Thread diameter g1 2 in mm. Cylindrical pipe thread BSP (BSPP). How to determine the pitch of an inch thread
Read also
Cylindrical pipe thread, G (BSPP)
Pipe cylindrical thread used in cylindrical threaded connections, as well as in internal connections cylindrical thread with external conical thread GOST 6211-81. Thread based B.S.W.(English) British Standard Whitworth, widely used inch pipe threads, also known as Whitworth threads) and is compatible with BSP(English) British standard pipe thread) and is denoted BSPP.
- GOST 6357-81. Basic norms of interchangeability. Cylindrical pipe thread.
- ISO R228
- EN 10226
- DIN 259
- BS 2779
- JIS B 0202
Thread parameters
Inch thread with a profile angle at the apex of 55°, theoretical profile height Н=0.960491Р.
Cuts on pipes up to size 6", pipes over 6" are welded.
Symbol according to GOST 6357-81: letter G, numeric value conditional passage pipes in inches, average diameter accuracy class ( A, IN), and letters L.H. for left-hand thread. For example, a thread with a nominal diameter of 1 1/8, accuracy class A- denoted as: G 1 1/8-A.
According to GOST 6357-81 Cylindrical pipe thread. Basic norms of interchangeability: cylindrical pipe thread pitch has four values.
| Thread size designation | Step P | Thread diameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Row 1 | Row 2 | d=D | d 2 =D 2 | d 1 =D 1 | |
| 1/16" | 0,907 | 7,723 | 7,142 | 6,561 | |
| 1/8" | 9,728 | 9,147 | 8,566 | ||
| 1/4" | 1,337 | 13,157 | 12,301 | 11,445 | |
| 3/8" | 16,662 | 15,806 | 14,950 | ||
| 1/2" | 1,814 | 20,955 | 19,793 | 18,631 | |
| 5/8" | 22,911 | 21,749 | 20,587 | ||
| 3/4" | 26,441 | 25,279 | 24,117 | ||
| 7/8" | 30,201 | 29.0З9 | 27,877 | ||
| 1" | 2,309 | 33,249 | 31,770 | 30,291 | |
| 1⅛" | 37,897 | 36,418 | 34,939 | ||
| 1¼" | 41,910 | 40,431 | 38,952 | ||
| 1⅜" | 44,323 | 42,844 | 41,365 | ||
| 1½" | 47,803 | 46,324 | 44,845 | ||
| 1¾" | 53,746 | 52,267 | 50,788 | ||
| 2" | 59,614 | 58,135 | 56,656 | ||
| 2¼" | 65,710 | 64,231 | |||
| 2½" | 75,184 | 73,705 | 72,226 | ||
| 2¾" | 81,534 | 80,055 | 78,576 | ||
| 3" | 87,884 | 86,405 | 84,926 | ||
| 3¼" | 93,980 | 92,501 | 91,022 | ||
| 3½" | 100,330 | 98,851 | 97,372 | ||
| 3¾" | 106,680 | 105,201 | 103,722 | ||
| 4" | 113,030 | 111,551 | 110,072 | ||
| 4½" | 125,730 | 124,251 | 122,772 | ||
| 5" | 138,430 | 136,951 | 135,472 | ||
| 5½" | 151,130 | 148,651 | 148,172 | ||
| 6" | 163,830 | 162,351 | 160,872 | ||
| where d is the outer diameter of the external thread (pipe); D - outer diameter internal thread(couplings); D 1 - internal diameter of the internal thread; d 1 - internal diameter of the external thread; D 2 - average diameter of internal thread; d 2 - average diameter of the external thread. When selecting the pipe thread size first row should be preferred second. | |||||
The thread size designation corresponds to the internal diameter of the pipe according to one of the standards (en:Nominal Pipe Size).
Tapered pipe thread, R (BSPT)
Pipe conical thread used in conical threaded connections, as well as in connections with external conical threads and internal cylindrical threads in accordance with GOST 6357-81. Thread based B.S.W.(English) British Standard Whitworth) and is thread compatible BSP(English) British standard pipe tapered thread ), called BSPT(sealing is achieved by compressing the threads at the threaded connection when screwing in the fitting).
- GOST 6211-81. Basic norms of interchangeability. Conical pipe thread.
- ISO R7
- DIN 2999
- BS 21
- JIS B 0203
Thread parameters
Inch thread with a taper of 1:16 (cone angle φ=3°34’48"). Profile angle at the tip is 55°.
