How to cover a roof with polycarbonate. How to make a polycarbonate roof? Types of polycarbonate plastic roofing
Read also
Currently on construction market new materials appear that immediately become popular due to their unique properties. This is exactly what polycarbonate is - a polymer material with the highest degree resistance to mechanical stress and temperature changes, which contributes to its widespread use, in particular in the construction industry.
Almost everything can be made from polycarbonate: fences, windows, gazebos, canopies, verandas, dropped ceilings. Moreover, today you can even build a roof from polycarbonate and, most importantly, you can do it yourself, since installation is not very difficult, but the result will please you. Arrange a transparent polycarbonate roofing it is possible above any structure, including above a residential building, a cold attic, above a balcony area, terrace, veranda - wherever daylight will not be superfluous.
Properties of polycarbonate

Since any roof must meet certain requirements, the material for its installation must have the appropriate characteristics. Polycarbonate is one of those materials that have the necessary properties:
- transparency of the material, thanks to which it is possible to provide natural light through the roof, approximately as shown in the photo, for a longer time every day than through windows;
- excellent impact resistance that can withstand even large hail and other falling objects;
- impact resistance and absence of possible damage chips and splinters;
- low degree of flammability and combustion resistance. In addition, even near an open fire, when the material melts, it does not emit harmful compounds;
- good performance in sound and thermal insulation properties;
- light weight of the material, making polycarbonate panels easy to deliver to the construction site, easy to process, do all the installation work, create fairly light polycarbonate roofs with your own hands, expanding the possibilities of design desires, and all this at a not so high cost;
- unique flexibility of the material, allowing you to create various architectural forms of any level of complexity. Moreover, polycarbonate bends perfectly in one direction, but in the opposite direction it is quite rigid. This allows it to withstand any serious loads;
- high load-bearing capacity;
- retains all its properties in the temperature range from +125 to -45 degrees, therefore it will serve equally in the summer heat and at the lowest temperatures in winter;
- lends itself to any type of processing: gluing, bending, drilling, cutting, thanks to which the structure will be reliable and durable, the main thing is that the angle of inclination flat roof was so sufficient that snow could not linger on the surface;
- relatively low cost;
- long service life, which, depending on the quality and thickness of the material, ranges from 7-8 to 25 years.
Design Features

Polycarbonate structures can be erected by yourself different shapes: flat, but having such an angle of inclination that rainwater could flow freely. In addition, you can make the upper part of the house in the form of a pyramid, prism, dome, hemisphere - there are simply no restrictions on the imagination of the owners of the house.
It is important to know: In order to give the roof the desired shape, you must first make a base frame, on which the roof surface will then be mounted.
You can create the foundation for constructing a polycarbonate roof with your own hands from aluminum or aluminum profiles. steel material. If you want to create a completely transparent building surface, you can purchase ready-made polycarbonate profiles and then the roof will not have any visible connections. This option allows you to create an original roof that seems to be floating above the building.
Required tools and materials
Before you plan to build any structure, you need to take care of purchasing necessary materials. In this case - polycarbonate plates. Depending on their quality, they are divided into several types:
- The most affordable and economical option, but it will last from 5 to 8 years.
- Optimal polycarbonate will last a couple of years longer. If you cover the roof with this type of material, you can not think about its repair and other types of maintenance for more than ten years, as happens on roofs made of other materials.
- The service life of elite polycarbonate is slightly longer - 12-15 years.
- Premium canvas has the longest service life; it will retain its appearance and properties for more than two decades.
Pricing for each type polycarbonate material depends on the amount of recyclable materials added at the manufacturing stage, as well as on the size of the sheets and their thermal resistance.
Tools required for work:
- plane, hammer;
- level or bar;
- sealant for filling voids and gaps;
- material for making a frame and subsequent laying of a polycarbonate roof with your own hands;
- tape for finishing ends;
- jigsaw, screwdriver, hacksaw;
- fastener Usually these are self-tapping screws with thermal washers.
DIY installation

The construction of a roof, like any other structure, begins with the preparation of a project or drawing, according to which the amount of material required for the work is calculated.
Installation of rafters
When installing a base under polycarbonate, you need to take only high-quality material, since the reliability of the operation of polycarbonate sheets depends on the strength of the rafters and appearance the buildings. Therefore, it is best to use a beam with a cross-section of 40-60 cm or a metal profile for the frame. Enhance roof structure You can install additional bars, placing them in the transverse and longitudinal direction between the beams.
When installing the rafters, in order not to cut the panels again, you will have to take into account that the width of the polycarbonate sheets is 210 cm plus a 5 mm temperature gap on each side. Knowing these subtleties will help you correctly calculate the length for an arched or flat roof.
Profile fastening

When installing connectors and fasteners, you need to ensure that the profiles selected for the job are those that are intended for use at this stage; there are models of profile products for sale for connecting operations, ridge, end, external and internal connections. In addition, the dimensions of any type of profile must match the thickness of the sheet. If the work will be performed on metal or aluminum profiles, then the end parts of the sheets must be sealed with tape.
The collapsible profile is attached in several stages - first the lower element, and then the panels are installed, and after them - top element profile.
On a note: To install a non-separable profile, no additional preparations are made: the polycarbonate lies on finished frame and is attached using a point technique or with fixing profiles.
When building a polycarbonate roof, the material should be placed in honeycombs only vertically; if placed across, moisture will accumulate inside and the material will darken. If the roof is rounded, the edges of the honeycomb are directed along the radius.
Cutting polycarbonate

When cutting off excess material, you should work with a cutting tool, and this can be a jigsaw or a circular saw, with sharp small teeth. The speed will have to be selected experimentally, since it is too high speed leads to overheating of the polymer and its melting, and if it is too low, chips form on the material. During operation, polycarbonate should not be allowed to vibrate; this can cause microcracks to form.
Drilling polycarbonate
When performing installation work using self-tapping screws, before screwing them in, you need to make holes, the diameter of which should be 2-3 mm larger than the diameter of the fastener.
Good to know: For the job, it is best to use a drill designed for non-ferrous metal.
But knowing how to make a roof from polycarbonate is not enough, you need to know how to secure it, you should never screw in the screws all the way, you need to leave room for the temperature play of the polycarbonate material.
And most importantly, for all types of work it is allowed to use only sharply sharpened tools and perform them only on a flat surface, while trying not to damage the protective film on polycarbonate sheets. If it is removed early, debris or even very small plastic particles may get inside the hollow channels, which will then need to be removed, or compressed air, or shake out the sheets themselves, which, given their size, is quite problematic.
To make a polycarbonate roof with your own hands, you need... If you put polycarbonate on the roof across the honeycomb, then inside there will be...
Building a lean-to polycarbonate roof: analysis of the nuances and subtleties of construction technology
In many of its qualities, modern polycarbonate roofing is not only not inferior to traditional pitched roof coverings, but even surpasses them! Lightweight, environmentally friendly, easy to install and light-diffusing. The fashion for the sky, which can be seen through the roof, already exists all over the world. We dreamed of such a ceiling in own home, favorite workshop or new veranda? Are you inspired by new architectural fads? Then all you have to do is figure out how a pitched roof under polycarbonate is constructed - and everything will work out! And you will be surprised how durable and aesthetically pleasing the roof will be, which will be no worse than the glossy samples from magazines about country construction.

