How to make a broken roof corner. Installation of a sloping roof. Do-it-yourself broken roof: step-by-step instructions
After lofts came into fashion, that is, essentially, attics converted into housing, sloping roofs became extremely popular. This is a kind of variation on the theme gable roof, but with a slightly more complex geometry. By installing a sloping roof in your home, it becomes possible to increase the useful living space of the attic - significantly raise the ceiling at the extreme points of the slope. In addition, as many believe, such a roof looks more unusual and much more impressive than a simple gable roof.
The construction of a sloping roof is somewhat more complicated than a gable roof, but easier than any four-slope roof - hip, half-hip, hipped, as well as others with more exotic geometry. However, before you begin to study this topic, it is recommended that you familiarize yourself with the basic terms and concepts and learn how to build more simple options roofs - single-pitch and gable.
broken roof: where to begin
In construction, even a doghouse cannot be built without planning, so the zero step in constructing a sloping roof will be drawing a drawing. It can be done on a computer or manually. First, we build a frontal projection of the foot (the foot, in short, is the base of a house without a roof) of our house. Now, also observing the proportions, we build on the drawing the roof we like. Don’t forget that there will be an attic underneath it, so you need to think about the height of the ceilings in it. This way we will get the approximate roof height, slope degree and other parameters.
On the proposed plan the break is located at a height of 3.1 meters, which, in fact, will be (conditionally, without taking into account the under-roofing pie) the final height of the ceiling in the attic. If the finishing is done with plasterboard, then in the end the ceiling in the attic floor will be about 2.5 meters - quite good. The outer angles of the slopes with the horizon are: ridge - 30°, side - 60°. By the way, if the angle of the slope is 60° or more, then the snow load may not be taken into account in the calculations - the snow will not be retained on it. Your own drawing may have other options.
Calculation of the components of the rafter system
To prevent our roof from collapsing under its own weight and the weight of the “roofing pie,” we need to accurately select the cross-sections of the beams and boards of the rafter system, and also calculate their maximum strength. To do this you need to use a special program " Calculation of rafters and floor beams».
To calculate the cross-section of the beams of the side slopes, you need to open the tab (they are at the bottom of the window) “Sling.1”. Next, we establish a suitable section and introduce from plan of our house is an indicator of the vertical reaction force (in the picture in the program it is a red arrow pointing upward) at the highest point of the rafters. Let's call this indicator Q1 kg.
When installing tie boards, under each one, somewhere in the middle of the length, we install a temporary support. This allows you to reduce the degree of sagging. You can use supports 2.5x15 cm (in the illustration you can see a support for only one puff). They are necessary so that during the installation of the rafters there is no fear that one of the beams will break, and also to prevent sagging.
We put a 2.5×15 board on top of the ties, which will tighten them and make the entire structure more stable. Important: this board cannot be installed exactly in the center - it will interfere with further installation. It will be enough to retreat from central axis about 20 cm to the right or left.


Now we install the side rafters as shown in the illustration. We do not forget that, despite all our efforts, the geometry of the roof base may not have been ideal. Therefore, first we make a template along the end beam. Then on all subsequent rafters we make only the top cut. After this, we place the rafter in the place we need and only then we finally file it down. Only after this we fasten the rafters.
If the length of the beam is not enough, it can be extended, but an additional stand must be placed under the joint.
Now you can install the plugs for insulation material as shown in the illustration.

Next, you can install the rafters of the upper ridge slope. We make a temporary stand: take a 2.5×15 board and place it exactly perpendicular to the extreme tightening, as done in the illustration. The right (or left) edge of the board should be aligned exactly with the center axis. Now we take a board of the same cross-section, apply it to our central post and make marks with a pencil where the upper and lower cuts will be - we have a template.


A sloping roof differs from a gable roof in the installation rafter legs on two levels. The following selection of videos about a sloping roof will help you understand the technology for creating such a two-level rafter system.
Broken roof on the bathhouse
Here you will see the construction of a sloping roof on a bathhouse made of timber. Workers first installed the interior supports and rafters for the lower tier. This was followed by the covering of the rafter system and gables. Only after this the team began installing the rafters of the upper part.
Sloping roof rafters for a timber house
IN next video Step-by-step instructions for assembling the rafter system are provided. First of all, you need to install a support beam of the required length, taking into account the overhangs. Look carefully at how to connect the two parts of the support beam. Pay attention to the location of the docking bar. It must be inside the house.
In the second part of the video you can watch the installation of a rafter system on a house. The sheathed front gable is installed first. Then the remaining elements of the system and the rear sheathed gable are raised.
Making roof overhangs correctly
In the following video you will see instructions for installing a roof overhang.
Do you want to learn how to design an attic sloping roof yourself? Many questions are answered in the following video. Using the recommended program, you can independently develop a sloping roof project for your home.





























Considering various options roofing for their home, many owners opt for a sloping roof. This article offers information about the features, pros and cons of the design, as well as about the different types sloping roof. After reviewing the proposed material, you will get an idea of the calculation of the roofing system, installation technology and the reasons for the economy of such systems.

House with an attic under a sloping roof
Broken roof: device features
The trend in modern construction is the desire to increase the functionality of a home without losing its visual appeal. The broken structure fully meets these needs: it not only transforms the appearance of the building, but also allows for rational use of the under-roof space. For this reason, despite the increasing complexity of the structure, broken roofs are increasingly decorating country cottages.
The broken roof is a derivative of the usual gable roof. Unlike the latter, each slope of a broken structure has a bend line along which the angle of inclination changes. Thanks to this detail, the number of slopes doubles, and the pediment (the side vertical surface between the slopes, usually triangular in shape) becomes pentagonal. This change is reflected in the rafter system of the sloping roof. It becomes more complex, lower and upper rafters appear, and the roof is characterized by the following parameters:
Lower rafters. Set a steeper angle, no less than 60°.

Schematic diagram of a sloping roof
Upper rafters. For them, an angle of about 30° is selected.
Location of the ramps. The support for the slopes can be the walls of the building or floor beams extended beyond the walls.
All these changes are needed in order to maximize the attic area. The resulting space is usually used to equip the attic, which is why this design is called an attic roof. A house with a sloping roof and a veranda, common in private housing construction, is considered the most comfortable for living; the roof in such buildings is equipped with the following additional elements:
Window. Current energy saving windows with safety glass (with internal laminated triplex glass).

Windows of various types in sloping roofs
Balcony or terrace. A good way to increase the level of comfort and usable area of the attic. The decision to acquire this spectacular detail will require a more complex design and additional strength calculations.

