How to treat dermatitis on a child’s body. Atopic dermatitis in children: how to completely cure it. What causes atopic dermatitis in children: causes of the disease
Read also
Dermatitis is a skin inflammation characterized by an increased reaction of the body to factors present in the external environment. This means that a child with dermatitis has a congenital or acquired tendency to allergic diseases. The development of dermatitis occurs in children in the first months of life, and is extremely rare after 4 years. The following groups of children are at higher risk of developing dermatitis:
- Children with one or both parents suffering from a certain form of allergy (food allergy, bronchial asthma, etc.);
- For those who suffer from frequent infectious diseases, as well as if the mother suffered from them during pregnancy, the reasons can always be in feeding;
- Frequently taking medications after birth or if the mother frequently took them during pregnancy;
- Born after a difficult pregnancy and childbirth;
- With improper feeding (artificial feeding with non-adapted formula milk, early complementary feeding, allergenic foods: chocolate, citrus fruits, eggs, nuts, etc.), all this provokes infantile dermatitis;
- After a long stay in an excessively chemicalized environment (dyes, exhaust gases, smoke, etc.)
- Insufficient hygiene measures for caring for children's skin (for the 1st year of life, in particular).
There are several types of childhood dermatitis with their own causes, course characteristics and treatment methods. Among the most common types of dermatitis in children are:
- Atopic;
- Contact;
- Diaper;
- Seborrheic.
Seborrheic dermatitis in a child
Seborrheic dermatitis of a child is an inflammation of the skin, most often found on the scalp (the localization of the disease may be different). The main symptom is the presence of yellow, greasy crusts on the surface of the skin.
Seborrheic dermatitis in babies is caused by the fungus Malassezia furfur, which multiplies on the surface of the child's skin and causes symptoms of the disease. The disease begins to develop on the part of the head where there is hair in children from infancy (2–3 weeks).
The main manifestation of seborrheic dermatitis in children is associated with oily, yellowish scales, or crusts (gneisses) on the scalp. Seborrheic dermatitis develops in children in such areas of the body as: the ears, neck, sternum, axillary and inguinal folds of the skin of the child’s body. Skin itching is practically not expressed or absent.
If seborrheic dermatitis is not treated, bacterial infections may develop, significantly complicating the course of the disease.
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis in children
In the process of treating seborrheic dermatitis in children, you should wash your hair with special shampoos every day and remove seborrheic crusts (gneisses) mechanically. For most children 6–8 weeks of age, symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp disappear spontaneously.
Sometimes pediatricians recommend the use of special agents in the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis. In the process of daily washing your hair with Nizoral or Quelual DS shampoos, skin inflammation with the formation of scales is significantly reduced.
This leads to a decrease in the activity of the fungus that contributes to seborrheic dermatitis. After the head is washed with shampoo and other affected areas are cleaned, the skin is dried, and special products are applied to the inflamed areas: Bioderma Sensibio DS cream, Saforel, Friederm zinc. Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis with medicated shampoos and creams is supervised by the attending physician.
Atopic dermatitis in children
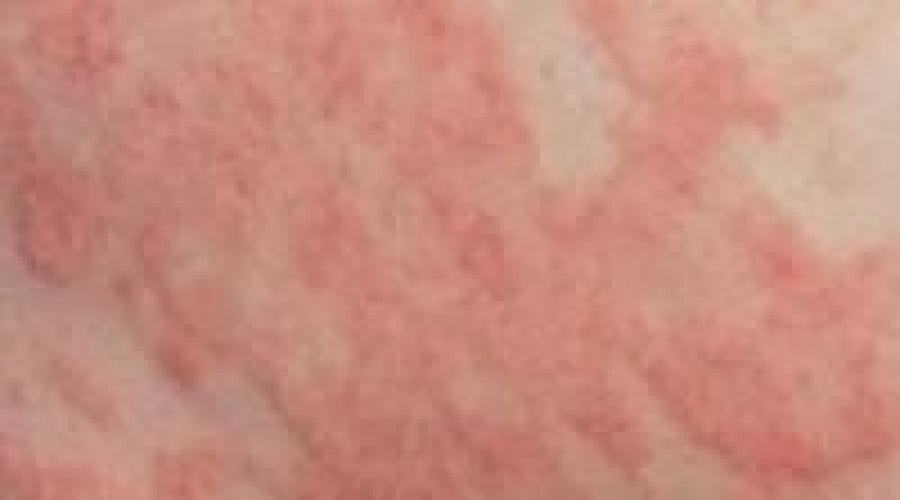
Atopic dermatitis in children is a skin inflammation characterized by the following symptoms: inflammation, dryness, redness, peeling of the skin, the appearance of blisters with liquid in the inflamed areas, and itching. At the moment, the cause of atopic dermatitis should be considered the innate predisposition of children's immunity to allergic reactions.
Reasons - the level of antibodies in the blood of children responsible for allergies (immunoglobulins type E, IgE), suffering from atopic  dermatitis, slightly increased. A small stimulus from the environment is enough for an allergic reaction to develop and go away.
dermatitis, slightly increased. A small stimulus from the environment is enough for an allergic reaction to develop and go away.
Most children with atopic dermatitis suffer from intestinal disease and dysbiosis (disturbed ratio of good and bad bacteria in the intestines). The development of atopic dermatitis in children mainly occurs before 6 months, but it also occurs somewhat later: up to 7 years, and even in adolescents and adults.
The main symptoms of atopic dermatitis in childhood (up to 2 years) are:
- Atopic dermatitis develops in children in the form of reddish rashes on the face, neck, flexor surfaces of joints (elbow joints, inguinal folds, etc.), buttocks;
- Redness of the skin;
- Peeling and dry skin;
- The appearance of cracks and bubbles with internal transparent liquid on the surface of the skin;
- Small yellowish crusts;
- Itching at the site of inflammation especially requires treatment.
- Characteristic symptoms of atopic dermatitis in childhood (2–7 years) are:
- Inflammation (rashes were discussed above), localized in the area of skin folds; atopic dermatitis of the palms and soles is possible;
- Protracted (chronic) atopic dermatitis, with exacerbations and remissions (symptoms disappear for a while);
- Thickening and dryness of inflamed areas of the skin with possible peeling or the presence of internal blisters with clear liquid;
- Severe itching of the skin and the sleep disorder that is associated with it.
If a child develops symptoms of atopic dermatitis, you should immediately contact a pediatrician and begin treatment, rather than looking for reasons for the necessary research and treatment. In addition to eliminating the symptoms, everything will be done to prevent a relapse (exacerbation) of the disease.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis in children
The main condition for remission (disappearance of symptoms) of atopic dermatitis is the elimination of irritating effects (allergens) on the child’s body. Without excluding the cause, the relapse will be permanent, so everything needs to be treated comprehensively.
For children suffering from atopic dermatitis, a hypoallergenic diet is recommended, during which chicken broth, egg whites, citrus fruits, chocolate, nuts, and cow's milk are excluded from the diet. Photos of atopic dermatitis clearly demonstrate its consequences.
 Treatment assumes that the diet of a child suffering from atopic dermatitis should include fermented milk products, various cereals, and pureed vegetables, the main thing is that it does not manifest itself.
Treatment assumes that the diet of a child suffering from atopic dermatitis should include fermented milk products, various cereals, and pureed vegetables, the main thing is that it does not manifest itself.
Children's clothing is also of utmost importance; there may be reasons for this as well. Exacerbation of atopic dermatitis can be provoked by wearing clothes made of wool and synthetic fabrics. The best option for a child is things made of cotton fabric; they will practically eliminate relapses, and the disease will not have to be treated.
The main method for the drug treatment of atopic dermatitis should be considered the use of topical glucocorticosteroids. These include ointments and creams based on glucocorticoids: Advantan, Afloderm, Lokoid, and antihistamines.
To facilitate stable remission of atopic dermatitis and the timely proper development of the children's immune system, doctors recommend drugs that are classified as immunomodulators.
Treatment with drugs also has contraindications: the prescription of immunomodulators is carried out exclusively by a doctor, as well as with an immunological examination of the child before the appointment, without fail.
The choice of drugs for independent use is made after undergoing the necessary safety studies, and does not require additional tests before use; this is the only way to treat a child.
Diaper dermatitis in children
Diaper dermatitis is characterized by inflammation of the delicate baby skin of the genitals, buttocks, and thighs (inner side). This occurs due to prolonged contact of this area of skin with urine and feces.
Diaper dermatitis can develop due to improper use of diapers (diapers that are larger or smaller than required rub the skin of the perineum, causing inflammation), infrequent washing, the use of irritating soaps when washing the child and washing clothes, an allergy to baby skin care cream , mother's dirty hands when changing diapers. In the photo, all the rashes are clearly visible with such an allergy.
The main symptoms of diaper dermatitis are expressed in redness of the skin, rashes in the perineal area, increased sensitivity of the skin in this area, if you touch it, itching. Children suffering from this disease are overly irritable, cry for no reason, eat poorly, and sleep restlessly.
When an infection occurs, pustules appear on the skin and an unpleasant odor occurs. Common causes of baby diaper dermatitis are intestinal dysbiosis with food allergies. Children with constant relapses of diaper dermatitis should have their stool tested to check for dysbacteriosis, and then undergo a course of treatment.
Diaper dermatitis and modern diapers
Despite the widespread belief that modern diapers cause diaper dermatitis, by using them correctly, the risk of developing baby diaper dermatitis is significantly reduced.
This is confirmed by most of the currently practicing pediatricians, as well as numerous large-scale studies in this area.
High quality diapers absorb liquid well, and the surface in contact with the baby’s skin remains almost dry.
The use of diapers significantly reduces the period of contact of children's skin with an irritant in the form of urine and helps maintain the normal acid-base balance of the skin.
Prevention of diaper dermatitis is associated with the use of high-quality diapers and changing them at least once every 4-6 hours.
Treatment of diaper dermatitis in children
Treatment of baby diaper dermatitis is based on eliminating irritating factors, timely changing diapers and strict adherence to hygiene rules, then it will go away quickly.
The baby's skin in the perineal area must be dry and clean. During the treatment of diaper dermatitis, very  air baths are effective.
air baths are effective.
You should periodically leave your baby warm and naked throughout the day. This way the skin of the perineum will ventilate and dry, this is a kind of complex and treatment. After washing, apply a moisturizer to the child’s skin: Topicrem or D-Panthenol emulsion. An effective effect in the treatment of diaper dermatitis is caused by ointments based on lanolin.
Contact dermatitis in children
Contact dermatitis in children is inflammation of children's skin in the area of direct exposure to an irritant (area of constant friction of clothing, seams, irritating cream, skin contact with metal objects, etc.), photos clearly demonstrate the consequences of this type of dermatitis. Contact dermatitis does not require special treatment and goes away on its own if further exposure to the irritant on the child’s skin is excluded.
