Fan coils in air heating systems of private houses. Fan coils in heating Advantages of heating with fan coils
Read also
Fan coil units are part of the climate control system. Units equipped with a heat exchanger and fan operate in cooling and heating modes. At any time of the year they provide a comfortable temperature in the house. When connected to a heat pump or autonomous boiler, fan coil units become heating devices, superior efficiency to radiators.
Fan coil heating principle
Operating principle of fan coil
The original name of the fan coil unit “fan coil” means “fan-heat exchanger”. The device is called a fan coil. This is the final element of a chiller-fan coil type system. The block consists of the following parts:
- heat exchanger made of copper tubes with aluminum fins;
- centrifugal fan;
- filter;
- Control block.
Water (in regions with mild climates) or ethylene glycol (for areas with low temperatures) circulates through the main line. Fan coils are installed in each room; they operate according to individual program. The number of connected modules depends on the chiller power.
The coolant temperature is 35-55°. A low indicator is enough for heating using new technology.
Steel batteries are gradually losing ground alternative systems space heating. One of modern options heating the house - fan coil instead of a radiator. Inside the block there is a heat exchanger with circulating hot water, supplied by the highway. The fan, which is part of the device, drives air masses through it. Forced circulation allows you to quickly increase the room temperature. The filter device cleans the flow warm air from dust and impurities.
The fan coil is connected by a pipe system to a heating boiler (chiller) and a hydraulic module. When installing a water circuit, there is no need to use expensive copper pipes. Plastic lines with insulation will replace metal. High-quality thermal insulation eliminates temperature loss even over a considerable distance. One of the advantages of plastic is low cost materials and installation work.

Chiller - external unit of the air conditioning system
Chiller – refrigeration machine with the ability to switch to a heat pump, installed outdoors or in a utility room. The hydraulic module consists of a pump, expansion tank and storage tank. The four-pipe system includes a heating boiler. With the onset of cold weather, a special valve turns on the heating mode.
Types of indoor units
Depending on the type of connection to the hydraulic circuit, there are two types of fan coil for heating a private house:
- Two-pipe - the unit is equipped with one water circuit. Its operating mode depends on the temperature of the coolant. This type is the most common and affordable.
- Four-pipe - a device with two heat exchangers, one of which circulates cold water, and the other hot. The systems operate independently of each other, which allows you to quickly change cooling and heating modes.
Mounting options
The design option of the fan coil is selected depending on the placement requirements:

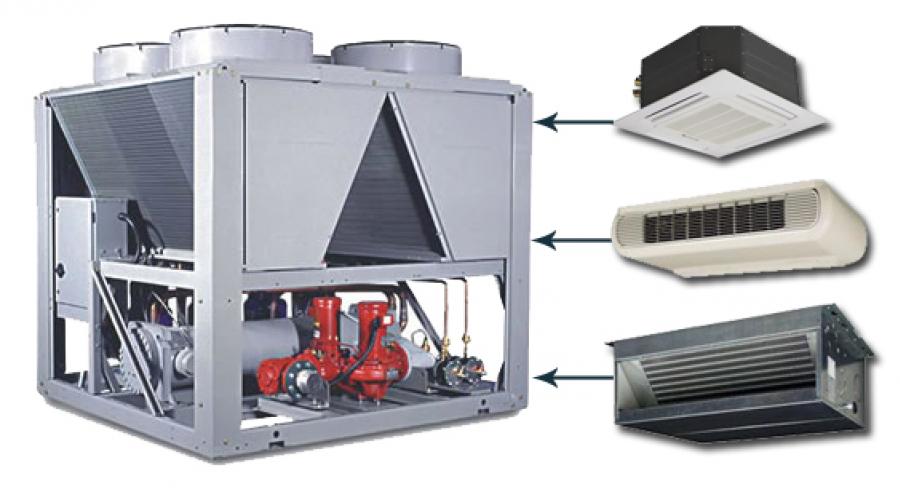
Cassette fan coil is installed behind a suspended ceiling
- Cassette - blocks are placed behind suspended ceilings. An air distribution grille is directed into the room. The devices are available in two and four pipes. They are supplied with a tray for collecting condensate.