House with a terrace on the attic floor
Bay window. Original architectural solution, which decorates the building and also expands living space. Usually they try to glaze a bay window to the maximum in order to increase daylight attics.

House with bay window
Cuckoo. This piece got its name because of its resemblance to the famous wall clock. The cuckoo has a separate rafter system connected to the main one. According to the form, they distinguish between one and gable structure, as well as hip and arched; the latter can be found on houses in the style of an Alpine chalet.

Gable cuckoo
Broken roof: advantages and disadvantages
Before making a choice in favor of this roof, it is worth getting acquainted with its pros and cons. The advantages include the following qualities:
You are getting additional living space, which is especially valuable for small areas where you have to save every meter of territory.
You are getting conveniently shaped room, in which (unlike a gable roof) large furniture can easily be placed. If desired, additional hidden cabinets can be placed in dead zones (between the slopes and walls).
Attic costs less than construction full second floors or expanding the perimeter of housing.
Well designed attic reduces heat loss, which means saving energy resources.
Appearance private houses with sloping roofs win compared to a classic gable roof.

Sloping roof in classic style
TO negative aspects sloping roofs include the following facts:
Finance. A sloping roof will cost more than a gable roof, since it will require more wood and materials for the roofing pie.
Restrictions on use. Such a roof is not the best solution for regions with snowy winters. Snow on sloping windows prevents sunlight from entering the attic. If the roof is designed incorrectly, snow gets clogged under the ridge or on the break line of the slopes and accumulates inside.
The importance of ventilation. Lack of ventilation leads to the accumulation of condensation in the thermal insulation layer and accelerated wear of the rafter system.
6 types of sloping mansard roofs
In country house construction, several options are used for arranging the attic. broken systems, which include:
Single-pitch. It looks like an inclined plane resting on walls of different heights. To implement such a roof, you will need the simplest rafter system, although you will not often see it on residential buildings. Externally, such a house looks non-standard; a panoramic window is often installed in the larger (high) wall of the attic floor.

House with garage and attic under a pitched roof
Gable. Classic private construction, typical for buildings rectangular shape. It has many solutions for vertical gables and different ridge positions. The ridge can be placed above the middle of the building (symmetrical design) or offset from the center (then the roof has an asymmetrical appearance). Due to the slope of the slopes, the space under the roof is used irrationally: it is impossible to arrange high ceilings, and a significant part of the area is lost in dead zones. You can raise the ceiling only by increasing the angle of the slopes and the height of the ridge; but such a solution is unsafe in regions with strong winds.

Attic under a gable roof
Variety gable mansard roof - one and a half floor. The walls are raised to a given level, and a roof structure with two slopes is installed on them. The building was called “one and a half floors”.
Broken. Each slope consists of two parts with a change in slope. House designs with sloping roofs allow you to significantly expand the usable area (attic space less area first floor by approximately 15%).

Project of a house with a sloping mansard roof
Three-slope. An asymmetrical design that can be found on attached buildings. The place of the pediment is occupied by the third broken slope.
Four-slope(hip). The place of the pediments is taken by broken slopes. Technically this is the most complex design, which requires precise calculation. The advantages are resistance to wind and snow loads, visual appeal and minimal load on the foundation. Disadvantages: reduced effective area(it is often possible to straighten up to your full height only in the center of the attic), increased costs for organizing the roofing pie.

Attic floor with a balcony under a hip roof
On our website you can find contacts of construction companies that offer roof repair services. You can communicate directly with representatives by visiting the “Low-Rise Country” exhibition of houses.
Attic under a sloping roof: profitable or not
At first glance, installing an attic floor under a sloping roof is a profitable venture, since you can save on the construction of walls and at the same time get additional area. This statement is half true; The savings will be spent on other components, which include:
Rafter system. To build a sloping roof from boards and other lumber, it is necessary to estimate the cost of the structure. The final estimate will be affected by the type of structure you choose and local lumber rates. The best choice would be lumber from coniferous species trees with a humidity of 18–22%.
Roofing pie components. If you are planning residential attic, you won’t be able to save on insulation, hydro- and vapor barriers. To maintain the proper temperature in the room, you will need a decent insulating layer (SNiP standards for the European part of Russia provide for a layer of mineral wool from 20 cm).
Video description
About a house with an attic and a balcony in the following video:
Window. Two types of window packages are used - vertical and in the plane of the roof. Windows located at an angle are one and a half to two times more expensive than windows in a house; they are equipped with a reinforced rotating frame and glass that can withstand snow cover. Their installation will also cost more, since it is necessary to ensure the tightness of the openings and think about snow guards over each window. For dormer windows a separate rafter system will be required, which complicates the roof topography and makes installation more expensive.
Choosing a roofing covering. Popular metal-based materials (metal tiles or corrugated sheets) are not the best choice for arranging such a structure. Metal-clad roofing is characterized by high thermal conductivity and a strong drum effect in rainy weather. These features will force you to use additional heat and sound insulation, which, quite expectedly, will lead to additional costs.

Dormer windows are designed for ventilation or access to the outside.
It may seem that building a sloping mansard roof is not as cheap an option as it seemed at first. However, real savings still exist and look like this:
Saving on foundation. Since the attic floor is lighter than a full floor, the foundation is laid less powerful than for two-story house. Since the cost of the foundation can be up to 25-30% of the construction cost, the gain will be tangible.
Saving on roofing material. By purchasing more expensive roofing, you can save on the filling of the roofing pie; However, for this you will have to calculate more than one option.
Delayed construction. Often lumber is purchased for the rafter system high humidity. If the roof is assembled right away, moisture will begin to be absorbed into the heat-insulating layer, which is not dangerous for a properly assembled pie, but will cause problems for a roof that is made incorrectly. Delaying commissioning will allow the wood to dry out properly, which will reduce the number of problems in the future.
Video description
About roof windows in the following video:
Nuances of calculating the attic roof
Roof calculation solves several problems:
Calculation of the rafter system during construction. It is especially important if there are additional details - windows, balconies, roof access, terraces. Such details increase the load on the rafters, and the design needs to be adjusted.
Calculation of the rafter system during reconstruction. Converting a non-residential attic into an attic is limited by the size of the existing building. All load-bearing elements will require a competent calculation of their cross-section.
Calculation of building materials. To ensure that the construction of the roof is not slowed down due to a sudden shortage of timber, metal tiles or self-tapping screws, first calculate required quantity materials.