Symbol: letter R for external threads and Rc for internal threads (GOST 6211-81. Basic norms of interchangeability. Conical pipe threads), numerical value of the nominal thread diameter in inches (inch), letters LH for left-hand threads. For example, a thread with a nominal diameter of 1 1/4 is designated as R 1 1/4.
| Size designation threads |
Step P | Thread length | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Working | Outer d=D |
Average d 2 =D 2 |
Interior d 1 =D 1 |
|||
| 1/16" | 0,907 | 6,5 | 4,0 | 7,723 | 7,142 | 6,561 |
| 1/8" | 6,5 | 4,0 | 9,728 | 9,147 | 8,566 | |
| 1/4" | 1,337 | 9,7 | 6,0 | 13,157 | 12,301 | 11,445 |
| 3/8" | 10,1 | 6,4 | 16,662 | 15,806 | 14,950 | |
| 1/2" | 1,814 | 13,2 | 8,2 | 20,955 | 19,793 | 18,631 |
| 3/4" | 14,5 | 9,5 | 26,441 | 25,279 | 24,117 | |
| 1" | 2,309 | 16,8 | 10,4 | 33,249 | 31,770 | 30,291 |
| 1¼" | 19,1 | 12,7 | 41,910 | 40,431 | 38,952 | |
| 1½" | 19,1 | 12,7 | 47,803 | 46,324 | 44,845 | |
| 2" | 23,4 | 15,9 | 59,614 | 58,135 | 56,565 | |
| 2½" | 26,7 | 17,5 | 75,184 | 73,705 | 72,226 | |
| 3" | 29,8 | 20,6 | 87,884 | 86,405 | 84,926 | |
| 3½" | 31,4 | 22,2 | 100,330 | 98,851 | 97,372 | |
| 4" | 35,8 | 25,4 | 113,030 | 111,551 | 110,072 | |
| 5" | 40,1 | 28,6 | 138,430 | 136,951 | 135,472 | |
| 6" | 40,1 | 28,6 | 163,830 | 162,351 | 160,872 | |
Round thread for sanitary fittings, Kr
Round thread for sanitary fittings. Threads are used for spindles, valves, faucets, toilet and water taps.
NPSM (National pipe thread) thread
Inch cylindrical pipe thread NPSM) - American thread standard according to ANSI / ASME B1.20.1. The standard covers thread sizes from 1/16" to 24" for ANSI/ASME B36.10M, BS 1600, BS EN 10255 and ISO 65 pipes.
| Size designation threads |
Threads per inch | Thread length | Thread diameter in the main plane | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Working | From the end of the pipe to the main plane | Outer d=D |
Average d 2 =D 2 |
Interior d 1 =D 1 |
||
| 1/16" | 27 | 6,5 | 4,064 | 7,895 | 7,142 | 6,389 |
| 1/8" | 7,0 | 4,572 | 10,272 | 9,519 | 8,766 | |
| 1/4" | 18 | 9,5 | 5,080 | 13,572 | 12,443 | 11,314 |
| 3/8" | 10,5 | 6,096 | 17,055 | 15,926 | 14,797 | |
| 1/2" | 14 | 13,5 | 8,128 | 21,223 | 19,772 | 18,321 |
| 3/4" | 14,0 | 8,611 | 26,568 | 25,117 | 23,666 | |
| 1" | 11½ | 17,5 | 10,160 | 33,228 | 31,461 | 29,694 |
| 1¼" | 18,0 | 10,668 | 41,985 | 40,218 | 38,451 | |
| 1½" | 18,5 | 10,668 | 48,054 | 46,287 | 44,520 | |
| 2" | 19,0 | 11,074 | 60,092 | 58,325 | 56,558 | |
| 2½" | 8 | 72,699 | ||||
| 3" | 88,608 | |||||
| 3½" | 101,316 | |||||
| 4" | 113,973 | |||||
| 5" | 141,300 | |||||
| 6" | 168,275 | |||||
| 8" | 219,075 | |||||
| 10" | 273,050 | |||||
| 12" | 323,850 | |||||
NPT thread (National pipe thread)
Inch pipe thread cone NPT) - American standard for threads with a taper of 1:16 (cone angle φ=3°34’48") or cylindrical (eng. NPS) carving ANSI/ASME B1.20.1. Thread NPT complies with GOST 6111-52. Conical inch thread with a profile angle of 60 degrees. There is also an NPTF thread - compaction occurs due to the compression of the threads. The standard provides thread sizes from 1/16" to 24" for pipes according to standards ANSI/ASME B36.10M, BS 1600, BS EN 10255 And ISO 65.