- Duct - devices are designed for installation in ventilation duct. Horizontal models installed behind a suspended ceiling, vertical ones - behind a false wall. Powerful fans allow you to serve multiple rooms. Blocks are managed remote control.
- Wall-mounted – the console block is placed openly, which simplifies the installation process. The device is manufactured keeping decorative appeal in mind. The housing does not differ in appearance from the internal unit of a split system. Works in two modes: cooling and heating. The device is equipped with a remote control. When installed above a window it creates thermal curtain, eliminating the appearance of drafts.
- Floor-standing - equipment is installed on the floor or at the bottom of the wall. The blocks replace radiators. Heated or cooled air is directed upward. They are equipped with two or four-pipe heat exchanger. Possible option horizontal installation under the ceiling. Models have built-in and remote controls.
The downside of the system is the increased noise level created by the fan.
Advantages of using fan coil units
- Thanks to forced circulation air, fan coils increase the room temperature faster than radiators operating on the principle of natural convection.
- The chiller-fan coil system heats the house in winter and switches to cooling mode in summer.
- The coolant temperature decreases.
- Heating costs are reduced, the savings are noticeable for homes large area.
- Automatic control makes it easy to adjust the temperature. All you need to do is set the required parameters on the remote control.
- Risk of occurrence emergency situation kept to a minimum.
- Installing fan coil units provides the opportunity to choose comfortable temperature for every room.
- Blocks with water coolant are more economical, durable and reliable heating elements than electric convectors.
Heating Features
The layout of heating elements is selected based on individual characteristics premises. The fan coil plays the role of a radiator in the heating system, so it is preferable to install it at the bottom. The number of blocks in a room is calculated taking into account several factors:
- square;
- ceiling height;
- window sizes;
- winter temperatures in the region.
Types of zoning

A multi-zone system allows you to heat some rooms while cooling others
Air conditioning systems are used of varying complexity. To maintain the same temperature in all rooms of a private house, a single-zone option is suitable. Work algorithm:
- In summer, water circulates in the pipes at a temperature of 7°. It is supplied to the heat exchangers of fan coil units, which cool the air in the rooms. The operation of the unit is regulated by a controller connected to a temperature sensor. The heated water is sent back to the chiller.
- In winter, the automation switches the coolant to the heating source (boiler, boiler).
A two-pipe circuit and blocks with one circuit are used. The house operates in cooling or heating mode, but in individual rooms you can change the microclimate parameters.
The multi-zone system offers expanded functionality. Some rooms heat up and others cool down at the same time. This possibility is provided by dividing cold and hot water into different branches. For installation, you will need blocks with two circuits and a four-pipe connection diagram.
The microclimate in the house is regulated by thermostats. Sensors are installed in every room. When the set value is reached, the heat supply to the fan coil units and the supply of electricity for fan operation are stopped. The device enters energy saving mode. In houses where it is provided at the design stage central air conditioning, it is advisable to use fan coil heating. The universal system replaces two climate control systems – water heating and air conditioning.
The very definition of “fan coil” is inseparable from such concepts as chiller and hydraulic module. Only in isolated cases can a fan coil be used separately and work with other climate control equipment.
Fan coil as a chiller element
Initially, the fan coil unit was used only in conjunction with the chiller and was its integral part, and since this entire system worked to cool the air in rooms with big amount rooms, then the fan coil unit was also intended only for cooling the air in the hot season. Water was used as a working substance that circulated from the chiller to the fan coil and back to the chiller. Ensuring such a continuous flow was provided by the hydraulic module - its one or more pumps.
Over time, heat transfer processes were studied more deeply, and a well-founded solution emerged - in addition to cooling the air, use fan coil units to heat the air. To implement this function, the chiller was equipped with a 4-way valve and other auxiliary elements. If in the cooling mode the refrigerant in the chiller moves in the direction: compressor - condenser (most often air) - throttling device - evaporator (most often plate) - and again the compressor, then in the heating mode the movement is in the opposite direction: compressor - evaporator - throttling device - condenser - compressor. It is in the evaporator, which in this case serves to condense the refrigerant, that a large amount of heat is taken from it, which heats the water that goes further into the fan coil units to heat the air in them.