Calculation diagram for a sloping roof
The procedure for calculating a sloping roof is as follows:
Calculated future roof area. Are measured linear dimensions each slope; The area is determined (by multiplying the length and width). The final number is the sum of the areas of all slopes.
Calculated required amount roofing material.
Calculated load bearing capacity . To do this, the average snow and wind load that the structure can receive during the season is determined.
The Internet offers an online calculator for calculating the rafter system of a sloping roof. As a rule, it allows you to calculate the angles of inclination of the slopes, sheathing parameters, permissible load and the required amount of roofing material. The result is based on the following parameters:
Laying width(projection of an inclined slope onto the base) of each element.
Lifting height(distance from the top of the slope to the base of the roof) of each slope.
Length of base and overhangs.
Roofing material(weight taken into account).
Video description
About calculation hip roof with a bay window in the following video:
The online calculator allows you to get approximate values and becomes practically useless if the roof has more complex geometry and additional details (hatches, windows). It is almost impossible to make the correct design calculations on your own without avoiding mistakes, despite numerous assurances to the contrary scattered across construction sites.
Only a person with an engineering education and work skills can create an accurate drawing with a detailed description of all components and connections, but not everyone has a friend who can be entrusted with such a responsible task. The most practical solution seems to be to contact a specialized construction organization, which offers many additional advantages:
Company specialists will calculate a roof of any complexity and will carry out turnkey installation.
The customer is provided detailed technical information about the advantages and disadvantages various types roofing coverings.
When calculating will be taken into account not only basic ones (as in an online calculator), but also Extra options: weight of waterproofing and insulation, presence of windows, weight of equipment that is supposed to be installed on the roof.

Turnkey installation of sloping roofs - quality guarantee
You will inform about prices for materials and expected consumption. The situation when there is not enough material or, conversely, a significant surplus remains, is excluded.
After agreeing on details a contract is concluded and an estimate is drawn up, delivery and payment terms are optimized.
Company provides a guarantee for the work performed.
Conclusion
Broken roofs have impressive dimensions and complex internal structure, however, they differ favorably from other roofs in that installation takes place according to modular design. Most of the components of the rafter system are assembled on the ground and raised up in the order in which they will be located. Heavy construction equipment is not needed for this work. The advantages of a sloping mansard roof lie on the surface - your house receives not only a roof, but also additional living space. Properly equipped, it will be suitable for year-round use.
Many owners of private houses, experiencing an understandable desire to get an extra living floor without special expenses, turn the attic into an attic. In this case, it is advisable to build a broken roof instead of a conventional roof with straight slopes. How and from what they are built similar designs, we will tell you in this article.
Types of sloping roofs
A sloping roof differs from a regular one in that its slope consists of two planes:
- the top is flat;
- the lower one has a slope of more than 45 o.
It looks as if an ordinary gable roof was taken by the middle of the slopes and stretched to the sides and upwards, thereby significantly increasing the volume of the attic space. But increasing the volume is only one of the advantages of such a solution. The second is the ability to make the roof higher. After all, its upper part, at the level of which the wind pressure is maximum, due to its slight slope, experiences less wind loads than regular roof with straight slopes.
The slope of a sloping roof consists of two planes with different angles of inclination
There are the following types of sloping roofs:
- Single-pitch. It consists of only one broken slope, while the walls have different heights. This type of roof is the simplest, but it is rare and mainly found on extensions.
- Gable. The classic version, including two drop-down different sides broken slopes. The ends of the roof - the gables - are vertical and represent a continuation of the walls.
- Three-slope. In this version, a third broken slope appears at one end instead of a pediment. This type of roofing looks more interesting and creates less load on the foundation. end wall. The gable roof is asymmetrical, so it is used mainly on attached buildings.
- Four-slope (hip). There are no pediments, there are broken slopes on all sides. It is being erected on a separate building. Disadvantage - the volume of the attic is reduced compared to the classic gable version. Advantages: spectacular architecture and minimal load on the foundation under the end walls.
The slopes of a sloping roof can rest on:
- Walls.
- Floor beams placed outside the walls. This option is more difficult to implement, but it allows you to make the attic more spacious.
Along with the usual ones, there are sloping roofs that have additional structural elements:

When installing a sloping roof, a combined rafter system is used. The upper flat rafters - they are called ridge rafters - are hanging, that is, they are supported only by the lower ends, and the upper ends are joined to each other. To prevent these rafters from moving apart under the influence of their own weight and snow load, they are connected by a horizontal element - a tie.
The side rafters are layered. They lean and bottom- on the walls using a Mauerlat, and on the top - on vertical racks.
In the sloping roof rafter system, both layered and hanging rafters are used simultaneously
Due to the simultaneous presence of both layered and hanging rafters, this system is called combined. In some cases, the side rafter has to be supported in the middle by a strut that rests on the base of the post.
The racks, in turn, rest on the floor beams. If attic floor made from concrete slabs, then to support the racks a wooden beam is laid on it - a bench. The racks form the frame of the walls attic room, and the puffs form its ceiling.
The frame of a sloping roof consists of rafters - hanging and layered - and additional elements that ensure structural rigidity
Rafter attachment points
The reliability of the rafter system depends on the correctly chosen method of fastening its elements.
Under the influence of load, the hanging rafters will move apart, sliding along the surface of the beam or tie. Used to prevent slipping following types connections:
- If the roof slope exceeds 35 o, a single-tooth lock is sufficient for fastening.
The tenon rests on the reciprocal groove of the tightening and does not allow the rafters to move apart
- For flatter slopes, a double tooth is used. To enhance the strength of the connection, two stops are cut out in the tightening. One of them - the outer one - is supplemented with a spike. An eyelet is cut out to fit its size in the mating part of the rafter.
For flat slopes, fastening the rafter leg to the tie is usually done using a double-tooth lock
- The most complex knot of a sloping roof is at the intersection hanging rafter, tightening and layered rafters. Therefore, it is reinforced with bolted connections.
A pair of bolts effectively counteracts the torque at the connection point between the rafters and the tightening
- The rafter leg is attached to the mauerlat using corners and staples. To facilitate installation and limit the movement of the rafter, a stop block must be nailed to its lower surface.
A support board or block placed on the bottom edge of the rafter leg prevents it from sliding down
Broken roofs with “cuckoo”, balcony, window
If the roof has a “cuckoo” roof, then its rafter system is connected to the main one. The “cuckoo” roof can be:

The presence of a “cuckoo” weakens the main rafter system; in addition, careful sealing of the junction is required different parts roofs. Because of this, it is better to entrust the design and construction of roofs with such elements to specialists.
A balcony in the attic can be organized in three ways:

To install a roof window, bars are secured between the rafters to outline the opening. They will play the role of a supporting contour for the window structure.
There are known cases when construction companies in order to expand the attic space, they decided to modify the classic rafter diagram sloping roof, abandoning the usual arrangement of racks.
The technical solution is as follows:

As a result of strengthening the break point of the slope with overlays, a pair of rafters works as one rafter leg of a curved shape.
Is it possible to make a sloping roof with a raised puff?
The location of the tightening is higher than usual - a technique that is sometimes used when constructing a gable roof with straight slopes. But in the case of a sloping roof, a raised tightening device is not practiced, since this requires moving the racks, as a result of which the attic space becomes less wide.
Calculation of the sloping roof truss system
To determine the dimensions of the rafters, you must:

To calculate the strength, you need to measure the angles of inclination of the rafters with a protractor.
Strength calculation
Today, the calculation of the rafter system of the attic roof can be done using specialized software systems. But you need to be able to do it manually, because field conditions The computer is not always available, and it will be useful to check the results before starting work.
To carry out calculations, you need to know the standard snow and wind loads characteristic of the construction region. This data should be found in SNiP 01/23/99* “Construction Climatology”. According to this document in Russian Federation There are 8 zones with standard snow loads from 80 to 560 kg/m2.
The map shows standard values snow load for each climatic region of our country
The value of the standard snow load can be taken from the reference table.
Table: standard snow load values by region
| Region No. | I | II | III | IV | V | VI | VII | VII | 80 | 120 | 180 | 240 | 320 | 400 | 480 | 560 |
The actual snow load will depend on the slope angle. It is calculated using the formula S = S n * k, where S n is the standard snow load in kgf/m 2, k is the correction factor.
The value of k depends on the angle of inclination of the slope:
- at angles up to 25 o k = 1;
- for slopes from 25 to 60 o k = 0.7;
- for more steep roofs k=0 (snow load is not taken into account).
Parts of the slope of a sloping roof have different slope, accordingly, the actual snow load for them will be different.
In a similar way, the country’s territory is zoned according to the magnitude of the wind load.
The territory of our country is divided into eight regions, in each of which the wind load has its own standard value
There is a reference table to determine the standard wind load.
Table: standard values of wind load by region
| Region No. | I a | I | II | III | IV | V | VI | VII | 24 | 32 | 42 | 53 | 67 | 84 | 100 | 120 |
The actual wind load depends on the height of the building, its surroundings and the angle of the slope. The calculation is made using the formula:
W = W n * k * C, where W n is the standard wind load, k is the tabular coefficient depending on the height of the building and the environment, C is the aerodynamic coefficient.
Table: correction factor taking into account the height of the building and type of terrain when calculating the actual wind load
| Height buildings, m | Terrain type | ||
| A | B | IN | |
| Less than 5 | 0,75 | 0,5 | 0,4 |
| 5–10 | 1 | 0,65 | 0,4 |
| 10–20 | 1,25 | 0,85 | 0,55 |
Terrain types differ according to the following characteristics:
- Zone A - open areas where the wind does not encounter obstacles (coast, steppe/forest-steppe, tundra).
- Zone B - areas where there are wind obstacles with a height of at least 10 m: urban development, forest, terrain folds.
- Zone B - densely built-up urban areas with buildings within 25 m in height.
Aerodynamic coefficient C takes into account the angle of inclination of the slopes and the prevailing wind direction. It should be understood that the wind can exert not only pressure: at small angles of inclination of the slope, a lifting force arises, tending to tear the roof away from the mauerlat. To determine the C coefficient, you need to use reference tables.
Table: aerodynamic coefficient values - the air flow vector is directed towards the slope
| Slope slope, hail | F | G | H | I | J |
| 15 | -0,9 | -0,8 | -0,3 | -0,4 | -1,0 |
| 0,2 | 0,2 | 0,2 | |||
| 30 | -0,5 | -0,5 | -0,2 | -0,4 | -0,5 |
| 0,7 | 0,7 | 0,4 | |||
| 45 | 0,7 | 0,7 | 0,6 | -0,2 | -0,3 |
| 60 | 0,7 | 0,7 | 0,7 | -0,2 | -0,3 |
| 75 | 0,8 | 0,8 | 0,8 | -0,2 | -0,3 |
Table: aerodynamic coefficient values - the air flow vector is directed towards the pediment
For those areas of the roof where lifting force occurs, the value of coefficient C is negative.
The actual snow and wind loads are summed up and, based on the result obtained, the cross-section of the rafters is selected (taking into account their pitch and maximum length). Below is a table for softwood rafters premium(for other varieties the values will be different). Its cells indicate the maximum permissible rafter length for the corresponding cross-section, pitch and load.
Table: maximum permissible length of rafters in accordance with the pitch of their installation and the magnitude of the snow load
| Section, mm | ||||||
| 100 kg/m2 | 150 kg/m2 | |||||
| Distance between rafters, mm | ||||||
| 300 | 400 | 600 | 300 | 400 | 600 | |
| 38 x 80 | 3,22 | 2,92 | 2,55 | 2,61 | 2,55 | 2,23 |
| 38 x 140 | 5,06 | 4,6 | 4,02 | 4,42 | 4,02 | 3,54 |
| 38 x 184 | 6,65 | 6,05 | 5,26 | 5,81 | 5,28 | 4,61 |
| 38 x 235 | 8,5 | 7,72 | 6,74 | 7,42 | 6,74 | 5,89 |
| 38 x 286 | 10,34 | 9,4 | 8,21 | 9,03 | 8,21 | 7,17 |
Installing rafters with a pitch of 600 mm should be considered the best solution: with such an inter-rafter distance, the rigidity and stability of the structure will be maximum, and for insulation it will be possible to use slabs of mineral wool or foam plastic of standard width.
Video: attic calculation
DIY construction of a sloping roof
A sloping roof is a building structure of medium complexity. If you have certain skills and several smart assistants, it is quite possible to build it with your own hands.
Selection of necessary materials
To build a sloping roof you will need:
- Vapor barrier film - polymer or anti-condensation film with an internal non-woven textile layer.
- Waterproofing. You can use a special polyethylene film or a so-called superdiffusion membrane, which retains moisture but allows steam to pass through.
- Annealed wire with a diameter of 3–4 mm, which is used as fasteners when constructing a rafter system.
- Other types of fasteners - bolts, nails, staples, special fastening plates with stamped teeth.
- Steel sheet with a thickness of 1 mm - linings will be cut from it for fastening the elements of the rafter system.
- Roofing material and screws (nails) for fastening it.
- Lumber.
- Insulation - mineral wool, URSA (fiberglass), polystyrene foam.
Rafters and other elements are usually made from the cheapest type of wood - coniferous. It should not contain rotten areas or signs of damage by bugs. All wood must be treated with antiseptics before installing the rafter system.
When constructing a sloping roof rafter system, pine beams and edged boards without defects or damage are used
The following lumber will be required:
- for floor beams - a beam with a section of 150x100 mm, if the beams rest on external and internal load-bearing walls, or with a section of 200x150 mm when supported only on the external frame of the building;
- for the manufacture of Mauerlat - timber with a section of 150x100 mm or 150x150 mm;
- for racks - usually a beam of the same cross-section is used as for floor beams;
- for rafters - a board or beam, the cross-section of which is determined by the above calculations;
- for some fasteners and subfloors - unedged boards of various thicknesses;
- for sheathing - edged board with a cross-section from 25x100 to 40x150 mm, depending on the pitch between the rafters and the type of roofing material;
- for counter-lattice - a board 50–70 mm thick and 100–150 mm wide.
The procedure for performing work on the construction of a sloping roof
The process of constructing a sloping roof is as follows:
- Mauerlat is laid on the walls. You must first lay a waterproofing layer made of roofing felt under the timber.
- The Mauerlat is attached to the wall using studs or anchor bolts embedded in it (in this case you will have to drill holes in the wall) with a diameter of 12 mm. The fastener must extend into the body of the wall at least 150–170 mm. The Mauerlat can also be tied to the wall with annealed wire embedded in it.
For buildings made of concrete or building blocks, it is most convenient to attach the Mauerlat to studs embedded in the armored belt when it is poured
- Install floor beams. If the floors are expected to extend beyond the walls, they must be laid on a mauerlat. Otherwise, the beams are laid on the walls through a roofing material pad and attached with corners or staples to the Mauerlat.
- Determine the middle of the floor beam and step back to the left and right exactly half the width of the attic room - this is where the racks will be installed.
- The timber is nailed and then set strictly vertically, using a plumb line and building level, and are finally attached to the floor beam using corners and wooden overlays.
