How to make bent parts from wood. Wood bending technology. Using chemical impregnation
Read also
When making furniture, you cannot do without curved parts. You can get them in two ways - sawing and bending. Technologically, it would seem easier to cut out a curved part than to steam, bend and then hold it for a certain time until it is completely ready. But sawing has a number of negative consequences.
First, there is a high probability of cutting fibers when working with a circular saw (this is what is used with this technology). The consequence of cutting the fibers will be a loss of strength of the part, and, as a consequence, of the entire product as a whole. Secondly, sawing technology requires more material consumption than bending technology. This is obvious and no comment is required. Third, all curved surfaces of sawn parts have end and half-end cut surfaces. This significantly affects the conditions for their further processing and finishing.
Bending allows you to avoid all these disadvantages. Of course, bending presupposes the presence special equipment and devices, but this is not always possible. However, bending is also possible in a home workshop. So, what is the technology of the bending process?
Technological process The production of bent parts includes hydrothermal treatment, bending of blanks and their drying after bending.
Hydrothermal treatment improves the plastic properties of wood. Plasticity refers to the ability of a material to change its shape without destruction under the influence of external forces and maintain it after the action of the forces is eliminated. Wood acquires its best plastic properties at a humidity of 25 - 30% and a temperature in the center of the workpiece at the time of bending of approximately 100°C.
Hydrothermal treatment of wood is carried out by steaming in boilers with saturated steam. low pressure 0.02 - 0.05 MPa at a temperature of 102 - 105°C.
Since the duration of steaming is determined by the time it takes to reach a given temperature in the center of the steamed workpiece, the steaming time increases with increasing thickness of the workpiece. For example, to steam a workpiece (with an initial humidity of 30% and an initial temperature of 25 ° C) with a thickness of 25 mm to achieve a temperature in the center of the workpiece of 100 ° C, 1 hour is required, with a thickness of 35 mm - 1 hour 50 minutes.
When bending, the workpiece is placed on a tire with stops (Fig. 1), then in a mechanical or hydraulic press the workpiece together with the tire is bent to a given contour; in presses, as a rule, several workpieces are bent simultaneously. At the end of bending, the ends of the tires are tightened with a tie. The bent workpieces are sent for drying along with the tires.
The workpieces are dried for 6 - 8 hours. During drying, the shape of the workpieces is stabilized. After drying, the workpieces are freed from templates and tires and kept for at least 24 hours. After holding, the deviation of the dimensions of the bent workpieces from the original ones is usually ±3 mm. Next, the workpieces are processed.
For bent workpieces, peeled veneer, urea-formaldehyde resins KF-BZH, KF-Zh, KF-MG, M-70 are used, particle boards P-1 and P-2. The thickness of the workpiece can be from 4 to 30 mm. Blanks can have a wide variety of profiles: corner, arc-shaped, spherical, U-shaped, trapezoidal and trough-shaped (see Fig. 2). Such blanks are obtained by simultaneously bending and gluing together veneer sheets coated with glue, which are formed into packages (Fig. 3). This technology makes it possible to obtain products of a wide variety of architectural forms. In addition, the production of bent-laminated veneer parts is economically feasible due to the low consumption of timber and relatively low labor costs.
Layers of plots are smeared with glue, placed in a template and pressed into place (Fig. 4). After exposure under the press until the glue has completely set, the assembly retains its given shape. Bent-glued units are made from veneer, hardwood and coniferous species, made of plywood. In bent-laminated veneer elements, the direction of the fibers in the veneer layers can be either mutually perpendicular or identical. Bending of veneer, in which the wood fibers remain straight, is called bending across the grain, and in which the fibers bend, bending along the grain.
When designing bent-laminated veneer units that bear significant loads during operation (chair legs, cabinet products), the most rational designs are those with bending along the fibers in all layers. The rigidity of such knots is much higher than knots with mutually perpendicular directions of wood fibers. With the mutually perpendicular direction of the veneer fibers in the layers, bent-glued units up to 10 mm thick are constructed, which do not bear large loads during operation (box walls, etc.). In this case, they are less susceptible to change in shape. Outer layer such nodes must have the lobar direction of the fibers (bending along the fibers), since when bending across the fibers, small lobar cracks appear at the bending points, which exclude good finish products.
