What to do if there are two phases in the outlet? How can two phases appear in a regular outlet? Is there a 2 phase power supply?
Read also
In the electrical equipment of residential apartment buildings, as well as in the private sector, three-phase and single-phase networks are used. Initially, the electrical network comes from a power plant with three phases, and most often a three-phase power network is connected to residential buildings. Further it has branches into separate phases. This method is used to create the most efficient transmission of electric current from a power plant to its destination, as well as to reduce losses during transportation.
To determine the number of phases in your apartment, just open the distribution board located on the landing, or right in the apartment, and see how many wires enter the apartment. If the network is single-phase, then there will be 2 wires -. Another possible third wire is grounding.
Three-phase networks in apartments are rarely used, in cases of connecting old electric stoves with three phases, or powerful loads in the form of a circular saw or heating devices. The number of phases can also be determined by the input voltage. In a 1-phase network the voltage is 220 volts, in a 3-phase network between phase and zero it is also 220 volts, between 2 phases it is 380 volts.
Differences
If we do not take into account the difference in the number of network wires and the connection diagram, then we can determine some other features that three-phase and single-phase networks have.
- In the case of a three-phase power supply, phase imbalance is possible due to uneven distribution of load phases. A powerful heater or stove can be connected to one phase, and a TV and washing machine to the other. Then this negative effect occurs, accompanied by asymmetry of voltages and currents in phases, which leads to malfunctions of household devices. To prevent such factors, it is necessary to pre-distribute the load across phases before laying the electrical network wires.
- A 3-phase network requires more cables, conductors and switches, which means you won't be able to save too much money.
- The power capabilities of a single-phase household network are significantly less than those of a three-phase network. If you plan to use several powerful consumers and household devices, power tools, then it is preferable to supply a three-phase power supply to the house or apartment.
- The main advantage of a 3-phase network is the low voltage drop compared to a 1-phase network, provided the power is the same. This can be explained by the fact that in a 3-phase network, the current in the phase conductor is three times less than in a 1-phase network, and there is no current at all on the conductor.