This function does not require any modification of the fan coil design. As before, the fan coil unit includes a heat exchanger through which water moves, a fan that blows air through such a heat exchanger, a temperature sensor, a port for receiving an infrared signal from the control panel (if available), air filter, condensate drain pan and 3-way valve (supplied separately).
Classification of fan coil units
Like others indoor units various systems air conditioning, regardless of operating mode, by location fan coil units are:- wall;
- cassette (single-stream and four-stream);
- cassette four-stream (standard and compact);
- channel (low - medium and high pressure);
- floor-ceiling
- two-pipe and four-pipe;
- two-row, three-row and four-row;
- cased and uncased.
- horizontally installed;
- vertically installed.
Fan coil efficiency
This is how a new name for a chiller operating on heat appeared - a heat pump. In addition to the use of electricity or the use of natural resources to produce heat, another method of producing heat has been obtained, and it is 2-4 times more efficient than the direct use of electricity in heating devices. The heat, which is subsequently used to heat the air passing through the fan coil, is obtained as a result of the work refrigeration circuit, and in particular, from the operation of the compressor when compressing the refrigerant. At the outlet of the compressor, the refrigerant can leave at a temperature of +60 ℃ to +100 ℃. This heat is subsequently used to heat the water, which enters the fan coil, and then into the air. Since heat work is also envisaged in winter period, then, to prevent water from freezing, it is replaced with any liquid that does not freeze at low temperatures, then the same liquid will flow into the fan coil units. In such situations, the initial selection and calculations must be made specifically for the liquid that will be poured in the future. Replacing one fluid with another during operation is prohibited. The operating efficiency of a heat supply system based on non-freezing liquids will be lower due to their increased viscosity, which entails additional resistance losses during heat transfer.
Where can fan coil units be used for heating?
All manufacturers manufacture chillers for both cooling and heating water, i.e., in most cases, they can operate in both cooling and water heating modes, while the temperature of the water supplied to the fan coil for air heating is usually +40…+55 ℃. There are separate cheaper models that work only for cooling or only for heating. The latter have a special name – heat pumps. They are installed in private houses and cottages and provide water heating not only for heating, but also for plumbing and household needs. Fan coils are used as internal devices various types. Fast heating of the air, intense forced circulation and noiselessness make such fan coil units the most high level among all possible heating devices. Fan coil units can be used separately, regardless of the chiller. This option is possible if there is some other source of heating water (liquid), which is sent to the fan coil units. The water (liquid) temperature in this case should not exceed +70 ℃, otherwise the fan coil unit will be damaged.
The multi-zone chiller-fan coil climate system is designed to create comfortable conditions inside a large building. It works constantly - it supplies cold in the summer, and heat in the winter, warming the air to the set temperature. It’s worth getting to know her device, don’t you agree?
The article we propose describes in detail the design and components of the climate system. Methods for connecting equipment are given and discussed in detail. We will tell you how this thermoregulation system works and functions.
The role of the cooling device is assigned to the chiller - external unit‚ producing and supplying cold through pipelines with water or ethylene glycol circulating through them. This is what distinguishes it from other split systems, where freon is pumped in as a coolant.
For the movement and transmission of freon, a refrigerant, expensive copper pipes are needed. Here they do an excellent job of this task. water pipes with thermal insulation. Its operation is not affected by the outside air temperature, while split systems with freon lose their functionality already at -10⁰. The internal heat exchange unit is a fan coil.
It takes in low temperature liquid, then transfers the cold to air environment premises, and the heated liquid is returned back to the chiller. Fan coil units are installed in all rooms. Each of them works according to an individual program.
The main elements of the system are a pumping station, a chiller, a fan coil. The fan coil can be installed at a great distance from the chiller. It all depends on how much power the pump has. The number of fan coil units is proportional to the chiller power
Typically, such systems are used in hypermarkets, shopping malls, structures built underground, and hotels. Sometimes they are used as heating. Then heated water is supplied to the fan coils through the second circuit or the system is switched to the heating boiler.
System design
According to the design, chiller-fan coil systems can be 2-pipe or 4-pipe. Depending on the type of installation, devices are distinguished between wall-mounted, floor-mounted, and built-in.
The system is evaluated according to the following basic parameters:
- chiller power or cooling capacity;
- fan coil performance;
- efficiency of air mass movement;
- length of highways.
The last parameter depends on the strength pumping unit and quality of pipe insulation.
