How to find the diagonal on the roof. General rules and regulations for roofing during the construction of the roof of a house. We mount the roofing crate with our own hands
Read also
The slopes of gable roofs should have the shape of a regular rectangle, the slopes of hip roofs - the shape isosceles triangles or trapezoid. This requirement is due to the fact that almost all piece elements of roofing have a rectangular shape. When laying them on a non-rectangular slope, for example, having a rhomboid or trapezoid shape at different elevations of the ridge or the wrong dimensions of the perimeter of the walls, an unclosed wedge will inevitably turn out. It can be closed only by fitting piece roofing materials, which creates additional difficulties, increases the consumption of materials, reduces the speed of construction and, finally, simply spoils appearance buildings, but most importantly - greatly increases the possibility of roof leakage.
Isosceles slopes of hip roofs make it possible to cut roofing materials in one or two patterns, and use halves of some roofing materials on opposite sides of the slope. For example, an ondulin sheet cut obliquely can be used on both sides of the ramp. If, according to the project or as a result of negligence, the roof slopes have different angles of inclination, the cutting of piece elements is carried out individually. As a result, the speed of work is significantly reduced, and there is no question of any savings in building materials.
For getting correct forms slopes, it is necessary to measure the length, width, diagonals and heights of the rebuilt skeleton of the building. A lot of unexpected surprises can open up here. Differences in height on opposite walls can reach several centimeters, and the perimeter of the walls can have angles other than straight lines. The check begins with a measurement of the diagonals along the upper edge of the walls on each of the rectangular sections of the building. If the length of the diagonals does not match, then this means that the walls either have different elevations, or the building does not have right angles and it has a rhomboid or trapezoid shape. In buildings with gables made of wall material, you need to check the height of opposite gables with a long stick.
After measurements, the identified wall defects are eliminated. Align the walls to the horizon and, if possible, make the corners rectangular. On buildings with pediments, due to the incorrect breakdown of the foundation, and then the construction of walls, elevation differences along the top of the pediments can sometimes reach 20 cm. Such a defect can be corrected only by re-laying the pediment, or you need to come to terms with the idea that the ridge will not be horizontal, but consequently, the slopes of the gables will be different. In principle, such a height difference is not very noticeable on the roof, but every rafter and every element roofing material will need to be customized.
Altitude differences along the perimeter of the walls bearing the roof are eliminated with a cement-sand screed. The walls along the entire perimeter are checked with a water level and a leveling screed is performed on top of them. A solution of a brand not lower than M150 is used. Large differences are eliminated by masonry with a split or the walls are not leveled, and wooden linings are inserted under the Mauerlat beams, which is much worse, as often as possible. The walls under the bed or the installation of racks of the sub-rafter structure are aligned to the horizon, but they do not have to be coordinated with the elevations of the outer walls. The inner walls for laying the bed can be higher or lower than the outer ones, but always horizontal. When laying the bed on brick columns in the horizon, the top of the columns is leveled.
All wooden structures before installation, they must be treated with antiseptics and kept for a time specified by the manufacturer of the chemical composition.
After setting the leveling screed outer walls roll out hydroisol, roofing felt or other rolled waterproofing material and fold it in half along the longitudinal axis. The resulting width of the waterproofing should ensure its bending on side surface Mauerlat, because in brick houses there is still laid a brick for the device of the cornice. In general, waterproofing should protect the wooden mauerlat from all possible contact with the wall material. If the Mauerlat is attached to the wall with anchors, then the waterproofing is pierced on the pins. If it is fastened with brackets, then the waterproofing is simply laid dry. Sometimes waterproofing is glued to the leveling screed with a bituminous primer, it is not prohibited, but there is no particular need for that.
There are many ways to mark rafters and rafters, including such exotic ones as the use of Swenson and Stanley rafter squares. We will describe how this most often happens in construction practice, when the roof is made by ordinary carpenters who have a very vague idea of \u200b\u200bgeometry as a science. However, they rarely make mistakes and their roofs are excellent.
By laying the Mauerlat, they try to correct the non-rectangularity of the perimeter of the walls. The beams are laid out on the wall and the diagonals of the building are checked, measuring already at the corners of the Mauerlat frame (Fig. 52). By shifting the beams along the wall, the diagonals are equal, and its final position is marked with a pencil. Mauerlat beams are sawn to make locks, assembled on the wall and finally fixed on it.
Rice. 52. Marking the installation site of the Mauerlat and the bed
When installing a Mauerlat frame, there is one subtle point. The height of the Mauerlat must be selected in advance, that is, it must be drawn at least preliminary design. Otherwise, the fillies nailed to the rafter leg may not pass over the edge of the wall and the walls will have to be hemmed. Therefore, given the height of the ridge, walls and rafters, it is better to draw a section of the roof on a scale in advance and select the height of the Mauerlat and its installation location. It is often necessary to observe a picture when, during the construction of roofs without a project, the craftsmen shift the Mauerlat to the very edge of the wall along the outer surface, otherwise they cannot release the filly. In general, there is nothing wrong with the fact that the Mauerlat is installed along the outer edge of the wall, but only if it is a non-thrust rafter system and this is the edge of the wall, but often it is a brick cornice in which the brick has already been released beyond the wall. It would be wiser to increase the height of the Mauerlat beam and leave it in the center of the wall or closer to the inner surface of the wall. If it is not possible to increase the height of the Mauerlat, then you just need to raise the parapet from the inside higher or disassemble part of the wall from the outside of the parapet. And that's it. Then the Mauerlat will remain where it should be and the filly will not hit the wall.
Next, mark the position of the bed. Measuring from the Mauerlat, we place it strictly in the middle, then we will get a roof with equal slopes. For the device of hip roofs, we shift the bed by the same distance, from its end to the Mauerlat, deep into the house, then the angle of inclination of the hip will be equal to the angle the slope of the main slopes. However, if it is planned to change the angle of inclination of the hip relative to the slopes, then we shift the bed to the distance that is needed. We lay the bed on two layers of waterproofing and fasten it with staples or wire twists with inner wall. The twists either had to be laid into the wall in advance during its construction, or they are attached to self-locking anchors (ruffs) installed in the wall. If the bed is laid on newly laid brick columns, then we fasten it to the wall, and not to the columns. In buildings with reinforced concrete floors twists can be tied to the mounting loops of the floor slabs. In buildings with gas silicate, foam concrete and other light walls needs to be done in advance monolithic belt and release the anchor. The bed is fastened with anchors. In general, in any of the ways we attach the bed to the wall in the design position, the top of the bed must be aligned to the horizon. If the roof is made without laying down, then the installation sites of the racks are marked in a similar way, and the bottom of the racks is subsequently fixed to each other by contractions.