Vertical posts are installed strictly vertically, and then connected with longitudinal girders and transverse ties
- Having installed both racks on the floor beam, they are connected at the top with a horizontal beam - a tie. Again, corners should be used for fastening.
- Side rafters are installed on the sides of the resulting U-shaped structure. At the bottom, each rafter rests on a mauerlat, for which it is necessary to cut a groove in it (the rafters). Fastening to the Mauerlat is carried out with brackets or corners.
The rafter leg is attached to the mauerlat using staples, angles and other special fasteners
- If the length of the rafter exceeds the maximum permissible, it is supported by a strut resting against the base of the rack. Additional stands and so-called contractions are also used.
To further strengthen the rafter legs, you can use struts, grabs and additional racks
- Determine the middle point on the tightening: it will be installed here vertical beam- grandma. Its function is to support ridge knot, that is, the junction of the upper rafters.
- Install the upper (ridge) rafters. In the ridge assembly they must be firmly attached to each other, for which it is necessary to use powerful bolts with washers or plates or a steel plate.
The connection of rafter joists at the ridge part of the roof can be done end-to-end, overlapping or half-timbered
- Place the headstock in its place.
- All roof trusses are assembled in a similar way. First, you should assemble the outer trusses - then between their key points it will be possible to stretch pieces of cord, which act as a guide when assembling the intermediate trusses.
- The trusses are fastened to each other with horizontal purlins, which should connect the upper parts of the racks. Purlins can be set to more early stage, immediately after installing the racks.
- The finished rafter system is covered on top waterproofing film. As already mentioned, along with conventional polymer films, membranes are produced today that act as a barrier to water but allow steam to pass through. IN different directions this membrane acts differently, so it needs to be laid right side(there are marks on the canvas). The film roll is unwound in horizontal rows, moving from bottom to top, and the next row should lie on the previous one with an overlap of 150 mm.
The waterproofing coating is laid parallel to the eaves overhang with an overlap of 150 mm
- The overlapping areas are taped with double-sided tape. The film should not be stretched - it should sag by 2–4 cm. To prevent the material from slipping, it is fixed with a stapler (construction stapler).
- Along the rafters, a counter-lattice is placed on top - boards 50–70 mm thick and 100–150 mm wide. This structural element necessary to create a ventilated gap between the waterproofing and roofing material- this will remove condensation formed due to steam penetrating under the coating.
- On top of the counter-lattice, in a direction perpendicular to it, a sheathing is stuffed - boards, slats or solid flooring, the parameters of which depend on the type of roofing material and the design load.
Counter-lattice bars form ventilation gap, and the longitudinal rows of the sheathing serve to fasten the roofing material
- The roof covering is attached to the sheathing.
Video: installing a sloping roof
Insulation of the roof is carried out after completion of the installation of the rafter system and laying of the waterproofing layer. A special feature of a sloping roof is that the insulation is laid along the lower rafters and the ceiling of the attic space formed by the ties. The upper triangle of the roof is left cold to ensure ventilation of the under-roof space.
Insulation boards must fit into the gaps between the rafter joists with a noticeable tension, so as not to create conditions for the formation of cold bridges
If a regular film was laid over the rafters as waterproofing, there should also be a ventilated gap of at least 10 mm between it and the thermal insulation. If a superdiffusion membrane was installed, there is no need to create a gap.
Insulation boards are laid in several layers with offset joints in each row. A vapor barrier membrane is mounted on top of the insulation.
The roof is a multi-layer structure consisting of protective films, insulation, roofing and ventilated gaps
Video: insulation of a broken attic roof
https://youtube.com/watch?v=UqWyrNQ4eq0Selection of roofing materials
It remains to decide what to cover the roof with. There are quite a lot of roofing materials today, we present comparative characteristics the most popular of them.
Ondulin
In appearance, ondulin resembles slate, only it is multi-colored. In terms of internal composition, it is structured completely differently: it is bitumen material, like roofing felt, only the base is not cardboard, but a rigid sheet of pressed cellulose. Ondulin costs a little more than slate, but still remains in the category of budget materials.
Disadvantages of ondulin:
- burns;
- has low strength;
- short-lived;
- in hot weather it can emit a characteristic bitumen smell;
- on the shaded side, like slate, it can become overgrown with moss, although manufacturers claim that this is impossible.
In addition to low cost and extensive color range The material also has quite tangible advantages:
- does not make “drumming” sounds during rain or hail;
- unlike slate, it is plastic, due to which it is more resistant to impact and can be used to cover roofs with complex contours (“unbending” slate would largely go to waste);
- has low thermal conductivity compared to metal coatings, so it does not heat up so much in the sun.
Corrugated sheet
Today, corrugated sheeting is one of the most popular roofing materials. “Profiled” translated into everyday language means “wavy”, only the waves of corrugated sheeting are not sinusoidal, like those of slate and ondulin, but trapezoidal.
Corrugated sheets are produced in the form of metal sheets with trapezoidal waves
Corrugated sheets are made from steel sheets, which are coated with a double protective layer: first with zinc, then with polymer. The material is very durable: its service life can reach 40 years. But you need to take into account that much depends on the type of protective polymer used:
- Acrylic. Least resistant variety coverings. It is easily damaged during installation, it fades quickly and can peel off after only 3 years of use.
- Polyester. Most often used. In terms of cost and durability, it is the best option for normal conditions, when there is not a large amount of pollution in the atmosphere and the roof is not subject to intense mechanical stress. Polyester is applied in a layer 20–35 microns thick, so during installation, special care must be taken to avoid damaging the coating.
- Plastisol (PVC-based polymer). It is applied in a layer 175–200 microns thick, therefore it has increased resistance to mechanical stress and withstands the chemical aggression of a heavily polluted atmosphere. But it is not designed for high temperatures and intense ultraviolet radiation, so for southern regions doesn't fit. Another drawback is that it burns out quickly (in 4–5 years).
- Pural. This polyurethane-based coating appeared relatively recently. It is applied in a layer 50 microns thick and is characterized by resistance to solar radiation, chemical influences, and temperature changes. It also gives the material wear resistance.
- Polydifluorionad. Corrugated sheeting with such a coating is the most expensive, but it is also the most durable. Designed for extreme climatic conditions or chemically active environments. For example, it is advisable to cover buildings located on the seashore or buildings with such corrugated sheeting chemical plant producing emissions into the environment.
Metal tiles
Metal tiles, like corrugated sheets, are made from steel sheets with polymer coating, only they are given more complex shape simulating surface ceramic tiles. It looks more impressive, but to give the desired shape you have to use thinner steel, so metal tiles are inferior in strength to corrugated sheets.
Metal tiles are superior in aesthetic qualities to corrugated sheets, but inferior in strength and durability
Metal tiles have the following advantages:
- Light weight.
- Economical.
- Aesthetics.
- Resistant to fading and abrasion.
But this material has disadvantages that can upset the homeowner:
- High level of sound transmission: during rain and hail, the house will be noisy.
- A large amount of waste when covering roofs of complex shapes.
Monolithic polycarbonate
Transparent roof made of monolithic polycarbonate- this is a rather exotic option. Insulation in this case, of course, is not provided, so such a solution would be appropriate only in a region with a warm climate.
Polycarbonate as a roofing covering is mainly used on non-residential buildings, agricultural structures and buildings located in the southern regions
For fixation plastic panels a frame made of aluminum or steel profiles is attached to the rafters. When fixing polycarbonate, you need to take into account that this material changes greatly in size with temperature changes, therefore:
- the diameter of the mounting holes should be 2–3 mm larger than the diameter of the screws;
- It is impossible to screw the screws tightly.
Monolithic polycarbonate is different:
- impact resistance;
- low specific gravity;
- resistance to fire and fading;
- inertness towards aggressive chemical elements;
- ease of handling and cleaning.
At the same time, this material is unstable to small sharp objects and has a high coefficient of linear expansion when heated.
Soft roll roofing
Traditionally, the following types of soft roll coverings are distinguished:

All these materials are produced on the basis of bitumen or a bitumen-polymer mixture. They can only be used on roofs with a slope of up to 25 o - such a coating can slide off steeper slopes in the heat. Not long ago, new varieties of soft roofing coverings appeared, the raw materials for which are rubber and petroleum-polymer resins. They can be laid on slopes of any steepness and, unlike bitumen ones, they withstand the effects of negative factors well. environment(service life is 25 years) and laid in one layer (bitumen-containing materials are laid in 3–5 layers).
We also produce such materials - these are Rukril and Cromel membranes. The roll width can reach 15 m, so there will be very few seams in the coating.
Membranes are attached either to special glue, or using self-tapping screws.
As can be seen from the drawings and diagrams, a sloping roof allows you to use with maximum benefit attic space. But at the same time, it surpasses the complexity of a conventional pitched roof, both in calculations and in implementation. Therefore, in the absence of sufficient experience, it is advisable to entrust its design and construction to a specialized organization.
The popularity of sloping roofs is due to the cost-effectiveness of construction and the ability to rationally use attic space. They are used to organize insulated and non-insulated attics. Construction technology roofing structures with a variable angle of inclination of the slopes differs from the traditional gable scheme.
Because those who want to acquire attic floor To successfully prove yourself in the field of a roofer, you need to know how the rafter system of a sloping roof is structured and how the dimensions of the materials for its construction are calculated.
The most striking and expressive representative of the class of sloping roofs is a pentagonal structure with a clear difference in the angles of inclination of the slopes. Even without delving into the specifics of its construction, one can understand that it is made of two tiers stacked on top of each other. In the lower solid tier there is an attic, which gave the second name to broken roofs. The less voluminous top tier, crowning the lower part, determines the shape of the structure in the ridge area.
Briefly about the specifics of the rafter structure
The rafter frame for both parts of the attic roof is constructed according to the rules dictated by the usual one. The lower part of the sloping roof frame is built by installing layered rafter legs. In the construction of the upper part, both layered and hanging rafters can be used. The bottom of the layered rafters has the right to rest on the mauerlat or on the floor beams. The support for the top is most often a wooden frame, which at the same time plays the role of a frame for one of the walls of the attic. In device upper tier They focus mainly on ease of use for the performer.
According to tradition, the angle of inclination of the slopes of the lower part of the sloping roof is much steeper than the upper one. They create a break - a clear indicator of application broken technology in roof construction. However, the steepness of the upper and lower parts the slopes may be equal, which is why the broken structure will look like an ordinary gable. But they are installed using the standard method for sloping roofs, because the frame of the lower tier must ensure the possibility of organizing the usable space. Those. the rafter system must have the necessary elements with a given load-bearing capacity for constructing the walls and ceiling of an insulated or cold attic.