What to do if your child has already been diagnosed with atopic dermatitis? We asked about this Elena Ilchenko, allergist.
This may surprise many, but it is known to everyone - not even a disease. This word, which is translated from Greek as “a tendency towards something,” only denotes that a person belongs to a certain genotype, which is predisposed to certain diseases or allergic reactions.
Diathesis, which occurs in 80-90% of children, should not necessarily be considered as the onset of atopic dermatitis, the frequency of which among children does not exceed 10%. But it is imperative to be wary, especially in cases of aggravated allergic heredity.
Reasons for appearance
| Nutrition rules | |
|---|---|
|
Can Foods that should not be consumed by a nursing mother and child: cow's milk, citrus fruits, nuts, chocolate, river fish, caviar and pickles. High allergenic activity in eggs and honey. It is also better to exclude strawberries, wild strawberries, persimmons, grapes, plums, currants and pineapples. Products made from wheat and rye, as well as beets, carrots, and sometimes even potatoes, can cause rashes. But that's not all! It is unacceptable to consume rich broths, veal, duck meat, sausages, sausages and canned food, as well as sauces, smoked meats, carbonated and alcoholic drinks. |
|
The nature of this disease remained unclear for a long time, which is why the name contains the word “atopic” (translated from Greek “atopos” - “strange, wonderful”). But medicine does not stand still, and in 1882, the French dermatologist E. Besnier first named the causes of such an allergic reaction.
It turned out that the mucous membranes of the respiratory and digestive tracts of people susceptible to atopic dermatitis easily allow foreign proteins to enter the body. The immune apparatus reacts in response with the excessive formation of special types of antibodies belonging to the class of immunoglobulins E. Contact of the allergen with these antibodies leads to the release of histamine - a substance that causes vasodilation, tissue swelling, itching, etc. Thus, the contact of antibodies and allergen becomes participant in skin damage.
Children are the weak link
It develops under the combined action of risk factors: hereditary predisposition, food allergies, exogenous and endogenous irritants, which, under certain conditions, “trigger” the pathological process.
In children of the first year of life, the protective function of the intestine is reduced, so atopic dermatitis develops mainly in babies. At this age, an insufficient amount of digestive enzymes and protective antibodies are produced and the permeability of the intestinal wall is increased. The combination of these age-related characteristics of the gastrointestinal tract of children leads to the fact that under-digested food components, primarily proteins, are easily absorbed into the bloodstream. These large fragments of molecules have pronounced antigenic properties, i.e., they trigger a chain of allergic reactions.
In most children, the first signs of illness appear when changing their diet. For example, with the early transfer of a child to artificial feeding, disruption of the diet, with the introduction of allergenic foods into the diet. The most common culprits of allergies are cow's milk, eggs, chicken, fish, raspberries, strawberries, citrus fruits, chocolate, tomatoes, carrots, beets, and cereals.
In a significant proportion of children, even the true one may disappear over time. In some children, atopy continues to progress, accompanied by an expansion of the spectrum of sensitivity to allergens. In older children and adults, the leading cause of atopic dermatitis can be house dust, pet hair, pollen, bacteria, and mold.
What are the dangers of atopic dermatitis?
The process of development of atopic dermatitis is called the “atopic march”: if the first symptoms appear at an early age and manifest themselves inactively, then the child’s parents may simply not pay due attention to it. The disease will slowly progress, and by the age of 2-3 the child will develop a respiratory allergy, accompanied by an allergic runny nose.
Unfortunately, it is difficult to recognize allergy sufferers in such patients, so they are often diagnosed with colds. In such a case, the patient does not receive appropriate allergic treatment, which can lead to the development of allergies not only in the upper respiratory tract, but also in the bronchi. By the age of 6-7 years, the baby can already develop a real one. In children, atopic dermatitis is combined with bronchial asthma in 34% of cases, and with allergic rhinitis in 33%. The presence of relatives in the family with allergic dermatitis or another form of atopy predicts a severe course of this disease: even after 20-30 years of illness, half of the patients may still have manifestations of atopic dermatitis. In most patients, the manifestations of atopic dermatitis subside by the age of 30, and by the age of 50 they disappear completely.
| Tips for moms | |
|---|---|
|
The room must be ventilated. It should not be too hot - dry and hot air causes increased sweating, and the salt contained in sweat has a negative effect on the affected areas of the skin, causing burning and itching. Such simple measures will help make the life of a person suffering from atopic dermatitis easy and joyful. Similar measures are used to prevent the disease at an older age. |
|
Taking into account the fact that allergies, starting with atopic dermatitis, progress and become more severe with age, its timely diagnosis and treatment is very important.
Traditional treatment
A chronic disease that requires long-term and complex treatment. First of all, these are elimination measures (diet, limiting contact with dust, pollen, fungi, animals, chemical agents, etc.).
It is mandatory to follow a food diet and keep a food diary. If breastfeeding is used, the mother is advised to exclude food allergens from the diet. If artificial feeding is used, then it is necessary to select hypoallergenic formulas for the child (as a rule, mixtures based on protein hydrolysates are used), then introduce complementary foods correctly, choose foods with a low allergenic potential (green varieties of apples, white currants, white and yellow cherries, buckwheat, corn, pearl barley, cauliflower, white cabbage, Brussels sprouts, zucchini, squash, lean pork, rabbit meat, turkey, horse meat). Avoid foods that increase the level of histamine in the blood - smoked meats, marinades, nuts, honey, chocolate, yeast, fermented cheeses, mayonnaise, vinegar, strawberries, as well as products containing chemicals: preservatives, stabilizers, dyes, etc. Allergy diagnostics are required. - skin and laboratory tests to exclude “culprit” allergens.
In case of exacerbation of allergic dermatitis, modern antihistamines are used as prescribed by a doctor, which quickly relieve itching and other inflammatory reactions of the skin without causing addiction, drowsiness, or lethargy. Enterosorbents are often used. Basic external therapy includes the use of moisturizing creams, and in severe cases, creams containing steroids. One of the progressive treatment methods is allergen-specific immunotherapy.
.jpg) Folk remedies
Folk remedies
In no case and under any circumstances do not neglect a visit to the doctor if you find it on your child’s skin. In this case, traditional medicine is not able to give a clearly targeted diagnosis, since the allergic reaction in each individual genotype can manifest itself with different intensity and have different causes.
The use of “folk recipes”, herbal infusions and herbal compresses can lead to aggravation of allergic symptoms, as there is a so-called “cross allergy”. For example, if you are intolerant to wormwood, sunflower, or ragweed, you may have an allergic reaction to chamomile, calendula, string, coltsfoot, or oman. If herbal baths or compresses are indicated for you and your baby, a doctor will prescribe them - and you will be treated without risk to health.
How does atopic dermatitis manifest?
First age period: signs appear in the first year of a child’s life.
Foci of bright erythema and weeping appear on the cheeks, later the process spreads to the forehead, behind-the-ear areas, scalp, and outer surface of the legs.
The process ends with the formation of crusts, popularly called “milk scab.”
The second age period appears from the age of 2 years to puberty. The rashes are localized in the elbow and popliteal folds, on the back of the neck, and are characterized by severe itching.
The disease is of the nature of chronic inflammation.
The third age period (older children and adults) is characterized by a predominance of crusts, papules, and skin infiltration.
Rashes appear on the skin of the face, neck, upper body, and arms.
Illustrations: Maria Deeva
How does dermatitis manifest in children? The attending physician will answer this question. After the birth of a child, the vulnerable child’s body has a hard time adapting to new living conditions in a completely different environment. Pediatricians around the world, especially in economically developed countries, note a significant increase in dermatitis in children of all ages. Atopic dermatitis is caused by a combination of allergens and toxins. Treatment of dermatitis may not always be successful even with modern technologies used in pharmacology. Often this phenomenon is associated with special causes. The development and course of dermatitis in children is purely individual, which in turn is associated with factors that provoke the appearance and exacerbation of dermatitis.
Manifestation of dermatitis in children
The child’s adaptive reactions during this period are immune defense and skin. Especially insidious for a child during this period are allergies and reactions that are caused by the presence of a provoking microorganism, which leads to the child developing a number of skin diseases. Among the diseases of this spectrum, due attention should be paid to such as dermatitis in a child.
What is dermatitis? This term refers to a set of diseases in which there is the presence of inflammatory damage to the skin and an increase in the degree of sensitivity of the body to existing irritants. In this case, children in the age group from birth to 4 years are at significant risk; they develop infantile dermatitis.
Neglect of the disease and lack of timely treatment leads to complications and complication of the treatment procedure. A relapse of the disease is possible, triggered by a secondary virus entering the child’s body.
Features of the flow
Typically, practical medicine considers the occurrence of dermatitis in childhood as a congenital disease. This is what creates certain difficulties in the area of how to treat dermatitis in a child and what is the main factor in the development of such a disorder. It is extremely rare that inflammatory skin diseases are isolated. When visiting a specialist, a sign of dermatitis and concomitant pathology are simultaneously detected. The most common in children are also hereditary diseases of the allergic type. Identification of various types of food allergies, hay fever, allergic rhinitis, conjunctivitis, bronchial asthma only confirms the diagnosis of congenital dermatitis in children, the treatment of which is directly related to certain difficulties. The disease is chronic, with frequent relapses, and is combined with other disorders of the functioning of organs and systems.
Today, pediatricians consider three types of childhood dermatitis:

- From birth, perhaps from 3 to 4 months, when they begin to introduce complementary foods into the diet or use infant formula until the age of three - infant.
- The period from the beginning of 4 years to 7 years of childhood-type atopic inflammation of the skin.
- After the age of seven and until the age of 12-14, doctors diagnose adolescent skin disease.
Another feature of the pathology is that the peak of the disease occurs in the first year of life. Before the first six months of life, it occurs in 45% of babies, mainly on the child’s bottom and cheeks. Upon reaching the first year of life, about 60-67% of children are already susceptible to allergic manifestations. By the age of five, dermatitis on the buttocks, in the folds of the buttocks, limbs or on the face can be found in 18–20% of all children examined. There is a very clear trend towards a decrease in susceptibility to dermatitis towards older preschool age, which is associated with an increase in the immune functions of the child’s body. So, what is the possibility of pathology occurring?
What types of dermatitis in children are there?

It is necessary to determine in detail the types of dermatitis in children. Taking into account the fact that dermatitis in children is a combination of diseases of an allergic nature, the following types are distinguished, differing in different etiologies, localization of the affected area, course and clinical picture.
Atopic is a secondary disease of a viral nature, which manifests itself as the presence of hypersensitivity to allergic pathogens, as well as irritants that are nonspecific in nature. In the medical field, these diseases are also referred to as neurodermatitis and atopic eczema. The disease is observed in early childhood and completely subsides at the age of 5 years.
The causes are hereditary factors, underdevelopment of the digestive system, the mother’s diet during gestation and other factors. The symptoms of the disease vary, most often in the presence of the disease there is redness of the skin and rashes on the skin folds. Dermatitis appears on the face, body, limbs and other parts of the body.