After laying and fixing the bed, they proceed to the construction of scaffolding. The most frustrating part of the job is wasting time and lumber on unproductive work. However, scaffolding must be made reliably, not only will you have to walk on it, but also work on it with a load of rafters and girders being raised. Scaffolding must necessarily be supported by struts and unfastened by cross-fights, otherwise they will lose stability and fall.
Next, the racks are cut out on the sub-rafter structure. Since the bed was set to the horizon, all racks are made of the same design length. In buildings with pediments made with marriage (of different heights), a cord is stretched between the top of the pediments and each rack is cut to the length that is necessary, taking into account the height of the run and rafters. When installing racks on a bed, they are checked for verticality in two planes (on two faces): transverse and longitudinal. Verticality is checked with a plumb line or level, placing it against the side surface of the uprights. After that, the racks are fixed in the design position. The easiest way is to fasten them with boards to the scaffolding.
What to do first: install scaffolding or racks? Who is more comfortable. You can first install the racks and temporarily unfasten them with struts, and then attach the scaffolding to them, you can, on the contrary, first securely put the scaffolding and unfasten the racks to them. Sometimes they try to work from ladders. Racks are exposed and unfastened, and for laying the run and rafters, a ladder is supported on the racks. This is dangerous. Firstly, under the weight of a person and the load that he holds, for example, when laying a run, the steps of the stairs can break. Secondly, a poorly braced rack can lose stability and fall along with the ladder leaning against it. And finally, thirdly. Try to work normally when you have a 60-centimeter perch of a ladder rung under your feet, and you need to move a heavy run or rafter in order to properly install it.
A run is laid on the racks. If everything is done correctly, the top of the bed is horizontal, the racks are of the same height and are installed vertically in two planes, then the run will simply fall into place. In buildings with uneven height gables, the top of the run should be parallel to the stretched cord. For hip roofs, do not forget to release the run behind the racks, forming consoles for supporting the rafters.
Once again we check the subrafter structure for verticality and the run for horizontality, correct, if necessary, and unfasten all the nodes to the design position: we nail the wooden lining, put brackets or metal plates, but leave the entire subrafter frame temporarily unfastened to the scaffolding or to the struts.
Next, we install a trial board of the rafter leg. There are several ways to cut and fit rafters. We will focus on the simplest and most commonly used ones, which do not require any devices other than the head and hands.
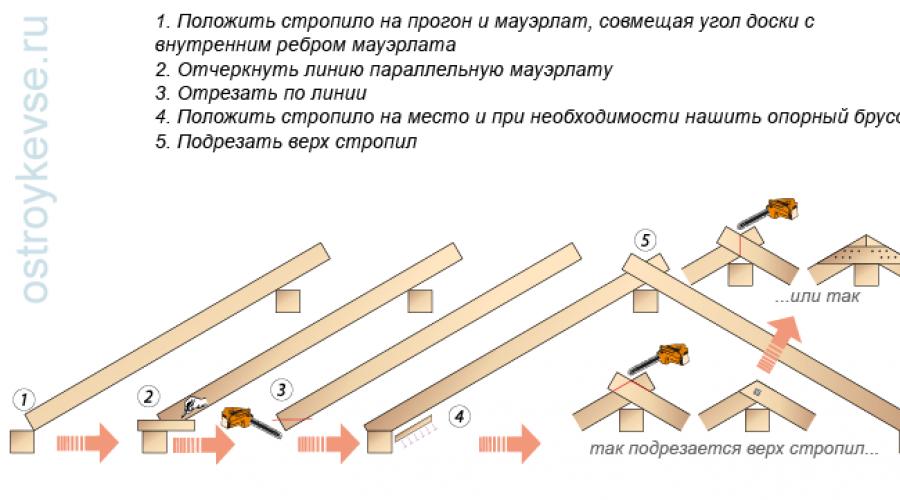
1. The rafters are marked on the slider and on the node with the support bar.
At the bottom there is a slider or a pivotally fixed support with a support bar, the top of the rafter is simply laid on the run and stitched with the other rafter leg with an overlap or rests against the other rafter leg.
The board is laid with its upper end on the upper edge of the run, the lower end on the inner upper edge of the Mauerlat (Fig. 53.1). One or two rafter trims are placed on the Mauerlat and a line is drawn parallel to the Mauerlat. When cutting on a slider, the rafter does not change the slope; it simply falls below and rests on the Mauerlat; if necessary, it can be supplemented with a support bar. If the rafter is marked and cut into a tooth, then after trimming the cut becomes incorrect.
 rice. 53.1. Marking and cutting rafters.
rice. 53.1. Marking and cutting rafters. Bottom with Reliance on Mauerlat, top - with Emphasis on each other or next to each other
After trimming and installing the first rafter leg, the opposite rafter is also installed and trimmed. Top rafter legs leave as is until complete installation all rafters. Then they are either cut along the edge of another rafter and bolted together or sewn together with a nail fight, or they mark the vertical on them and saw off the excess, joining the rafters into each other. Sawing two tops of the rafters at the same time is not recommended, since the thickness of the saw teeth will leave a large gap and the rafters will not fit tightly. It is better to push the rafters apart and saw off the tops of them separately, one to the left of the line, the other to the right. With good quality work, the rafters will dock without a gap.
2.Bottom and top pivotally fixed supports.
At the bottom of the rafter leg, a notch is made to engage with the Mauerlat with a tooth, and at the top, a notch with a triangle. If the upper notch is made exactly according to the profile of the run, then the knot will work as a pivotally fixed support, if the vertical cheek of the notch is made with a bevel, then the knot will turn into a pivotally movable one.
The rafter board is laid with an edge on the run and the Mauerlat (Figure 53.2). Bottom part boards at an angle rests on the Mauerlat at any point on its surface. A template is laid on the side of the Mauerlat, for example, it can be a cut of a rafter with well-cut edges (the ends are sawn off at a right angle) edges. The template is shifted to the inner corner of the Mauerlat and aligned with its vertical surface. The bottom of the rafter leg begins to move along the Mauerlat, ensuring that a cut with a tooth is obtained on the rafter. It is quite simple, laying the template board and moving the rafter, you can visually see what kind of cutting will turn out. Having achieved right size cuttings, outline the lines along which the rafters will be cut. The template is transferred to the upper cut, and more often, another person stands at the top of the scaffolding and he has his own template (cut from the same board, so they are the same), at the command of the first one, he sets the template for the run, aligning its end with the vertical plane of the run, and outlines the second notch. The rafter is not removed from the run and the Mauerlat, they turn over and cut out the cuts. Then set it to the design position.
