20th century most likely inventor. Interesting inventions of the 20th century
Read also
The twentieth century transformed people's lives. Of course, the development of mankind has never stopped, and in every century there have been important scientific inventions, but truly revolutionary changes, and even on a serious scale, occurred not so long ago. What discoveries of the twentieth century were the most significant?
Aviation
Brothers Orville and Wilbur Wright went down in human history as the first pilots. Not least the great discoveries of the 20th century - these and new ones - Orville Wright managed to make controlled flight in 1903. The plane he and his brother developed stayed in the air for only 12 seconds, but it was a real breakthrough for aviation of those times. The date of the flight is considered the birthday of this type of transport. The Wright brothers were the first to design a system that would twist the wing panels with cables, allowing the car to be controlled. In 1901, a wind tunnel was also created. They also invented the propeller. Already by 1904 it saw the light new model aircraft, more advanced and capable not only of flight, but also of performing maneuvers. In 1905, a third option appeared, which could remain in the air for about thirty minutes. Two years later, the brothers signed a contract with the US Army, and later the French bought the plane. Many began to think about carrying passengers, and the Wrights made the necessary adjustments to their model, installing an additional seat and making the engine more powerful. Thus, the beginning of the 20th century opened up completely new opportunities for humanity.
X-ray
Like many great discoveries of the 20th century, this was partly done back in the 19th, but then people were not able to achieve success right away. For example, X-rays were first used in 1885. Then he discovered that photographic plates darken under the influence of a special spectrum, and when parts of the body are irradiated, an image of a skeleton can be obtained. Nevertheless, he had to work for 15 years to make research on organs and tissues possible. That is why the name “X-ray” is associated with the beginning of the 20th century: previously it was not known to the general public. By 1919, many hospitals were already using this technique. The advent of x-rays changed the development of medicine: new branches of diagnostics and analysis appeared in it. To date, the device has saved millions of lives. So in cases where outstanding scientists are mentioned, it is necessary to mention Wilhelm Roentgen.

TV
Scientific and technological inventions transformed life in the twentieth century. One of key events was the emergence of a new way of disseminating information - television. In 1907, it was patented by Russian physicist Boris Rosing. For this purpose he used a photocell to convert the signals. By 1912, he had finalized his invention, and already in 1931, a method of broadcasting in color was first proposed. The first television channel began operating in 1939. In 1944, the modern television standard was created. Perhaps other discoveries of scientists of the 20th century were more significant in scientific terms, but the impact of this innovation on people's lives cannot be denied. Television has changed the way we communicate and transformed people's perceptions of the world.

Mobile phone
Nowadays, imagining life without a smartphone seems almost impossible. they appeared quite recently. Scientific inventions allowed people to communicate by telephone, but wireless connection was invented only in 1973. Martin Cooper, the creator of the cell phone, was able to call the office from the streets of Manhattan. After ten years Cell phones became available to a wide range of buyers. The first Motorola cost almost four thousand dollars, but the idea impressed Americans so much that people signed up to buy it. Moreover, the device bore little resemblance to a modern smartphone: the handset was simply huge, weighed almost a kilogram, and on the tiny display you could only see the number being dialed. The charge was enough for half an hour of conversation. Nevertheless, mass production of various models soon began, and with each generation of phones, people were waiting for more and more new ones. interesting discoveries. Today, a completely small device is a real miniature computer with many functions that the creators of the Motorola cellular did not even think about in 1973.

Internet
Not all discoveries of the last century are used by people every day. But the invention of the Internet has transformed life even in small things; today it is used in almost every country in the world. This is a means for communication, searching for information, and exchanging data. It is a universal source of communication. Therefore, when listing the great discoveries of the 20th century, we must not forget about the Internet. It is believed that the first steps in this direction were taken by Dr. Licklider, a scientist who headed the American military information exchange project. This is how the Arpanet network was created, with the help of which in 1969 data was transferred from the University of Los Angeles to the Utah laboratory. A start was made, and in 1972 the Internet was introduced to the public. The concept appeared Email. The invention of the Internet became known throughout the world, and within a few years thousands of people were using it. By the end of the twentieth century there were already twenty million of them.