Seborrheic variety is the presence of inflammatory processes in the scalp area. The causative agent is a fungus that infects the skin and thereby causes the manifestation of the disease. In pediatrics, seborrheic dermatitis in children under 1 year of age is called gneiss. Most often, gneiss is characteristic of newborns.
What does dermatitis look like in children? This question worries parents and teachers who work with children, observe and record their condition and development. This type of disease is characterized by the presence of crusty neoplasms of a yellowish color, including redness of the affected areas of the skin.
Most often, gneiss formations are characteristic of the parotid region; they appear on the head, neck, chest, and groin of the child.
Diaper dermatitis in children. The name diaper itself speaks for itself. With the advent of diapers and their widespread use in newborns, cases of this type of dermatitis in children have become more frequent. With the advent of diapers, the number of washes, including money for purchasing SMS, has decreased, but everything needs a reasonable approach, and modern parents, due to saving money, save money not only on powder, but also on their own children, trying to use one diaper to the maximum for a whole day, which, in turn, affects the child’s health.
Contact dermatitis in children. This variety is localized at the site of skin contact with an irritant from the external environment. Such an irritant can be a metal object, cosmetics, or seams on clothing.
This type of allergic reaction does not require treatment with medications; you need to isolate the irritant and use a specialized cream base to alleviate the symptoms of the disease.
In addition to the above classification, there is viral dermatitis, septic.
The formation of viral dermatitis is facilitated by the penetration of infection into the body. The disease may be secondary or may be independent. Sometimes the cause can be an enterovirus, that is, a combination of several viruses.
Fungal dermatitis in children is a disease of secondary origin, located on smooth skin and in the area where hair is located. Often it becomes a complication of existing diseases or is provoked by allergies, which introduces certain difficulties in its diagnosis.
Septic dermatitis or erythema are processes of a pathological nature occurring in the body, accompanied by the presence of red spots on the skin. It develops when a pathogen enters the body - an infection caused by a microorganism. In this case, the pathogen must be in the patient’s blood.
Interstitial granulomatous dermatitis is a rare complication. A response to the causative agent of the disease is produced by tissue structures of a granulomatous type, while immune complexes and collagen derivatives are formed in the blood fluid.
According to age criteria there are:
- dermatitis in preschool children;
- dermatitis in children under one year of age;
- dermatitis in adolescents.
Each of the above types of disease has its own characteristics.
It is necessary to highlight the characteristics of each type of dermatitis in children. It is not recommended to prescribe treatment for dermatitis on your own. Your starting point in treating the disease is an appointment, examination and consultation with a specialist.