Pros and cons of polycarbonate as a roofing material
You will be interested to know that such a popular and familiar polycarbonate was born completely by accident! One day, a German scientist mixed the ingredients needed for the experiment in a new way, and a dense transparent sediment settled at the bottom of the flask. This is where they began to make new translucent structures. They differed in that they weighed 6 times less than glass, but were stronger.
And modern roofing polycarbonate is valuable for the following qualities:
- Does not emit toxic substances.
- Does not support combustion, is difficult to ignite.
- It is light in weight.
- Simply cut and processed.
- Easily bends into the desired shape.
- Flexible and easily bears the weight of snow.
- It is heat-resistant and does not change its properties in hot weather and severe frost.
- Available in a variety of colors.
And as a material for a pitched roof it has the following additional advantages:
- Excellent sound absorption. That is why today it is actively used as an acoustic screen along busy highways - to reduce harmful noise for residential buildings. Those. under such a roof it will be not only warm, but also quiet.
- One side has a protective layer against ultraviolet radiation, and the second - with reflective particles. Moreover, the material reflects up to 60% of sunlight, which significantly reduces the thermal load of the entire building in hot weather. This means that you won’t have to purchase air conditioners.
- Virtually indestructible: extreme impact resistance ranges from 900 to 1100 kJ/m2, while the strongest polystyrene has only 10 kJ/m2.
And to give roofing polycarbonate necessary qualities, modern manufacturers cover sheets with special films:
- Anti-condensation film. With this coating pitched roof under polycarbonate will not collect moisture on the inner surface.
- UV film. This type of UV protective coating protects the sheet from clouding and yellowing.
Ultraviolet protection is applied to polycarbonate using the co-extrusion method in the factory. A new level technical progress in this area – polycarbonate roofing sheets with double ultraviolet protection. They have the highest wear resistance - only 4 delta yellowing index units, compared to 10 for conventional sheets.
Of course roofing polycarbonate has its disadvantages, some of which are quite serious:
- Collects static electricity.
- It is not always designed for the point pressure of the weight of the person doing the repairs.
- In the event of a fire, it melts and drips hot drops onto everything in the room.
But regarding the last point, we note that in the event of a fire, very little remains unharmed. Therefore, refuse fashionable polycarbonate roof It's not worth it because of this.
And we note that the quality and properties of roofing polycarbonate are getting better every day. New shades of toning appear and new additives are introduced that block the amount of glare, and as a result, the sunlight that passes through the sheet is cleaner. And what else is to come!
Types of modern roofing polycarbonate
But let's first figure out what kind of polycarbonate you can use for roofing.
Monolithic polycarbonate
Monolithic polycarbonate is a solid plate with a thickness of 2 to 12 mm. It is much stronger than glass, but at the same time much lighter, which is why it tops the rating of modern vandal-proof plastics.

Monolithic polycarbonate for roofing is produced in cast or corrugated form.
Profiled monolithic polycarbonate
Corrugation is a profile that we see in the form of a wave-like shape or a square outline. It's not only beautiful! A carefully selected profile makes this material 2-3 times stronger, plus rainwater rolls off much more easily. But attaching one to the roof, of course, is more difficult - you will have to use additional silicone supports.
Modern roofing polycarbonate sheets are produced mainly in three types of sections:
Moreover, working with corrugated polycarbonate is no more difficult than with cellular or monolithic ones.

Profiled monolithic polycarbonate has many more advantages than sheet polycarbonate:
- Higher strength, like a metal profile.
- Service life up to 30 years.
- High wear resistance.
- Transparency level up to 92%.
- Easy to install and handle.
- High plasticity.
- Light weight - only 1.7 kg per square meter.
- Wide range of colors.
- Resistance to temperature changes, burnout and adverse precipitation.
And finally, aesthetic appeal!
Individual corrugated sheets are produced in shades of grey, bronze, milky white and opal: these provide excellent protection against harmful effects ultraviolet rays. This means that under such a roof various materials will fade and deteriorate less.
Cellular polycarbonate
Cellular polycarbonate, which is slightly less transparent than monolithic, is also valuable as a roofing covering. But it has an important function - scattering rays. You will choose just such a roof covering if, for example, you are building a winter garden or greenhouse: direct rays burn the delicate leaves of plants. The same applies to utility and storage facilities - not a single item will be durable under the scorching sun.
Diffused light is also considered more valuable due to the fact that it penetrates more into the dark corners of the room and does not give such nasty things as fungi and mold a chance to live there. But how does this happen? The fact is that monolithic polycarbonate has a holistic and transparent structure, and therefore the light beam that passes through it only slightly changes its angle, and that’s all. And a cell phone is made not only of horizontal planes - it has many vertical partitions. As a result, the passing beam is divided into thousands of smaller ones, each with its own angle. This is diffused light.
Cellular polycarbonate for roofs is produced today in the following types according to the type of internal structure:
- Single-chamber standard, with a thickness from 4 to 10 mm.
- Two-chamber standard, with sheet thickness of 16 mm.
- Reinforced, reinforced, but with a thickness of 4-6 mm.
- Four-chamber, with a sheet thickness of 25 mm.
Cellular polycarbonate consists of two panels, which are interconnected by stiffening ribs. Therefore, in fact, most of the cellular polycarbonate is air.
Internal stiffening ribs give polycarbonate special strength, thanks to which it can easily withstand severe wind and snow loads. The range of extreme temperatures is from -20° to +80°C. What other roofing covering boasts similar parameters?

Cellular polycarbonate, the honeycombs of which are filled with airgel - the new kind products. It has high impact resistance and thermal insulation, which surpassed triple-glazed windows with argon.
Choosing the thickness of roofing sheets
Any polycarbonate is not suitable for you. The fact is that the construction market today offers PC sheets of various thicknesses - both for greenhouses and for glazing with increased load. Therefore, when choosing polycarbonate for a roof, proceed from what exactly you want to cover.
Sheets 4-6 mm thick are the most fragile. They are used for greenhouses and greenhouses, advertising stands and small translucent roof inserts:

Sheets 6-8 mm thick can already be safely used for the roof of a gazebo and a small outbuilding, awnings and glazing of the ends of a pitched roof. Working with it is as easy as shelling pears:

Polycarbonate 10 mm thick is usually used for vertical glazing in order to create a noise-absorbing barrier. This polycarbonate will be an excellent transparent wall in the attic under a pitched roof.

PC sheets with a thickness of 16 to 32 mm are used where there will be increased load: for the roofs of private houses, production premises And winter gardens. And for the roof of the house, of course, you will need polycarbonate with a thickness of 16 mm and above. But don’t think that it’s better for them to finish everything at once: both the ends and the complex parts. The fact is that the thicker the PC sheet, the denser and stiffer it is, and the greater the load it can withstand, but its flexibility has already been reduced significantly.