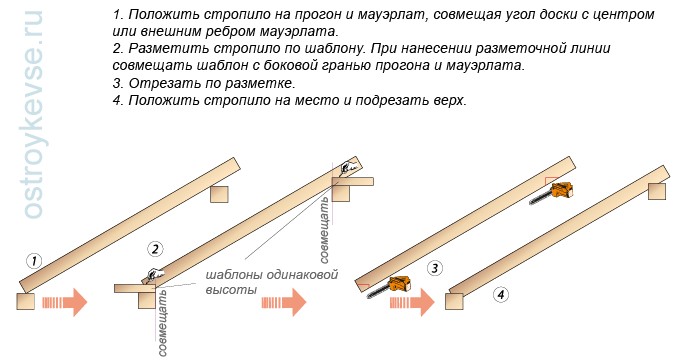 rice. 53.2. Marking and cutting rafters.
rice. 53.2. Marking and cutting rafters. Bottom with an emphasis on the Mauerlat, top - with a horizontal notch with an emphasis on the run
Why is a trimmed board cut off used as a template, because you can also use a level and a tape measure? It is possible, but the cutting of the board gives a visual representation of the future profile of the cut, and in this case it is better not to use the level at all. wooden beams, due to drying, are far from the correct rectangular geometry, most often, with apparent evenness, they are actually humpbacked and twisted. Therefore, it is better to put another board on their plane and outline the cuts along it. Carpenters use a hacksaw for this purpose, for example, when outlining a cut for landing on a run, they apply a hacksaw with an edge without teeth to the vertical edge of the run and draw a line on the rafter with a pencil. No matter how the run beam spins, the line will repeat its profile, but the level showing the vertical would give an error. So it's better to use age-old wisdom: cut the board, trim it and use it as a template. The thickness of the board is chosen depending on the depth of the cuts and each project has its own, most often, the template is made from the same board as the rafters.
3. At the bottom is a pivotally movable support (slider), at the top - pivotally fixed.
At the bottom of the rafter leg, support is made on a slider, which, if necessary, by installing support bars, can be turned into a pivotally fixed support. At the top, a cut is made into a triangle, which, in turn, by cutting the lateral cheek, can transfer the knot from a pivotally fixed to a pivotally movable one (Fig. 53.3).
 rice. 53.3. Marking and cutting rafters.
rice. 53.3. Marking and cutting rafters. Bottom with Support on the Mauerlat, top - with a horizontal notch with an emphasis on the run
Everything is done the same as in the second option described above, with the only difference, when the lower end of the rafter leg is moved along the rafter, then the rafter is cut in the same plane, that is, without gearing.
4. At the bottom and at the top of the rafter leg are pivotally fixed supports.
At the bottom of the rafter leg, a cut is made on the tooth, at the top, the end of the rafter leg rests against a run or a diagonal (diagonal) rafter.
The rafter board is laid with an edge on the run and the Mauerlat. The bottom corner of the board is combined with the outer edge of the Mauerlat. At the top, a template or a hacksaw is applied to the vertical surface of the run and a cutting line is drawn on the rafter. For the connection device to the rafter legs, two lines are drawn on both sides of the board being processed. The length of the cut line (x) is measured: pencil marks are made on the template with a tape measure. The template is transferred to the lower support node, it is attached to the inner vertical plane mauerlat and from its edge lay the size (x) on the rafter board. Then, in any way, most often, by applying a board, a line is drawn parallel to the upper plane of the Mauerlat (Fig. 53.4).
 rice. 53.4. Marking and cutting rafters.
rice. 53.4. Marking and cutting rafters. Bottom with Emphasis on the Mauerlat, top - with Emphasis on the run
By shifting the bottom of the rafter leg along the Mauerlat, an increase or decrease in the depth of the cut of the tooth is achieved. on rooftops with steep slopes the tooth may not work out at all, it’s not scary, the installation of a support bar will help. By changing the size (x) when transferring it to the lower node, you can change the nature of the support in the upper node, that is, align the rafter along the upper or lower edge of the run. If you decrease (x), the rafter at the top will rise, increase - it will fall.
The board is turned over, sawn according to the marks and set to the design position. In the rafters, resting on the cranial bars of the oblique rafter leg, the cut is marked, the board is turned over again, the cut is made and put in place. The cut for landing on the cranial bar is done in the same way, you just need to raise the bottom of the rafter to the height of the cranial bar: put a piece of the cranial bar under it or simply support the end of the board in weight while the assistant marks the cut.
5. Marking of the rafter leg extended beyond the wall, that is, the rafter is installed without fillies.
At the top is a pivotally fixed support, at the bottom - a slider (Fig. 53.5).
 rice. 53.5. Marking and cutting rafters.
rice. 53.5. Marking and cutting rafters. The bottom with the Support on the Mauerlat and the removal of the rafters from the wall, the top - with a horizontal cut with an emphasis on the run
The rafter board is laid with an edge on the run and Mauerlat. The bottom of the board is taken out of the wall and held on weight. Templates are installed on the Mauerlat and the run with the alignment of the ends along the outer vertical surface of the beams. The cutting line is outlined, the board is turned over and cuts are cut. The rafter is installed in the design position.
6. Marking only the lower support node, at the bottom and at the top are pivotally movable supports - sliders. The stability of the structure is ensured by the ridge knot when tying the top of the rafter legs.
Everything is done the same as in the previous case, but a template is placed on the run, which maintains the angle of inclination of the ramp. After the lower cut is cut out, and the template is removed from the run, the rafter moves into the design position (Fig. 53.6).
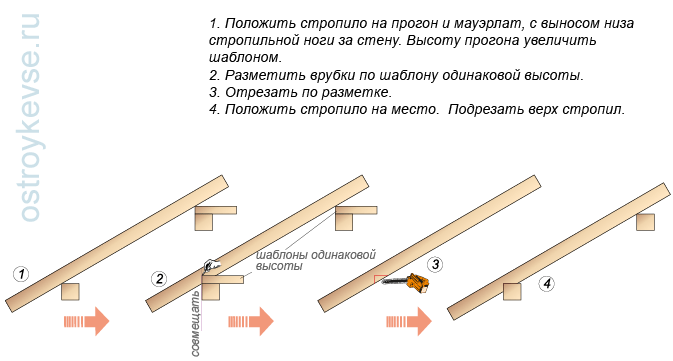 fig.53.6. Marking and cutting rafters.
fig.53.6. Marking and cutting rafters. Bottom with Reliance on the Mauerlat and the removal of the rafters from the wall, top - with Reliance on the run
All of the listed options for trimming the rafters work according to the same principle: the rafter board is installed in the required position, from which, after the device is cut, it slides into seats top or side, without changing the angle of inclination.