Image gallery








Connecting the chiller and fan coil
The smooth functioning of the system occurs by connecting to one or more fan coil units through thermally insulated pipelines. In the absence of the latter, the efficiency of the system drops significantly.
Each fine coil has an individual piping unit, through which its performance is adjusted both in the case of heat and cold generation. The refrigerant flow in a separate unit is regulated by means of special valves - shut-off and control valves.

To direct chilled water to the heat exchanger, one pipe is connected to the fan coil unit, and the other, to drain the liquid, is connected to the chiller. The system design allows mixing of refrigerant with coolant
If mixing of coolant and refrigerant is not allowed. the water is heated in a separate heat exchanger and the circuit is completed circulation pump. To provide smooth adjustment flow of working fluid through the heat exchanger when installing the piping circuit, a 3-way valve is used.
If a two-pipe system is installed in the building, then both cooling and heating occurs due to a cooler - a chiller. To improve heating efficiency using cold period In addition to the chiller, the system includes a boiler.
Unlike two-pipe system with one heat exchanger, 2 of these units are included in a four-pipe system. In this case, the fan coil can operate for both heating and cold, using in the first case the liquid circulating in the heating system.
One of the heat exchangers is connected to a pipeline with refrigerant, and the second to a pipe with coolant. Each heat exchanger has an individual valve controlled by a special remote control. If such a scheme is used, the refrigerant is never mixed with the coolant.
Since the temperature of the coolant in the system is heating season ranges from 70 to 95⁰ and for most fan coil units it exceeds the permissible value; it is first reduced. Therefore, the supply from the central heating network to the fan coils passes through a special heating point.
Main classes of chillers
The conditional division of chillers into classes occurs depending on the type of refrigeration cycle. Based on this feature, all chillers can be conditionally classified into two classes - absorption and steam compressor.
The structure of the absorption unit
An absorption chiller or ABCM uses a binary solution with water and lithium bromide present in it - an absorber. The principle of operation is the absorption of heat by the refrigerant in the phase of converting steam into a liquid state.
Such units use the heat generated during operation industrial equipment. In this case, an absorbent absorber with a boiling point significantly higher than the corresponding parameter of the refrigerant dissolves the latter well.
The operating diagram of a chiller of this class is as follows:
- Heat from an external source is supplied to a generator, where it heats a mixture of lithium bromide and water. When boiling working mixture The refrigerant (water) is completely evaporated.
- The steam is transferred to the condenser and becomes a liquid.
- The refrigerant enters the throttle in liquid form. Here it cools and the pressure drops.
- The liquid enters the evaporator, where water evaporates and its vapors are absorbed by a lithium bromide solution - an absorber. The air in the room is cooled.
- The diluted absorbent is reheated in the generator and the cycle starts again.
Such an air conditioning system has not yet become widespread, but it is completely in tune with modern trends‚relating to energy saving, therefore it has good prospects.
Design of vapor compression units
Most of the systems operate on the basis of compression cooling. refrigeration units. Cooling occurs due to continuous circulation, boiling at low temperatures, pressure and condensation of the coolant in a closed-type system.
The design of a chiller of this class includes:
- compressor;
- evaporator;
- capacitor;
- pipelines;
- flow regulator.
The refrigerant circulates in closed system. This process is controlled by a compressor, in which a gaseous substance with a low temperature (-5⁰) and a pressure of 7 atm is compressed when the temperature is raised to 80⁰.
Dry saturated steam in a compressed state goes into the condenser, where it is cooled to 45⁰ at a constant pressure and converted into liquid.
The next point on the path of movement is the throttle ( pressure reducing valve). At this stage, the pressure decreases from the value corresponding to condensation to the limit at which evaporation occurs. At the same time, the temperature drops to approximately 0⁰. The liquid partially evaporates and wet steam is formed.

The diagram shows closed loop‚ according to which the vapor compression installation operates. In the compressor (1), wet saturated steam is compressed until it reaches pressure p1. In the compressor (2), the steam gives off heat and is transformed into liquid. In the throttle (3), both pressure (p3 - p4) and temperature (T1-T2) decrease. In the heat exchanger (4), pressure (p2) and temperature (T2) remain unchanged
Having entered the heat exchanger - evaporator, the working substance, a mixture of steam and liquid, gives off cold to the coolant and takes heat from the refrigerant, drying at the same time. The process occurs at constant pressure and temperature. Pumps supply low temperature liquid to the fan coil units. Having passed this path, the refrigerant returns to the compressor to repeat the entire vapor compression cycle again.