We don’t particularly take wind loads into account, because... The pitched roof has a low windage area.
What kind of rafter system is needed?
As rafters for a pitched polycarbonate roof, we advise you to use both wooden blocks, and square pipes and rectangular shape. Here is a detailed master class on such construction:


But remember that minimum slope polycarbonate pitched roof - 10%.
Which fasteners and profiles to choose
Unlike usual, more traditional types roofs, where everything is prosaic and the method of fastening is indicated by the manufacturer, you will have to tinker with polycarbonate. And first of all, you need to decide how exactly it will be more profitable to connect the sheets together.
Profiling systems
These are made from polycarbonate or aluminum. The profiling systems are two structural connecting elements that close the ends of the slabs using bolts and sealants. And today special profiles are sold for polycarbonate roofs:
- UP - end. Naturally, the ends of roofing sheets are sealed with this profile.
- PSK or PSB – connecting. They connect panels in the same horizontal plane.
- RP – ridge. They connect panels in a gable roof.
- HP is a one-piece profile that is used for mounting small planes and arches. Those. You will make such a fastening only once, and later you will not be able to remove it.
- SP and HCP are split profiles that are used for installation pitched roofs and their vertical parts.
- PT is an end profile for polycarbonate, which has an improved design. There is already a drip and a drainage channel, thanks to which the outflow of water is improved.
And all these profiles differ in the material from which they are made.
Polycarbonate profiles
Take polycarbonate ones if maximum transparency of the roof is vital for you and in no case should there be any shadows there. Quite life situation, by the way. In the modern world of design and architecture, for example, it has become fashionable to make the attic absolutely transparent, from where you can see everything - both the sky and the city. And inside, equip a personal office, a small gym for all family members, or a mini-bar for frequent gatherings with friends.
Aluminum profiles in this case will look terrible - like prison bars, and, of course, will ruin the entire aesthetics. It is for such design whims that transparent polycarbonate profiles were developed, which are almost invisible. And at the same time, we note that they are quite durable:

Such profiles, of course, are not load-bearing, but they can be bent as easily as polycarbonate itself. Plus, they heat up under the sun much less than aluminum ones, while having additional ultraviolet protection.
Aluminum profiles
Aluminum profiles are indispensable if you plan to build an unusual or architecturally complex roof. Such profiles provide excellent tightness and meet all reliability requirements. Therefore, if snow and wind loads are above average in your area, it is better to use such a mount.
The advantages of an aluminum profile include its length - more than 6 meters. This means that you can easily use this profile for large structures, without any joints.

An aluminum profile is also suitable for the roof. facade system" It has a special decorative cover that covers the profile and thus masks the screws. The cover itself is factory painted in a color according to the RAL table, and therefore you can use both white and colored for the roof, adding bright accent design of the whole house.
But for aluminum profiles it will be necessary to use special EPDM seals, which will protect the roofing polycarbonate from transferring heat to the aluminum parts and protect against moisture getting inside. Such seals are installed using rubber mallet and roller shutters.
Special thermal washers
Simple roofing screws Polycarbonate cannot be fixed - there are special thermal washers for this. What is their difference? The fact is that polycarbonate is a mobile material, subject to thermal expansion and contraction. And under ordinary self-tapping screws, the fastening points will eventually become covered with cracks, which will gradually increase:


All these rubber spacers and neoprene discs are necessary to ensure that the cellular polycarbonate does not get squeezed. If this happens, then rain or melt moisture will easily get inside the panel, and this is already a round of new problems.
Note that the lion's share special seals that are used are made of elastomer. This material behaves well in terms of thermal expansion and ensures complete tightness of the connections. For a roof, these parameters are especially important, you will agree:

Another one important task What thermal washers for polycarbonate are designed to solve is getting rid of the so-called cold bridges. We are talking about places through which cold penetrates into the structure and where, due to temperature differences, condensation forms directly on the surface of the sheet. And thermal washers allow you to give the entire structure a finished and aesthetic look. A special snap-on lid hides the screws, and the color of the washers does not stand out against the background of the entire sheet.
Moreover, such washers are sold in two types:
- Polycarbonate washers. Frost-resistant, last 10 years or more, perfectly match polycarbonate in color. An additional advantage is that they are equipped with a special four-circuit sealing ring made of elastomer.
- Polypropylene washers. They last about 2 years, they are afraid of ultraviolet radiation, which makes them brittle. The color of the washers does not always match the shade of the tinted polycarbonate roof. But it’s more affordable, if that’s important to you.
Of course, polycarbonate washers are more suitable for building a roof from the same material. But it is also important to attach them correctly:
- Step 1. Select the mounting location. This must be done slowly and carefully, because the “random” hole will also have to be closed with the same washers. At least aesthetically you will lose.
- Step 2. Calculate the distance between the washers - for this we have presented a detailed table for you below.
- Step 3. Select the diameter of the hole.
- Step 4. Screw on the washer. This must be done accurately, not too loosely and not too tightly, so as not to press the washer. Just make sure that the sealing material does not stick to the sheets.
A screwdriver will help to secure such a washer:

Sealing tapes
All lower edges of installed roofing sheets must be covered with aluminum tape and UP profile. And not with a simple aluminum tape, but with a perforated one, which is capable of releasing condensate that has accidentally accumulated in the honeycombs. Why are holes also required to be pre-drilled in the UP profile?
Where the next panel overlaps along the wave of the sheet, use sealing tape, as well as along the fixation lines of the lower and upper overlap.
So, step by step:
- Step 1. At the top of the wave, drill holes for screws - 10 mm each.
- Step 2. Now fasten the screws into the drilled holes - on the left side.
- Step 3: Drive screws into every other wave, starting at the bottom beam.
- Step 4: Now attach screws to every third wave.
- Step 5. Start fastening the last, topmost sheet on the left side.
- Step 6. Fix the side overlaps of the sheets every 30 cm.
Here's more detail:

Roofing sealant
To install a polycarbonate roof, be sure to use a special roofing sealant. Moreover, you need to purchase one that is intended specifically for this material, because... they are produced on a neutral basis and do not destroy the polycarbonate itself. Sealant will be needed to seal all joints and fastenings of the transparent roof.
Secrets and subtleties of technology from the pros
So, we figured out a little about the sheathing. Now let's move on to working with sheets. You cannot step on the polycarbonate itself during its installation, so make special platforms.
In this case, you need to work only at positive temperatures, not lower than -5°C, so that cracks from the fastening do not appear. The fact is that roofing polycarbonate itself can easily withstand cold down to -20°C, but unless holes are drilled in it at that moment.
Otherwise, it is important to adhere to certain rules:

How to work with polycarbonate roofing sheets?
Roofing polycarbonate can be cut using either conventional cutting or a laser. But these are already machine operations, where the laser power and cutting speed are adjusted in the factory. But with this method, the edges of the cut will no longer be transparent - either white or brown, depending on the cutting speed.
To drill through polycarbonate sheets, you will need high-speed drill bits, either designed for metal or with a carbide insert. This is the only way to maintain the sharpness of the cut edges of the sheets.
And one more point: during drilling, any tool heats up the polycarbonate. Therefore, if you want the drilled holes to be clean and not melted, then work with the sheets not in the hot sun, but in a cool workshop - at least. It is ideal if you can cool the polycarbonate a little in advance - but not below zero temperature, so that there is no cracking. In general, do everything you can to reduce the amount of heat generated while working on your roof.
All this is really important. After all, incorrectly made holes in polycarbonate for the roof are a whole problem. This only doesn’t really interfere in a greenhouse if water flows through the fastenings onto the plants when it rains, but for a residential building, as you understand, this doesn’t bode well.
How to properly secure sheets to the roof?
Try to use not too long panels for the roof - only up to 7 meters. In this case, always lay polycarbonate sheets with ultraviolet protection towards the top. The easiest way to cut polycarbonate is with a hacksaw with fine teeth and a circular saw.
Always make the overlap length 200 mm, 100 mm for each sheet from the fixation line on the support. Place the last fixation line within 50-100 mm. If you are making a monolithic polycarbonate roof, be sure to leave gaps in the frames to accommodate thermal expansion.
There are also special silicone linings for fastening with thermal washers for profiled polycarbonate. For wavy ones:

And for trapezoidal polycarbonate they are:

Are connecting profiles required?
But few people know that roofing polycarbonate sheets can also be glued together, and not just connected with special profiles. So, it is only important to follow just a few rules:
- Clean the ends of the sheets from any contamination, especially subtle dust.
- All surfaces of future glued ends must be smooth and even.
- The varnish or solvent used should not thicken or change its appearance.
- The room where you do all this should have as low a humidity as possible.
- Use low-active varnishes - this is the only way to avoid bleaching.
- The glued surfaces must remain under pressure until final curing.
- Be sure to wear funds personal protection respiratory organs.
The easiest way to clean polycarbonate sheets is with isopropyl or methyl alcohol, or mild soap solutions.
If you decide to make a rather complex polycarbonate pitched roof, you will also need welding in the process. You will process it finished parts. Thus, welding with a hot pad (300°C) will help to achieve strength in the joints of the sheets, and welding with hot air with a welding rod (120°C) will pre-dry these welded areas. Ultrasonic welding is also used, with processing at 20 kHz in the range of 25-40 microns.
And finally, you will need to sand down any unsightly parts. The easiest way to do this is to use silicon sandpaper with a grit of 400 or 600.
What about the ventilation of such a roof?
So, you have chosen polycarbonate, you have drawn up a roof design, and now it’s time to think about ventilation of the under-roof space. The fact is that in the case of a pitched roof, ventilation is not often thought about at all; even dormers are not always installed. And this, when using polycarbonate as a roofing material, will lead to its overheating, which in the heat can even cause some parts to change shape slightly.
Moreover, you should not give up partial insulation of a pitched polycarbonate roof:

As you can see, everything is simple! Got new ideas? Go for it!
Do-it-yourself shed roof under polycarbonate: instructions, diagrams, drawings
Everything about the types and work with roofing polycarbonate: fasteners, insulation, profile selection and even insulation. How to properly build a pitched roof under polycarbonate -
DIY polycarbonate roof
Polycarbonate is a modern material often used in construction for the construction of partitions, walls, curtain walls and decorative elements. Polycarbonate has also become widespread as roofing. Roofs of houses, gazebos, open terraces, awnings and canopies over the entrance. A polycarbonate roof allows you to realize the most bold ideas thanks to the properties of this material.

DIY polycarbonate roof
The advantages of polycarbonate include:
- Low weight with high mechanical strength;
- Ability to transmit light;
- Wide range of shades and color solutions;
- Original and elegant appearance;
- Ease of installation and processing;
- Polycarbonate does not rust, is not destroyed by chemicals and microorganisms, and is resistant to temperature changes if installed correctly.
Polycarbonate also has disadvantages. One of them is instability to UV radiation if the protective layer is damaged, so during installation it is necessary to monitor the integrity protective film and remove it only after completing all work. Another feature of polycarbonate that should be considered carefully is its high coefficient of thermal expansion. It is necessary to install polycarbonate using special self-tapping screws through pre-drilled holes of larger diameter. Otherwise, when the temperature changes, the material may deform.
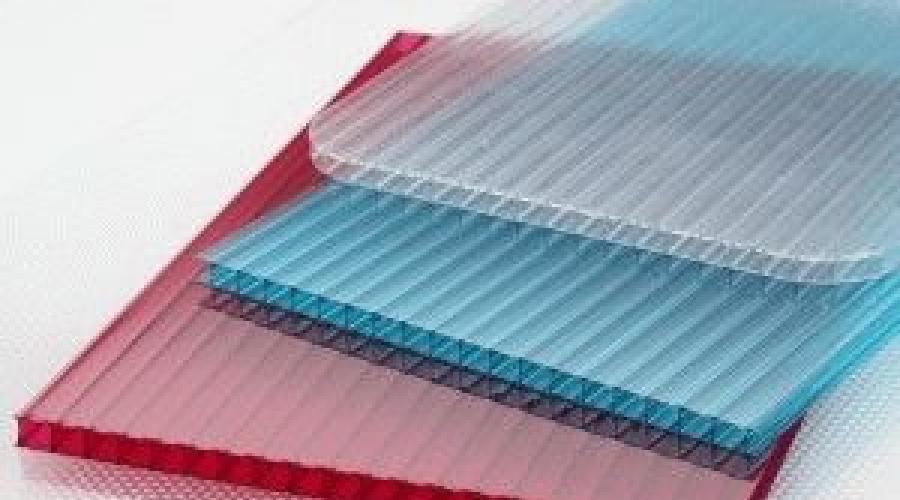
Types of polycarbonate
Polycarbonate is divided into monolithic and cellular. Monolithic polycarbonate has high strength and has a standard thickness from 2 to 12 mm. The dimensions of the monolithic polycarbonate sheet are 2.05x3.05 meters. Its area of application is roofs of various configurations that experience heavy snow and wind loads. Monolithic polycarbonate with a thickness of 12 mm is considered vandal-proof and can withstand a hammer blow without the slightest damage.

Cellular polycarbonate has significantly less weight due to its cellular structure: the sheet consists of two or more thin sheet polycarbonate, connected by stiffening ribs along the entire length of the sheet. This material structure allows for high mechanical strength at low weight. Arched structures, domed roofs and other complex elements are made from cellular polycarbonate. Cellular polycarbonate can be either transparent or matte and has a wide range of shades. Standard thickness is from 4 to 32 mm, sheet dimensions are 2.1 x 6.1 or 2.1 x 12.1 meters.

Materials for making the frame
The polycarbonate roof frame can be made from various materials. The decisive factor in the choice is the basic style of the building and the expected weight of the structure, taking into account the snow load. IN wooden buildings when making a straight roof, use rafter system made of wooden blocks or boards, on which transverse lathing and polycarbonate sheets are laid. This design fits perfectly into the overall style and gives the building lightness, volume and light.
Arched structures of canopies, verandas, as well as domed roofs are usually made on a frame made of aluminum or steel profiles. Steel is used for bulky structures and high snow loads. For light buildings, light is enough aluminum profile. For arches of large radius, additional supports and struts, transverse stiffeners from the profile are also used.
The polycarbonate is fastened to the profile using special self-tapping screws with a sealing washer. The joints of the sheets are connected using an H-shaped profile for polycarbonate.
Direct polycarbonate roof: implementation technology
A straight polycarbonate roof is usually used when constructing open terraces, gazebos, and small garden houses. Choosing polycarbonate as a roofing covering allows you to get natural light, create a feeling of lightness and open space. At the same time, such a roof cannot be properly insulated without losing its transparency, therefore it is of little use for buildings used in winter.
- A straight polycarbonate roof can be of any design: single-pitch, gable or hip. The rafter system depends on the type of roof. Rafters for such a lightweight material as polycarbonate can be made from boards 40 mm thick. The wood is treated with an antiseptic and fire retardant solutions; if desired, it can be given a certain shade.
- The pitch between the rafters must be selected based on standard width sheet so that the distance between the bars is the same, and the joints of the sheets fall on the rafters. The transverse lathing is made from 50x20 mm bars, cutting them into the rafter board laid at the end.