If it was possible to place the Mauerlat frame horizontally and align the diagonals, and install the run horizontally, then it is enough to make one rafter leg, and do all the others along it, using the first one as a template. If the walls of the house are so crooked that the diagonals on the Mauerlat frame could not be aligned, or if the gables are of different heights on houses with gables, then a pair of rafter legs is installed on both ends of the building. Cords are stretched between them and all other rafters are made individually, since each of them will be different from the previous one. During installation, the flatness of the slopes is constantly checked. This is done either by pulling the cords between the extreme rafters, or a long, even board is placed on top of the rafters, which is moved along the edges of the rafter legs and checked for clearance.
Rafters are installed at a certain distance from each other, this distance is called a step. When designing a roof, the installation step of the rafters is set along the longitudinal axes of the rafter legs; this is not very convenient during installation. Therefore, to measure the pitch, 2-3 slats are made with a length equal to the rafter pitch minus the thickness of the rafter, that is, the length of the slat will be equal to the distance between the edges of the rafters - the distance in the clearance. Having installed one rafter leg, the location of the other is determined by attaching it to the first rail.
After all the rafters are installed, the distance between them is checked again and the support nodes are fixed in the design position: they are fixed with brackets, special metal plates, wooden bosses, nail fights, bolts.
Then proceed to the installation of filly. The filly (Fig. 11) is the release of the rafters behind the wall, providing an overhang of the roof. Usually they are made from a board of half height and thickness from the section of the rafter leg. The fillies are attached to the rafters with a nail fight. The length of the fastening part is about 60–80 cm, and the free overhang above the wall is 40–50 cm.
The overhang of the cornice is selected, no matter how strange it may sound, from the length of the arms. The cornice overhang is subsequently often hemmed with molded materials, therefore, you need to somehow reach out, for example, with a lining board to the end of the overhang, hold the board in the design position and nail it. If the overhang is short, then the wall of the building can get wet from slanting rain, if it is long, there will not be enough hands for filing and it is necessary to install scaffolding, and at heights up to 10 m this is very problematic for an amateur builder. In brick houses, the walls are laid out with the release of bricks and the installation of a cornice from the wall material, thereby increasing the overhang. In houses made of lightweight concrete materials, the overhang is either 40-50 cm, or we come up with scaffolding. If the cornice is not hemmed with anything, then the overhang can be made longer, but not more than 60 cm. Longer overhangs should be supported by consoles released (or fixed in another way) from the wall, which can also perform a decorative function.
With all the variety of roofing materials, the device of roofs is not much different from each other. They share common rules.
Rule 1 The slopes of gable roofs should have the shape of a regular rectangle, the slopes of hip roofs should have the shape isosceles trapezoids and isosceles triangles.
This requirement is due to the fact that almost all piece elements of roofing have a rectangular shape. When laying them on a slope that does not have right angles, for example, having a diamond-shaped outline, an unclosed wedge will inevitably turn out. Such a wedge can be closed only by cutting and fitting piece roofing materials, which creates additional difficulties, increases the consumption of materials, reduces the speed of construction, and, finally, simply spoils the appearance of the building. But the most important- greatly increases the possibility of roof leakage.
Isosceles slopes of hip roofs make it possible to cut roofing materials in one or two patterns, and use halves of some roofing materials on opposite sides of the slope. For example, an asbestos-cement corrugated sheet, cut obliquely, can be used on both sides of the slope. If, by design or as a result of negligence, the ramps roofing have different angles of inclination, cutting of piece elements is carried out individually. Eventually- the speed of work is significantly reduced, there is no question of any savings in building materials.
To obtain the correct forms of slopes, you first need to measure the length, width, diagonals and heights of the rebuilt skeleton of the building. Here, a lot of unexpected surprises can open up for the developer. The building in the plan can take the form of a rhombus or a trapezoid. Differences in height on opposite walls can reach several centimeters. Such errors are formed not only due to carelessly performed work on the construction of walls. They may have arisen due to different angles when cutting wood or laying brick walls there were unworked masons or carpenters. For example, two unworked masons, constantly standing at opposite corners of the masonry, can give an error of 1 cm per 1 m of height just because one masonry seam is 1 mm thicker, and this despite the fact that both are good masons. What then to say about amateurs, who will have errors not only in height, but also in linear dimensions because of blockages of corners outside and inside. After carrying out the measurements, it is necessary to eliminate the identified defects of the walls, if possible. In order for the roof ridge to be strictly horizontal, and the roof slope to lie in the same plane with the horizon, a number of measures are taken to arrange the truss system. Mauerlat and bed for layered rafters and lining for hanging rafters set according to the water level (Fig. 1), thereby achieving their horizontal position.
Then measure the distance between the Mauerlat and the bed (it should be the same) ( fig. 2) and check the diagonals. If necessary, the design is corrected. Linings for hanging rafters are checked in the same way - they measure the distance between them and diagonally.
This preparatory stage sometimes takes a lot of time, but the more carefully it is done, the easier it will be build a roof. The bed can be made above or below the Mauerlat beams, this does not play any role, the main thing is that it be horizontal. Mauerlat should lie at the same height around the entire perimeter of the building, lining the same way. After installing the bed, racks are attached to it. They are prepared with the same design height and installed on a plumb line, and the verticality of the installation of the racks is checked both in the longitudinal and transverse directions. Then a run is laid on the racks. Since the bed was set horizontally, and the racks are the same in height and set vertically, it means that the run will lie horizontally. After installation between the bed and the run of the wind struts, rafter legs can be attached.
Rafters are installed at a certain distance from each other. This distance is called the installation step of the rafters and is determined by calculation. The correct installation of the rafters is determined by laying a flat board on 3-4 rafter legs. If there is a visible gap between the board and the rafter leg, the rafter is rearranged. If there are no gaps, then the rafters are set correctly, that is, in the same plane. The final control is carried out visually - the rafter system is viewed from edge to edge. When attaching the rafters, the installation of twisted and humpbacked boards should be avoided, since they will have to be hemmed under the crate, which means that the calculated cross section should be reduced. Boards with a large number of knots, as well as boards with through knots directed across the fibers, it is strictly forbidden to put them - they can break.
Triangular hanging rafter patterns are difficult to assemble in vertical position, so they are assembled on the ground or on a hard floor and then installed in finished form. When installing them, make sure that ridge knot was strictly above the center line of the building. Because roof trusses have the same dimensions, and the linings are set according to the level, their horizontal position is obtained automatically. Farms are exposed on a plumb line and fixed with wind ties.
