no more than 2.7 m;
- not at all “French” windows with a good five-chamber profile with a width of at least 70 mm and double-glazed window filled with argon and internal low-emissivity glass (I-glass);
- the correct external insulated door, "Finestra" type.
Then you will be guaranteed warmth even during periods of bitter frost, comfortable for the ears due to excellent sound insulation and optimally balanced in price/effect, while heating costs will pleasantly surprise you;)
In addition to the above, I strongly recommend that you familiarize yourself with a comparison of the characteristics of walls made of different materials and different designs.
There is an excellent calculator that will allow you to calculate required thickness thermal insulation of your frame house, taking into account the region - I highly recommend it! Just don’t forget that the wall consists not only of insulation, but also of posts and strapping, and these are “cold bridges”!
And we must take into account that in the case of a floor on joists with an unheated foundation (MZLF, screw piles, etc.), insulation is also needed in the joist/grillage space, and at least 50 mm thicker than in the walls. And put 100 mm more insulation in the ceiling than in the walls - you won’t regret it, since it is the ceiling that provides the greatest relative heat loss, because the air masses tend upward as they heat up!
What should be the thickness of the walls of a frame house for winter accommodation in him? There is a clear answer to this question. at the same time, he is not there. Why? Because the minimum thickness of the walls of a frame house for winter living depends on the region where you built this structure.
Let's sort everything out piece by piece. Depending on what region you live in, you will need a certain thickness effective insulation to keep the inside of your home warm during the winter.

If you live in a warm region, then a thickness of 50 mm of foam or basalt wool will be enough for you. If you live in the North, then 150 mm of insulation will not be enough for you; you will need 200 or 250 mm. Any less will lead to excessive consumption of fuel or energy for heating your home.

How to find out what the minimum and optimal thickness walls? Very simple. For this purpose, there is a table on the thermal resistance of enclosing structures for each region of Russia.

This table shows the R indicators, which, according to the new SNiP standards, developers must adhere to when building or reconstructing residential buildings.

Use this simple formula calculating the thickness of insulation depending on its thermal conductivity indicators:

R = p/K, where p is the thickness of the insulation (in meters), R is the thermal resistance of the wall for a given region, K is the thermal conductivity coefficient of the insulation.

This way you will get its minimum thickness. IN frame house in fact, the thickness of the insulation is equal to the thickness of the wall. This way you will know what thickness it should be for winter living in it.

Calculation example. We are building a frame house in the Volga region. Indicator R = 2.1 m2*C*W for this region. We use basalt wool with a thermal conductivity of 0.056 W/(m*C) as insulation. We calculate according to the formula given above. We find that the thickness of the frame wall with insulation should be at least 12 centimeters.

Note. The thermal resistance of a wall differs from the same indicator for attic and basement floors, as well as windows and doors. For example, for the same region, the thermal resistance for floors will be equal to R = 3.2 m2*C*W. This means that the minimum thickness of the ceiling insulation will be already 18 centimeters.

To imagine what the wall pie of a frame house with mineral wool as insulation looks like, just look at the diagrams located on this page. For different conditions...
Any wall of a frame house, the construction of which is thought out in advance or is carried out according to albums technical solutions leading construction companies, performs its functions perfectly. After all, wall pie...
Any frame house design, the components of which are calculated and competently executed, is reliable by default. You can count the frame nodes yourself using a calculator, or you can use ready-made...
Design frame wall determines its thickness, which is important for choosing the size of the foundation strip. The thickness of the wall is also influenced by the choice of insulating material, its width, and the choice of interior and exterior wall decoration. How thick can a frame house be? And how to calculate its value for various options insulation?