Computer
The great discoveries of the 20th century are most often associated with technical progress. The computer is no exception. If we understand by this word an arithmetic machine, then such mechanisms have existed since the seventeenth century. But the device is modern understanding appeared only in the twentieth. In 1927 it was created and developed in America. By the middle of the century there appeared electronic device. The Mark I machine was created - the first real computer. After that, progress began at a record pace. The method of storing data changed from punched cards to floppy disks, and then to compact disks and storage drives. Programming languages also changed. The first computer was suitable only for performing algebraic operations, and modern devices They are a multifunctional device suitable for a variety of tasks.

Instant noodles
While listing the great discoveries of the 20th century, we must not forget about what seems at first glance a trifle. Noodles instant cooking- habitual household product, but its appearance changed the situation with nutrition in conditions without a kitchen or in the workplace and was also a serious achievement. This type of pasta was invented by the Japanese Ando Momofuki. Post-war Japan was in need of food, and affordable food without much difficulty in preparing it would clearly improve the situation. So Ando decided to start searching for special noodles. He tried many cooking methods until he came across a yeast-free batter that was perfect for drying. In 1958, he began producing his noodles, and today more than forty billion servings of this product are consumed annually. Another discovery of Ando Momofuki was the use of special plastic cups that would allow him to prepare a quick dish without utensils.
Penicillin
Many outstanding scientists of the 20th century are associated with exact sciences, but a major breakthrough also occurred in medicine. It was during this century that penicillin, a drug that saved the lives of millions, was introduced. It was invented by an Englishman in 1928 who discovered the effect of mold on bacteria. It is interesting that the great discoveries of the 20th century might not have been supplemented by the advent of antibiotics. All of Fleming's colleagues believed that the main thing was not fighting germs, but strengthening the immune system. Antibiotics seemed pointless and remained unclaimed for a couple of years after their creation. Only by 1943 did the medicine begin to be widely used in medical institutions. Fleming did not give up studying microbes and not only improved penicillin, but also created several paintings with the help of his discovery, drawing bacteria on a special substance.