Straight polycarbonate roof

Arched polycarbonate roof
Arched roofs are most often performed during the construction of canopies, canopies, summer gazebos. They are extremely simple in design, and the most challenging task is to make arcs from a profile or square pipe. Actually, the difficulty is to bend it evenly around the entire circumference, and for this it is better to use a template.
Do-it-yourself polycarbonate roof - step-by-step method!
Find out more about what a polycarbonate roof is and how to make it yourself. Detailed methodology and the video will help you figure it out.
Currently, new materials are appearing on the construction market, which immediately become popular due to their unique properties. This is exactly what polycarbonate is - a polymer material that has the highest degree of resistance to mechanical stress and temperature changes, which contributes to its widespread use, in particular in the construction industry.
Almost everything can be made from polycarbonate: fences, windows, gazebos, canopies, verandas, suspended ceilings. Moreover, today you can even build a roof from polycarbonate and, most importantly, you can do it yourself, since installation is not very difficult, but the result will please you. You can install a transparent polycarbonate roof over any structure, including over a residential building, a cold attic, over a balcony area, a terrace, a veranda - anywhere where natural light would be useful.
Properties of polycarbonate

Since any roof must meet certain requirements, the material for its installation must have the appropriate characteristics. Polycarbonate is one of those materials that have the necessary properties:
- transparency of the material, thanks to which it is possible to provide natural light through the roof, approximately as shown in the photo, for a longer time every day than through windows;
- excellent impact resistance that can withstand even large hail and other falling objects;
- impact resistance and absence of chips and splinters in case of possible damage;
- low degree of flammability and combustion resistance. In addition, even near an open fire, when the material melts, it does not emit harmful compounds;
- good performance in sound and thermal insulation properties;
- light weight of the material, making polycarbonate panels easy to deliver to the construction site, easy to process, do all the installation work, create fairly light polycarbonate roofs with your own hands, expanding the possibilities of design desires, and all this at a not so high cost;
- unique flexibility of the material, allowing you to create various architectural forms of any level of complexity. Moreover, polycarbonate bends perfectly in one direction, but in the opposite direction it is quite rigid. This allows it to withstand any serious loads;
- high load-bearing capacity;
- retains all its properties in the temperature range from +125 to -45 degrees, therefore it will serve equally in the summer heat and at the lowest temperatures in winter;
- lends itself to any type of processing: gluing, bending, drilling, cutting, thanks to which the structure will be reliable and durable, the main thing is that the angle of inclination of the flat roof is so sufficient that snow cannot linger on the surface;
- relatively low cost;
- long service life, which, depending on the quality and thickness of the material, ranges from 7-8 to 25 years.
Design Features

Polycarbonate structures can be erected in a variety of shapes: flat, but with an angle of inclination so that rainwater can flow freely. In addition, you can make the upper part of the house in the form of a pyramid, prism, dome, hemisphere - there are simply no restrictions on the imagination of the owners of the house.
It is important to know: In order to give the roof the desired shape, you must first make a base frame, on which the roof surface will then be mounted.
When building a polycarbonate roof with your own hands, you can create the foundation from profiles made of aluminum or steel material. If you want to create a completely transparent building surface, you can purchase ready-made polycarbonate profiles and then the roof will not have any visible connections. This option allows you to create an original roof that seems to be floating above the building.
Required tools and materials
Before you plan to build any structure, you need to take care of purchasing the necessary materials. In this case - polycarbonate plates. Depending on their quality, they are divided into several types:
- The most affordable and economical option, but it will last from 5 to 8 years.
- Optimal polycarbonate will last a couple of years longer. If you cover the roof with this type of material, you can not think about its repair and other types of maintenance for more than ten years, as happens on roofs made of other materials.
- The service life of elite polycarbonate is slightly longer - 12-15 years.
- Premium canvas has the longest service life; it will retain its appearance and properties for more than two decades.
The pricing of each type of polycarbonate material depends on the amount of recyclable materials added at the manufacturing stage, as well as on the size of the sheets and their thermal resistance indicators.
Tools required for work:
- plane, hammer;
- level or bar;
- sealant for filling voids and gaps;
- material for making a frame and subsequent laying of a polycarbonate roof with your own hands;
- tape for finishing ends;
- jigsaw, screwdriver, hacksaw;
- fastener Usually these are self-tapping screws with thermal washers.
DIY installation

The construction of a roof, like any other structure, begins with the preparation of a project or drawing, according to which the amount of material required for the work is calculated.
Installation of rafters
When installing a base under polycarbonate, you need to take only high-quality material, since the reliability of the operation of polycarbonate sheets and the appearance of the building depend on the strength of the rafters. Therefore, it is best to use a beam with a cross-section of 40-60 cm or a metal profile for the frame. The roof structure can be strengthened by installing additional bars, placing them in the transverse and longitudinal direction between the beams.
When installing the rafters, in order not to cut the panels again, you will have to take into account that the width of the polycarbonate sheets is 210 cm plus a 5 mm temperature gap on each side. Knowing these subtleties will help you correctly calculate the length for an arched or flat roof.
Profile fastening

When installing connectors and fasteners, you need to ensure that the profiles selected for the job are those that are intended for use at this stage; there are models of profile products for sale for connecting operations, ridge, end, external and internal connections. In addition, the dimensions of any type of profile must match the thickness of the sheet. If the work will be performed on metal or aluminum profiles, then the end parts of the sheets must be sealed with tape.
The collapsible profile is attached in several stages - first the lower element, and then the panels are installed, and after them - the upper element of the profile.
On a note: To install a non-separable profile, no additional preparations are made: the polycarbonate is placed on the finished frame and secured using a point method or with fixing profiles.
When building a polycarbonate roof, the material should be placed in honeycombs only vertically; if placed across, moisture will accumulate inside and the material will darken. If the roof is rounded, the edges of the honeycomb are directed along the radius.
Cutting polycarbonate