Advantages of a 1-phase network
The main advantage is the cost-effectiveness of its use. Such networks use three-wire cables, compared to five-wire cables in 3-phase networks. To protect equipment in 1-phase networks, you need to have single-pole protective circuit breakers, while in 3-phase networks you cannot do without three-pole circuit breakers.
In this regard, the dimensions of the protection devices will also differ significantly. Even on one electric machine there is already a saving of two modules. And in terms of dimensions it is about 36 mm, which will significantly affect when placing the machines in. And during installation, the space saving will be more than 100 mm.
Three-phase and single-phase networks for a private home
Electricity consumption by the population is constantly increasing. In the middle of the last century, there were relatively few household appliances in private homes. Today the picture is completely different in this regard. Household energy consumers in private homes are multiplying by leaps and bounds. Therefore, in your own private property there is no longer a question of which power supply networks to choose for connection. Most often, in private buildings, power networks with three phases are installed, and a single-phase network is abandoned.
But is a three-phase network worth such superior installation? Many people believe that by connecting three phases, it will be possible to use a large number of devices. But this does not always work out. The maximum permissible power is determined in the technical conditions for connection. Typically, this parameter is 15 kW for the entire private household. In the case of a single-phase network, this parameter is approximately the same. Therefore, it is clear that there is no particular benefit in terms of power.
But, it must be remembered that if three-phase and single-phase networks have equal power, then for a 3-phase network it can be used, since the power and current are distributed over all phases, therefore, there is less load on the individual phase conductors. The rated current of the circuit breaker for a 3-phase network will also be lower.
The size is of great importance, which for a 3-phase network will be noticeably larger. This depends on the size of the three-phase one, which has dimensions larger than the single-phase one, and the input machine will also take up more space. Therefore, the distribution board for a three-phase network will consist of several tiers, which is a disadvantage of this network.
But three-phase power also has its advantages, which are expressed in the fact that three-phase current receivers can be connected. They can also be other powerful devices, which is an advantage of a three-phase network. The operating voltage of a 3-phase network is 380 V, which is higher than in a single-phase type, which means that more attention will have to be paid to electrical safety issues. The same applies to fire safety.
Disadvantages of a three-phase network for a private home
As a result, several disadvantages of using a three-phase network for a private home can be identified:
- You need to obtain technical conditions and permission to connect the network from the power supply.
- There is an increased risk of electric shock and also a risk of fire due to the increased voltage.
- Significant overall dimensions of the power input switchboard. For owners of country houses, this disadvantage is not of great importance, since they have enough space.
- Installation in the form of modules on the input panel is required. In a three-phase network this is especially true.
Advantages of three-phase power supply for private homes^
- It is possible to distribute the load evenly across phases to avoid phase imbalance.
- Powerful three-phase energy consumers can be connected to the network. This is the most tangible advantage.
- Reducing the nominal values of protection devices at the input, as well as reducing the input.
- In many cases, it is possible to obtain permission from the energy sales company to increase the permissible maximum level of power consumption of electricity.
As a result, we can conclude that practically introducing a three-phase power supply network is recommended for private buildings and houses with a living area of more than 100 m2. Three-phase power is especially suitable for those owners who are going to install a circular saw, a heating boiler, or various drive mechanisms with three-phase electric motors.
Other owners of private houses do not need to switch to three-phase power supply, as this can only create additional problems.
A three-phase connection makes it possible to switch on high-power generators and electric motors, as well as the ability to work with different voltage parameters, this depends on the type of load connection to the electrical circuit. To work in a three-phase network, you need to understand the relationship of its elements.
Three-phase network elements
The main elements of a three-phase network are a generator, an electrical energy transmission line, and a load (consumer). To consider the question of what linear and phase voltage is in a circuit, we will give a definition of what a phase is.
A phase is an electrical circuit in a system of multiphase electrical circuits. The beginning of the phase is the terminal or end of the electrical conductor through which the electric current enters it. Experts have always distinguished electrical circuits by the number of phases: single-phase, two-phase, three-phase and polyphase.
The most commonly used is three-phase connection of objects, which has a significant advantage over both multiphase circuits and single-phase circuits. The differences are as follows:
- lower costs for transporting electrical energy;
- the ability to create an EMF for the operation of asynchronous motors - this is the operation of elevators in multi-storey buildings, equipment in the office and in production;
- This type of connection makes it possible to simultaneously use both linear and phase voltage.
What is phase and line voltage?
Phase and line voltages in three-phase circuits are important for manipulations in electrical power panels, as well as for the operation of equipment powered by 380 volts, namely:
- What is phase voltage? This is the voltage that is determined between the beginning of a phase and its end; in practice, it is determined between the neutral wire and the phase.
- Line voltage is when the value is measured between two phases, between the terminals of different phases.
In practice, the phase voltage differs from the linear voltage by 60%, in other words, the parameters of the linear voltage are 1.73 times greater than the phase voltage. Three-phase circuits can have a line voltage of 380 volts, which makes it possible to obtain a phase voltage of 220 V.

What is the difference?
For society, the concept of “phase-to-phase voltage” is found in apartment buildings, high-rise buildings, when the first floors are provided for office space, as well as in shopping centers, when building objects are connected by several power cables of a three-phase network that provide a voltage of 380 Volts. This type of connection at home ensures the operation of asynchronous lift motors, the operation of escalators, and industrial refrigeration equipment.
In practice, wiring a three-phase circuit is quite simple, given that a phase and a neutral wire go to the apartment, and all three phases + a neutral wire go to the office space.

The difficulties of a linear connection diagram lie in the difficulty of identifying the conductor during installation, which can lead to equipment failure. The circuit differs mainly between phase and linear connections, connections of load windings and power supply.
Connection diagrams
There are two schemes for connecting voltage sources (generators) to the network:
- "triangle";
- "star".
When a star connection is made, the beginning of the generator windings are connected at one point. It does not provide the ability to increase power. A delta connection is when the windings are connected in series, namely, the beginning of the winding of one phase is connected to the end of the winding of the other. This gives the ability to triple the voltage.