Acceptable (radii of curvature of bent-laminated veneer elements depend on the following design parameters: veneer thickness, number of veneer layers in the package, package design, bending angle of the workpiece, mold design.
When manufacturing bent-profile units with longitudinal cuts, it is necessary to take into account the dependence of the thickness of the bent elements on the type of wood and the thickness of the bent part.
In the tables, the elements remaining after the cuts are called extreme, the rest - intermediate. Minimum distance between cuts that can be obtained is about 1.5 mm.
As the bending radius of the slab increases, the distance between the cuts decreases (Fig. 5). The width of the cut depends on the bending radius of the slab and the number of cuts. To obtain rounded nodes, after veneering and sanding, select a groove in the slab in the place where the bend will be. The groove can be rectangular or dovetail type. The thickness of the remaining plywood jumper (bottom of the groove) should be equal to the thickness facing plywood with an allowance of 1-1.5 mm. A rounded block is glued into the rectangular groove, and a strip of veneer is inserted into the dovetail groove. Then the plate is bent and held in the template until the glue sets. To give the corner greater strength with inside You can put a wooden square.
If there is a need to create a curved wooden element, then most likely you will encounter a number of difficulties. It may seem easier to cut the required component in a curved form, but in this case the wood fibers will be cut and weaken the strength of the part. In addition, the execution results in a fairly large waste of material.
Stages of performing work on bending boards at home:
| Preparation. Choice suitable variety trees and familiarization with general principles work with him. | |
 |
Wood bending options. Heating in a steam box, chemical impregnation, delamination, cutting. |
Wood is cellulose fibers bound together by lignin. The straight arrangement of the fibers affects the flexibility of the wood material.
Tip: reliable and durable wood material to create various products can only be achieved if the wood is well dried. However, the change in form is dry wooden blank- a rather complicated process, since dry wood can easily break.

Having studied the technology of bending wood, including its main physical properties of wood, which allow you to change its shape, it is quite possible to perform bending wooden material at home.
Features of working with wood
Bending of a wooden material is accompanied by its deformation, stretching outer layers and compression of internal ones. It happens that the tensile force leads to rupture of the outer fibers. This can be prevented by pre-hydrothermal treatment.
You can bend blanks of timber made of laminated wood and solid wood. In addition, peeled and sliced veneer is used to give the required shape. The most plastic is hardwood. Which includes beech, birch, hornbeam, ash, maple, oak, linden, poplar and alder. Glued bent blanks are best made from birch veneer. It should be noted that in the total volume of such blanks, about 60% falls on birch veneer.

According to manufacturing technology bentwood, when steaming a workpiece, its ability to compress significantly increases, namely by a third, while the ability to stretch increases by only a few percent. Therefore, you cannot even think about bending wood thicker than 2 cm.
How to bend a board at home: heating in a steam box
First you need to prepare a steam box, which can be done by yourself. Her the main task- hold the tree that needs to be bent. It must have a hole for steam to escape. Otherwise, an explosion may occur under pressure.

This hole should be in the bottom of the box. In addition, the box must have a removable lid through which the bent wood can be removed after it has received the desired shape. In order to hold the bent wood workpiece in the required shape, it is necessary to use special clamps. You can make them yourself from wood or purchase them at a hardware store.
Several round scraps are made from wood. Holes are drilled in them, offset from the center. After that, you should push the bolts through them, and then drill another one through the sides in order to push them in tightly. Such simple crafts can perfectly serve as clamps.

Now you can start steaming the wood. To do this, you need to close the wooden piece in a steam box and take care of the heat source. For every 2.5 cm of product thickness, the time spent on steaming is about an hour. After its expiration, the tree should be removed from the box and given the required shape by bending it. The process should be carried out very quickly, and the bending itself should be gentle and careful.
Tip: due to different degrees of elasticity, some types of wood will bend more easily than others. Different ways require the application of varying amounts of force.