When cutting off excess material, you should work with a cutting tool, and this can be a jigsaw or a circular saw, with sharp small teeth. The speed will have to be selected experimentally, since too high a speed leads to overheating of the polymer and its melting, and if it is too low, chips will form on the material. During operation, polycarbonate should not be allowed to vibrate; this can cause microcracks to form.
Drilling polycarbonate
When performing installation work using self-tapping screws, before screwing them in, you need to make holes, the diameter of which should be 2-3 mm larger than the diameter of the fastener.
Good to know: For the job, it is best to use a drill designed for non-ferrous metal.
But knowing how to make a roof from polycarbonate is not enough, you need to know how to secure it, you should never screw in the screws all the way, you need to leave room for the temperature play of the polycarbonate material.
And most importantly, for all types of work it is allowed to use only sharply sharpened tools and perform them only on a flat surface, while trying not to damage the protective film on the polycarbonate sheets. If it is removed earlier, debris or even very small plastic particles may get inside the hollow channels, which will then need to be removed either with compressed air or by shaking out the sheets themselves, which, given their size, is quite problematic.
Video about roof installation
How construction material It has been known in developed countries since 1960; currently, global production exceeds 3 million tons. Polycarbonate roofing – good option covering most outbuildings- from very prestigious verandas, gazebos, swimming pools to the production of ordinary carports or greenhouses. This material allows you to create strong, durable and beautiful structures at relatively low financial costs.
Unique physical characteristics make it possible to use roofing polycarbonate in almost all climatic regions our country, and modern innovative fillers make it more resistant to mechanical damage and adverse climatic influences.
Prices for cellular polycarbonate
Cellular polycarbonate
Currently, the construction industry produces several types of materials used to cover roofs for various purposes. They all have their own individual differences.
Table. Types of polycarbonate for roofing
| Type of polycarbonate | Brief operational and physical characteristics |
|---|---|
| The most famous among developers is polycarbonate, it has a cellular structure with various sizes and geometry. To protect surfaces from harsh ultraviolet radiation, a special film is used; it is glued only on the front side. Due to the use of innovative film, the service life can exceed ten years. Panel thickness 4–25 mm, specific weight 0.8–3.5 kg/m2, bending radius 0.7–4.3 m. |
| It is made from monolithic material; by giving the sheets different geometries, the bending resistance parameters are significantly increased. It has a wide range of products, differing in appearance and size. | |
| It is used quite rarely; reinforced frames are required for installation. Such requirements increase estimated cost coatings, which makes it uncompetitive among other types of coatings. |
To facilitate and speed up the installation process, the industry produces special additional profile elements:
- end profile;
- corner profile;
- ridge profile;
- connecting one-piece;
- connecting detachable.

Prices for polycarbonate profiles
Polycarbonate profiles
Additional elements can have different designs and be supplemented with special details. But these changes do not affect their main purpose and technology of use. High-quality without the use of connecting and decorative elements is impossible.

Advantages of polycarbonate coatings
Roofing material has a number of undeniable advantages over traditional coatings.
- High strength with low specific gravity. One of the most important advantages polycarbonate. In terms of impact strength per unit weight, polycarbonate is 8 times stronger than PVC and acrylic plastics and 200 times stronger than ordinary window glass. Wherein volumetric mass 16 times less glass and 3 times less acrylic materials.

- Low thermal conductivity coefficient. Due to this property, it is possible to reduce heat losses by approximately 30–50% compared to other types of roofing coverings. Considering the high cost of coolants at present, this is a very important advantage; it is widely used during the design of greenhouses, indoor swimming pools, winter gardens, insulated terraces and other heated premises.

- High transparency and weather resistance. Depending on the manufacturing technology, the transparency of the coating ranges from 72–90%, which allows significant savings financial resources on lighting interior spaces. This indicator is especially important for greenhouses and winter gardens. The material is approved for use at temperatures -40°С…+120°С. In this interval, polycarbonate retains its original physical characteristics.

- Chemical inertness. The coating is not afraid of contact with aggressive chemical compounds, can be used in urban environments with a lot of smog. By fire safety the material is considered to be highly flammable and self-extinguishing.

- Manufacturability. Polycarbonate plates are easy to cut and process, they can bend and do not crack during an accidental fall. Installation work do not require the use of special expensive tools and devices. Coating is done quickly, impact climatic conditions minimal.

Polycarbonate can be used to cover various types of roofs: arched and flat, inclined and complex broken. But regardless of the types of rafter systems, there are universal recommendations for all types of work.
Work can begin only after the frame is completely ready, materials, additional elements and hardware have been purchased. Tools must be prepared and a work plan drawn up.

Cutting and drilling
Taking into account the thickness, the sheets can be cut with an ordinary sharp mounting knife, electric jigsaw, portable circular saw or grinder. It is recommended to select the type of tool taking into account the thickness of the sheet and the volume of work. To prevent the appearance of microcracks during impact cutting cutting tools The sheet must be firmly fixed on both sides.

It is strongly recommended to drill holes between the ribs of cellular polycarbonate. The distance between the holes is at least 20 cm, the distance from the ends is more than 40 mm. The drill must be sharp and located at right angles to the surface.

Prices for popular models of screwdrivers
Screwdrivers
End sealing
The technology concerns only cellular polycarbonate. One of the disadvantages of this material is that dust gets into the honeycombs, then mosses and lichens begin to grow on it. The appearance of the coating deteriorates significantly; it is even theoretically impossible to clean the honeycombs. You have to either put up with the current situation or completely change the roof.
To prevent such negative phenomena, the upper open honeycombs should be tightly covered with special, especially strong self-adhesive tapes and additionally use decorative overlays. The lower ends are covered with perforated tape, through small holes the condensate that forms in the honeycombs due to temperature changes is removed. If there are decorative elements at the bottom, it is recommended to drill small holes in them. Monolithic sheets don't have this problem.

Sheet orientation
The main condition is that a special protective layer from ultraviolet rays should be located on the front side. Polycarbonate itself reacts very negatively to UV radiation. The service life is increased by using a special film, but it is very expensive and in order to reduce the cost of the material, it is glued only on one side. It is on this side that there is a protective polyethylene film with the manufacturer’s logo.

Cellular polycarbonate can only be bent along the direction of the honeycomb, the bending radius depends on the specific technical characteristics and is indicated in the manufacturer's instructions. Monolithic profiled sheets, on the contrary, can only be bent across the profiles.

Fixing sheets with hardware
To fasten the roof, it is recommended to use special self-tapping screws with thermal washers. Such elements eliminate the possibility of leaks and at the same time compensate for thermal expansion. It is strictly forbidden to use ordinary nails or self-tapping screws, to overtighten the fasteners, and not to leave gaps where the sheets join.

Rules for connecting panels with additional elements
These elements perform not only a decorative function, they are involved in creating a durable and airtight roof structure. Panels can be connected to each other using two methods:
- using one-piece profiles;
- using split profiles.
At junctions with vertical walls wall profiles are used. In every specific case The technician must make a separate decision on the optimal sealing method. You can use factory rubber bands and gaskets or seal the joints with modern sealants.

Step-by-step instructions for installing polycarbonate
Before starting work, you should make sure that all materials and tools are available, check the readiness and correctness of assembly. In the required quantity, you should purchase special screws and sealing washers, end and side profiles, sealing tapes, etc. It is strongly recommended that you carefully read the manufacturer’s instructions and strictly follow their recommendations.

Plan the work in such a way that all preparatory operations are carried out on the ground; prepared slabs with the required dimensions and drilled holes must be supplied to the structure. This minimizes material losses, reduces time, improves quality and increases work safety.
Important. Never walk on cellular polycarbonate. During installation, decisions and technologies should be made that do not require the technician to move along the already installed roof.
Step 1. Prepare the slabs of the required dimensions, unscrew the protective cover around the entire perimeter from the outside plastic film with the manufacturer's logo and carefully glue the end sealing tape. Cover the open honeycombs with end profiles and press them tightly into place. When adjusting the position, hit better by hand, but it is also possible to use a rubber mounting hammer.

When cutting slabs for arc covering, you need to keep in mind that the length of the arc is always greater than a straight line. It is recommended to pre-measure it with a tape measure; if this is not possible, then cut the sheets with a margin. Exact sizing will be done after installing the sheets on the frame. Please note that the length connecting profiles on an arched frame the length of the slabs is greater.

Step 2. Lay the first sheets on the roof, making sure that the internal stiffeners are strictly parallel to the direction of the slope of the slope. The slabs should be aligned along the top edge of the structure. The bottom edge should protrude slightly beyond the last run of the system.