For a better understanding of connection diagrams, experts define what phase and line currents are:
- line current is the current that flows in the connection between the source of electrical energy and the receiver (load);

- phase current is the current flowing in each winding of an electrical energy source or in the load windings.
Linear and phase currents are important when there is an asymmetrical load on the source (generator), this often occurs in the process of connecting objects to the power supply. All parameters related to the line are linear voltages and currents, and those related to the phase are parameters of phase quantities.
From the star connection it is clear that linear currents have the same parameters as phase currents. When the system is symmetrical, there is no need for a neutral wire; in practice, it maintains source symmetry when the load is asymmetrical.
Due to the asymmetry of the connected load (and in practice this happens with the inclusion of lighting devices in the circuit), it is necessary to ensure independent operation of the three phases of the circuit; this can also be done in a three-wire line, when the phases of the receiver are connected in a triangle.
Experts pay attention to the fact that when the line voltage decreases, the phase voltage parameters change. Knowing the value of the phase-to-phase voltage, you can easily determine the value of the phase voltage.
How to calculate line voltage?

and Ohm's law:

When an extensive system of supplying an object with electricity is being implemented, sometimes there is a need to calculate the voltage between two wires “zero” and “phase”: IF = IL, which indicates that the phase and linear parameters are equal. The relationship between phase wires and linear ones can be found using the formula:

Finding the element of voltage relationships and assessing the power supply system by specialists is performed using linear parameters when their value is known. Four-wire power supply systems are marked 380/220 volts.
Conclusion
Using the capabilities of a three-phase circuit (four-wire circuit), connections can be made in different ways, which makes it possible for its wide application. Experts consider three-phase voltage for connection to be a universal option, since it makes it possible to connect high-power loads, residential premises, and office buildings.
In apartment buildings, the main consumers are household appliances designed for a 220 V network; for this reason, it is important to distribute the load evenly between the phases of the circuit; this is achieved by connecting apartments to the network according to the checkerboard principle. The distribution of the load of private houses differs; in them it is carried out according to the load values on each phase of all household equipment, and the currents in the conductors passing during the period of maximum switching on of the devices.
Newcomers to the world of electrics and homeowners sometimes have the question of what is in household electrical wiring. This is due to the need to repair some electrical appliance.
In the situation that has arisen, the master’s highest priority should be compliance with safety regulations, and not the manifestation of applied skills and abilities. Knowledge of the elementary laws of the functioning of current and the processes taking place inside household electrical appliances will not only help to cope with the majority of malfunctions that arise in them, but will also make this process the safest.
Designers and engineers do everything possible to prevent accidents when working with electricity in the home. The consumer's task is to comply with the prescribed standards.
- single phase current;
- two-phase current;
- three-phase current.
Single phase current.
Alternating current, which is obtained by rotating a conductor or a system of conductors connected into one coil in a magnetic flux, is called single-phase alternating current.
As a rule, 2 wires are used to transmit single-phase current. They are called phase and zero, respectively. The voltage between these wires is 220 V.
Single phase power supply. Single phase current can be connected to the consumer in two different ways: 2-wire and 3-wire. In the first (two-wire) one, two wires are used to supply single-phase current. One carries phase current, the other is intended for the neutral wire. Thus, power supply is supplied to almost all houses built in the former USSR. In the second method for summing up single-phase current- add another wire. This wire is called grounding (PE). It is designed to prevent electric shock to a person, as well as to drain leakage currents and prevent devices from breaking.
Two-phase current.
Two-phase electric current is a set of two single-phase currents shifted in phase relative to each other by an angle Pi2 or 90 °.
A clear example of the formation of two-phase current. Let's take two inductance coils and arrange them in space so that their axes are mutually perpendicular, after which we power the system of coils two-phase current, as a result we get two magnetic fluxes in the system. The vector of the resulting magnetic field will rotate at a constant angular velocity, as a result, a rotating magnetic field appears. A rotor with windings made in the form of a short-circuited “squirrel wheel” or a metal cylinder on a shaft will rotate, driving the mechanisms.
They transmit two-phase currents using two wires: two phase and two neutral.
Three-phase current.
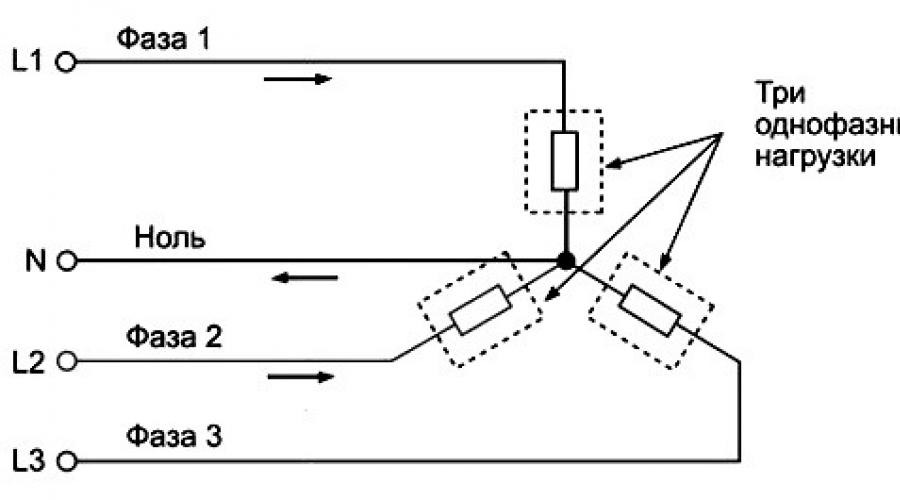
Three-phase electrical circuit system is called a system that consists of three circuits in which there are alternating emfs of the same frequency, shifted in phase relative to each other by 1/3 of the period (φ = 2π/3). Each individual circuit of such a system is briefly called its phase, and the system of three phase-shifted alternating currents in such circuits is simply called three-phase current. Three phase current easily transmitted over long distances. Any pair of phase wires has a voltage of 380 V. A pair - a phase wire and a neutral - has a voltage of 220 V.
Distribution three-phase current for residential buildings is performed in two ways: 4-wire and 5-wire. A four-wire connection is made with three phase and one neutral wire. After the distribution board, two wires are used to power sockets and switches - one of the phases and zero. The voltage between these wires will be 220V.
Five-wire connection of three-phase current - a protective grounding wire (PE) is added to the circuit. In a three-phase network, the phases must be loaded as evenly as possible, otherwise phase imbalance may occur. What kind of electrical wiring is used in the house determines what electrical equipment can be included in it. For example, grounding is required if high-power devices are connected to the network - refrigerators, stoves, heaters, electronic household appliances - computers, televisions, water-related devices - Jacuzzis, showers (water is a current conductor). Three-phase current is necessary to power motors (relevant for a private home).
Household electrical wiring.
Initially, electricity is generated at a power plant. Then, through the industrial electrical network, it enters the transformer substation, where the voltage is converted to 380 volts. The connection of the secondary windings of the step-down transformer is made according to the “star” circuit: three contacts are connected to the common point “0”, and the remaining three are connected to terminals “A”, “B” and “C”, respectively. For clarity, a picture is provided.
The combined contacts “0” are connected to the grounding loop of the substation. Also here the zero is split into:
- Working zero (shown in blue in the picture)
- PE conductor performing a protective function (yellow-green line)
Zeros and current phases from the output of the step-down transformer they are supplied to the distribution panel of the residential building. The resulting three-phase system is distributed across panels in the entrances. Ultimately, a phase voltage of 220 V and a PE conductor, which performs a protective function, enters the apartment.
So, what is zero? A zero is a current conductor connected to the ground loop of a step-down transformer and serves to create a load from the current phase connected to the opposite end of the transformer winding. In addition, there is a so-called “protective zero” - this is the PE contact described earlier. It serves to drain current when a technical malfunction occurs in the circuit.
This method of connecting residential buildings to the city power grid has been proven for decades, but it is still not ideal. Sometimes malfunctions appear in the above system. Most often, they are associated with poor connection quality in a certain section of the circuit or a complete break in the electrical wire.
What happens in zero and phase when a wire breaks.
A break in an electrical wire is often caused by the technician’s elementary absent-mindedness - forgetting to connect it to a certain device in the house current phase or zero - as easy as shelling pears. In addition, there are frequent cases of zero burnout on the access panel due to the high load on the system.
If the connection between any electrical appliance in the house and the panel is broken, this device stops working - because the circuit is not closed. In this case, it does not matter which wire is broken - zero or .

A similar situation occurs when a gap is observed between the distribution board of an apartment building and the board of a specific entrance - all apartments connected to the entrance board will be de-energized.
The situations described above do not cause serious difficulties and do not pose any danger. They are associated with the break of only one conductor and do not pose a threat to the safety of electrical appliances or people in the apartment.
The most dangerous situation is the disappearance of the connection between the grounding loop of the substation and the midpoint to which the load of the in-house electrical panel is connected.
In this case, the electric current will flow through circuits AB, BC, CA, and the total voltage on these circuits is 380 V. In this regard, a very unpleasant and dangerous situation will arise - there may be no voltage at all on one electrical panel, as the owner of the apartment considered it necessary turn off electrical appliances, and on another there will be a high voltage close to 380 volts. This will cause failure of most electrical appliances, because the rated operating voltage for them is 240 volts.
Of course, such situations can be prevented - there are quite expensive solutions for protection against power surges. Some manufacturers build them into their devices.
How to determine zero and phase on your own.
To determine the zero and phase of the current, there are special tester screwdrivers.