As soon as the desired result is achieved, the bent workpiece must be fixed in this position. Fastening the tree is possible during the process of forming its new shape, due to which it will become much easier to control the process.How to bend a board at home using chemical impregnation
Since lignin is responsible for the durability of wood, its bonds with the fibers must be broken. This can be achieved chemically, and it is quite possible to do this at home. Ammonia is best suited for such purposes. The workpiece is soaked in a 25% aqueous solution of ammonia, which significantly increases its elasticity. This will make it possible to bend, twist it, or squeeze out any relief shapes under pressure.

Tip: Please note that ammonia is dangerous! Therefore, when working with it, you must strictly adhere to all safety regulations. Soaking of wood should be carried out in a tightly closed container, which is located in a well-ventilated area.
The longer the wood is soaked in an ammonia solution, the more plastic it will become later. After soaking the workpiece and forming its new shape, you should leave it in a similar curved form. This is necessary not only to fix the shape, but also to evaporate ammonia. However, bent wood should be left in a ventilated area. Interestingly, when the ammonia evaporates, the wood fibers will regain the same strength as before, allowing the workpiece to retain its shape!

How to bend a board at home: layering method
First, it is necessary to harvest wood, which will subsequently be subject to bending. It is extremely important that the boards are slightly longer than the length of the required part. This is explained by the fact that the bending tames the lamellas. Before you start cutting, you will need to draw a diagonal straight line with a pencil. This must be done across the bottom side of the workpiece, which will make it possible to maintain their sequence after moving the lamellas.
The boards need to be cut with a straight-layer edge, and not with the right side. This way they can be put together with smallest change. A layer of cork is applied to the mold, which will help avoid any unevenness in the shape of the saw and will make it possible to make a more even bend. In addition, the cork will keep the delamination in shape. After this, glue is applied to the upper side of one of the lamellas with a roller.

It is best to use urea-formaldehyde glue, consisting of two parts. He has high level clutch, but takes a long time to dry.
You can also use epoxy resin, but such a composition will be very expensive, and not everyone can afford it. Standard option Wood glue will not work in this case. Although it dries quickly, it is very soft, which in this case is not welcome.

The bentwood product must be placed into the mold as soon as possible. So, another one is placed on the lamella coated with glue. The process must be repeated until the bent workpiece receives required thickness. The boards are fastened together. After completely dry glue, you should shorten it to the required length.
How to bend a board at home: cut
The prepared piece of wood must be sawn through. The cuts are calculated at 2/3 of the thickness of the workpiece. They should be located on the inside of the bend. You need to be extremely careful, as rough cuts can not only deform the tree, but even break it completely.
Tip: The key to cutting success is to keep the distance between cuts as even as possible. Perfect option 1.25 cm.
The cuts are made across the grain of the wood. Then you need to compress the edges of the workpiece, which will allow you to connect the resulting gaps into one whole. This is the shape it gets bent at the end of the work. After that it is corrected.
In most cases, the outer side is treated with veneer, less often with laminate. This action makes it possible to correct the bend and hide almost any defects made during the manufacturing process. Gaps in bent wood are hidden very simply - for this, sawdust and glue are mixed, after which the gaps are filled with the mixture.
Regardless of the bend option, after the workpiece is removed from the mold, the bend will relax a little. In view of this, it should be made a little larger in order to subsequently compensate for this effect. The sawing method is used when bending metal corner or parts of a box.
So, using these recommendations, you can bend a tree with your own hands without any problems.Despite all their strength and durability, wooden parts can be easily and simply bent if suddenly during the construction process some special or original oval or oval parts are needed round shape. Tree at correct processing can easily be changed in shape, and you can carry out this procedure with your own on our own without resorting to the help of professionals.