Wall design and thickness
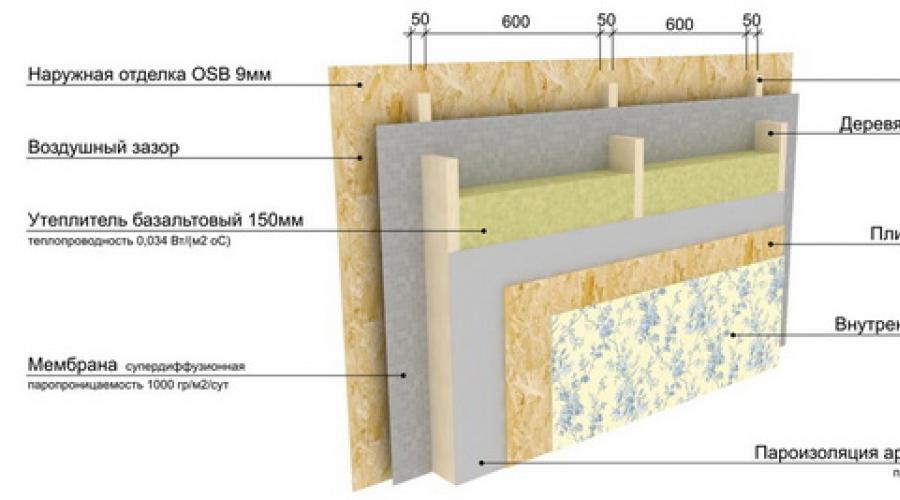
The thickness of the walls of a frame house is determined by their design, the presence of ventilation gaps and the choice of insulation. Traditionally, a frame wall consists of the following layers:
- Outdoor wall cladding– its thickness can vary from several millimeters (if it is a metal profiled sheet) to several centimeters (if it is a more massive cladding - OSB chipboard or cement bonded particle boards DSP).
- Ventilation gap between the outer wall cladding and the insulation - it is at least 30-50 mm and ensures free air movement.
- Mineral insulation must be used with membrane protection. The membrane itself does not take up much space. Its width is measured in microns. But mineral insulation will determine the size of the wall, since it is the thickest material of the wall “pie”. The width of insulation varies depending on climate conditions and the purpose of the house (seasonality of residence - all year round or only summer). Usually it is at least 50 mm for a summer building and more than 150 mm for a year-round one. Wall thickness of a frame house for permanent residence– more, since the building is used during cold periods and winter temperatures. If necessary, the heat insulator is placed in two layers, increasing the thickness outer wall. Then the thickness of the insulation of the frame house can double.
- Internal wall cladding - its thickness also depends on the choice wall material. The inner lining can be thicker than the outer if it is made of wooden materials(block house, timber). Possible thin interior lining– plywood or MDF panels.
Now let’s take a closer look at how to build a frame house, what thickness of the walls will the building have?
Insulation thickness
When calculating the thickness of the walls, they begin by finding out what thickness of insulation is needed in a frame house. All other calculations are made from it, since the type of insulation determines not only its dimensions, but also the choice internal structure the wall itself. Cotton insulation requires a ventilation gap. Expanded polystyrene or polyurethane foam insulation is made without a hollow gap in the wall. Therefore, let's start with choosing a heat insulator.
Insulation with mineral wool
Traditional insulation of frame walls is mineral wool. She has high performance heat saving and average durability. Mineral wool mats limit 99% of heat loss and transmit tenths of W per 1 square meter. m area.
On a note
The main indicator of the ability to isolate internal warm room is a characteristic of thermal conductivity. For glass wool it is 0.035-0.055 W/m°C, for mineral basalt wool – 0.039-0.045 W/m°C. This means that from 1 sq. m of wall, no more than 0.055 (or 0.045 for basalt wool) W of heat can leak.
The difference in thermal conductivity characteristics is determined by the structure and rigidity of the material. If mineral wool is in the form of rigid slabs intended for plaster, then it has a dense structure and greater thermal conductivity(0.04-0.045 W/m°C). If mineral wool is supplied in the form of compressible mats, its structure is more porous. For such mineral wool, thermal conductivity indicators correspond to the lower limit - 0.035 - 0.039 W/m°C
For effective insulation choose a material with the lowest possible thermal conductivity characteristic. Depending on this characteristic, its thickness is calculated. What thickness of insulation for a frame house will be needed for year-round living?
You can select the thickness using special tables that indicate the width of the heat insulator depending on street temperatures, -5°С, -10°С, -15°С or -20°С. The thickness of the mineral wool of a frame house is selected taking into account extreme winter temperatures. For example, if the temperature is stable in January -10, but sometimes it happens -20 or -25, then the insulation is designed for the most low temperature cold month.
Table - thickness of mineral wool for insulating the walls of a frame house
| Regioncity | Mineral wool thickness |
| Magadan | 170-180 mm |
| Irkutsk | 160 -170 mm |
| Novosibirsk | 150-160 mm |
| Ekaterinburg | 140-150 mm |
| Saint Petersburg | 130-140 mm |
| Krasnodar | 90-100 mm |
| Sochi | 70-80 mm |
Calculation of mineral wool insulation
S = wall thermal resistance x thermal conductivity coefficient.