Septic dermatitis or erythema is accompanied by the presence of red spots on the skin
How to determine dermatitis on the face? It's very simple - look in the mirror. This disease is dangerous because it develops gradually and proceeds unnoticed by the patient until it enters the indicated phase. Symptoms observed:
- instant formation on the face of minor redness and irritated areas of the skin;
- the presence of a rash in the mouth, near the nose, forehead and cheeks;
- peeling of the skin combined with itching;
- increased sensitivity of the skin layer, pain;
- migraines and pain in joint tissue, extremely rarely, there is a sharp increase in temperature.
Complex of reasons
In order to effectively eliminate any organic disorder, including cure dermatitis, it is necessary to accurately determine why the child suffers from such a pathology:

- The main reasons, according to modern medicine, are that there is a genetic predisposition to allergic symptoms.
- The influence of unfavorable environmental factors.
- The influence of heredity is a very serious reason. When the father and mother show hypersensitivity to various allergens, the child has an 80-85% risk of getting dermatitis. Violations in one of them can lead to an inflammatory process on the skin of infants in 42 - 45% of cases.
- To determine exactly how to treat a child, it is necessary to find out whether the source is a food intolerance factor. It is from the first days of birth until 4–6 months that the baby is affected by the mother’s incorrect diet during gestation and lactation.
- Very serious reasons for the early onset and severe course of the disease are possible overfeeding of the baby, breastfeeding is minimized or completely excluded by the mother, early introduction of complementary foods.
- In order to plan how to cure dermatitis in childhood, it is necessary to take into account the possibility of the influence of health problems in women. This is a natural or artificial termination of pregnancy, exacerbation of the chronic course of pathologies, maternal and intrauterine infections, acute or chronic hypoxia of the newborn.
- It is also necessary to identify causes such as metabolic imbalance, digestive dysfunction, infectious and viral diseases that the baby simultaneously suffers from.
What are the symptoms of dermatitis?

The pathology is quite complex, its exacerbation causes a lot of unpleasant sensations. Therapy should be comprehensive, its methodology is based on the study of symptoms, a consultation of doctors, which includes a dermatologist, allergist, nutritionist, gastroenterologist, psychoneurologist, ENT. Symptoms and treatment are completely interrelated; atopic dermatitis is characterized by:
- The appearance of severe itching, burning, rashes of various types.
- Eczema affects numerous parts of the body - primarily on the face, in the groin; clearly defined dermatitis on the arms, head, buttocks, and thighs appears a little later.
- Symptoms of the disease in preschool and early school age increase, rashes appear in the groin, armpits, and on the skin of the folds of the upper and lower extremities. Skin dermatitis appears near the mouth, in the eyelids and neck, accompanied by keratinization of the skin and very painful microcracks.
- A prolonged course is associated with wetting of the rash sites, the formation of crusts, peeling, pustular formations, swelling and the release of exudate, which may smell bad. The appearance of serous discharge in 4 places is especially common - on the bends of the elbows, knees, armpits, and groin.
- Insomnia, nervousness, general malaise.
How activated charcoal helps cope with illness
Regardless of its origin, skin dermatitis and its varieties are treatable. A universal remedy for the treatment of diseases of this type is talkative for children. Activated carbon provides significant assistance in the treatment of the disease. Activated carbon has proven itself in the treatment of a whole range of diseases; allergies, which intensify with the onset of warm days, are no exception.
Summer is a time when the air is saturated with a large number of allergens: dust particles, nectar from flowers, wool and poplar fluff. It’s great if you don’t have an allergic reaction to the above allergens, and if you do, your salvation is to take activated carbon.