It works on the principle of passing low voltage current through the body of the person using it. The screwdriver consists of the following parts:
- Tip for connecting to the phase potential of the socket;
- A resistor that reduces the amplitude of the electric current to safe limits;
- LED that lights up when potential is present current phases in a chain;
- Flat contact to create a circuit through the operator's body.
The principle of working with a tester screwdriver is shown in the picture below.

In addition to test screwdrivers, there are other ways to determine which contact of the socket is connected to and which is zero. Some electricians prefer to use a more accurate tester by using it in voltmeter mode.

The voltmeter needle readings mean:
1. Presence of 220 V voltage between phase and zero
2. No voltage between ground and zero
3. No voltage between phase and zero
Actually, in the latter case the arrow should show 220 V, but in this particular case the central contact of the socket is not connected to ground potential.
In our rapidly developing information age, we have to keep abreast of all events, and the desire to learn more and apply knowledge in practice is increasing more and more. Even if the light suddenly goes out in the apartment or the outlet doesn’t work, we try to find the reasons ourselves and find a solution to why this is happening. It must be remembered that when working with electricity, it is important to follow safety precautions, do only what you are absolutely sure of and remember that if you handle electricity carelessly, you can feel the current and 220V voltage surge, which can lead to dire consequences.
The socket in the apartment does not work: what to do?
There is one fault in electrical wiring that confuses novice electricians. Although, at first glance, everything is in order: the machines are turned on, the wiring is intact, but the electrical appliances have stopped working, and the indicator on the screwdriver is on, thereby indicating the presence of two phases on both wires. This also indicates that the zero is missing. This phenomenon is not uncommon, but it will leave an inexperienced electrician scratching his head.

If your socket stops working, then an indicator screwdriver will help you check for the absence of a zero and the presence of another phase in the socket.
This situation has several consequences: all devices will remain working, or the equipment and lamps will simply burn out. The thing is that there are phases of the same name, and there are different phases. A common household appliance called a tester will help us figure out the type of phase in an outlet. It can be used to check various electrical parameters. To do this, you need to connect the device to an outlet and measure the voltage between two phases. If voltage is present, the phases are of the same name, and if it is absent, then the phase is of the same name.
Why there are two phases in the socket: a simple explanation
To get the answer to this question, it’s worth understanding a little about how electricity comes to our apartments. There are four wires from the main electrical main to the substation of high-rise buildings: zero and three phases - this is a three-phase network with a voltage of 380 volts. The phases are then separated to different sides of the courtyard. Each entrance switchboard receives one phase and one more neutral wire. This is a single-phase network and its voltage is 220 Volts. There are 2 wires coming from the access distribution board to the apartments (in new buildings, another wire is added - grounding).
Only one phase is supplied to the apartment through the electric meter and the circuit breaker panel.