Ball pen
When studying scientific and technical inventions, you can forget about small household improvements that are of serious importance. For example, the familiar ball pen appeared only in 1943. It was invented by someone who observed the printing process of newspapers and wondered why not fill the pen reservoir with the same quick-drying ink? They should be thick. To prevent them from clogging the hole in the handle, a ball should be placed there. Having thought about all this, Biro created prototype. Having emigrated to Argentina, he found a sponsor and began producing ink fountain pens. The first buyers were pilots, who could use them at altitude: a regular pen would leak in the absence of pressure. In 1953, the Frenchman Marcel Bic transformed the shape of the ink pen and was able to create cheap options that became accessible to anyone and conquered the whole world.
Washing machine
Another invention that has significantly improved everyday life helps most people cope with dirty clothes. The washing machine appeared only in 1947, replacing the laundresses at the post. For the first time such an invention was offered on the American market by two companies - General Electric and Bendix Corporation. The cars were noisy and uncomfortable; only functionality mattered. Whirlpool developers decided to change the situation by creating new version washing machine in the mid-twentieth century. It was covered with plastic covers that reduced noise; the models could be made in different colors, and general design solution became much more elegant. Since then washing machine turned into a completely aesthetic object. the first such device appeared in 1975 and was called “Volga-10”, but the most successful was only “Vyatka-automatic-12”, which began to be produced in 1981. Modern cars can be built-in and with a drying function, have different ways downloads, displays, delayed start by timer and are even able to connect to the Internet.
Over the past few centuries, we have made countless discoveries that have helped to significantly improve the quality of our Everyday life and understand how the world around us works. Assessing the full importance of these discoveries is very difficult, if not almost impossible. But one thing is for sure - some of them literally changed our lives once and for all. From penicillin and screw pump before X-rays and electricity, here is a list of the 25 greatest discoveries and inventions of mankind.
25. Penicillin
If Scottish scientist Alexander Fleming had not discovered penicillin, the first antibiotic, in 1928, we would still be dying from diseases such as stomach ulcers, abscesses, streptococcal infections, scarlet fever, leptospirosis, Lyme disease and many others.
24. Mechanical watch
Photo: pixabay
There are conflicting theories about what the first mechanical watch actually looked like, but most often researchers adhere to the version that they were created in 723 AD by the Chinese monk and mathematician Ai Xing (I-Hsing). It was this seminal invention that allowed us to measure time.
23. Copernican heliocentrism
Photo: WP/wikimedia
In 1543, almost on his deathbed, Polish astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus unveiled his landmark theory. According to the works of Copernicus, it became known that the Sun is our planetary system, and all its planets revolve around our star, each in its own orbit. Until 1543, astronomers believed that the Earth was the center of the Universe.
22. Blood circulation
Photo: Bryan Brandenburg
One of the most important discoveries in medicine was the discovery of the circulatory system, which was announced in 1628 by the English physician William Harvey. He became the first person to describe the entire circulatory system and properties of the blood that the heart pumps throughout our body from the brain to the tips of the fingers.
21. Screw pump
Photo: David Hawgood / geographic.org.uk
One of the most famous ancient Greek scientists, Archimedes, is considered the author of one of the world's first water pumps. His device was a rotating corkscrew that pushed water up a pipe. This invention advanced irrigation systems to new level and is still used in many wastewater treatment plants.
20. Gravity
Photo: wikimedia
Everyone knows this story - Isaac Newton, the famous English mathematician and physicist, discovered gravity after an apple fell on his head in 1664. Thanks to this event, we learned for the first time why objects fall down and why planets revolve around the Sun.
19. Pasteurization
Photo: wikimedia
Pasteurization was discovered in the 1860s by French scientist Louis Pasteur. It is a process heat treatment, during which pathogenic microorganisms are destroyed in certain foods and drinks (wine, milk, beer). This discovery has had a significant impact on public health and development. Food Industry worldwide.
18. Steam engine
Photo: pixabay
Everyone knows that modern civilization was forged in factories built during the Industrial Revolution, and that it all happened using steam engines. The steam engine was created a long time ago, but over the last century it has been significantly improved by three British inventors: Thomas Savery, Thomas Newcomen and the most famous of them, James Watt.
17. Air conditioning
Photo: Ildar Sagdejev / wikimedia
Primitive climate control systems have existed since ancient times, but they changed significantly when the first modern one appeared in 1902. electric air conditioner. It was invented by a young engineer named Willis Carrier, a native of Buffalo, New York.
16. Electricity
Photo: pixabay