The profile angle at the apex is 60°, the theoretical profile height is Н=0.866025Р.
| Size designation threads |
Threads per inch | Thread length | Thread diameter in the main plane | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Working | From the end of the pipe to the main plane | Outer d=D |
Average d 2 =D 2 |
Interior d 1 =D 1 |
||
| 1/16" | 27 | 6,5 | 4,064 | 7,895 | 7,142 | 6,389 |
| 1/8" | 7,0 | 4,572 | 10,272 | 9,519 | 8,766 | |
| 1/4" | 18 | 9,5 | 5,080 | 13,572 | 12,443 | 11,314 |
| 3/8" | 10,5 | 6,096 | 17,055 | 15,926 | 14,797 | |
| 1/2" | 14 | 13,5 | 8,128 | 21,223 | 19,772 | 18,321 |
| 3/4" | 14,0 | 8,611 | 26,568 | 25,117 | 23,666 | |
| 1" | 11½ | 17,5 | 10,160 | 33,228 | 31,461 | 29,694 |
| 1¼" | 18,0 | 10,668 | 41,985 | 40,218 | 38,451 | |
| 1½" | 18,5 | 10,668 | 48,054 | 46,287 | 44,520 | |
| 2" | 19,0 | 11,074 | 60,092 | 58,325 | 56,558 | |
| 2½" | 8 | 72,699 | ||||
| 3" | 88,608 | |||||
| 3½" | 101,316 | |||||
| 4" | 113,973 | |||||
| 5" | 141,300 | |||||
| 6" | 168,275 | |||||
| 8" | 219,075 | |||||
| 10" | 273,050 | |||||
| 12" | 323,850 | |||||
Notes
see also
| ISO Standards | |
|---|---|
| Lists: List of ISO standards List of ISO romanizations List of IEC standards Categories: Category:ISO Standards Category:OSI Protocols |
|
| 1 By 9999 |
1 2 4 7 16 (-0, -1, -2, -3, -4, -5, -6, -7, -8, -9, -10, -11, -12, -13) 128 226 228 259 269 296 302 306 428 ( , , , -5, -6) 690 732 764 843 898 1000 1007 1073-1 1413 1538 1745 2014 2015 2022 2145 2146 2281 2709 2711 2788 3029 ( , , ) 3307 3602 3864 3977 4031 4157 5776 5964 6166 6344 6346 6425 6429 6438 6523 6709 7001 7002 7388 7736 7810 7811 7812 7813 7816 8000 8217 8571 8652 8691 8807 8820-5 ( , , , , , , , , , -10 , -11 , -12, -13 , -14 , -15 , -16) 9126 9407 9506 9529 9564 9897 9984 9985 9995 |
| 10000 By 19999 |
10006 10118-3 10160 10161 10165 10206 10303 10303-11 10303-21 10303-22 10303-238 10303-28 10383 10585 10589 10664 10746 10861 10957 10962 10967 11073 11170 11179 11404 11544 11783 11784 11785 11801 11898 |
This article will discuss concepts related to threaded connections such as metric and inch threads. To understand the intricacies associated with a threaded connection, it is necessary to consider the following concepts:
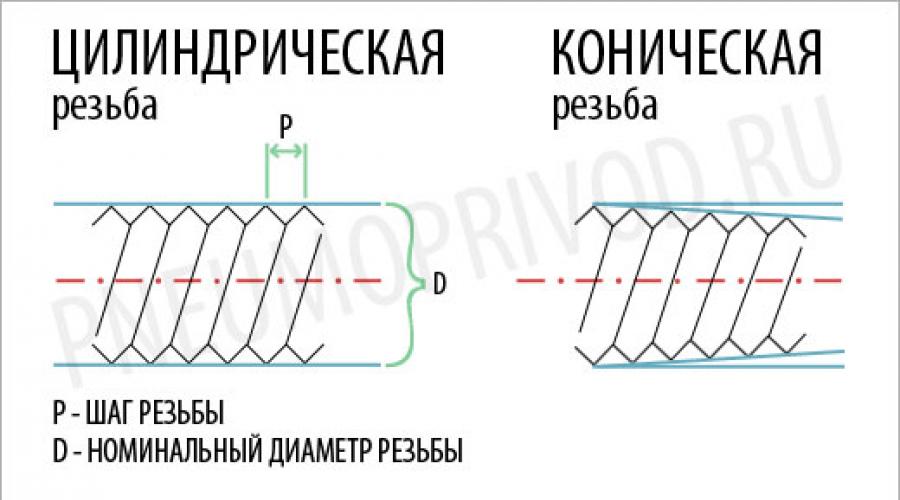
Tapered and cylindrical threads
The rod itself with tapered thread is a cone. Moreover, according to international rules, the taper should be 1 to 16, that is, for every 16 units of measurement (millimeters or inches) with increasing distance from the starting point, the diameter increases by 1 corresponding unit of measurement. It turns out that the axis around which the thread is applied and the conditional straight line drawn from the beginning of the thread to its end along the shortest path are not parallel, but are at a certain angle to each other. To explain it even more simply, if we had a threaded connection length of 16 centimeters, and the diameter of the rod at its starting point was 4 centimeters, then at the point where the thread ends, its diameter would already be 5 centimeters.