Specifics of a vapor compression chiller
In cold weather, the chiller can operate in natural cooling mode - this is called free cooling. At the same time, the coolant cools the street air. Theoretically, free cooling can be used at an external temperature of less than 7⁰C. On practice optimal temperature for this 0⁰.
When configured in “heat pump” mode, the chiller operates for heating. The cycle undergoes changes, in particular, the condenser and evaporator exchange their functions. In this case, the coolant must be heated rather than cooled.

The simplest are monoblock chillers. They compactly combine all the elements into one. They go on sale 100% complete, right down to the refrigerant charge.
This mode is most often used in large offices. public buildings‚ in warehouses. The chiller is refrigeration unit, producing 3 times more cold than it consumes. Its efficiency as a heater is even higher - it consumes 4 times less electricity than it produces heat.
What is the difference between refrigerant and coolant?
A refrigerant is a working substance that, during the refrigeration cycle, can exist in different states of aggregation at different meanings pressure. The coolant does not change phase states. Its function is to transfer cold or heat over a certain distance.
The transport of refrigerant is controlled by a compressor, and the coolant is transported by a pump. The temperature of the refrigerant can fall below the boiling point or rise beyond it. The coolant, unlike the refrigerant, constantly operates at temperatures that do not rise above the boiling point at the current pressure.
The role of the fan coil in the air conditioning system
Fan coil - important element centralized climate control system. The second name is fan coil. If the term fan-coil is translated from English literally, it sounds like a fan-heat exchanger, which most accurately conveys the principle of its operation.

The design of the fan coil unit includes a network module that provides connection to the central control device. Durable housing hides structural elements and protects them from damage. A panel is installed outside, evenly distributing air flows in different directions.
The purpose of the device is to receive media at low temperatures. The list of its functions also includes both recirculation and cooling of air in the room where it is installed, without the intake of air from outside. The main elements of the fan-coil are located in its body.
These include:
- centrifugal or diametrical fan;
- heat exchanger in the form of a coil, consisting of copper tube and aluminum ribs mounted on it;
- dust filter;
- Control block.
In addition to the main components and parts, the design of the fan coil unit includes a tray for collecting condensate, a pump for pumping out the latter, an electric motor, through which the air dampers are rotated.

The photo shows a Trane duct fan coil. The productivity of double-row heat exchangers is 1.5 – 4.9 kW. The unit is equipped with a low-noise fan and a compact housing. It fits perfectly behind false panels or behind a suspended ceiling structure
Depending on the installation method, there are ceiling fan coils, duct units, mounted in ducts through which air flows, unframed units, where all elements are mounted on a frame, wall-mounted or console units.
Ceiling devices are the most popular and have 2 versions: cassette and duct. The first ones are installed in large rooms with suspended ceilings. Behind suspended structure position the body. The bottom panel remains visible. They can disperse air currents on two or all four sides.

If the system is planned to be used exclusively for cooling, then the best place for him - the ceiling. If the structure is intended for heating, the device is placed on the wall in its lower part
The need for cooling does not always exist, therefore, as can be seen in the diagram depicting the operating principle of the chiller-fincoil system, a container is built into the hydraulic module that acts as an accumulator for the refrigerant. The thermal expansion of water is compensated by an expansion tank connected to the supply pipeline.
They control fan coils in both manual and automatic modes. If the fan coil operates for heating, then manual mode cut off the supply cold water. During operation, it is turned off for cooling. hot water and open the way for the flow of coolant working fluid.

Remote control for controlling both 2-pipe and 4-pipe fan coil units. The module is connected directly to the device and placed near it. The control panel and wires for its power are connected from it.
To operate in automatic mode, the panel sets the temperature required for a specific room. The set parameter is maintained by means of thermostats that adjust the circulation of coolants - cold and hot.