The fateful discovery of electricity is attributed to the English scientist Michael Faraday. Among his key discoveries, it is worth noting the principles of action electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism and electrolysis. Faraday's experiments also led to the creation of the first generator, which became the forerunner of the huge generators that today produce the electricity we are familiar with in everyday life.
15. DNA
Photo: pixabay
Many believe that it was the American biologist James Watson and the English physicist Francis Crick who discovered it in the 1950s, but in fact this macromolecule was first identified in the late 1860s by the Swiss chemist Friedrich Maischer Miescher). Then, several decades after Maischer's discovery, other scientists conducted a series of studies that finally helped us clarify how an organism passes on its genes to the next generation and how the work of its cells is coordinated.
14. Anesthesia
Photo: Wikimedia
Simple forms of anesthesia, such as opium, mandrake and alcohol, have been used by people for a long time, and the first mention of them dates back to 70 AD. But pain management moved to a new level in 1847, when American surgeon Henry Bigelow pioneered the introduction of ether and chloroform into his practice, making extremely painful invasive procedures much more tolerable.
13. Theory of relativity
Photo: Wikimedia
Comprising Albert Einstein's two related theories, special and general relativity, the theory of relativity, published in 1905, transformed the entire theoretical physics and astronomy of the 20th century and eclipsed the 200-year-old theory of mechanics proposed by Newton. Einstein's theory of relativity became the basis for much of scientific works modernity.
12. X-rays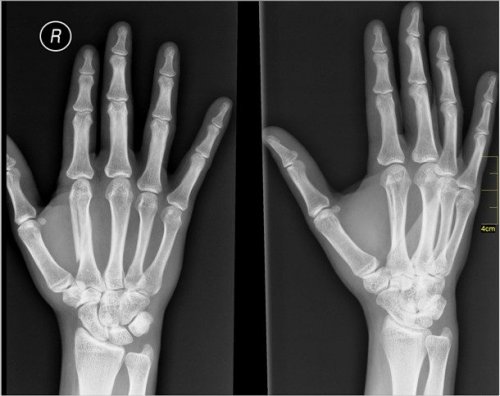
Photo: Nevit Dilmen / wikimedia
German physicist Wilhelm Conrad Rontgen accidentally discovered X-rays in 1895 when he observed fluorescence produced by a cathode ray tube. For this pivotal discovery, the scientist was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1901, the first of its kind in the physical sciences.
11. Telegraph
Photo: wikipedia
Since 1753, many researchers have experimented with establishing long-distance communication using electricity, but a significant breakthrough did not come until several decades later, when Joseph Henry and Edward Davy invented the electrical relay in 1835. Using this device they created the first telegraph 2 years later.
10. Periodic table of chemical elements
Photo: sandbh/wikimedia
In 1869, Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev noticed that if you arrange chemical elements according to them atomic mass, they are conditionally arranged into groups with similar properties. Based on this information, he created the first periodic table, one of the greatest discoveries in chemistry, which was later nicknamed the periodic table in his honor.
9. Infrared rays
Photo: AIRS/flickr
Infrared radiation was discovered by British astronomer William Herschel in 1800 when he was studying the heating effect of light different colors, using a prism to split light into a spectrum, and measuring the changes with thermometers. Today infrared radiation used in many areas of our lives, including meteorology, heating systems, astronomy, tracking heat-intensive objects and many other areas.
8. Nuclear magnetic resonance
Photo: Mj-bird / wikimedia
Today, nuclear magnetic resonance is continually used as an extremely accurate and effective diagnostic tool in the medical field. This phenomenon was first described and calculated American physicist Isidor Rabi in 1938 while observing molecular beams. In 1944, for this discovery, the American scientist was awarded Nobel Prize in physics.
7. Moldboard plow
Photo: wikimedia
Invented in the 18th century, the moldboard plow was the first plow that not only dug up the soil, but also stirred it, making it possible to cultivate even very stubborn and rocky soil for agricultural purposes. Without this weapon Agriculture, as we know it today, would not have existed in northern Europe or central America.
6. Camera obscura
Photo: wikimedia
The predecessor of modern cameras and video cameras was the camera obscura (translated a dark room), which was an optical device used by artists to create quick sketches while traveling outside their studios. A hole in one of the walls of the device served to create an inverted image of what was happening outside the chamber. The picture was displayed on the screen (on the wall of the dark box opposite the hole). These principles have been known for centuries, but in 1568 the Venetian Daniel Barbaro modified the camera obscura by adding converging lenses.
5. Paper
Photo: pixabay
The first examples of modern paper are often considered to be papyrus and amate, which were used by ancient Mediterranean peoples and pre-Columbian Americans. But it would not be entirely correct to consider them real paper. References to the first production of writing paper date back to China during the reign of the Eastern Han Empire (25-220 AD). The first paper is mentioned in chronicles dedicated to the activities of the judicial dignitary Cai Lun.
4. Teflon
Photo: pixabay
The material that keeps your pan from burning was actually invented completely by accident by American chemist Roy Plunkett when he was looking for a replacement refrigerant to make household life safer. During one of his experiments, the scientist discovered a strange, slippery resin, which later became better known as Teflon.
3. Theory of evolution and natural selection