Rod with cylindrical thread is a cylinder, therefore there is no taper.
Thread pitch (metric and inch)
 The thread pitch can be large (or main) and small. Under thread pitch refers to the distance between the threads from the top of the thread to the top of the next thread. You can even measure it using a caliper (although there are also special meters). This is done as follows - the distance between several tops of the turns is measured, and then the resulting number is divided by their number. You can check the measurement accuracy using the table for the corresponding step.
The thread pitch can be large (or main) and small. Under thread pitch refers to the distance between the threads from the top of the thread to the top of the next thread. You can even measure it using a caliper (although there are also special meters). This is done as follows - the distance between several tops of the turns is measured, and then the resulting number is divided by their number. You can check the measurement accuracy using the table for the corresponding step.
| Cylindrical pipe thread according to GOST 6357-52 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Designation | Number of threads N by 1" |
Thread pitch S, mm |
Outside diameter thread, mm |
Average diameter thread, mm |
Inner diameter thread, mm |
| G1/8" | 28 | 0,907 | 9,729 | 9,148 | 8,567 |
| G1/4" | 19 | 1,337 | 13,158 | 12,302 | 11,446 |
| G3/8" | 19 | 1,337 | 16,663 | 15,807 | 14,951 |
| G1/2" | 14 | 1,814 | 20,956 | 19,754 | 18,632 |
| G3/4" | 14 | 1,814 | 26,442 | 25,281 | 24,119 |
| G7/8" | 14 | 1,814 | 30,202 | 29,040 | 27,878 |
| G1" | 11 | 2,309 | 33,250 | 31,771 | 30,292 |
Nominal thread diameter
The labeling usually contains nominal diameter, which in most cases is taken to be the outer diameter of the thread. If the thread is metric, then you can use a regular caliper with scales in millimeters to measure. Also, the diameter, as well as the thread pitch, can be viewed using special tables.
Metric and inch threads with examples
 Metric thread
– has the designation of the main parameters in millimeters. For example, consider an elbow fitting with an external cylindrical thread. EPL 6-GM5. IN in this case EPL says that the fitting is angled, 6 is 6 mm - the outer diameter of the tube connected to the fitting. The letter “G” in its marking indicates that the thread is cylindrical. “M” indicates that the thread is metric, and the number “5” indicates the nominal diameter of the thread, equal to 5 millimeters. Fittings (from those we have on sale) with the letter “G” are also equipped with a rubber o-ring, and therefore do not require fum tape. The thread pitch in this case is 0.8 millimeters.
Metric thread
– has the designation of the main parameters in millimeters. For example, consider an elbow fitting with an external cylindrical thread. EPL 6-GM5. IN in this case EPL says that the fitting is angled, 6 is 6 mm - the outer diameter of the tube connected to the fitting. The letter “G” in its marking indicates that the thread is cylindrical. “M” indicates that the thread is metric, and the number “5” indicates the nominal diameter of the thread, equal to 5 millimeters. Fittings (from those we have on sale) with the letter “G” are also equipped with a rubber o-ring, and therefore do not require fum tape. The thread pitch in this case is 0.8 millimeters.
Main settings inch thread , according to the name, are indicated in inches. This can be a 1/8, 1/4, 3/8 and 1/2 inch thread, etc. For example, let's take a fitting EPKB 8-02. EPKB is a type of fitting (in this case a splitter). The thread is conical, although there is no reference to this using the letter “R”, which would be more correct. 8 - indicates that the outer diameter of the connected tube is 8 millimeters. A 02 - that the connecting thread on the fitting is 1/4 inch. According to the table, the thread pitch is 1.337 mm. The nominal thread diameter is 13.157 mm.
The profiles of the conical and cylindrical threads coincide, which allows fittings with conical and cylindrical threads to be screwed together.
MAIN PARAMETERS OF INCH THREADS
(BSW (Ww), BSF, UNC, UNF standards)
The peaks and valleys of the inch thread profile, similar to the metric thread, are cut flat. The pitch of an inch thread is determined by the number of threads (turns) per inch 1", but its apex angle is 55° (Whitworth thread - British standard BSW (Ww) and BSF), apex angle is 60° (American standard UNC and UNF ).
The outer diameter of the thread is measured in inches 1" = 25.4 mm- bar (") symbol for inches. Inch thread is characterized by the number of threads per inch. According to American standards, inch threads are made with coarse (UNC) and fine (UNF) pitch.
NPSM- American standard for inch cylindrical pipe threads.
NPT- American standard for inch conical threads.