The squareness of the roof slopes is provided by the crate. Before installing it, it is desirable to already have roofing material available. With data on physical and mechanical characteristics and the dimensions of the material, it is possible to calculate the amount of lateral extension of the crate beyond the walls and the length of the fillies, i.e., determine actual dimensions roof slope. When installing the crate, it is carried out beyond the walls a little more than required. The width of the slope at roofing calculated taking into account the overlap of adjacent sheets of piece roofing material. It is best to do this calculation in real conditions, i.e. lay out one row of roofing elements directly on the roof or on the ground, and then measure with a tape measure. This is exactly the situation when you need to measure seven times, and cut off once. The distance obtained as a result of measurement or as a result of calculation is measured on the roof ridge, from extreme points set aside right angles and saw off the excess crate. In the same way, the length of the filly is calculated, providing their cornice overhang. When calculating the eaves overhang, one should not forget about the free overhang of the roofing elements by 2-10 cm. A free overhang is performed so that raindrops torn off by the wind do not wet the bottom board of the crate. After all these not very complicated calculations, there will be an integer number of elements on the roof slope, both in vertical and horizontal rows. And since the corners are straight, there will be no hassle with the roofing. Get sleek and smooth roof. A right angle is laid using a wooden square ( fig. 3) with sides of 3, 4, 5 m or with smaller sides that are multiples of these numbers.
On the hip roofs, as mentioned above, we must try to make the same slope angles of the slopes, which is possible only with correct installation Mauerlatov and beds.
Rule 2 Before the installation of the coating from the main roofing material, the grooves, valleys, junctions of pipes to the roof and junctions of dormer windows are covered with galvanized roofing steel along a continuous crate(Fig. 4 and 5). To cover the junction of pipes and dormers, a blank is made and installed together with the main coating.
Rule 3 The bottom bar of the batten must be higher than all subsequent bars by the thickness of the roofing material being laid. To understand what this is for, just look at Fig. 6.
Whether this bar is the same as all the others, the cornice element of the roof will "nod".
Rule 4 All roofs are covered from the bottom up, towards the rain stream.
Some roofs, for example wavy sheets, stacked towards the prevailing winds from left to right or, conversely, from right to left.
A lot of roofing materials already have holes for nails or wire twists in their construction, or they are made on self-adhesive backing, or included in the kit special adhesives and sealed gaskets. Roof device from such materials is not difficult, as it is fully thought out.
Roofing materials only need to be assembled on the roof, like a children's designer. Roofing materials that do not have fixing holes (cement-fiber corrugated sheets, metal tiles, profiled flooring) are supplied with roofing nails to match the color of the coating. These nails are fastened to the comb of a piece element with a rubber sealing washer.
In addition to fasteners, kits of modern roofing materials are supplied with ridge and cornice elements, cuttings for pipes and much more.
Rule 5 Under roofs mansard roofs lay an additional waterproofing layer of polyethylene film, roofing felt or roofing material. Under "cold" roofs, additional waterproofing is desirable, but not required. In all subsequent drawings, additional waterproofing will be shown, but this does not mean that it is mandatory.
Rule 6 On device warm roofs don't forget the airflow
between the insulation and the crate, which should be from 2 to 5 cm, otherwise the insulation will lose its properties due to saturation with moisture.
Rule 7 When installing roofs, you must not forget to tie yourself to the ridge
, and when laying the last ridge element consider a method of evacuation from the roof. Very often one has to descend on a rope thrown over the ridge of the roof and tied to something heavy lying on the ground on the other side, or the rope is tied to the ridge of the roof and passed under the upper roofing element, then after the descent, the rope is pulled out and the roof is corrected from the inside. Of course, such a descent requires a certain physical preparation. Why is such a stunt method of descent mentioned, when you can make a walking ladder and leave it on the roof forever? Because, as a rule, roofs are very often performed without a ladder.
And lastly, if a person experiences even the slightest dizziness when ascending to a height, then he has nothing to do on the roof, let others do it - not everyone is born astronauts.
Larisa Georgievna Bakanova
I have a house in a village in the Volkhovsky district. It was necessary to do roof repairs and installation downpipes and gutters.
I turned to the company "Top Stroy". The measurer promptly left for the object, did everything necessary measurements. On the next day, the contract and estimate were ready. The material was delivered in a timely manner. The work was done quickly, the roofing masters were wonderful, their hands were “golden”, professionals, it was easy to communicate, they resolved all issues constructively. Working with galvanized iron is difficult, they did it perfectly, I am very pleased, the roof is beautiful, the gutters look great. I am very pleased. I recommend this company to everyone.
Sincerely, L.G. Bakanova 06/05/2013
Leningrad region, Volkhov district, village of Seliverstovo, private house
Galkin Petr Ivanovich
For roof restoration/replacement country house turned to Verkh Stroy (I found information and reviews about them on the Internet).
Roof repair work completed. The attitude of the team of workers to the fulfillment of contractual obligations and the quality of work performed on good level. Thank you!
LO, Vsevolozhsky district, pos. Priyutino, Gardening "Granite", country house
Andrey Anatolievich Mishchenko
We contacted Verkh Stroy for emergency roof insulation. The work was done quickly and efficiently and delivered on time as agreed. The brigade worked Russian. Communication is businesslike and polite. I recommend this company to anyone who is looking for real professionals! Thanks a lot!
Leningrad region, Priozersky district, Torfyanoe village, private cottage
Chairman of the Board of HOA "Graftio" Ishchenko Svetlana Nikolaevna
In September 2012, there was a need for repairs in the HOA "Graftio" soft roof on an area of 70 sq.m. 6 (six) contractors were considered, incl. "Top Build".
At our request, Master Chernykh V.Yu. came to our site. On the spot, an examination of the roof was carried out and a commercial offer was promptly drawn up, which completely satisfied us.
Directly roofing works supervised by Poknya I.M.
The work was completed in full, quickly and efficiently. No more leaks are observed.
Our HOA is grateful to Verkh Stroy and we look forward to further cooperation.
Multi-storey residential building, St. Petersburg, Graftio street, 3

Tumilyanis Andrei Vladimirovich
Thanks for the service. The roof was leaking. Repaired with TechnoNIKOL deposited material. To the old shingles, welded a new layer of 130 m2. Very prompt. Communicate politely. Punctuality is great! All is well, thanks for your work!
October 11, 2012
Leningrad Region p. Volodarsky, private cottage
Natalya Anatolyevna Lobasova
I rated the work of the masters of the Verkh Stroy company at 5 +. They worked quickly (two days), efficiently, neatly. I am very satisfied with the work done. Pleasant in communication. Work in any weather. I don't think I would have found better masters.