The value of the wall’s thermal resistance is selected depending on the region of construction. It takes into account the level of winter temperatures and extreme cold. The thermal conductivity coefficient is a characteristic of the insulation material. It is indicated on the product packaging, and its value can also be determined using reference tables.
Table - thermal resistance of house walls by region
Using an example, we will look at how the construction of frame houses is carried out in Vladivostok. How to correctly calculate the thickness of insulation for the walls of a frame house if the insulation is performed with mineral wool with a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.04 W/m°C.
For Vladivostok, the thermal resistance of the walls of a residential building should be equal to 3.25 m 2 °C/W. Total we get: 0.04 x 3.25 = 0.13 m or almost 130 mm.
Most manufacturers produce mineral wool in two thicknesses - 50 or 100 mm. Therefore, it is necessary to use two layers of insulation - one 100 mm each, and the other 50 mm each.
In this case, the house will be insulated with a heat insulator thickness reserve of 20-30 mm. 100 mm of mineral wool is replaced by a heat capacity of 2 m. brick wall or 400 mm. tree. Accordingly 30 mm. additional insulation will replace 600 mm. brickwork.
Insulation with polystyrene foam
This type of insulation is often used in frame-panel construction, when the wall of a house is constructed from ready-made blocks, insulated during production at the factory. Sometimes walls are insulated with polystyrene foam frame houses, using it in addition to mineral wool. How thick should the walls of a frame house be? For warm winter V southern regions 70 mm thick foam is used. For Moscow, slabs with a thickness of 150 mm are required.
For wall insulation, it is recommended to use foam plastic with a density of at least 25 kgm 3. This characteristic also affects the choice of slab width. For comparison: insulation with foam plastic with a density of 25 kgm 3 and a width of 100 mm is equivalent to insulation with foam plastic with a density of 35 kgm 3 and a thickness of 50 mm. Density and width vary by choosing best option material.
Expanded polystyrene has almost the same thermal conductivity characteristics as mineral wool. They lie in the range of 0.03-0.045 W/m°C. The calculation of the thickness of polystyrene insulation will be similar. It is necessary to multiply the thermal resistance of the wall in your region by the thermal conductivity characteristic.
For the Moscow region we get 0.035 x 3.9 = 140 mm of insulation.
On a note
When ordering foam boards, you can specify the thickness of their sawing. Thus, it is possible to carry out insulation in the required size - 115 mm, without overpaying for extra millimeters of material.
Polystyrene foam is used in floor insulation. Therefore, its thickness is important when determining the thickness of the slab of a frame house. Which affects its heat capacity, the ability to retain heat inside. The stronger the street cold, the greater the thickness of the insulating layer should be.
Ventilation gap
The vapor permeability of a wall is a characteristic that shows the presence. If vapor permeability is low or absent, then there is a need to build forced exhaust. The walls of natural materials characterized by natural vapor permeability. They are said to "breathe". For many artificial materials, foam insulation, there is no vapor permeability. Therefore, they block gas exchange through the wall.
A wall made only of mineral wool has a high vapor conductivity. At the same time, condensation accumulates in the insulation, which disrupts the thermal conductivity properties of the insulation. In order for the wall to keep the cold out, it is necessary to correctly. To protect against vapors from the house, a vapor barrier is made, a membrane film is installed on the outside and a ventilation gap is provided.
A good frame house is insulated with mineral wool with the obligatory installation of a ventilation gap between the insulation and the outer wall cladding. In this case, the outside of the insulation is covered with a vapor barrier membrane, which prevents steam from penetrating into the insulation. But it does not prevent possible steam from escaping from the insulating layer. Thus, the ventilation gap in a frame house is a gap through which wet steam can escape from the wall.
The ventilation gap also prevents condensation on the inside of the cladding.
The need to use a ventilation gap
- If mineral insulation loses its heat-saving properties when wet.
- If exterior decoration made of material that does not allow steam to pass through. In this case, a frame house without a ventilation gap will condense moisture from inside siding.
The thickness of the ventilation space between the insulation and the outer skin is determined by its location and the length of the wall; the longer it is, the wider the ventilation gap should be. The width of the ventilation gap in a frame house from the outside is at least 25 mm. At large area walls it should be at least 50 mm.