Standards:
ASME/ANSI B1.1– 2003 Unified Inch Screw Threads, UN & UNR Thread Form
ASME/ANSI B1.10M– 2004 Unified Miniature Screw Threads
ASME/ANSI B1.15– 1995 Unified Inch Screw Threads, UNJ Thread Form
AMERICAN INCH THREAD
Basic parameters of inch thread:
d(D)– outer diameter of the thread of the bolt and nut, respectively;
d p (D p)– average thread diameter of the bolt and nut, respectively;
d i (D i)– internal diameter of the thread of the bolt and nut, respectively;
n– number of threads per inch.
American thread with coarse pitch - UNS
|
Thread sizes, inches (mm) |
D |
Dp |
D i |
Thread sizes, inches (mm) |
D |
Dp |
D i |
||
|
№1 (1,8542) | |||||||||
|
№2 (2,1844) |
1 (25,4) |
||||||||
|
№3 (2,5146) |
1 1/8 (28,58) |
||||||||
|
№4 (2,8448) |
1 1/4 (31,75) |
||||||||
|
№5 (3,1750) |
1 3/8 (34,925) |
||||||||
|
№6 (3,5052) |
1 1/2 (38,10) |
||||||||
|
№8 (4,1656) |
1 3/4 (44,45) |
||||||||
|
№10 (4,8260) |
|||||||||
|
№12 (5,4864) |
2 (50,8) |
||||||||
|
2 1/4 (57,15) |
|||||||||
|
1/4 (6,3500) |
2 1/2 (63,5) |
||||||||
|
5/16 (7,9375) |
2 3/4 (69,85) |
||||||||
|
3/8 (9,5250) |
|||||||||
|
7/16 (11,1125) |
3 (76,2) |
||||||||
|
1/2 (12,700) |
3 1/4 (82,55) |
||||||||
|
9/16 (14,2875) |
3 1/2 (88,9) |
||||||||
|
5/8 (15,8750) |
3 3/4 (95,25) |
||||||||
|
3/4 (19,0500) |
4 (101,6) |
||||||||
|
7/8 (22,2250) |
|||||||||
American fine pitch thread - UNF
|
Thread sizes, inches (mm) |
D |
Dp |
D i |
Thread sizes, inches (mm) |
D |
Dp |
D i |
||
|
№0 (1,524) |
3/8 (9,525) |
||||||||
|
№1 (1,8542) |
7/16 (11,1125) |
||||||||
|
№2 (2,1844) |
1/2 (12,700) |
||||||||
|
№3 (2,5146) |
9/16 (14,2875) |
||||||||
|
№4 (2,8448) |
5/8 (15,875) |
||||||||
|
№5 (3,1750) |
3/4 (19,050) |
||||||||
|
№6 (3,5052) |
7/8 (22,225) |
||||||||
|
№8 (4,1656) |
|||||||||
|
№10 (4,8260) |
1 (25,4) |
||||||||
|
№12 (5,4864) |
1 1/8 (28,58) |
||||||||
|
1 1/4 (31,75) |
|||||||||
|
1/4 (6,350) |
1 3/8 (34,925) |
||||||||
|
5/16 (7,9375) |
1 1/2 (38,10) |
||||||||
American thread with extra fine pitch – UNEF
|
Thread sizes, inches (mm) |
D |
Dp |
D i |
Thread sizes, inches (mm) |
D |
Dp |
D i |
||
|
№12 (5,4864) |
|||||||||
|
1 (25,4) |
|||||||||
|
1/4 (6,350) |
1 1/16 (26,987) |
||||||||
|
5/16 (7,9375) |
1 1/8 (28,58) |
||||||||
|
3/8 (9,525) |
1 3/16 (30,162) |
||||||||
|
7/16 (11,1125) |
1 1/4 (31,75) |
||||||||
|
1/2 (12,700) |
1 5/16 (33,337) |
||||||||
|
9/16 (14,2875) |
1 3/8 (34,925) |
||||||||
|
5/8 (15,875) |
1 7/16 (36,512) |
||||||||
|
11/16 (17,462) |
1 1/2 (38,10) |
||||||||
|
3/4 (19,050) |
1 9/16 (39,687) |
||||||||
|
13/16 (20,637) |
1 5/8 (41,27) |
||||||||
|
7/8 (22,225) |
1 11/16 (42,86) |
||||||||
|
15/16 (23,812) |
|||||||||
Thread sizes are the outer diameter of the thread expressed in fractional inches. One of the main characteristics of an inch screw thread is the number of turns per inch of thread length (n). The number of turns and thread pitch P are related by the relation:
American standards provide two thread forms:
A thread with a flat recess, which is designated by the letters UN;
- thread with a radius cavity, which is designated by the letters UNR.