Roof covering with ondulin 85 m2.
mr. Berndgardovka, country house.

Repair of the roof (roof) of the container was completed without remarks and on time. I have no complaints about the quality.
09/01/2012
Chudinovskikh V.A. Mechanic "Amron"

Malysheva Nadezhda Viktorovna
In August 2012 We contacted the Verkh Stroy company regarding the repair of the roof of a country house, entering their website and sending a preliminary application. I wanted to find competent specialists. Everything that we were offered before was alarming by the unprofessional approach. On the first working day, the manager of the company called and acquainted with the cost of work and sent the contract. The Master quickly went to the place, took into account all our wishes and professionally and unobtrusively advised us to correct them. We decided everything on the spot. The next day the new contract was ready.
The company promptly purchased and delivered the material. A professional Russian team completed the dismantling of the slate, the repair of the batten, the installation of metal tiles, the installation of gutters on time and with high quality, and neatly stored the waste.
I had to work during a rainy period, but I was especially pleased that the company covers the house in any weather at night with an awning, relieving any stress from the customer.
We were satisfied.
Sincerely, Malysheva N.V.
Dacha cooperative Sosnovy Bor.

Alexey Alexandrovich Shiryaev
I turned to the company "Top Stroy", to block the roof of a country house of 237 m2. Very well explained and constructive possible types works. Together with the master, we chose the most optimal variant of work in terms of "price-quality".
All organizational work, coordination and delivery of the material, the company "Verkh Stroy" took over.
The work on the installation of the roofing was carried out within the agreed time frame.
Competent specialists and the manager are focused on the result and on the fact that their work is sure to please the Customer.
Thank you so much!
Replacing the old slate with bituminous tiles in the country house of the village. Ends LO

Kirill Stepanovich Golubev
Thanks for the good work. The roof was made quickly and efficiently, the roofing felt was removed, the crate was repaired and the corrugated board was laid. Arrived within two weeks as agreed.
Private house, p. Luzhki LO
Maria Guzhel
We turned to the company "Top Stroy" to sort out the roof in the country house of 82 m2. They removed the old slate and made an ondulin coating. Now you can open the season. The prices are acceptable. Best deal I've found. They were afraid that migrant workers would come, but Russian guys worked. You are just great! Thank you!
Horticulture "Movement" of the Kirovsky district of the Leningrad Region
To do it right calculate and set the diagonal of the foundation or formwork foundation - it is very good to hire specialists. But if you have already seen the program several times " square meter”, Have you heard a conversation about how to build several times, and a bunch of jokes about construction? - another thing. This gives us “full right” to assume that we ourselves will cope with such a simple matter as the corners and diagonals of the foundation formwork. It is precisely such a high opinion of everyone who plans to build a bathhouse with their own hands (Ha ha!)
I wrote about the beginning of marking and designing the foundation and formwork in an article. At the time of driving the stakes and installing the outer formwork boards, I already checked the length of the diagonal. Everything converged to the millimeter. This is the most important condition for obtaining right angles for the log cabin of the bath. But after the first markup, there were manipulations with the installation of the bottom of the grillage, the installation of internal formwork panels, the completion of the formwork of the posts from ground level to the bottom of the future foundation. Of course, I tried very hard not to move anything, and I drove the stakes deep.
But as with any construction project, there was a twist. It's not as scary as if I didn't notice it or I didn't know about it. Therefore, before laying the reinforcement, I decided to check the diagonals again. The difference turned out to be 2 cm. It's good that it was discovered before the concrete was poured.
How to display the formwork diagonal?
To simplify the construction of the correct formwork, I made the length of the walls absolutely equal. Therefore, the skew can only turn out in the form of a rhombus. In the figure, the degree of skew of the formwork is deliberately increased for clarity.
To correct the situation, they did the following:

This combined movement of one of the sides of the formwork (northern in the figure) was not too difficult, since the stakes and the original position of the formwork corresponded correct position. Therefore, the diagonal displacement was minimal and efforts to “correct” the position of the shields did not cause mechanical stress and effort.
 The method of setting angles along equal diagonals can only be used if the sides are equal. Diagonal equalities will be sufficient!
The method of setting angles along equal diagonals can only be used if the sides are equal. Diagonal equalities will be sufficient!
 For formwork sides with a large size, it is possible to apply the rule of the "golden" triangle. If such a triangle, according to the Pythagorean theorem, has sides 3, 4, then the hypotenuse is equal to 5 units. Thus, it is enough to measure on the sides of the formwork parts that are multiples of 3 and 4 at the top right angle and then the distance between the control points will be 5 parts! This will be a guarantee of right angles and equality of diagonals!
For formwork sides with a large size, it is possible to apply the rule of the "golden" triangle. If such a triangle, according to the Pythagorean theorem, has sides 3, 4, then the hypotenuse is equal to 5 units. Thus, it is enough to measure on the sides of the formwork parts that are multiples of 3 and 4 at the top right angle and then the distance between the control points will be 5 parts! This will be a guarantee of right angles and equality of diagonals!
For implementation proper planning formwork installation I highly recommend using the wear-and-tear method, which allows you to installation work check corners, remove and reinstall foundation perimeter cords.
 Before pouring the foundation, do not be too lazy to check the diagonals again. It won't be redundant! Concrete cannot be repaired easily and quickly. Mistakes are very expensive and time consuming to fix. The foundation for a log house has more quality requirements than the foundation for a stone house. The solution will not even out anything!
Before pouring the foundation, do not be too lazy to check the diagonals again. It won't be redundant! Concrete cannot be repaired easily and quickly. Mistakes are very expensive and time consuming to fix. The foundation for a log house has more quality requirements than the foundation for a stone house. The solution will not even out anything!
Do not forget before pouring for easy dismantling!
It is impossible to equip a roofing system without lathing, which is laid on top of the rafter legs. It serves as a place for direct fastening of the roof finish sheathing.
What is the roof made of?
Thanks to the roof, the building not only receives a decorated appearance: it also has a protective function to prevent rain, snow, heat and cold from getting inside the ceilings. In addition, thanks to the roof, the impact of wastewater on walls and basement surfaces is noticeably reduced, which significantly increases their service life. Most often, there are 2 or 4 slopes on the roof of the building: moreover, the second design involves several arrangement options.
As part of the usual gable roof includes:
- rafters. To connect these vertical or horizontal supports, a corner connection is usually used, equipped with bolts and brackets.
- Mauerlat. This bar is in a horizontal position. It relies on individual elements rafters.
- overhangs. This is the name of the lower sections of the rafters.
- Skate. It is located on top of the structure, in the area where the rafters join.
- Lathing, counter lathing. Basic parts for laying roofing materials and insulation.