Step 3. Firmly screw the base profile to the structure and check its position again. If everything is normal, then insert the first sheet into it and fix its position. To do this, you should use special hardware; the distance between the screwing points of the lower purlin is 15–50 cm. The diameter of the hole is approximately 1 mm larger than the diameter of the screw.

Step 4. After fixing the first sheet of polycarbonate, attach a clamping profile to its extreme side. Using the same algorithm, continue fixing the sheets along the entire length of the slope.

Step 5. Remove the protective film from the outside of the cover. As mentioned above, underneath there is a special layer that prevents ultraviolet rays from reaching the polycarbonate.

Important. Don't leave on a long period time, plastic film remains on surfaces and becomes difficult to remove over time. And the remnants of the film have Negative influence on the appearance of the structure.
Prices for popular models of laser levels
Laser level
Is it possible to install polycarbonate in winter?
This issue worries a large number of developers. They want to reduce construction time as much as possible by performing some roofing work in the winter. Moreover, manufacturers allow this option for installing polycarbonate.
- It is difficult to predict the magnitude of thermal expansions. For example, if the dimensions of the gap between the slabs at sub-zero temperatures leave it within 1–2 mm, then in summer there is a high probability of warping of the coating.
- Plasticity parameters decrease. The slabs become brittle and are more difficult to cut and drill. In addition, installation of the coating on semicircular structures becomes much more complicated.
Thermal expansion is an important factor to consider during installation.
A well-installed coating will be used without problems for a long period of time. To periodically clean surfaces from accumulated dirt, you need to use ordinary detergents. Acids, alkalis, chlorine and ammonia are prohibited. During care, all precautions should be taken to prevent mechanical damage protective film.
Video - Roofing polycarbonate
Laying polycarbonate roofing does not require professional skills or special equipment. Even a novice master can cope with the installation of this material; the main thing is to carefully read the instructions. You can read about how to make a polycarbonate roof for a terrace yourself.
Polycarbonate – relatively new material. They began to use it for roofing quite recently. Strength, transparency, sustainability and opportunity quick installation contributed to the emergence of new architectural forms. The presence of unique characteristics and relatively low cost make this material available for constructing roofs, gazebos, greenhouses, etc. A do-it-yourself polycarbonate roof for a small building is, in fact, an ordinary greenhouse mounted on the top floor.
Building a large house with such a roof with your own hands is quite problematic; it is better to invite professionals. But, for example, a greenhouse, a bathhouse or a garage is quite possible.
Features of a unique sheet polymer
Monolithic polycarbonate is in many ways superior to other translucent structures; its strength is 200 times higher than ordinary glass and 8 times higher than plexiglass.
In addition, the following characteristics are also attractive:
- ease;
- flexibility and plasticity;
- ease of processing and installation;
- fire resistance;
- impact resistance;
- chemical resistance to aggressive environments;
- durability.
Cellular polycarbonate – fashionable solution for roof
Polycarbonate sheets are used in construction, and polycarbonate roofs provide additional opportunities to arrange pavilions, greenhouses and greenhouses on the top of houses - an excellent example of the rational use of space. Typically the roof has rounded shape, and it does not retain moisture from rain or snow.
A material made in the form of a multi-chamber cellular structure formed from several layers with numerous stiffeners is called cellular polycarbonate. To put it simply, it looks like a honeycomb.

Cellular polycarbonate is a hard, colorless polymer plastic with a cellular structure.
Light transmission quality
Light-transmitting polycarbonate panels dissipate up to 80% sun rays. No other material can compete in this property, not even glass. Useful property scattering sheets of honeycomb structure allows the sun's rays to pass through different angles. This is very important if green plants are grown under the roof. Reflecting from walls or other surfaces, the rays hit the plants in a diffuse form and cannot damage or cause rapid wilting.
It is cellular polycarbonate that can be considered as good decision For suburban construction.
It is important to know!
Already at the planning stage, it is important to note the only drawback of such roofs: there are practically no side overhangs. To save the wooden walls of the structure from negative impact natural precipitation, the roof will need to be equipped with additional and effective drainage systems.

Installation of polycarbonate: preparation for work
Polycarbonate profiles come in detachable and non-detachable types, as well as transparent or colored. The length of sheets of material can reach 12 meters. The thickness of the profiles and grooves must correspond linear dimensions. In rectilinear structures, the thickness of the sheet is determined depending on the slope of the roof and the length of the space between the crossbars.
For example, with a slope of 30 degrees and a length of 40 cm, a thickness of 4 mm is suitable; with a smaller slope, it is better to use materials with a thickness of at least 6 mm. The same sheets are chosen if the distance between the crossbars increases. For areas adjacent to the wall, a wall polycarbonate profile is used. The ridge uses a ridge profile with wings up to 40 mm.
The material should be stored flat, without bending. If it is not possible to leave them indoors, you need to cover them with polyethylene.

small roof made of polycarbonate can easily be assembled with your own hands
Sheet cutting principles
Cellular polycarbonate panels are easy to prepare for use. Prepare spicy construction knife They can easily cut sheets from 4 to 10 mm. On protective film Marking is carried out and removed at the end of the work along with the film. For professional cutting, a special high-speed saw with a stop is used; the cutting device is a blade with small, unset teeth made of hard reinforced alloys. It is also convenient to cut with a regular jigsaw. The sheets are tightly stacked and supported to eliminate vibration. Professionals remove chips with compressed air.

Preparing cellular polycarbonate for work - cutting sheets
Drilling rules
Standard metal drill bits (taper and stepped) work best. You need to drill between the stiffeners, maintaining a distance of at least 40 mm from the edge of the panel, at an angle of 110° - 130°.
Sealing panel ends
In order to properly cover the ends of the panels, prepare continuous aluminum self-adhesive tape for the upper ends and perforated tape to protect against dust and condensate drainage. Polycarbonate or aluminum profiles for sealing the ends are selected by color. The profile design itself is designed in such a way that additional fastenings are not required - the fixation will already be quite tight. For arched structures, only perforated tape is used.
Note:
If you leave the ends of cellular polycarbonate open, the translucency decreases over time. But the ends of the panels cannot be hermetically sealed, even with ordinary tape. To ensure condensate drainage, you need to drill several small holes in the profile.

Correctly use sealing and perforated tape and u-profile
How to orient and pinpoint panels
To prevent the roof surface from turning into noodles over time when frozen moisture ruptures, the structural panels should be oriented in such a way that there is a place for the condensation that forms to be discharged outside. For this purpose, internal channels of the panels are provided, therefore the stiffeners should be positioned vertically with vertical glazing and along the slope in pitched structures. In arched structures, the arrangement of stiffeners is arched. On the outer surface of the sheets there is a special marking of a protective UV-stabilizing layer. The panels are mounted in a film, which is removed after completion of work.
One more nuance:
Manufacturers indicate the permissible bending radius of the panel depending on the thickness and structure. It is strictly not recommended to exceed these parameters.
It is also necessary to follow the rules for the orientation of the panels - the protective layer must be facing outward, otherwise the roof surface may be damaged by ultraviolet radiation, which will negatively affect the strength and durability of the structure. It is easy to determine where the protective layer is located by the inscriptions and pictograms. The slabs are mounted only vertically, they should be bent in a cold state, the direction should be chosen only transversely, parallel to the stiffeners.