The standard defines three classes of thread accuracy. These classes are designated as 1A, 2A, 3A, 1B, 2B, 3B. Accuracy classes 1A, 2A, 3A refer to external threads; accuracy classes 1B, 2B, 3B refer to internal threads. Accuracy class 1A, 1B is the coarsest and is used in cases where quick and easy assembly is required, even with partially dirty and dented threads. Accuracy class 2A, 2B are the most common and are used for general threads appointments. Accuracy class 3A, 3B imposes the most stringent requirements on threads and is used in cases where it is necessary to ensure a minimum clearance in a threaded connection.
Thread designation. First, the nominal size is written down, then the number of threads per inch of thread, thread group symbols and accuracy class symbol. The letters LH at the end of the entry indicate left-hand thread. Nominal size is the outside diameter, defined as a fractional size or thread number, or their decimal equivalent.
For example: 1/4 – 20UNS – 2A or 0.250 – 20UNC – 2A
BRITISH STANDARD INCH THREADS
(BSW (Ww) and BSF)
| Designation threads | BSP size in |
thread pitch | largest diameter | smallest diameter | A/F mm |
length mm |
pipes | thread hole diameter (for drill) mm |
||||||||
| in (TPI) |
mm | mm | in | mm | in | DN mm |
O.D. mm |
O.D. in |
thickness mm |
BSP.PL (Rp) |
BSP.F (G) |
|||||
| -1 | 1 / 16 | 28 | 0,907 | 7,723 | 0,304 | 6,561 | 0,2583 | 4±0.9 | 6,60 | 6,80 | ||||||
| -2 | 1 / 8 | 28 | 0,907 | 9,728 | 0,383 | 8,565 | 0,3372 | 15 | 4±0.9 | 6 | 10,2 | 0,40 | 2 | 8,60 | 8,80 | |
| -4 | 1 / 4 | 19 | 1,337 | 13,157 | 0,518 | 11,445 | 0,4506 | 19 | 6±1.3 | 8 | 13,5 | 0,53 | 2,3 | 11,50 | 11,80 | |
| -6 | 3 / 8 | 19 | 1,337 | 16,662 | 0,656 | 14,950 | 0,5886 | 22/23 | 6.4±1.3 | 10 | 17,2 | 0,68 | 2,3 | 15,00 | 15,25 | |
| -8 | 1 / 2 | 14 | 1,814 | 20,955 | 0,825 | 18,633 | 0,7336 | 27 | 8.2±1.8 | 15 | 21,3 | 0,84 | 2,6 | 18,75 | 19,00 | |
| -10 | 5 / 8 | 14 | 1,814 | 22,911 | 0,902 | 20,589 | 0,8106 | 16 | 2,6 | - | 21,00 | |||||
| -12 | 3 / 4 | 14 | 1,814 | 26,441 | 1,041 | 24,120 | 0,9496 | 32 | 9.5±1.8 | 20 | 26,9 | 1,06 | 2,6 | 24,25 | 24,50 | |
| -16 | 1 | 11 | 2,309 | 33,249 | 1,309 | 30,292 | 1,1926 | 43 | 10.4±2.3 | 25 | 33,7 | 1,33 | 3,2 | 30,40 | 30,75 | |
| -20 | 1 1 / 4 | 11 | 2,309 | 41,910 | 1,650 | 38,953 | 1,5336 | 53 | 12.7±2.3 | 32 | 42,4 | 1,67 | 3,2 | 39,00 | 39,50 | |
| -24 | 1 1 / 2 | 11 | 2,309 | 47,803 | 1,882 | 44,846 | 1,7656 | 57 | 12.7±2.3 | 40 | 48,3 | 1,90 | 3,2 | 45,00 | 45,00 | |
| -32 | 2 | 11 | 2,309 | 59,614 | 2,347 | 56,657 | 2,2306 | 70 | 15.9±2.3 | 50 | 60,3 | 2,37 | 3,6 | 56,75 | 57,00 | |
| -40 | 2 1 / 2 | 11 | 2,309 | 75,184 | 2,960 | 72,227 | 2,8436 | 17.5±3.5 | 65 | 76,1 | 3,00 | 3,6 | ||||
| -48 | 3 | 11 | 2,309 | 87,884 | 3,460 | 84,927 | 3,3436 | 20.6±3.5 | 80 | 88,9 | 3,50 | 4 | ||||
| -64 | 4 | 11 | 2,309 | 113,030 | 4,450 | 110,073 | 4,3336 | 25.5±3.5 | 100 | 114,3 | 4,50 | 4,5 | ||||
| -80 | 5 | 11 | 2,309 | 138,430 | 5,450 | 135,472 | 5,3335 | 28.6±3.5 | 125 | 139,7 | 5,50 | 5 | ||||
| -96 | 6 | 11 | 2,309 | 163,830 | 6,450 | 160,872 | 6,3335 | 28.6±3.5 | 150 | 165,1 | 6,50 | 5 | ||||
Related documents:
GOST 3469-91 - Microscopes. Lens thread. Dimensions
GOST 4608-81 - Metric thread. Preference fits
GOST 5359-77 - Eyepiece thread for optical instruments. Profile and dimensions
GOST 6042-83 - Edison round thread. Profiles, dimensions and limits
GOST 6111-52 - Conical inch thread with a profile angle of 60 degrees
GOST 6211-81 - Tapered pipe thread
GOST 6357-81 - Cylindrical pipe thread
GOST 8762-75 - Thread round diameter 40 mm for gas masks and calibers for it. Main Dimensions
GOST 9000-81 - Metric threads for diameters less than 1 mm. Tolerances
GOST 9484-81 - Trapezoidal thread. Profiles
GOST 9562-81 - Single-start trapezoidal thread. Tolerances
GOST 9909-81: Tapered thread of valves and gas cylinders
GOST 10177-82 - Persistent thread. Profile and main dimensions
GOST 11708-82 - Thread. Terms and Definitions
GOST 11709-81 - Metric thread for plastic parts