How does activated carbon work? Activated carbon is prescribed primarily to cleanse the body of existing pathogens. When you have another allergy attack, it is so important to have these tablets on hand. Activated carbon removes waste and toxins from the body. As a result of thorough cleansing measures, the body activates its defense mechanisms with renewed vigor, helping to improve immunity, releasing immune units and using them in the fight against infection.
Principles of therapy for atopic dermatitis
Before developing an individual therapy system, the attending physician conducts a complete diagnosis of the patient. The main goal of the treatment plan is to change the course of the disease, reduce the severity of exacerbation, and monitor possible relapses for a long period.
Basic concept of therapy:
- Corticosteroid medications in combination with skin softening medications. Relevant in case of severe dermatitis to quickly eliminate it.
- Antibiotics are prescribed externally to eliminate the development of skin infections. Miramistin, chlorhexidine, fucaseptol, hydrogen peroxide, brilliant green 1-2%, fucorcin has an excellent effect. The use of ointments is no less important. Applying ointments of Bactroban, Fucidin, Levosin, Levomikol up to 2 times a day allows you to avoid suppuration.
- Antihistamines that reduce the severity of an allergic reaction. It is acceptable to prescribe Cetrin, Eodac, Zyrtec, Erius. The minimum course is at least 4 months.
- Painkillers, sedatives and sedatives - tavegil, suprastin, cromoglycic acid and ketotifen, traditional calcium chloride solution.
- Increasing signs of pyoderma require the use of systemic antibacterial agents. Before treatment with antibiotics, tests should be carried out to determine the susceptibility of microorganisms.
- General strengthening and vitamin complexes, decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs, folk remedies should be used strictly individually.

It is important for therapy to eliminate factors that lead to exacerbations. The exclusion of contact, food, inhalation, and chemical irritants and a strictly selected diet will reduce the risk of developing pathology. Physiotherapeutic procedures, mud treatment, balneotherapy are indicated. Parents should not take their child’s diagnosis as a death sentence; however, even the most thorough treatment can completely cure no more than 25–32% of young patients; the rest are accompanied by dermatitis throughout their lives.
Atopic dermatitis is a non-contagious chronic inflammation of the skin, often caused by allergic reactions and of genetic origin. Atopic dermatitis in children is usually called diathesis, but this name cannot be considered correct. It is known that a child can develop the disease with an 80 percent chance, provided that both parents had dermatitis. If only one parent suffered the disease, then the chances that atopic dermatitis will be passed on to the child are 50 percent. Let's look at this pathology in detail, give clinical recommendations, find out its types, and tell you what treatment is suitable for atopic dermatitis in infants.
Types of atopic dermatitis in children
There are several forms of this disease, characteristic of different ages:

- Infantile - in newborns it manifests itself before the age of 2, the provoking factor is food. Features: exudative form of the disease. Expressed by redness, swelling, blisters and crusts form. Location: ears, cheeks, genitals.
- Children - age of manifestation: 2 - 10 years. Features: the skin has a grayish tint, dryness, cracks, and scales form. The location of the disease is in the folds of the skin (in the neck, behind the ears, in the bend of the limbs). Among the provoking factors are food and medications.
- Lichenoid form - age of manifestation: 5 - 15 years. Features: small plaques under the knees, on the elbows and hands.
- Teenage. Age of manifestation: after 10 years. Formation of rashes on the skin of various parts of the body.

Cause of atopic dermatitis in children
Often the cause of atopic dermatitis in children is an allergic reaction. For the most part, it is the food product that provokes the reaction. It can also be allergens that enter the body through the respiratory tract, that is, the causes of allergies can be animal hair or skin, dust, air freshener, fish food, and the like.

Areas of disease formation in children
If you come into frequent contact with an allergen due to particularly strong skin sensitivity, the irritants can be clothing or particles that fall on it, detergent powder, soap, fabrics, or even your own sweat secretions. Such allergens only intensify inflammatory processes.
With minor inflammation, small blisters appear on the skin. After some time, they open and a crust forms. All this leads to severe itching, which is very difficult to tolerate. It haunts me especially at night. The child begins to scratch the skin, which can lead to a new infection. This can lead to bacterial inflammation. We cannot exclude the factor of the climate in which the child is forced to live.
According to the popular pediatrician Komarovsky, children often develop atopic dermatitis during artificial feeding.
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis in children
At the initial stage, children experience diaper rash. In children, redness appears in the buttock area, behind the ears, and in the folds of the skin. Sometimes they cause wet wounds. Peeling and roughness appear on the skin. A crust appears on the scalp. Gradually, the disease spreads from the skin of the face to the body.
Severe symptoms of the disease:
- Itching (moderate to severe);
- Redness (observed on the bends of the limbs - elbows, knees; in the folds of the skin, in the cervical region);
- Rash.

Criteria for diagnosing atopic dermatitis
Consequences and complications of atopic dermatitis in children
The most dangerous thing is when a child begins to scratch the itchy area. This can lead to the formation of small wounds, which, in turn, become infected with fungus and other microorganisms, which can lead to a secondary infection (pyoderma). It is usually treated with antibiotics. All this affects both the skin and the child’s health. It is increasingly difficult for him to fall asleep, as a result he does not get enough sleep, and any body movements, bathing or clothing lead to uncomfortable sensations.
Often, fungi, viruses and bacteria can “attack” the baby immediately, as a result he will develop a purulent inflammatory process and a “cold”. With timely treatment and proper preventive measures, such difficulties can be avoided.
Only a doctor can identify atopic dermatitis in a child, and he will prepare the necessary treatment. First of all, it is necessary to exclude what can provoke this disease and subsequent exacerbations. Although this disease cannot be fully cured, there are a number of remedies that reduce itching, redness and other symptoms. Treatment of atopic dermatitis in a child occurs by the following means:
- Diet;
- Moisturizing preparations (Emollients);
- Creams and ointments;
- Use of non-steroidal drugs;
- Preparations for eliminating itching;
- Antibiotics.