Orientation of polycarbonate sheets
How to attach polycarbonate to metal
In arched structures, an aluminum base is most often used, while the joining rigid profile allows the use of a minimum of load-bearing structures, which means its weight is significantly reduced. DIY installation of cellular polycarbonate is carried out pointwise.
This you need to know:
Profiles are used for lightweight structures only when slabs are selected with a width of more than 500 mm. Distance between load-bearing structures will be 6-8 m, for different types of slabs. In such cases, the construction of rafters is not required, and transverse purlins are used as load-bearing longitudinal elements.

How to properly attach polycarbonate to the frame
Do not use ordinary nails, rivets or other unsuitable materials. Polycarbonate sheets are attached to the frame using a point method using thermal washers and self-tapping screws. A snap-on lid is located on a plastic washer with a leg (corresponding to the thickness of the panel in height). The kit also includes a sealing washer - without it, the roof can easily be blown away by a gust of strong wind. Sealing washers contain a layer of rubber or silicone that provides reliable fastening. Diameter 3.3 mm.
Interesting: this design of the thermal washer helps prevent the panels from creasing when fastened to the structure frame, and also prevents the formation of “cold bridges” that can arise from self-tapping screws.
The holes in the panel should be made a few mm larger than the diameter of the leg. This will compensate for possible expansion of the material as the temperature rises.
This is important: the step of point fastening of panels is 300-400 mm. Make sure that the screws are well tightened, but do not overtighten them!

So, do-it-yourself installation of cellular polycarbonate includes the following sequential operations:
- Holes are drilled in the base, the diameter is selected to be 2-3 mm more sizes self-tapping screw Step 300 mm.
- The surface of the base is coated with sealant.
- The “base” is attached with self-tapping screws to the longitudinal supports of the frame, the panels are laid with a thermal gap of 3-5 mm.
- The profile cover is snapped into place with a wooden mallet along its entire length. A special plug is installed at the end of the profile.
Joining profile systems
To fasten the elements to the sheathing, use additional fasteners to the one-piece connecting profiles(4, 6, 8, 10 mm), otherwise the sealing of the joints will not be reliable. Without additional fastenings, it is only possible to connect the joints of the edges of slabs in vertical structures if there are no high loads.
Reliable sealing of joints is achieved using detachable joining profiles (8, 10 and 16 mm), while the clamping of polycarbonate plates is strengthened.

Taking into account thermal expansion when installing cellular polycarbonate
The continental Russian climate contributes to the expansion of cellular polycarbonate in the summer heat and its contraction in winter. This should be taken into account when installing in hot weather The slabs should be installed more tightly; the necessary gap to remove condensate will be obtained when the temperature decreases. In winter, on the contrary, you should retreat more.
It is important to remember that the thermal expansion value for transparent slabs is 2.5 mm/m, and the value for colored slabs is 4.5 mm/m. Such materials are used at temperatures from -40 to +120 degrees Celsius.

Polycarbonate is one of the most promising building materials
Thus, a reliable guarantor of the durability and strength of the structure is compliance with the installation technologies of cellular polycarbonate. And in no case should you save on components, because the saying “the miser pays twice” has not yet been canceled. If you dream of cozy home with a beautiful stable roof, greenhouse, garage or carport, it is better to turn to professionals, at least for a consultation. Then all the positive qualities of the material will be revealed in full, and all you have to do is enjoy the beauty and comfort.
Polycarbonate is a modern material often used in construction for the construction of partitions, walls, curtains and decorative elements. Polycarbonate has also become widespread as a roofing covering. Roofs of houses, gazebos, open terraces, awnings and canopies over the entrance are erected from it. A polycarbonate roof allows you to realize the most daring ideas thanks to the features of this material.
The advantages of polycarbonate include:
- Low weight with high mechanical strength;
- Ability to transmit light;
- Wide range of shades and color solutions;
- Original and elegant appearance;
- Ease of installation and processing;
- Polycarbonate does not rust, is not destroyed by chemicals and microorganisms, and is resistant to temperature changes if installed correctly.
Polycarbonate also has disadvantages. One of them is instability to UV radiation if the protective layer is damaged, so during installation it is necessary to monitor the integrity of the protective film and remove it only after completion of all work. Another feature of polycarbonate that should be considered carefully is its high coefficient of thermal expansion. It is necessary to install polycarbonate using special self-tapping screws through pre-drilled holes of larger diameter. Otherwise, when the temperature changes, the material may deform.
Polycarbonate is divided into monolithic and cellular. Monolithic polycarbonate has high strength and has a standard thickness from 2 to 12 mm. The dimensions of the monolithic polycarbonate sheet are 2.05x3.05 meters. Its area of application is roofs of various configurations that experience heavy snow and wind loads. Monolithic polycarbonate with a thickness of 12 mm is considered vandal-proof and can withstand a hammer blow without the slightest damage.

Cellular polycarbonate has significantly less weight due to its cellular structure: the sheet consists of two or more thin sheets of polycarbonate connected by stiffening ribs along the entire length of the sheet. This material structure allows for high mechanical strength at low weight. Arched structures, domed roofs and other complex elements are made from cellular polycarbonate. Cellular polycarbonate can be either transparent or matte and has a wide range of shades. Standard thickness is from 4 to 32 mm, sheet dimensions are 2.1 x 6.1 or 2.1 x 12.1 meters.

Materials for making the frame
The polycarbonate roof frame can be made from various materials. The decisive factor in the choice is the basic style of the building and the expected weight of the structure, taking into account the snow load. In wooden buildings, when making a straight roof, a rafter system made of wooden bars or boards is used, on which transverse lathing and polycarbonate sheets are laid. This design fits perfectly into the overall style and gives the building lightness, volume and light.
Arched structures of canopies, verandas, as well as domed roofs are usually made on a frame made of aluminum or steel profiles. Steel is used for bulky structures and high snow loads. For light buildings, a lightweight aluminum profile is sufficient. For arches of large radius, additional supports and struts, transverse stiffeners from the profile are also used.
The polycarbonate is fastened to the profile using special self-tapping screws with a sealing washer. The joints of the sheets are connected using an H-shaped profile for polycarbonate.
Direct polycarbonate roof: implementation technology
A straight polycarbonate roof is usually used when constructing open terraces, gazebos, and small garden houses. Choosing polycarbonate as a roofing material allows you to obtain natural light and create a feeling of lightness and open space. At the same time, such a roof cannot be properly insulated without losing its transparency, therefore it is of little use for buildings used in winter.

Arched roofs are most often used in the construction of canopies, canopies, and summer gazebos. They are extremely simple in design, and the most difficult task is making arcs from a profile or square pipe. Actually, the difficulty is to bend it evenly around the entire circumference, and for this it is better to use a template.

- The basis of the arched roof design are the arcs. In order to make an arc from a metal profile, you need to cut it at equal intervals with metal scissors on both sides. The more such notches there are, the smaller the arc radius can be made, however, it should be remembered that polycarbonate has a minimum permissible bend radius, which is not recommended to be reduced. When folding, the sides should remain inside the arc.
- Having bent one arc from the profile, it is tried on at the installation site, aligned if necessary, and stiffeners are attached to it. After this, the arc is used as a template for making the remaining arcs.
- Polycarbonate is attached to metal profile the same way as for wood, using self-tapping screws with a sealing thermal washer. Joints and ends are processed using the same technology.