Sometimes, in order to reduce the cost of a building, they use. This insulation is airtight and therefore does not require an air ventilation gap. Is a ventilation gap necessary in a frame house?
- The insulation material is vapor-proof.
- Outdoor wall decoration lets through steam. Mineral wool can be covered with plaster without a ventilation gap, if plaster mixture has high vapor permeability, higher than that of mineral wool.
In this case, the thickness of the insulation of the walls of the frame house does not require the installation of a ventilation gap inside and outside.
Wall thickness
Exterior wall decoration serves two important functions. She protects interior wall from precipitation and maintains the strength of the house, strengthens the frame. The choice of wall cladding takes into account not only the characteristics of water and moisture resistance, but also bending strength and the ability to withstand wind loads.
External wall cladding
External wall cladding can be done various materials. Metal profiles, cement particle boards, wooden boards– lining, block house, timber. Each of them has its own characteristics and dimensions.
Most often used OSB boards– due to affordability. The choice of their thickness is determined by the number of storeys of the building. The thickness of OSB for the walls of a frame house in one-story buildings is at least 9 mm. For two-story houses it must be at least 12 mm. Thus, in a frame house, the thickness of the OSB determines its strength, durability, and resistance to hurricane winds.
Internal wall cladding
Internal wall cladding can be done sheet materials. It can be OSB with a thickness of 9 or 12 mm. It can also be assembled from thin materials– plywood, MDF, the thickness of which does not exceed 5 mm. It can be made of plasterboard, the thickness of the sheets is 12-13 mm.
Thickness calculations
Now let’s give an example of what the thickness of the walls of a frame house should be for winter living in the Moscow region.
The thickness of the insulation, determined earlier, is 200 mm. External cladding OSB houses 12 mm thick. Exterior plaster– up to 5 mm. Ventilation gap – 70 mm. Internal wall cladding – plasterboard – 13 mm. In total, after summing up the thickness of all the materials in the frame “pie,” the wall thickness is almost 230 mm.
The most important stage in finishing any room is insulating the floors. Many people underestimate the amount of heat loss through the floor, but properly selected insulation can save up to 30% of energy on heating. Particularly large savings are achieved when using a heated floor system, which simply needs to be insulated from below so that it does not heat the floors or the ground.
Select the type of insulation, the best way suitable for your space is only half the battle. It is important that the insulation layer is of sufficient thickness, because even the most best insulation will not provide sufficient thermal insulation if laid in too thin a layer. On the other hand, it is unnecessary thick layer insulation reduces the height of the ceilings in the room and is an unjustified waste of money.
It is important to understand that the required thickness of insulation depends on climatic conditions in your area. It is obvious that when using the same insulation in the same type of houses in Sochi and Norilsk, it will be necessary to completely different thickness layer. Therefore, you need to take into account that all recommendations in the article are given for a typical climate middle zone Russia, where winter temperatures rarely drop below -25 degrees. If you live in a milder or more severe climate, then the recommendations need to be adjusted up or down.
Let's consider the main types of thermal insulation and the required layer thickness when used in various types floors.
Usually this word refers to foamed polystyrene and extruded polystyrene (penoplex). By chemical composition and thermal insulation properties of these materials are practically the same, however, penoplex has much greater bending strength and resistance to crumbling than traditional polystyrene foam. For this reason, recently most consumers are abandoning foamed polystyrene (foam) in favor of extruded polystyrene (penoplex).
Advantage of this type thermal insulation is low price, ease of installation and moisture resistance. The disadvantages include the flammability of this material, and when polystyrene burns, it releases a large number of toxic substances.
Polystyrene slabs are produced in thicknesses from 5 mm to 50 mm; a special chamfer is made on the edges of the slabs so that during installation, gaps and, consequently, “cold paths” do not appear at the joints.
If a layer thickness of more than 50 mm is required, then two or even three layers of polystyrene are laid, with each new layer being laid offset relative to the previous one so that the joints of the slabs of the upper row fall on the centers of the slabs of the lower one.
When insulating a floor located directly above the ground, the foam layer must be at least 300 mm for a house with a wooden floor, and 200 mm for a house with self-leveling concrete floors. You should lay at least 4 layers of the thickest foam panels, offset from each other.
If there is under the floor cold basement, then the foam layer can be reduced by 50mm.
To insulate floors between floors of a private house, 150 mm of foam is enough for wooden floors and 100 mm for concrete floors.