Types of loads and their combination
Tricky formulas according to which designers calculate the sloping roof truss system construction companies, we will not bring it. The builders know them without us. For those who decide to build one or two roofs on suburban area, such fundamental information is not needed at all. There are plenty of programs on the Internet that perform complex mathematical operations in a couple of seconds to calculate the cross-section of rafters, supports and beams. Let’s better understand what data will be required to be entered into the program, as well as what types of loads on the floor, rafters of the upper and lower tier should be taken into account.

Download the program itself here -(you only need Excel to work). Further we will give examples of working specifically with it.
Why are limits needed?
Each element of the sloping roof truss system will be affected by different kinds loads The sum of the loads should not lead to deformations and damage requiring mandatory repairs. According to the rules, load-bearing structures are calculated taking into account two limit values, these are:
- Ultimate strength is a condition, the excess of which leads to the destruction of the building structure, loss of endurance or stability.
- Limiting deformation is a condition, the excess of which leads to unacceptable deflections, as a result of which not only the geometry of the structure changes, but the nodal joints are disrupted.
For both types of specified limit states designers make calculations. An independent roofer does not need these subtleties too much. The calculation programs available on the Internet with their formulas already take into account the limits. They are entered into the calculation algorithm in the form of signal values of the type:
- N tr. strength - the size of an element of the rafter system, a decrease in which will lead to a loss of strength.
- N tr. deflection is the size of an element, the reduction of which will lead to threatening deformation.
When turning to automatic computing help, you need to pay close attention to such values. This is an extreme minimum indicating that actual design values should be higher.
The list of loads acting on the roof includes the weight of winter precipitation, wind force, dead weight, the weight of furniture and people using the attic. Loads can act simultaneously, alternately or in any combination such as snow + furniture + people; snow + wind, etc. Calculations are carried out to the maximum in an effort to provide for the likelihood of exposure to the greatest load.

How to determine the weight of snow cover
To determine the weight of the snow cover, you do not need any special knowledge. It is carried out by determining whether the construction site belongs to a specific “snow region”. We found a region on the map with a number assigned to it, then looked at the sign to see how much snow would press on the horizontal surface.
For the rafters of the upper and lower tier of a sloping roof, the snow weight indicators will be different. The slopes of a sloping roof in most cases are unequal in angle of inclination. Solid sediments have a greater opportunity to linger and lie on a surface close to the gently sloping top than on steep slopes lower part. It should be taken into account that on slopes with a steepness of up to 30º, the weight of snow is taken equal to one unit of the average value accepted in the region based on long-term observations of the weather service. It is believed that on slopes with a steepness of 60º or more, snow does not linger at all, i.e. equal to zero. The value of the snow weight in the interval between the indicated slopes is found by interpolation. For example, if the angle of inclination is 45º, then the table indicator should be multiplied by a factor of 0.5, for 50º by 0.33, etc.

How to find wind load
Wind load is needed to calculate the stability of the rafter system. To determine it, we again use a zoning map, but this time compiled from wind pressure values. This indicator is necessary for the rafters of both tiers of the roof, because a gusty wind can tear off and carry away the flat part, and simply overturn the steep part. Information about wind strength determined from the map is corrected by multiplying by a coefficient developed for different types terrain.
In regions with high wind loads, the frequency of attaching rafter legs to the walls increases, i.e. they are fastened with wire twists more often than not. For stability, the number of wind connections increases - struts, supports, boards or slats nailed to three or more rafters. Their weight must be taken into account when calculating the total weight of the roof structure.

Roof weight load
The weight of the roof is a prefabricated characteristic with individual parameters. Essentially, this is the mass of the roofing pie of a specific insulated or cold design with a certain type of covering and a continuous or sparse lathing specially arranged for the covering. It is calculated per meter of roofing area.
The average weights of coatings can be found on the plate. It should be taken into account that when using embossed roofing materials, the weight of the snow cover should be increased by 10%. For example, if you are making corrugated sheeting with a large wave, you should remember that the snow cover in the recesses can accumulate and lie for a long time.

The weight of the lathing depends on the type of coating. Device soft roof requires continuous flooring made of boards, sheets of moisture-resistant plywood or OSB boards. Profiled sheet metal, slate, clay tiles mounted on bars installed at a certain pitch. The weight of the sheathing will increase due to the installation of diagonal wind ties in regions with high wind loads. The weight of insulation and the rafter system itself with struts, supports, purlins and other elements is also calculated individually.
For preliminary calculations, there are approximate average indicators:
- weight wooden sheathing from 10 to 12 kg/m²;
- weight of layered rafter legs with a run from 5 to 10 kg/m²;
- the weight of the hanging legs of the truss is from 10 to 15 kg/m².
The readings calculated using the programs should not differ too much from the figures given. For insulated attics, the list of loads should be supplemented with the weight of the sheathing. In the case of using insulation with a thermal conductivity coefficient slightly different from 0.04 W/m×°C, its mass can be neglected.

We showed where and how to find values to enter into calculation systems. All other information for the mathematical determination of the cross-section of rafters, beams, and supports is entered according to the design data. If the calculation system warns that the “condition is not met” or the load-bearing capacity is not ensured, the dimensions of the elements should be increased.

Construction of a broken rafter system
Before you begin constructing a rafter system for a future sloping roof, you need to make a project and make calculations of the structural elements. We will assume that the design stage has been completed.
Let's consider one of the typical examples of constructing an attic with two tiers of layered rafters installed above a brick frame. We will attach the rafter system to the mauerlat - wooden frame made of timber 150x200mm, laid flush with the inner perimeter of the walls. A row of bricks is laid along the outer edge of the box, masking the Mauerlat and removing part of the thrust load. The upper plane of the mauerlat should be 2-3 cm higher than the brick trim.
Installation of floor beams
We begin the construction of the floor by installing the outer beams, the extension of which determines the width eaves overhangs. Next, along a cord stretched between the outer beams, we install intermediate elements with a step equal to the distance between the rafter legs. For insulated roofs, it is recommended to make the pitch equal to the width of the thermal insulation slab, so that the insulation fits tightly in the space between the rafters intended for it. For non-insulated structures, the pitch is calculated so that a whole number of roof trusses with equal distances between them fit.
The size of the timber for the construction of the floor is 100×200mm. When laying beams, we level their upper plane if it is not possible to align them strictly to the horizon. Leveling is carried out by lifting the Mauerlat or placing wood chips under the beam. After attaching the beams to the Mauerlat, we attach a short beam to their end, so that they form a plane for the end eaves overhangs. The spacing between short beams doesn't matter, maybe 1m or so.