The advantage of a fan coil unit is expressed not only in the use of a safe and cheap coolant, but also in quick elimination problems in the form of water leaks. This makes their service cheaper. The use of these devices is the most energy-efficient way to create a favorable microclimate in a building
Since any large building has zones with different requirements To temperature conditions, each of them must be served by a separate fan coil or a group of them with identical settings.
The number of units is determined at the system design stage by calculation. The cost of individual components of the chiller-fan coil system is quite high, therefore both the calculation and design of the system must be performed as accurately as possible.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video #1. Everything about the design, operation and principle of operation of the thermoregulation system:
Video #2. On how to install and commission the chiller:
Installation of a chiller-fan coil system is advisable in medium and large buildings with an area exceeding 300 m². For a private home, even a huge one, installing such a thermoregulation system is an expensive pleasure. On the other hand, similar financial investments will provide comfort and wellness, and this is a lot.
Please write comments in the block below. Ask questions about points of interest, share your own opinions and impressions. Perhaps you have experience in the installation of a chiller-fan coil climate system or a photo related to the topic of the article?
Initially, the fan coil is an element of a system that also includes a hydraulic module and a chiller. A fan coil is a complete unit consisting of the following components:
- heat exchanger - used to circulate water;
- fan - its task is to blow air over the heat exchanger;
- air filter;
- pan - a reservoir in which condensate accumulates;
- temperature sensor;
- sensor for receiving a signal from the controller;
- three-way valve(optional).
Chiller-fan coil system
At the very beginning, the fan coil was inextricably linked with the chiller. Such an installation also included a hydraulic module, which ensured the movement of water in the circuit and was equipped with several or only one pump. Water has always been used as a coolant. The system only provided cooling for a large number of rooms in the summer heat.
As the heat transfer process was studied, fan coil units were improved, and it became possible to use them for heating. To realize this idea, the chillers were improved by adding additional elements to the design.
During cooling, the refrigerant circulates in the chiller block in the following order:
- Compressor block.
- Capacitor.
- Throttling installation.
- Heat exchanger block.
- Compressor block again.
If there is a need to heat the air, the refrigerant moves in the opposite direction. In the heat exchanger, heat is exchanged between the refrigerant and water. The advantage of this operating scheme is that the appearance of the heating function did not lead to a change in the design of the fan coil unit.
What types of fan coils are there?
Cooling units are classified according to many parameters:
- Depending from the installation location: wall and floor-ceiling, duct (low-pressure, medium-pressure and high-pressure), cassette (single- and four-flow (standard and compact sizes)).
- By design features : two-pipe (or single-circuit) and four-pipe (or double-circuit); 2, 3 and 4-row; with or without a housing.
- By location relative to the plane: horizontal and vertical
Using fan coil units as a heat pump
A fan coil that provides air heating also has an alternative name - a heat pump. If previously electricity and heat from gas or coal were used as a heating source, now it has become possible to fully heat buildings using a chiller-fan coil system. Moreover, this method is 2-4 times more effective.
The peculiarity of the fan coil operation is the quality heat pump is as follows:
- The compressor unit, compressing the refrigerant, increases its temperature to 60℃-100℃
- The heated refrigerant transfers its heat to water, which, entering the fan coil, helps to heat the air in the room.
- To ensure that the heating system can operate in winter, the installation must be protected from water freezing.
- To do this, even before installing the blocks, the water is replaced with a liquid that is not subject to crystallization, since it is impossible to make any changes during operation.
An important point is that initially all parameters are calculated taking into account the use of non-freezing liquid. Since its viscosity is much higher than water, system performance may be reduced.
Areas of application of fan coil units for heating
Most chiller models are capable of heating/cooling functions. The temperature of the water that enters the fan coil to heat the air reaches about 40℃-55℃.
There are also units that operate only for heating or only for cooling. The first type is called heat pumps. They are often used in private households. Moreover, the devices are used not only as a room air heater. They also heat water for showering, washing dishes and other needs. Such fan coil units are distinguished by their ability to quickly heat the air and ensure its intensive movement. In addition, they are practically silent during operation.
If exists alternative way submissions warm water for a fan coil unit, it is absolutely not necessary to purchase a chiller either. You just need to comply with the requirements for liquid temperature - no more than 70℃.