If you are insulating floors in an apartment building, then for all floors except the first it is enough to lay one layer of foam plastic 50 mm thick. On the ground floor the thickness can be increased to 80-100 mm.
| Index | Polyspen | Polyspen Standard | Polyspen 45 | Control method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density, kg/m3 | 30-38 | 30-38 | 38,1-45 | 5.6 each |
| Bending strength, MPa, not less | 0,4 | 0,4 | 0,4 | 5.8 each |
| Water absorption in 24 hours, % by volume, no more | 0,4 | 0,4 | 0,4 | 5.9 each |
| Thermal conductivity at 25+-5 degrees Celsius, W/m * °C, no more | 0,028 | 0,028 | 0,030 | at 5.10 |
| Toxicity, Hcl 50, g/m3 | T2 moderately hazardous | T2 moderately hazardous | T2 moderately hazardous | at 5.11 |
| Flammability group | G-3 normal-flammable | G-4 highly flammable | G-4 highly flammable | at 5.12 |
| Flammability group | B-2 moderately flammable | B-3 flammable | B-3 flammable | at 5.13 |
| Smoke coefficient | High smoke generating ability | High smoke generating ability | at 5.14 | |
| Compressive strength at 10% linear deformation, MPa, not less | 0,2 | 0,2 | 0,3 | 5.7 each |
This liquid version polystyrene foam, which has the same pros and cons as solid version. Its advantage is that it can be poured into hard to reach places and after hardening forms monolithic coating no seams.
The disadvantages include the fact that you need to think about the method of supplying penoizol for pouring, on high floors this could be a problem. In most cases, penoizol is used at the stage of construction of private houses, when insulating floors in apartment buildings It is more convenient to use polystyrene foam and penoplex.
The required thickness of the penoizol layer is the same as that of solid foam.
Glass wool and mineral wool
Perhaps this is one of the most budget options thermal insulation. In addition to its low price, cotton wool does not burn at all and has good vapor permeability, so it is excellent for insulating wooden floors. That's all the pros of this material are ending. The disadvantages include the fact that cotton wool tends to accumulate moisture and this causes rotting and mold growth, the second disadvantage is that over time the wool crumbles if the thermal insulation layer under the floor is not sealed tightly enough, as a result, particles of fibers can pass through the finishing coating become airborne and cause irritation respiratory tract. Also, wool has very low strength, easily breaks and deforms, which makes it impossible to use it under a concrete screed.
Despite the disadvantages, mineral wool is widely used as insulation, usually in wooden floors.
Most manufacturers produce glass wool and mineral wool in rolls or sheets with a thickness of 50 to 200 mm. Sheets can be laid in several layers with offset joints for better thermal insulation.
To use mineral wool on the first floors located above the ground, very good waterproofing. Cotton wool instantly absorbs moisture, after which it loses its thermal insulation properties. For this reason, it is better to use foam plastic for thermal insulation of the first floors. If for some reason it is still necessary to use mineral wool, then its layer should be at least 400 mm.
If there is a basement under the floor of the first floor, then a layer of mineral wool 300 mm thick is sufficient.
When insulating wooden floors between floors of a private house, the layer of wool must be at least 200 mm, and in wooden floors apartment buildings A thickness of 100 mm is sufficient.
| Name | Advantages | Minuses | Thermal conductivity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sawdust | Cheap, environmentally friendly material, lightweight | Flammability, susceptibility to rotting | 0.090-0.180 W/mK |
| Eco-friendly, durable material, not subject to rotting, non-flammable | Heavy weight, fragility | 0.148 W/mK | |
| Does not rot, is waterproof, lightweight and easy to install | Low vapor permeability, cannot withstand high temperatures, releases toxins when melted | 0.035-0.047 W/mK | |
| Mineral wool | Low thermal conductivity, easy to install, environmentally friendly, fireproof | When moistened, it shrinks and loses its insulating properties. | 0.039 W/mK |
This material is very similar in characteristics to mineral wool, but is made from cellulose fibers, therefore it is absolutely safe for health. Just like mineral wool, ecowool is afraid of water and is easily deformed. Therefore, in most cases it is used to insulate wooden floors between floors.
The big advantage of ecowool is that it is installed by spraying under pressure from a special pipe. Thus, the insulation can be “blown out” under the already assembled floor; for this you only need to make several small technological holes.
The required thickness of the ecowool layer corresponds to the thickness of the mineral wool layer, all other things being equal.