Types of work
There are two main ways to bend wood to the desired shape, one of them is cold, the other is hot. As the name implies, the methods differ only in the use of hot temperatures; in terms of effectiveness, both of these methods are exactly the same, just hot way fixing the tree is much faster. For each method you will need glue, pva or wallpaper, depending on what you have at hand, you don’t need to buy anything special. And with the help of metal parts you can create a kind of press or frame that will hold the tree in in the required form. In order to bend the beam, you need to lubricate it with glue, firmly and thoroughly, without fear that the wood will become wet. In fact, under the influence adhesive solution all excess moisture will leave the tree, and it will become even more durable and strong,  which is extremely important. After the timber has been lubricated with glue, it must be secured using tools in the desired shape, and in the case of a cold work process, simply left fixed to dry. If you choose a hot one, then cover the timber with regular film so that it dries faster and all the moisture evaporates.
which is extremely important. After the timber has been lubricated with glue, it must be secured using tools in the desired shape, and in the case of a cold work process, simply left fixed to dry. If you choose a hot one, then cover the timber with regular film so that it dries faster and all the moisture evaporates.
Durability
Whichever method is chosen, they are both effective and work the same way. The beam is completely fixed in its new form, and will no longer return to the old one. You can bend a wet beam with glue as much as possible without fear that it will break. And as a result you will get an original and beautiful item interior or detail to create even more attractive interior house or its facade. A beam bent with glue will not even need to be treated with anything for durability, which is extremely convenient. Moisture will not penetrate through the adhesive solution, and insects will not attack wood that contains much more glue. That is why this method is the most optimal and practical if you urgently need to bend a wooden beam.
In the woodworking industry large quantities produce curved parts. The manufacture of curved parts is carried out in two ways: cutting from boards or slabs And bending straight bars (solid bent parts) or layers of wood with simultaneous gluing (bent-glued parts).
Technological process of bending wood. The technological process of bending solid wood bars includes the following operations: procurement of material for bending, hydrothermal treatment, bending and drying.
Preparation of material for bending. Blanks for bending are obtained from unedged boards by cutting them into circular saws. The following requirements apply to blanks for bending.
The cross-layer should not exceed 10°. With conventional bending methods, knots are absolutely not allowed in the workpieces. In workpieces with simultaneous pressing, knots are allowed within large limits, which sharply increases the yield of workpieces. Workpieces should be cut out taking into account allowances for subsequent processing of parts. When bending with simultaneous pressing, in addition to the processing allowance, an allowance must be provided for pressing the wood across the fibers and an increased allowance along the length of the workpiece. In order to increase the yield of blanks for bending, it is recommended to cut the boards after preliminary marking.
In small enterprises, the method of obtaining blanks for bending by splitting blocks has been preserved. The split billet does not have a cross-layer, therefore, when bending, it produces a lower percentage of rejects. However, this method is very labor-intensive, as it is done manually and gives a 20-25% lower yield of blanks from the ridge than when sawing it.
After cutting (or splitting) the blanks for parts round section are processed on turning-copying or round-bar machines, and blanks for parts rectangular section- on longitudinal milling machines. You can also bend unplaned workpieces, but in this case the boards are cut with planing saws, which give a clean and accurate cut.
Hydrothermal treatment. Hydrothermal treatment of wood before bending is carried out in order to increase the plasticity of wood. Optimal plasticity of wood is achieved when it is heated while wet. This is explained by the fact that when heated, some of the substances that make up the cells transform into a colloidal state.
As a result, the ability of cells and the entire wood to deform increases. When drying deformed (bent) wood, colloidal substances harden and retain the shape given to the workpiece.
Hydrothermal treatment of wood before bending is carried out by boiling in hot water or steaming. For boiling, use wooden vats or metal baths and tanks. The water in baths and vats is heated by steam.
The water temperature is maintained at 90-95°C, without bringing it to a boil. The duration of boiling depends on the initial humidity, size and type of wood.
When boiling, it is difficult to obtain a uniform temperature and humidity throughout the entire workpiece; the outer layers become oversaturated with water. Therefore, boiling in hot water is used only in cases where steaming is technically difficult.
Most wide application In production, wood was steamed in an atmosphere of saturated steam. Steaming allows you to heat the wood to the desired temperature (70-80°C), regulate the moisture content of the wood and always obtain it close to optimal for bending, i.e. about 25-30%.