GOST 13535-87 - Reinforced thrust thread 45 degrees
GOST 13536-68 - Round thread for sanitary fittings. Profile, main dimensions, tolerances
GOST 16093-2004 - Metric thread. Tolerances. Landings with clearance
GOST 16967-81 - Metric threads for instrument making. Diameters and pitches
GOST 24737-81: Single-start trapezoidal thread. Main Dimensions
GOST 24739-81 - Multi-start trapezoidal thread
GOST 25096-82 - Persistent thread. Tolerances
GOST 25229-82 - Metric tapered thread
GOST 28487-90: Conical locking threads for drill string elements. Profile. Dimensions. Tolerances
It would seem that there is something complicated in the pipes? Connect and twist... But, if you are not a plumber or an engineer with a specialized education, then you will definitely have questions for answers to which you will have to go wherever you look. And most likely the first thing they look at is the Internet)
Earlier we already talked about diameters metal pipes in this material. Today we will try to clarify the threaded connections of pipes for various purposes. We tried not to clutter the article with definitions. Basic terminology contains GOST 11708-82 which everyone can familiarize themselves with.
Pipe cylindrical thread. GOST 6357 - 81

Direction: Left
Accuracy class: Class A (increased), Class B (normal)
Why in inches?
The inch size came to us from Western colleagues, since the requirements of the current in the post-Soviet space GOST and are formulated on the basis of thread B.S.W.(British Standard Whitworth or Whitworth carving). Joseph Whitworth (1803 - 1887) design engineer and inventor back in 1841 demonstrated the screw profile of the same name for detachable connections and positioned it as a universal, reliable and convenient standard.
This type of thread is used both in the pipes themselves and in the elements of pipe connections: locknuts, couplings, elbows, tees ( see picture above). In the profile section we see isosceles triangle with an angle of 55 degrees and roundings at the tops and bottoms of the contour, which are made for high tightness of the connection.
Threading of threaded connections is carried out on sizes up to 6”. All larger pipes are fixed by welding to secure the connection and prevent rupture.
Symbol in the international standard
International: G
Japan: PF
UK: BSPP
The letter G and the bore diameter (internal Ø) of the pipe are indicated in inches. The outer diameter of the thread itself is not included in the designation.
Example:
G 1/2- cylindrical external pipe thread, internal pipe Ø 1/2"". The outer diameter of the pipe will be 20.995 mm, the number of steps over a length of 25.4 mm will be 14.
The accuracy class (A, B) and the direction of turns (LH) can also be indicated.
For example:
G 1 ½ - B- cylindrical pipe thread, internal Ø 1 ½ inches, accuracy class B.
G1 ½ LH- B- cylindrical pipe thread, internal Ø 1 ½ inches, accuracy class B, left.
The make-up length is indicated by the last one in mm: G 1 ½ -B-40.
For internal pipe cylindrical threads, only the Ø of the pipe for which the hole is intended will be indicated.
Parallel Pipe Thread Size Chart
| Thread size |
Thread pitch, mm |
Threads per inch |
Thread diameters |
|||
How to determine the pitch of an inch thread

I’ll give you a picture from the English-language Internet that clearly demonstrates the technique. Pipe threads are characterized not by the size between the tops of the profile, but by the number of turns per 1 inch along the thread axis. A regular tape measure or ruler can help. Apply it, measure one inch (25.4 mm) and visually count the number of steps.
In the picture with an example ( see above) threads - from English these are literally “threads of thread”. In this case there are 18 of them. by one inch.
It’s even easier if you have a thread gauge for inch threads lying around in your tool box. It is very convenient to take measurements, but it must be remembered that inch threads may differ in the apex angle of 55° and 60°.