Let's consider a situation where we wanted to hang a shelf in a room on the wall, connected a drill and started drilling the wall. Suddenly the machine on the dashboard goes off, the lights in the apartment go out and the drill stops working. However, using an indicator screwdriver, we established that there are two phases in the socket. Most likely, when drilling, we touched the wiring with the drill, and thus we managed to short-circuit 2 wires, which caused a short circuit and the circuit breaker tripped. Thus, we got the phase of the same name in our apartment. To eliminate this malfunction, it is necessary to de-energize the apartment, inspect the place where the drilling was carried out and connect the broken wire. In private sectors, where power lines are located on poles, it is possible that one of the phases shorts to the neutral wire when they come into contact. In this case, two opposite phases may appear in houses and this can lead to failure of household appliances.
There are two phases in the socket: what to do?
The presence of a phase on the neutral wire is due to the fact that the phase is under constant load: a refrigerator, light bulb or other electrical appliance. Electrical wiring in houses and apartments is designed in such a way that all wires are connected to the zero bus in the electrical panel. To make sure of this, just turn off all electrical appliances. So, all your devices are turned off, but a phase still appears on the neutral wire.
Universal solution methods:
- Turn off all electricity in the apartment;
- Check that each switch is set to the “off” position;
- Unplug all household appliances from the outlets, no matter how many you have;
- Visually diagnose a malfunction on the panel or at the work site;
- Call qualified electricians.
In any case, to reliably diagnose the true cause and eliminate the malfunction, you need to resort to qualified help.
Two phases in the socket: reasons and solution
There are a number of most likely reasons for the occurrence of two phases in an outlet - from the banal burnout of a safety plug or the shutdown of a circuit breaker on the electrical panel, to the shorting of wires and the appearance of induced currents.
3.jpg)
The most common reasons for the occurrence of two phases:
- Strong winds or tree branches have shorted the wires;
- A short circuit in which the braid of the wires melts and they close;
- Zero is closed to phase, for example, when drilling;
- Induced current – due to the presence of nearby high-voltage power lines;
- Overvoltage - an increase (up to 380 Volts) or a decrease (up to 40 Volts) in voltage values;
- The neutral wire burned out in the internal electrical wiring system.
When troubleshooting, you need to carefully analyze and consider all possible cases.
Reasons for appearance: two phases in the socket (video)
Remember, electricity punishes incompetence. If you don't know what to do or have any concerns about faulty wiring or appliances, call a professional immediately. This will help avoid unwanted consequences in more than half of cases, and can help save life and property.
In the normal state of the electrical wiring in the outlet, one contact has 220 Volts, and the second is not energized. This is ideal... Sometimes the indicator can show two phases in the socket at the same time.
To a novice electrician or amateur, such a situation may seem absurd, but it is reality. In some violations, this is exactly the picture observed.
Single-phase current of 230 volts is supplied to residential buildings. According to this diagram, it turns out that two phases cannot appear in the socket. In older buildings, the wiring is made of two-core cables. Along one line (phase) the current goes to the consumer, and along the other (zero) it returns.
With such a circuit, the reasons for the appearance of two phases in the plug connector may be different. New houses have grounding, which can cause accidents only if there is unqualified intervention in the electrical circuit of the home.
Break of zero at the input
If the zero wire in the incoming cable is disconnected, the lights in the apartment will go out and electrical appliances will stop. Checking with an indicator will show the presence of a phase on each contact of the socket. The classic question arises: “Who is to blame and what to do?”
In the absence of zero, the current searches for a free line. If the lamp is turned on, it does not light, but the phase through the filament passes to the neutral wire, then to the bus, and from there to the neutral line of sockets. The phase can also come from a device connected to any plug connector in the apartment.
Now there is a phase on each socket of the socket. The indicator emits a light signal when each contact is touched.
A multimeter helps to easily clarify the situation. If you measure the voltage difference between two phases, the device will show a zero value. It is clear that this is the same phase. It is enough to turn off the lamps and disconnect the devices from the sockets and the second phase in the socket will disappear, because the voltage and neutral supply lines do not have other connection points.
It is necessary to restore the incoming zero line. It is possible that the wire has simply become disconnected from the bus. This problem can be dealt with even at home. De-energize the apartment by opening the phase input and check the absence of voltage. Insert the neutral lead into the terminal and tighten the screw.
Breakage of the neutral wire in the junction box or in the wall
Sometimes a zero break occurs in the junction box. In this case, part of the apartment's wiring is functioning normally, but the line connected to this box is inoperative. It is enough to find where the zero broke off or burned out and restore the connection.
It happens that two phases appear in the plug connector due to damage to the neutral wire inside the wall. The cause of the malfunction is negligence when drilling holes. If you break the insulation by breaking through the wire, the neutral conductor will be welded to the phase conductor. In this case, there will also be two phases in the outlet. It is necessary to lay a new line or open the damaged area and repair the wiring.
Automatic protection on the zero line
In old houses, protective devices are installed at both phase and neutral (nowadays such a connection scheme is prohibited). If an overload occurs, it is possible that the circuit breaker will operate only on the zero line. The consequences are the same as if the zero broke off or burned off.
Induced currents
Everything works fine, but the indicator detects voltage on each pin of the plug connector. Moreover: the device shows two phases in the socket when the power supply to the entire apartment is turned off. This completely unrealistic situation can happen if a high-voltage power line runs near your home.
This is the so-called pickup or, to put it more correctly, induced voltage. Even experienced electricians can get confused here. Work in this case is associated with a high risk of electric shock, so only professionals should perform it.