Construction of attic walls
We mark on the arranged ceiling the location lines of a number of supports for the rafter legs of the lower tier. Along with their supporting function, they play the role of a frame for the walls of the attic.
We proceed as follows:
- We install corner supports, for the manufacture of which we use 100x150mm timber 10cm longer than the final height of the attic ceiling. We check the verticality of the supports with a plumb line; we will fasten them only after we are convinced that the installation is perfect. For stability, we fix their position with temporary braces. By analogy, we install supports in the middle of the gable walls.
- We connect the corner supports with string to indicate the installation location of the intermediate posts. For the manufacture of intermediate supports, a material of 50×150mm with a height equal to the corner supports is suitable.
- On top of two rows of supports we lay purlins made from 50x150mm boards. Temporary spacers will no longer be needed; the constructed walls of the future attic are stable even without them.
- We install a board edgewise on the purlins; it will form the ceiling of the attic.
- We lay a 25x150mm board on top of the ceiling of the attic under construction. It does not need to be installed along the axis of the building. It is better to lay it parallel, 20-30cm away from the axis.
The result of the efforts made is finished frame attics and supports for installing the upper tier of rafter legs.

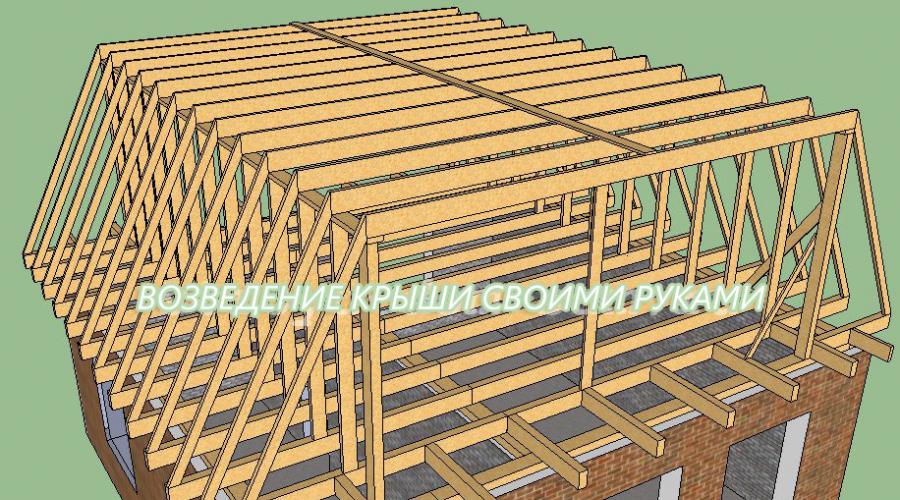
Installation of rafters of the lower tier
The rafters of the lower tier of a sloping roof are manufactured and installed using the standard layered method:
- We apply a 25x150mm board of the required length to the end of the structure being constructed and, in fact, mark the lines of the upper and lower cuts with a pencil. This is a template that can be used to make all rafters of the lower tier, if there are no deviations in the geometry of the rafter system.
- If there are doubts about the perfection of the previous work, install only the outer legs and stretch the lace between them. Using the template, we make only the top cut on the remaining rafters. We will mark the bottom line after the fact, aligning the top plane of the workpiece with the cord guide.
- We install the rafter legs. We fasten them to the floor beams with brackets or metal corners, and at the top to the purlins with two or three nails.
It happens that to cover the entire length of the lower slope, one board is not enough. In such situations, the rafter is assembled from two short boards, sewn together with a piece of material of a similar cross-section, 1 m or more in length. True, it is still advisable to order lumber of the required length, so as not to weaken the structure with stitched sections.

Installation of rafter legs of the upper slopes
To manufacture and install the upper rafters, you must first mark the central axis. To do this, the inch piece should be nailed to the outermost ceiling board of the attic strictly vertically. One of the cutting edges must exactly coincide with the central axis of the sloping roof rafter system indicated on the diagram, then:
- We try on an inch to the end to make a template and mark the cut lines on it, the top of which we draw straight along the axis marked by the cut.
- We make a pair of rafter legs for the upper slopes according to the template. If we have no doubt about the geometry of the constructed frame, we make several blanks at once. Otherwise, we do the same as with our lower brothers.
- We install the first pair of rafters, calling for the assistance of two pairs of working hands. You can’t handle the installation alone, because they don’t have an upper support. To prevent the newly erected roof truss from falling, we support it with a strut.
- We install the remaining trusses of the upper tier. We support them with struts every 3-4 pieces. The angle of inclination of the struts must be more than 45º. The direction of their tilt should be alternated.
Please note, in order to prevent stretching and sagging of the attic ceiling boards, each top roof truss it is necessary to equip it with a suspension made of boards approximately 25x150mm.

The photo selection will familiarize you with the specifics of the nodal connections of the truss system of a broken-type roof:
Along the ridge line and the break lines of the slopes, the sheathing is made continuous, regardless of the designed type and pitch of its installation. Two boards are nailed across the direction of the rafter legs with a gap of 2-3mm between them. A similar continuous flooring is installed in the valleys, if any, around the roof windows and openings for the passage of the chimney pipe. In the case of using soft types of roofing coverings, the sheathing is arranged continuous over the entire area of the slopes.
If the thickness of the insulation is equal to or greater than the width of the rafters, a counter-lattice is installed in front of the sheathing, constructed by installing a spacer bar. It is necessary to form a gap between the waterproofing and the roofing material. Nail the spacer bar from the outside of the system to the rafter edge. If the thickness of the thermal insulation boards allows you to leave a ventilation gap without remote tricks, there is no need to install a distance bar. It is also not needed in the construction of an uninsulated roof.

Upon completion of the installation of the rafter system, the cornices and gable walls, called gables in wooden house construction, are sheathed. Short overhangs adjacent to the gable walls are built, after which it is time to lay the roofing.
Video selection for self-builders
For those wishing to visualize the process of constructing a sloping roof, three videos with step-by-step work will help:
It is impossible to consider all options for constructing truss structures for sloping roofs in one article. Roofing types, architectural parameters, and regions vary. There are many nuances that apply to specific construction conditions. However, the examples we have given perfectly demonstrate the general technological principle. This information about calculation rules and construction schemes should help both home craftsmen and owners supervising the work of the hired team. Leave your questions, if any, in the comments.