Tapered pipe threads


drawing of pipe tapered threads
Tapered pipe thread GOST 6211-81 (1st standard size)
Parameter Unit: Inch
Corresponds to the rounded profile of a cylindrical pipe thread with an angle of 55°. Cm. top part (I) of the three-dimensional image "drawing of pipe tapered threads".
Symbol
International: R
Japan: PT
UK: BSPT
The letter R and the nominal diameter Dy are indicated. The designation R means external view thread, Rc internal, Rp internal cylindrical. By analogy with cylindrical pipe threads, LH is used for left-hand threads.
Examples:
R1 ½- external pipe thread, nominal diameter Dy = 1 ½ inches.
R1 ½ LH- external pipe thread, nominal diameter Dy = 1 ½ inches, left.
Conical inch thread GOST 6111 - 52 (2nd standard size)
Parameter Unit: Inch
Has a profile angle of 60°. Cm. lower part (II) of the three-dimensional image "drawing of pipe tapered threads". It is used in pipelines (fuel, water, air) of machines and machines with relatively low pressure. Usage of this type connection assumes tightness and thread locking without additional special means(linen threads, yarn with red lead).
Symbol
Example:K ½ GOST 6111 - 52
It stands for: inch conical thread with an outer and inner diameter in the main plane approximately equal to the outer and inner Ø of a cylindrical pipe thread G ½
Table of main parameters of tapered inch threads
| Thread size designation (d, inches) | Number of threads per 1" n | Thread pitch S, mm | Thread length, mm | Outer thread diameter in the main plane d, mm | |
| Working l1 | From the end of the pipe to the main plane l2 | ||||
| 1/16 | 27 | 0,941 | 6,5 | 4,064 | 7,895 |
| 1/8 | 27 | 0,941 | 7,0 | 4,572 | 10,272 |
| 1/4 | 18 | 1,411 | 9,5 | 5,080 | 13,572 |
| 3/8 | 18 | 1,411 | 10,5 | 6,096 | 17,055 |
| 1/2 | 14 | 1,814 | 13,5 | 8,128 | 21 793 |
| 3/4 | 14 | 1,814 | 14,0 | 8,611 | 26,568 |
| 1 | 11 1/2 | 2,209 | 17,5 | 10,160 | 33,228 |
| 1 1/4 | 11 1/2 | 2,209 | 18,0 | 10,668 | 41,985 |
| 1 1/2 | 11 1/2 | 2,209 | 18,5 | 10,668 | 48,054 |
| 2 | 11 1/2 | 2,209 | 19,0 | 11,074 | 60,092 |
Metric tapered thread. GOST 25229 - 82

Parameter unit: mm
Produced on surfaces with a taper of 1:16
Used when connecting pipelines. The angle at the top of the turn is 60°. The main plane is shifted relative to the end ( see pic above).
Symbol
The letters MK are followed by an indication of the diameter in the main plane and the thread pitch in mm: MK 30x2
Metric Tapered Thread Size Chart
| Thread diameter d for row | Step P | Thread diameter in the main plane | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | d = D | d2=D2 | d1=D1 | l | l1 | l2 | |
| 6 | --- | 1 | 6,000 | 5,350 | 4,917 | 8 | 2,5 | 3 |
| 8 | --- | 8,000 | 7,350 | 6,917 | ||||
| 10 | --- | 10,000 | 9,350 | 8,917 | ||||
| 12 | --- | 1,5 | 12,000 | 11,026 | 10,376 | 11 | 3,5 | 4 |
| --- | 14 | 14,000 | 13,026 | 12,376 | ||||
| 16 | --- | 16,000 | 15,026 | 14,376 | ||||
| --- | 18 | 18,000 | 17,026 | 16,376 | ||||
| 20 | --- | 20,000 | 19,026 | 18,376 | ||||
| --- | 22 | 22,000 | 21,026 | 20,376 | ||||
| 24 | --- | 24,000 | 23,026 | 22,376 | ||||
| --- | 27 | 2 | 27,000 | 25,701 | 24,835 | 16 | 5 | 6 |
| 30 | --- | 30,000 | 28,701 | 27,835 | ||||
| --- | 33 | 33,000 | 31,701 | 30,835 | ||||
| 36 | --- | 36,000 | 34,701 | 33,835 | ||||
Characteristics of cylindrical pipe/inch threads relative to metric
The main characteristics of "inch" and "pipe" cylindrical threads in relation to "metric" threads for basic sizes.
|
Nominal thread diameter in dm |
Inch thread |
Pipe thread |
||||
|
outer diameter, mm |
number of threads per 1" |
outer diameter, mm |
number of threads per 1" |
|||