How can you cure atopic dermatitis in a child?
Diet for children
The famous doctor Komarovsky gives the following recommendations on diet for children:
- The diet should not contain products that contain certain harmful substances. All this can only worsen the baby’s health;
- The room temperature should be balanced, the child should not sweat;
- Eliminate foods that cause allergies from the diet (chocolate, honey, citrus fruits, nuts); there should also be no pets in the house, whose fur can cause an allergic reaction.
- It is necessary to ensure that the child does not have constipation. If you notice the first such symptoms, you can give your baby a mild laxative, and then be sure to put him on a diet.
- It is worth remembering that a nursing mother must follow a diet. It is better to exclude milk, butter, broth, and lard from the list of products.
According to Komarovsky, you should not overfeed your child. You also need to make sure that there is no excess protein in baby food.
Emollients for children

Emollient creams for children names
Additional treatment involves skin moisturizing. And here we will talk about emollients for atopic dermatitis in children. Emollients have softening properties for the skin and increase the amount of moisture. Moreover, emollients themselves do not moisturize, but only prevent the moisture that remains from decreasing. There are several types of emollients:
- Bath emollients;
- Emollients for application to the skin;
- Emollients for washing.
It is possible to classify emollients in each of the above groups. But only a doctor can tell you which type is exactly right for your child. It all depends on the inflammatory process, complexity, infections (if any), and so on.
Emollients should be applied a couple of times a day to children's skin, and once after washing.
It is necessary to bathe the child in warm water, but it is not advisable to continue the bathing process for more than 10 minutes. Also, doctors do not recommend drying a baby or newborn immediately after washing. Firstly, the skin must receive sufficient moisture (and the emollient will retain this moisture), and secondly, minor injuries may form on it.
The list of emollients for children suffering from atopic dermatitis is very large:
- Emolium;
- Locobase Ripea;
- A-Derma Exomega;
- Losterol;
- Mustela Stelatopia;
- Topicrem.
It is worth remembering that baby cream cannot completely replace emollient. Based on research, it wears off quickly, can cause allergies in a child and does not have a wide range of therapeutic effects.
Creams for children
In today's pharmaceutical market there is a large arsenal of ointments and creams for atopic dermatitis in children. Here is a list of some non-hormonal drugs:
- Protopic – it contains tacrolimus and is used for the treatment of Atopic dermatitis in children.
- Exoderil is an antifungal agent, sometimes it shows results, provided that the origin of the inflammatory skin process or dermatitis has not been precisely determined.
- Panthenol - this remedy is usually prescribed for the treatment of dryness in various types of dermatitis.
- Eplan - this remedy is used for various skin diseases (psoriasis, eczema, acne, and so on).
- Gistan is a dietary supplement that contains herbal extracts.
- Elidel is a drug that has an anti-inflammatory effect in atopic dermatitis. However, it refers to means with unproven effectiveness.
- Naftaderm - has a resolving effect.
Nonsteroidal drugs for children
This technique has been used recently. TIC medications (Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors) provide long-term control of the disease, helping to cope with itching and redness. They especially help cope with the disease during an exacerbation and ensure remission.
Anti-itch medications
Doctors also prescribe antihistamines. Many of them have the side effect of drowsiness. Therefore, it is better to use it at night, before going to bed.
Antibiotics for children
For infectious skin diseases, antibiotics are prescribed to kill the pathogen and other pathogens. Just don’t overuse antibiotics, because after some time bacteria can adapt to them.
Folk remedies
There are many traditional methods that help cope with inflammation. At home you can prepare:
- Therapeutic baths;
- Ointments;
- Herbs;
- Compresses.
Let's share several recipes for medicinal baths:
- When bathing your baby, add 5 tablespoons of sea salt;
- You can add 1 liter of milk and 100 ml of unrefined olive oil to the bath;
- Birch buds are very effective. Pour 120 grams of the plant into 1 liter of boiling water. After tincture for 3 hours, the contents should be poured into the bath;
- While bathing, add a decoction of burdock root, celandine, nettle, and violet. They are often used to treat this disease.
Prevention and prognosis of atopic dermatitis in children
With timely treatment, the prognosis for atopic dermatitis is often positive, but complete recovery is excluded. To improve the well-being and condition of a child, doctors recommend isolating him from allergenic foods, which include chocolate, citrus fruits, some berries (for example, strawberries, nuts, cocoa, etc. However, an allergic reaction may be individual in nature and will spread to that food, to which others are usually not allergic. Therefore, this issue needs to be discussed with the treating pediatrician separately. First, after detecting symptoms, specialists conduct an appropriate study: they take samples and do a blood test.
Let's look at preventive measures point by point:
- Eliminate factors that cause dry skin. It is necessary to maintain the correct climate balance (humid and cool) in the baby’s room, walk a lot, and do not overly wrap the baby. Make sure your baby drinks enough fluids, especially during the hot summer months.
- The child should not overeat. Due to excess nutrition, the skin may become dry, redness may occur, and cracks may form. This way, the toxins will act from the inside.
- Don't go overboard with cleanliness. Many mothers try to wash their child as cleanly as possible, but this increases the risk of atopic dermatitis. The fact is that the skin lipid layer is destroyed, resulting in vulnerability. It is better to bathe your baby once a day, using special cosmetics for children. After a year, bathing can be done once every 2 days.
- Make sure that your child’s clothes are made only from natural materials; they should not cause discomfort to the child and can be washed easily.
Dermatitis in children is a local inflammation of the skin due to infection, toxic effects or allergies. Dermatitis in an infant in the form of a rash, crusts, and redness appears on various parts of the body (arms, legs, stomach, back, bottom), causing unpleasant itching, pain and discomfort. The main methods of treating dermatitis are limiting contact with the irritant, using ointments and diet.
External manifestations of dermatitis are easy to recognize if you know what the disease looks like:
- Dry skin on the arms and legs, elbows, on the face around the mouth;
- Red spots in the groin, buttocks, back and abdomen;
- Small blisters with fluid on the legs, arms, face around the mouth, neck, back and buttocks;
- Pustules in folds of skin (in the groin) and on open areas of the body (on the face, arms, legs).
Severe dermatitis is complicated by inflammation and swelling, discomfort, and soreness of the skin. After opening the blisters, small wounds form through which the infection penetrates.
Causes
The causes of dermatitis are associated with exposure to an irritating substance on the child's skin. The cause may be a substance that gets on the skin from the environment, then contact dermatitis is called. If a substance first enters the gastrointestinal tract, then into the blood and manifests itself as a reaction on the skin, the disease is called toxicoderma.
Contact
The child may have:
- Wet diapers - a rash on the body appears in places of constant contact with the skin, on the back, buttocks, stomach, groin;
- Staying in a full diaper causes a rash and redness in the groin, butt and stomach;
- Synthetic clothing and bedding can cause a reaction on the neck, head, and around the mouth;
- Unsuitable children's cosmetics cause rashes in those parts of the body where the cream was used: in the groin, on the buttocks, on the cheeks;
- Household chemicals are also an irritant; when they come into contact with a baby’s diapers and clothes, they cause rashes on the body.
The rashes on the body become extensive and cause great discomfort. In places where rashes are most common (on the hands and elbows, cheeks and around the mouth), the skin loses elasticity, pigmentation, and becomes thin and vulnerable. If the allergen periodically affects the child, the atypical reaction intensifies.
Treatment for contact dermatitis involves limiting any contact with the irritant.
With proper care, the allergic mood of the body decreases in 80% of children. Signs of dermatitis weaken first on exposed parts of the body (on the face, around the neck, on the back and abdomen, on the legs), and then in closed areas (in the groin, on the arms, and buttocks).
Toxicoderma
Causes of toxicoderma:
- Food allergens are the most common cause of facial dermatitis in infants;
- Inhalation of exhaust gases (when traveling along roads);
- Medicines (often vitamins and cause allergic reactions);
- Infectious diseases (form so-called infectious dermatitis in young children).
The disease is also called. The age of the child most susceptible to rashes is up to 3 years. At this age, signs of the disease (rash and redness on the face, around the mouth, in the groin) appear much more often.
Kinds
Dermatitis is divided into the following types:
- (aka allergic);
- (fungal);
- (occurs due to contact with urine and feces).
All types of the disease have characteristic symptoms and it is difficult to confuse them.
Atopic