For steaming, saturated low pressure steam (0.02-0.05 MPa) is used, which corresponds to a temperature of 102-105 ° C. Steaming of wood is carried out in hermetically sealed metal drum boilers or concrete chambers. The capacity of the boilers and chambers is small, designed for laying bars in the amount of 30-40 pieces.
The boilers are located at each bending machine and are connected to each other by a steam line into a battery. The bars in boilers and chambers are placed on gaskets to ensure better washing with steam.
The duration of steaming depends on the initial humidity and temperature of the wood, the size of the bars and the steam pressure in the boiler. The steaming time is determined according to a special diagram. For example, for workpieces with a thickness of 40 mm at an initial humidity of 30% and a steam pressure in the steaming boiler of 0.03-0.05 MPa, the steaming duration is 12-13 minutes, and for workpieces with a thickness of 80 mm - 65 minutes.
Plywood, when bent to small radii of curvature, can also be subjected to hydrothermal treatment. Plywood glued with synthetic glues is boiled, but plywood glued with casein or albumin glue is only steamed.
Workpieces removed from the steaming boiler or cooking tank must be bent immediately. The outer layers of wood, which experience the greatest stress when bending, should not be allowed to cool.
Wood bending and equipment. Wood bending machines are divided into two types: cold And hot forms.
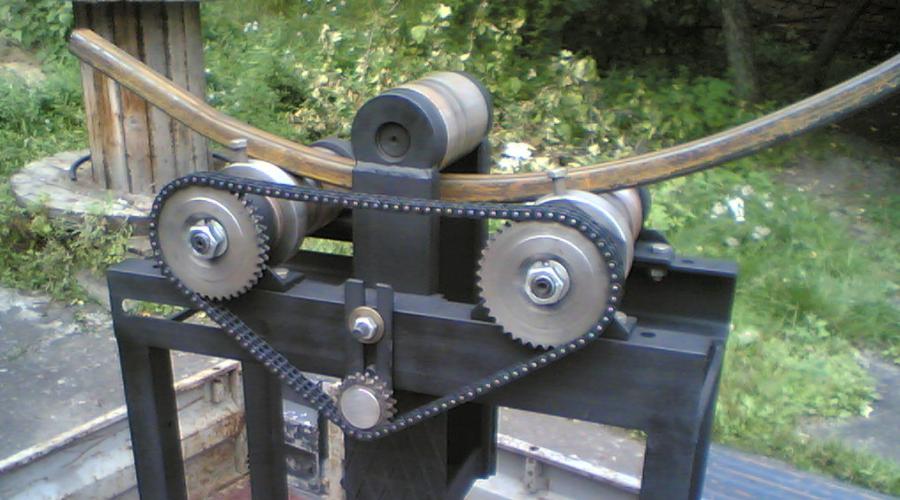
Machines of the first type (Fig. 4.13) are used for bending on a closed loop. The bars bend around a removable, unheated rotating template 6. Template with tire 2 is put on the vertical shaft 8 , which is given in rotational movement from the electric motor through the gearbox 7.
The free end of the tire is fixed in the carriage 4, sliding along guides 3. Bar 5 is placed between the template 6 and tire 2 and is secured with a movable stop. Then the electric motor turns on, and the shaft rotates 8 with a template put on it and the block bends along with the tire.
At the bend there is a roller / that tightly presses the block to the template. The rear end of the tire is secured with a bracket to the template. The template with the bar and the tire are removed from the machine and sent to drying, and a new template is put on the machine, and the operation is repeated.
Rice. 4.13.
7 - pressure roller; 2 - tire; 3 - guide; 4 - block; 5 - workpiece;
b - template; 7 - gearbox; 8 - shaft

Rice. 4.14.
7 - hook; 2 - template; 3 - emphasis; 4 - tire; 5 - blank
Bending machines with hot forms are called bending-drying machines; they can be with two-sided or one-sided heating. Machines with double-sided heating are a hydraulic or pneumatic press with heated profile template plates, between which bent bars are clamped. In these machines, the bars are kept in a clamped state until the shape is completely fixed and the workpieces are dried.