- Waterproofing and insulation materials. With their help, warm attics are equipped.
- roof deck. May be hard or soft.
In general, the roof is divided into cold and warm subspecies. The first option involves laying thermal insulation in the attic space: the roof in such a scheme is not insulated. The second method involves laying insulation and waterproofing. Basically, this approach is used to design attic residential floors.
The purpose of the lathing in the roofing system
Thanks to the crate, the following tasks are achieved:
- There is a reliable fastening of roofing materials.
- The space between the roof and the insulation in this case is well ventilated: this is especially important for adjacent areas of warm and cold roofing layers.
- It is convenient to fix a layer of insulation and waterproofing on the roof sheathing.
- The truss system receives protection from excessive load in cases of heavy snowfall.
What tools and materials will be needed
Before making the crate on the roof, you should prepare the following tools and materials:
- Wooden beam of the first grade, 6 m long, without knots and other defects. The section is selected depending on which finishing material will apply. Under the metal tile you will need products with a section of 50x50 mm, metal roof equipped with a bar 60x40 mm. Ceramic tiles are laid on a beam with a square section of 75x75.
- Edged board 25x100 mm, 6 m long. Small flaws in the form of rare knots are allowed here. Some cases involve replacing boards with OSB boards, plywood or chipboard panels.
- Hacksaw, chainsaw.
- Mounting foam.
- Hammer, perforator.
- Bolts with nuts of large sizes. Fastening is also carried out with staples and nails.
- Building level, tape measure.
Varieties of roofing lathing
When studying the question of how to properly make a roof sheathing, it is important to know about the most popular system designs. Choice suitable option battens directly depends on the roofing material used.

There are two main types of crates:
- Solid. When laying the beams, a gap of 10 mm is assumed. Design solid crate usually under soft tiles, roll laying, flat slate or metal tiles. To give the roof additional reliability, fixing the structure on top is used. eaves overhangs, as well as in the areas of junction of slopes. Making a choice in the direction of this crate, you need to prepare for a significant consumption of material.
- sparse. The gap between the timber in this case can reach several centimeters, which is very convenient for laying. natural tiles, metal sheets and wave slate.
We mount the roofing crate with our own hands
After the rafter system is fully equipped, a careful measurement of the roof is carried out. This is done with a rope, which simplifies the measurement of the diagonals. When comparing two indicators, it is desirable that they do not differ from each other by more than 20 mm. If this tolerance is exceeded, subsequent work may encounter certain difficulties. Next, the vapor barrier and insulation are laid, in the form of mineral wool or other suitable material.
Do-it-yourself roof lathing is assembled on top of the previously laid waterproofing film, when laying which an overlap of 15 cm is observed. It is most convenient to mount the canvases from the top and down, taking the directions of the rafters. For fastening film fit construction stapler. On top of the rafters, slats are stuffed to create a counter-lattice.

It is important not to forget about ventilation gaps separating the film and the laid roofing material. Simply put, when laying the film, it is important to leave sagging. In the same way, the separation of the film and insulation is carried out. To simplify the task of how to properly make a crate on the roof, a crate template is used, which is designed to strictly comply with the design parameters.
If a soft roof is laid, then the installation of the elements of the crate is carried out by the method of alignment and docking. To avoid subsequent deformation, the solid structure must be fastened with particular care, using at least two nails on each beam.
How to attach under roll material
For laying roll sheets, you need a solid type roofing lathing, made of beams and boards with a thickness of at least 25 mm. In this case, the flooring should have a dense, without cracks, laying. The pitch of the crate is chosen not less than 15 cm, otherwise the roofing material will begin to deform. It is important to achieve the ideal smoothness of the lathing surface, with the obligatory drowning of nail heads and self-tapping screws deep into the wood.
How to make a soft roof
Installation of the roof lathing soft type occurs most often, due to the high popularity of this roof. Such material is inexpensive, and it is very easy to mount it. Here you will also need to equip a solid type crate, which is equipped with a special calibrated board. Such laying has a two-layer structure, in compliance with the maximum evenness of the joints.

Under these conditions, grooved board and roofing plywood, which have undergone preliminary antiseptic impregnation, have proven themselves well. To avoid damage to the soft roof in the corner areas, the ends of the boards must be rounded.
Under the tiles
According to experts, it is tiled roofs that have the most optimal operational characteristics in terms of quality and durability. Usually these are single-layer structures, the crate under which is equipped with bars with a cross section of at least 6 cm.

The laying step is guided by the dimensions of the tiles used. Some situations involve the creation of a double crate, from the same material. To achieve a uniform fit of the tiles, it is required to build the most even plane of the structure. This implies the use of timber with the same size.
What is the difference between the crate for slate and metal tiles
For arranging the crate, one or two layers of laying can be used. The first option involves the use of a bar with a square section of 50 mm. The optimal step in this case is 50 cm, with the elements laid in a parallel direction to the ridge. If a unified profile is used instead of the usual wavy slate, then the step can be increased to 80 cm, with an increase in the cross section of the beam to 75 mm. The main thing at the same time is that under each slate span there should be at least three crossbars.
Most of all, in this design, the cornice is loaded, so its thickness should be increased. Skates and overhangs are made out by continuous floorings. To achieve an even distribution of load and density sheet stacking, even bars are made thicker than odd ones by 30 mm. In order for the structure to last as long as possible, before attaching the crate to the roof, all of it wooden details need to be processed special formulations fire-fighting and antiseptic action (for more details: “How and with what to process the rafters and the crate - we choose an antiseptic”). To apply them you will need paint brush: impregnation is carried out in two layers.

To test the quality of a fire-fighting substance, it is enough to chip off a small piece of treated wood and try to set it on fire. A well-protected material ignites only when it is exposed to an open flame: upon its removal, the substance immediately dies out.
Competent design and arrangement of the roof will be the key to both the aesthetic beauty of the house and its protection from all external influences. At the same time, it is important to achieve good quality each individual part roof structure. The crate, despite its invisibility, plays a very important role, therefore, when arranging it, it is important to observe all necessary requirements and norms on how to make a roof crate. Particular attention is paid to the selection of suitable building materials of appropriate quality.
Roof sheathing: how to fix, installation on the roof, how to make the right roof sheathing with your own hands
Roof sheathing: how to fix, installation on the roof, how to make the right roof sheathing with your own hands
Roof crate: do-it-yourself creation
To build a beautiful, comfortable home for a family is a city dweller's dream. Having studied all the subtleties of building art, you will be able to bring the idea to life. But, during the work, one of the main questions will be - how to make a roof crate? Approach it correctly, because the protective and aesthetic properties of the roof depend on the quality of execution. 