Atopic dermatitis is an allergic reaction on the skin of a child. Symptoms of atypical dermatitis can be seen on the face, cheeks, back, arms and legs of an infant. In children, a characteristic rash appears on the skin, most often on the face and around the mouth.
Blood tests show an increase in IgE, indicating a widespread allergic reaction.
Atopic dermatitis constantly recurs - it worsens in the winter, and in the summer there is a period of remission. Treatment of allergic dermatitis is based on mandatory diet and the use of antihistamines.
Seborrheic

Seborrheic dermatitis is a fungal infection of the skin of a child. The causes of seborrheic dermatitis are due to the activity of opportunistic Malassezia fungi. Yeast-like fungi live on the skin, feeding on fatty acids from sebum.
If the sebaceous glands do not function correctly, intensely secreting secretions, the fungi begin to multiply rapidly. This is how seborrheic dermatitis occurs - inflammation of the skin, peeling and severe itching. Seborrheic eczema is located on the scalp, most often on the temples and forehead.
Diaper

Diaper dermatitis is an inflammation of the groin, buttocks and lower back where wet diapers adhere closely to the skin. Even with careful care, urine and feces irritate the baby's skin, causing the characteristic symptoms of dermatitis.
Diaper dermatitis most often affects newborns and infants. The rash is located on the butt, groin, legs and abdomen. With age, the problem appears less and less often, and after giving up diapers in favor of a potty, it will disappear completely.
Treatment
To cure dermatitis or reduce its symptoms on any part of the body (elbows, back, scalp in the hair and around the mouth), you must adhere to the following rules:
- Avoiding contact between the child and the irritant (gentle diet, control of household chemicals, natural clothing);
- External treatment is carried out with antiseptic dressings (medicinal ointment, special cream), folk remedies (herbal baths and rubbing infusions) help.
- Internal treatment consists of taking antiseptics and medications to reduce the allergic reaction.
- Medicines to improve intestinal function (bifidobacteria), calcium containing vitamin complexes, and a healthy diet (natural products without additives) help.
Means for the treatment of dermatitis (pharmaceuticals and medications, external ointment and cream) must be combined with diet and prevention of contact with the irritant.
Diet and nutrition
A hypoallergenic diet is necessarily included in the complex therapy of dermatitis, especially atypical ones, since the cause of diathesis is food products. Foods that cause allergies should be excluded from the diet of a child under 3 years of age and a nursing mother.
A child on a diet should not be given:
- Milk and fermented milk products;
- Bird eggs;
- Vegetables, fruits and red berries;
- Citrus;
- Fatty meats and fish;
- Smoked meats and pickles;
- Chocolate;
- Nuts.
When introducing complementary foods, give the baby a teaspoon a day of each new product, observing the reaction. Following a diet for dermatitis relieves the allergenic load on the baby’s body and helps prevent relapses.
Antiseptic cream, medicinal ointments, wipe the rash with disinfecting solutions, herbal infusions.
What creams can be applied:
- For weeping atopic eczema, steroid and antihistamine ointments will help;
- Seborrhea should be treated with antifungal creams;
- For diaper rash, dry the skin with solutions of potassium permanganate and apply moisturizing creams.
Bathe your baby daily in a decoction of chamomile and string, you can wash it with a weak solution of potassium permanganate 2-3 times a day to dry irritated skin.
Prevention
It is impossible to cure dermatitis in children in one day. Sometimes treatment for dermatitis takes several years.
Ointment and cream can only relieve the symptoms of the disease. The best remedy for food rash is constant monitoring of the menu of mother and baby, the use of creams to combat allergic reactions and diaper rash, and the prevention of infection and acute skin inflammation. With the strengthening of the body and the formation of intestinal microflora, the rashes on the hands and head disappear.