In machines with one-sided heating (Fig. 4.14), workpieces 5 are placed between a hot template 2, heated steam, and tire 4 and are secured with a stop 3. The curved blanks 5 together with the tires are secured to the template with special hooks /. The workpieces remain in the machine until the shape given to them is fixed.
This is achieved by drying the wood to approximately 15% humidity, which takes 90-180 minutes. To increase the productivity of bending-drying machines, it is recommended to dry the workpieces before bending to 20% humidity, keep them in the machine until the humidity reaches 12-15%, and the final drying of the workpieces removed from the machine to production humidity in drying chambers.
Bending of plywood is carried out in templates consisting of two parts: a matrix and a punch, between which the plywood is laid and bent. In this case, they are used special devices, screws, pneumatic and hydraulic presses.
Bending with simultaneous pressing consists in the fact that the wood is bent around a template equipped with a notch, and in the process of bending with outside the workpiece is pressed against the template through a tire using a pressing roller.
The workpiece is rolled. The thickness of the workpiece decreases, the layers of wood on the concave side of the workpiece take on a wave-like shape due to the pressing of the template notch, and the outer layers are compacted. This helps to increase the compressive resistance of the concave layers in the wood and the tensile strength of the outer layers.
Bending with simultaneous pressing significantly improves the bending ability of wood and allows you to bend wood with large knots located on the outside of the workpiece. It is used for bending coniferous and soft hardwood wood.
Drying blanks after bending. The curved workpieces are dried in drying chambers to operational humidity, and the workpieces are placed in the chamber together with templates and tires covering them. The design of drying chambers is similar to those used for drying lumber.
The dried workpieces are unloaded from the chambers and sent to the cooling compartment, where they are kept for at least 48 hours for leveling. internal stresses. Only after this the workpieces are freed from templates and tires and sent to the machining shop.
The sequence and principles of mechanical processing of bent workpieces on machines, i.e. Giving them final dimensions and a clean surface is not fundamentally different from processing straight workpieces.
Production of bent-glued parts. To obtain bent-glued parts, hydrothermal treatment of wood before bending and drying after bending are not required. Bent-glued parts are made from peeled veneer or plywood. The technological process for producing bent-glued parts consists of preparing raw materials (veneer, plywood or thin planks), applying an adhesive solution to the bonded surfaces, gluing the workpieces with simultaneous bending in molds or in templates and holding parts after pressing to equalize moisture and stress.
Gluing is done either in blocks or individual parts. Pressing is carried out in hydraulic presses with molds or templates. One of three types of heating of the pressed package is used: electric contact, steam or high frequency currents (HF). HDTV heating is the most progressive. This method requires less pressing time and the temperature is distributed more evenly across the cross section of the bag.
Adhesives based on high concentration urea resins and increased speed curing. The consumption of such adhesives per 1 m2 of surface to be spread is 110-120 g.
If you decide to decorate the room with wood or start creating beautiful furniture V classic style- then you will need to make curved parts. Fortunately, wood is a unique substance because it allows to an experienced master play with the shape a little. It's not as difficult as it seems, but not as easy as we would like.
Previously, the site already had a publication on bending plywood. In this article we will understand the principles of bending solid boards and timber, and learn how this is done in production. We will also give useful tips from professionals who will be useful to the home craftsman.
Why bending is better than sawing
Curvilinear wooden part can be obtained by two methods: by bending a flat workpiece, or by cutting out the required spatial shape. The so-called “sawing” method attracts users with its simplicity. For such production of parts and structures, you do not need to use complex devices, you do not have to spend a lot of time and effort. However, in order to cut out a curvilinear wooden product, it is necessary to use a workpiece that is obviously too large, and a lot of valuable material will be irretrievably lost as waste.
But the main problem is the performance characteristics of the resulting parts. When cutting a curved part from ordinary edged lumber, the wood fibers do not change their direction.
As a result, cross sections fall into the radius zone, which not only worsen appearance, but also significantly complicate the subsequent finishing of the product, for example, its milling or fine grinding. In addition, in the rounded areas that are most vulnerable to mechanical stress, the fibers run across the section, which makes the part prone to fracture in this place.