The need for a frame
Before moving on to listing the types of roof battens, figure out what a batten is and what it is used for. The lathing used for the roof of private buildings is a construction made of wooden beams and boards. The process of installing a roofing system is necessary in order to:
- evenly distribute the load of a person who walks along the surface during its maintenance;
- fix the materials with high quality - a frame welded from metal or made of wood is used on the crate;
- correctly create a ventilation space between the ceiling and waterproofing, which protects the building from condensation;
- in a timely manner to prevent the accumulation of moisture in places of the border of warm and cold roofing layers;
- fully protect the rafters from the effects of weather precipitation (snow and ice).
The number of layers that the crate has will depend on the slope of the roof. For a shed roof, a horizontal single-layer coating is sufficient. The two-layer method involves working with the lower bearing bars fixed in 50-100 cm increments. A layer of plywood or wooden planks attached over it. The reception will save material and align with the help of the roof lathing the errors of the truss system. 
Types of roof frames
Roofing needs a reliable and durable surface on which it will fit. An incorrect construction algorithm will lead to deformations, the lack of protective functions of the dwelling during bad weather.
Depending on the number and frequency of mounted strips, the type of material used, the angle of inclination, the frame is divided into the following types:
- Double layer. It is used in cases where the maximum reinforcement of the structure is required. The first layer is laid with a large step, and the second - with a regular or without a gap.
- Solid. It is carried out at intervals of about 1 cm and prevents the appearance of deformations during shrinkage or swelling of the tree.
- Normal, with a step of 20-40 cm. It is mainly used to reinforce the coating of metal profile sheets.
- Sparse. The gaps between the board reach 75 cm. It is used for lightweight floors.
To choose the right desired material, purchase a tool, you need to draw up a drawing of the crate and carry out preparatory manipulations. 
Used materials and tools
It is difficult to choose a floor material for covering a building. Slate, corrugated board, tiles - which of these positions is suitable for overlapping? It all depends on your desires and financial capabilities.
Cost calculation
To find out how to make the crate correctly, you need to carry out calculations. The basic rule of construction is precise planning of costs and quantity of raw materials. For calculations, you will need the following data:
- roof size;
- material type;
- roofing structure.
If a independent design seems challenging task use the online program. Enter the size of the coating, all known parameters of the materials used - the program will automatically perform the calculation. 
Purchase of building materials for wooden crates
Use dried wood, without visible defects. The presence of knots, cracks can lead to a violation of the integrity of the structure and to subsequent destruction. The following materials and tools are used for work:
- wooden beam with a section of 50 × 50, 60 × 60, 75 × 75 mm;
- edged boards for the crate with a section of 150 × 20, 150 × 50 mm;
- fasteners (self-tapping screws, nails) with a length twice the size of the timber;
- level, pencil, tape measure for marking;
- circular saw used when cutting roofing material;
- a hammer for nails or a screwdriver, if self-tapping screws are used.
Lumber must be marked and cut according to the drawing. If electrical equipment is not available, it can be bought or rented. 
Installation technology
Having completed preliminary calculations, having made a purchase necessary materials and tools, you can proceed with the installation. For different types flooring there are separate technological nuances. But general order production looks like this:
- Carefully measure the roof after the truss frame is installed. To do this, it is necessary to check the diagonals on all slopes with a nylon cord. Deviations should not exceed 20 mm, because the run-up will cause difficulties in the further fastening of the roof.
- Process all wooden elements antiseptic solutions to avoid rotting and insect damage.
- Lay waterproofing materials on the rafters.
- Install the bottom rails. Use for these purposes a beam of large section.
- Continue the work by laying the boards with the selected pitch. For each type of flooring, it is selected individually. An incorrectly performed step can lead to weakening of the entire structure.
- If necessary, make insulation, place on the first layer mineral wool, and, after that, a second layer of crate can be made.
- Lay the edge boards next to each other to use for the subsequent decoration of the ridge.
- Fasten on both sides, and with a large overhang, make additional fixation.
These rules should be followed when installing the frame under any type of roofing material. But there are some minor differences. 
Features of moisture protection of the crate
To create a waterproofing layer, vapor-barrier or hydro-barrier materials are used. When working with them, an overlap of 10-15 cm should be maintained. Waterproofing is mounted in the direction from the eaves to the ridges, with a slight tension. Ventilation holes are formed due to the sagging of the film material, which is fixed with a construction stapler. 
How to make a crate for corrugated board?
The roof lathing under the corrugated board differs in some nuances. The profile sheet has a large load - a person can walk along it without fear of falling through. When working with a profiled sheet, consider several important nuances:
- for a corrugated roof, it is required to clearly maintain the step between the boards. Its distance can be varied from 50 to 150 cm, focusing on the wave of the material and its marking (sheets with the H index will be optimal for roofing systems);
- using sheets with a height of less than 35 millimeters for work, the step should be kept to a minimum. This will increase the strength and rigidity of the coating;
- standard parameters wooden planks less than the size of the slope, so it is necessary to carry out their splicing;
- in the horizontals, the joints must be shifted so that the structure does not weaken;
- used for corrugated board special fasteners– galvanized self-tapping screws with rubber washers to prevent sheets from crushing during fastening. The connection is carried out using rivets.
If from the profile sheet was built shed roof with a slight slope, you need to make a solid frame of boards 60-70 mm wide. Nail heads are sunk as much as possible. The board for the crate is laid strictly at an angle of 45 degrees. Only well-dried wood is used so that warping does not occur when it is tightly packed. 
Lathing for slate roofing - specificity
For crates under the slate, it is desirable to purchase bars of increased cross section. Three beams must be placed under each sheet to evenly distribute the load. Fastening is carried out with special slate nails in places where the wave touches the wood. Use lumber without deflections to ensure a tight, gap-free fit of the slate sheet.
We make a frame for a metal tile
In addition to profile sheets, there is another type of durable and durable coating- metal tile. When building a house, it is placed in a single layer. The crate can be made by stuffing bars with a cross section larger than 1 mm onto the rafters. The construction step depends on the parameters of the tile. For a uniform fit of the roof, the frame is made as even as possible. The location of the boards is checked by the level. 
Advantages of self-construction
Roofing installed in compliance with the requirements technological process, will serve long years, will save your house from destruction. After studying the recommendations on the issue, you can personally perform time-consuming tasks. Having made a set of measurements with the required accuracy, following the recommendations for installation, you will receive a solid and strong protection from all sorts of adversities, ensure peace and comfort of living in a country house. 
Roof crate: how to make and install with your own hands?
Roof crate: frame creation, views roof frames, materials and tools used, lathing for various types of roofing