Ecology of consumption. Estate: One of the most modern systems heating and air conditioning for private houses is a chiller-fan coil system. This system will allow you to create in your home favorable microclimate, will maintain the freshness of the air and preserve the health of the household.
One of the most modern heating and air conditioning systems for private homes is the chiller-fan coil system. This system will create a favorable microclimate in your home, maintain fresh air, and preserve the health of your household. This system especially stands out against the background of traditional split systems, so we’ll talk about its features in this article. First, let's look at the design of the system as a whole, then we'll touch on the fan coils themselves.
The main purpose of the chiller-fan coil system is air conditioning. It consists of two main parts: a chiller and a fan coil. A chiller is a device that is directly responsible for heating or cooling, and a fan coil is essentially an air conditioner that serves to cool or heat the air in the room in which the fan coil itself is located.
Unlike a conventional air conditioner, refrigerant does not circulate through the fan coil; water or antifreeze liquid often circulates through it. As for the chiller, it can run, for example, on solid fuel or operate on a heat pump system.
In addition to the main parts, the system contains: a hydraulic module, automation, connecting elements, storage and expansion tanks, coolant and refrigerant. A hydraulic module is, in fact, a pumping station whose task is to ensure the movement of coolant in the system. Automation provides control and regulation of the system during its operation.
Connecting elements are pipes connecting parts of the system, units, to each other. The coolant used is ethylene glycol (for regions with cold or temperate climates) or water (for regions with hot climates). The refrigerant is a gas, often freon.
The distinctive advantages of the chiller-fan coil system lie in a number of its features.
Firstly, the system is very easy to maintain - the filters are easy to remove, clean or change.
Secondly, it is possible to install several fan coil units (in separate rooms), while the chiller operates alone for the entire system, and the number of fan coil units is determined only by the capacity of the chiller.
Thirdly, the chiller is installed immediately in one specific place; it does not require several places, that is, it does not consume a lot of space.
Fourthly, well-organized thermal insulation of pipes will allow the coolant to be transferred to long distance, that is, heated or air-conditioned rooms may be located far from the chiller.
During installation, ordinary pipes are used, standard shut-off valves, typical automation. The system is environmentally safe; if a solution of ethylene glycol in water has some toxicity, then if there is a leak, a person will instantly start coughing and leave the room - he will be safe. As for the refrigerant, it circulates only in the chiller, that is, in a unit in the attic or on the roof, outside the living quarters. This system allows you to combine both heating and supply and exhaust ventilation at a relatively low installation cost.
The coolant entering the chiller is heated or cooled, similar to what happens in an air conditioner. Water or non-freezing liquid, serving as a coolant, is supplied to the fan coil units using a pump module, where the room air is mixed with the air of the unit using a fan installed inside.
A heated or cooled coolant gives off or takes away heat from the air in the room, thus achieving correct microclimate. This is the principle of operation of chiller-fan coil systems, which show themselves remarkably well as systems air heating private houses.
The heat exchanger of the chiller itself is connected to the pump and storage tank(battery), then an expansion tank is installed, and then the coolant is supplied through pipes to the fan coils, while control valves installed in the pipeline adjust the system to the correct mode.
For a particular house, the system design is developed individually by specialists, and if somewhere the chiller can only be installed on the roof, then otherwise the attic is best suited for placing the chiller. When designing, all the features of the premises, garden infrastructure and household microclimate requirements are taken into account. The type of chiller is selected individually, as is the number of fan coil units, depending on the load intensity and individual requirements customer to the peculiarities of the system operating modes.
The devices included in the system can work together or separately, again depending on the type of system. Chillers are reversible, vapor compressor or absorption. The reversible chiller is capable of both heating and cooling. The steam compressor will remove heat from the coolant circulating inside the unit into a special chamber.
And the absorption one can, by changing state of aggregation liquid, take away heat from it or vice versa - heat it up; the absorbent transfers heat to the consumer. Cooling can be air or water, and the cooling circuit can be remote. Fan coil units themselves can be cassette or duct, wall-mounted, floor-mounted or ceiling-mounted.
When choosing a system, it is important to evaluate the following parameters: chiller power, fan coil performance, power pumping station, pipeline length, pipe thermal insulation. Thus, a chiller-fan coil system can be designed for any building, not only for a private home, but also, for example, for a supermarket or hotel. published