Whereas when bending, the opposite picture is usually observed, when the wood only becomes stronger. On the edges curved beam or the boards do not come out with “end” fiber cuts, so subsequently such workpieces can be processed without restrictions, using all standard operations.
What happens in wood when it bends?
Bending technology is based on the ability of wood, while maintaining its integrity, to change its shape within certain limits as force is applied, and then retain it after the mechanical impact is removed. However, we all know that without preparatory activities lumber is elastic - that is, it returns to its original state. And if the applied forces are too great, then the beam or board simply breaks.
Layers of a wooden workpiece do not work equally when bent. Outside the radius, the material is stretched, inside it is compressed, and in the middle of the array, the fibers experience virtually no significant loads and have little resistance to the forces acting on the workpiece (this inner layer is called “neutral”). With critical deformation, the fibers at the outer radius break, and at the inner radius, “folds” usually form, which are a fairly common defect when bending soft wood. The fibers of plastic hardwood or softwood can compress by 20 percent or more, while the tensile limit is about one to one and a half percent.
That is, to determine the possibility of bending (without destruction) more important indicator there will be a limit to the relative elongation of the stretched layer. It directly depends on the thickness of the part and determines the radius that needs to be obtained. The thicker the workpiece and the smaller the radius, the greater will be the relative elongation along the fibers. Having data about physical properties popular types of wood, it is possible for each of them to formulate the maximum possible ratio of thickness and radius of parts. In numbers it will look like this:
Bending using a steel bar
Bending without using a tire
These data indicate that softwood lumber, in comparison with dense hardwoods, is less adapted to free bending. To work with lumber at aggressive radii, it is necessary to use combined methods preliminary preparation parts and mechanical protection.
Tire as an effective way to avoid wood destruction during bending
Since the main problem is fiber breakage on the outer radius side, it is this surface of the workpiece that needs to be stabilized somehow. One of the most common methods is to use an overhead splint. The tire is a steel strip with a thickness of half a millimeter to two millimeters, which covers the beam or board along the outer radius and bends on the template along with the wood. The elastic strip absorbs part of the energy when stretched and at the same time redistributes the destructive load along the length of the workpiece. Thanks to this approach, coupled with humidification and heating, the permissible bending radius is reduced significantly.
In parallel with the use of steel bars in bending devices and machines, mechanical compaction of wood is achieved. This is done using a pressing roller, which presses on the workpiece along the outer bending radius. In addition, the template form in such a device is often equipped with 3 mm teeth (in increments of about 0.5 cm), oriented towards the movement of the workpiece.
The purpose of the jagged surface of the template is to prevent the workpiece from slipping, to prevent mutual shift of the fibers in solid wood, and also create a small depressed corrugation in the concave radius of the part (the fibers are pressed inside the array, therefore, problems with folds are solved).

Pressing with a tire allows you to minimum percentage reject bending bars and boards made of coniferous and soft deciduous wood. Please note that parts made of relatively hard wood when bent with pressing become approximately ten to twelve percent thinner, and pine and spruce blanks become 20-30% thinner. But to positive aspects this method must be attributed to a significant increase in strength characteristics finished product, as well as a significant reduction in requirements for the presence of defects in wood blanks.
How to improve the plasticity of wood
In normal condition, lumber has elasticity, significant spatial rigidity and resistance to compression. Wood receives these valuable properties from lignin, a natural “mesh” polymer that gives plants a stable shape and strength. Lignin is located in the intercellular space and in cell walls, connecting cellulose fibers. Coniferous wood contains about 23-38 percent of it, in hardwoods- up to 25 percent.
Essentially, lignin is a kind of glue. We can soften it and turn it into a “colloidal solution” if we heat the lumber by steaming, boiling, treating with high frequency current (for small parts A household microwave is also applicable). After the lignin has melted, the workpiece is bent and fixed - as it cools, the molten lignin hardens and prevents the wood from returning to its original shape.