Cork material
The main advantage of natural cork insulation is the extremely high sound insulation of the coating. High price material is compensated by the fact that you simultaneously solve the problem of heat and sound insulation. In addition, cork insulation almost does not burn, is not afraid of moisture, is resistant to rotting and is extremely durable, which allows it to be used as insulation under self-leveling floors.
Due to its rather beautiful texture, cork insulation is sometimes left even as finishing coating. In this case upper layer covered with a special varnish that protects it and at the same time emphasizes the design.
Cork insulation is available in rolls and sheets with thicknesses from 3 mm to 200 mm. Sheets maximum thickness They allow you to insulate floors above the ground in just one layer, but at the same time they are very expensive. Price square meter thick cork insulation can cost up to 5,000 rubles. For this reason, cork insulation on the first floors of buildings is rarely used.
The thickness of cork insulation on the ground floor of a private house with concrete floors must be at least 100 mm, in floors between floors with concrete floors A layer of 50 mm is enough; if the floors are wooden, then the layer needs to be increased to 70 mm. In an apartment building, cork insulation is laid in a layer of 10 mm to 30 mm, this is quite enough for effective thermal insulation and complete sound insulation from neighbors below.
Video - Cork insulation
It's comparative new material for insulation, it combines the strength of concrete and the lightness of polystyrene. The material has excellent heat and sound insulation properties and at the same time is a durable screed. It is ideal for thermal insulation of large rooms as it is very easy to pour and level, team experienced craftsmen per day can pour up to 500 m2 of polystyrene concrete.
Due to its low weight, polystyrene concrete does not place a large load on the floors, unlike traditional liquid screed. It does not require waterproofing or additional insulation. You can lay tiles or laminate on a thick backing directly on top of polystyrene concrete. For styling soft coverings, such as carpet or linoleum, a thin layer of traditional screed, no more than 30 mm thick, is poured over the insulation.
For effective thermal insulation of the first floors of private houses, 300 mm of polystyrene concrete above the ground is sufficient; if there is a basement under the floor, then the layer can be reduced to 200 mm. 100 mm of insulation is usually poured into the floors between the floors of private houses; in apartment buildings, a layer of 50 mm is sufficient.
| General characteristics of polystyrene concrete | Values |
|---|---|
| Flammability group | G1 |
| Density | from 150 to 600 kg/m³ |
| Frost resistance | from F35 to F300 |
| Strength characteristics | from M2 to B2.5 |
| Coefficient of thermal conductivity | ranging from 0.055 to 0.145 W/m °C |
| Vapor permeability of polystyrene concrete | 0.05 mg/(m h Pa) |
Expanded clay is a popular thermal insulation material used in wooden floors and floors with dry screed based on gypsum fiber board. In the latter case, in addition to thermal insulation, it is also a leveling material.
Expanded clay is one of the cheapest materials for thermal insulation; it does not burn, is safe for health and is lightweight. At the same time, it easily absorbs water, which reduces its thermal insulation properties and significantly increases its weight. Therefore, the use of expanded clay requires reliable waterproofing. Another disadvantage of expanded clay is that when working with it, a large amount of dust rises into the air.
Using expanded clay for insulation. The photo shows expanded clay being poured with lean concrete
For effective thermal insulation of the first floors of buildings from the ground, the expanded clay layer must be at least 400 mm when using wooden floors and 300 mm when using concrete floors.
Between the floors of private houses, at least 200 mm of expanded clay should be poured into the floors at wooden floors and 150 mm for concrete. In apartment buildings, a layer of expanded clay of 50-80 mm is sufficient.
| Indicators | 10-20 mm | 5-10 mm | 0-5 mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bulk density, kg/m3 | 280-370 | 300-400 | 500-700 |
| Crushing strength, N/mm2 (MPa) | 1-1,8 | 1,2-2 | 3-4 |
| Grading, % | 4 | 8 | 0 |
| Frost resistance 20 cycles, gravel weight loss, % | 0,4-2 | 0,2-1,2 | not regulated |
| Percentage of crushed particles, % | 3-10 | 3-10 | No |
| Thermal conductivity, W/m*K | 0,0912 | 0,0912 | 0,1099 |
| Water absorption, mm | 250 | 250 | 290 |
| Specific effective activity of natural radionuclides, Bq/kg | 270 | 270 | 290 |
Video - Thickness of floor insulation