Practice shows that optimal temperature for bending solid wood (block, strip, board) it will be 100 degrees Celsius. This temperature must be obtained not on the surface, but inside the workpiece. Therefore, the time of temperature exposure will largely depend on how massive the part is. The thicker the part, the longer it will have to be heated. For example, if you use steaming to prepare for bending a 25 mm thick rail (with a humidity of about 28-32%), then on average it takes about 60 minutes. It is noteworthy that the steam exposure time for parts of similar dimensions for any species is approximately the same.
By the way, it is believed that it is also impossible to overheat the part, since lignin after hardening may lose its elasticity and become too brittle.
The boiling method is not often used, since the workpiece is strongly and unevenly moistened, and such water-saturated fibers and cells can tear when bent, at least with the formation of lint. After cooking, the parts have to dry for too long. But this method works well if you need to process only part of the workpiece for bending.
Steaming allows the workpiece to be heated evenly, and its output humidity tends to approach the optimum. The most suitable humidity for achieving maximum ductility of lumber is considered to be in the range of 26-35 percent (the moment of saturation of wood fibers).
To steam wood for bending at home, use homemade cylindrical chambers made of metal/polymer pipes or rectangular wooden boxes. Heating tanks, electric kettles and other similar devices act as a source of steam, which can provide a temperature of about 105 degrees and slight pressure. This is always followed by the stage of drying the part (+ holding the fixed shape) to about fifteen percent and finishing it.



Chemical methods for plasticizing wood
It is also known that it is possible to make lumber more pliable using impregnation various compositions. There are ready-made impregnations that make wood cells more plastic, for example, “Super-Soft 2”. Some practitioners soak wood in so-called textile conditioners, obtaining a similar result.
But quite primitive “recipes” can also be used containing ammonia and ethyl alcohol, glycerin, alkalis, hydrogen peroxide, dissolved alum... Many of them act extremely simply - they increase the ability of the workpiece to absorb water and help retain moisture in the fibers.
Thin products such as veneer are processed by spraying, but preparatory chemical impregnation of normal lumber is usually carried out using the method total immersion. It takes time for the working substances to get inside the bar or slats, usually from 3-5 hours to several days (although heating helps reduce the wait).
Largely because of the length of the process, chemical plasticization is not often used, although there are other problems: the cost of chemicals, changes in colors, the need to provide protection from harmful fumes, the increased tendency of such curved parts to straighten...

Tips for bending lumber using hydrothermal preparation
- Select the quality of the blanks for bending very carefully. It is better not to use material with cracks, knots (even live and fused ones), or sloping fibers. If there are no options for this, then orient the part in the bending device (machine or template) so that the defects fall into the concave radius zone, and not into the tension zone at the outer radius. Give preference to the splint bending method.
- When selecting a workpiece, it is necessary to provide for a change in the size of the part after molding. For example, the thickness of a coniferous beam can be reduced by 30 percent if bending with pressing is performed.
- Even if you are planning an extensive finishing- do not leave too much material. The thinner the workpiece, the easier it bends without breaking.
- If the amount of work is small, then it is better not to cut out the workpieces, but to prick them from lumps. This way it is possible to avoid cutting the fibers and, as a result, defects during bending.
- For bending, it is advisable to use lumber with natural humidity. If you use dry workpieces, then preference should be given to those that have not been processed in drying chamber, and were dried under a canopy - in an atmospheric way.
- After steaming, work with softened wood very quickly, as lignin begins to harden almost immediately, especially in the most vulnerable outer layers of solid wood. Usually you need to focus on a time reserve of half an hour to 40 minutes, so there is no point in making large cameras if you simply do not have time to install all the material from them into templates.
- Place the material in the steaming chamber so that the surfaces facing the outer radius are freely exposed to the steam jets.
- To save time, many carpenters refuse to use templates with clamps. Instead, they use metal brackets and wedges or stop posts on the templates.
- Keep in mind that a curved bar or rail will still tend to straighten. And this straightening always occurs by a few percent. Therefore, when required high accuracy in the manufacture of a part, it is necessary to conduct tests and, based on the results obtained, adjust the shape of the template (reduce the radius).
- After the part has cooled in the mold, let it stand some more. Some experienced furniture makers They prefer to age for 5-7 days. The tire, as a rule, is left attached to the part during this entire time.