Photo: wikimedia
Inspired by his observations during his second voyage of exploration in 1831-1836, Charles Darwin began writing his famous theory of evolution and natural selection, which, according to scientists around the world, became a key description of the mechanism of development of all life on Earth
2. Liquid crystals
Photo: William Hook / flickr
If the Austrian botanist and physiologist Friedrich Reinitzer had not discovered liquid crystals during testing physical and chemical properties various cholesterol derivatives in 1888, today you would not know what LCD televisions or flat panel LCD monitors are.
1. Polio vaccine
Photo: GDC Global / flickr
On March 26, 1953, American medical researcher Jonas Salk announced that he had successfully tested a vaccine against polio, a virus that causes a severe chronic disease. In 1952, an epidemic of the disease diagnosed 58,000 people in the United States and claimed 3,000 innocent lives. This spurred Salk on a quest for salvation, and now the civilized world is safe at least from this disaster.
In December 1903, the first controllable aircraft was created by the Wright brothers, called Flyer 1. It was not for history, but its main feature was the developed new theory flight “on three axes of rotation.” It was this theory that allowed aircraft manufacturing to develop further, focusing the attention of scientists not on the installation of more powerful parts, but on the efficiency of their use. Flyer 1 stayed in the air for almost a minute, flying 260 meters.Computer
The invention of the computer and the first full-fledged programming language is credited to the German engineer Konrad Zuse. The first fully functional Calculating machine was presented to the public in 1941 and was called Z3. It should be noted that the Z3 had all the properties that computers have today.After the war, the Z3, like its predecessors, was destroyed. However, its successor Z4 survived, from which sales of computers began.
Internet
Initially, the Internet was conceived by the US Department of Defense as a reliable channel for transmitting information in case war broke out. Several research centers were commissioned to develop the first network, which eventually were able to create the first Arpanet server. Over time, the server began to grow, and more and more people connected to it scientific workers for information exchange.First remote connection(at a distance of 640 km) Charlie Cline and Billy Duvalley managed to complete it. This happened in 1969 - this day is considered the birthday of the Internet. After this operation, the sphere began to develop at tremendous speed. In 1971, a program for sending electronic mail was developed, and in 1973 the network became international.
Space exploration
A rock in the 20th century in relations between the United States and Soviet Union there was development in space exploration. First artificial satellite was launched by the USSR on October 4, 1957.The first scientist who put forward the idea of creating a rocket traveling between planets was K. Tsiolkovsky. By 1903, he managed to design it. The main thing in his development was the speed of the aircraft he created, which is used to this day in rocket science.
The first vehicle to visit was the V-2 rocket, launched in the summer of 1944. It was this event that laid the foundation for further accelerated development, demonstrating great opportunities rockets.
Many new things were invented in the 20th century. New ones were built construction projects, developed military equipment, space was being explored. Let's try to note the most outstanding inventions and buildings that were made in the twentieth century and left a significant imprint on the history of mankind.
1. Titanic
This famous cruise ship of the British company White Star Line, the largest of its time, was launched on May 31, 1911. The construction of such a large steamship aroused truly enormous interest among people. Still would! Its length was as much as 268.83 m, its width reached 28.19 m, and its height reached 54 m. The liner could carry 2,556 passengers and another 892 crew members.
On April 2, 1912, the Titanic successfully passed sea trials on the water and a few days later set off on its first voyage. Only very wealthy people could get on board the ship, because... the ticket price reached 4,350 dollars (this is about 60 thousand according to modern course). But, unfortunately, the Titanic's maiden voyage turned out to be its last.

On April 10, 1912, she set sail from the port of Southampton with 1,316 passengers and 891 crew on board. The ultimate goal the trip was supposed to be the Irish port of Cobh... But on April 14, 1912, the ship crashed after colliding with an iceberg, as a result of the disaster more than 1,500 people died, only 704 survived....
2. Vostok spaceship

A real breakthrough in space exploration was the human flight to space! It’s nice to know that Soviet scientists were the first to succeed in this matter. Spaceship Vostok, intended for flights in low-Earth orbit, was designed under the leadership of Sergei Pavlovich Korolev.
Only one cosmonaut could be on board the ship, and the flight duration was no more than five days. The launch of the first manned spacecraft took place on April 12, 1961, piloted by Yuri Alekseevich Gagarin. “Vostok” made one revolution around our planet, spending 108 minutes on it.
3. Sydney Opera House

Perhaps the most striking symbol of Australia, besides the kangaroo, is the famous Sydney Opera House. This architectural structure (with an area of 2.2 hectares), built in 1973, is recognized as one of the outstanding examples modern architecture(it is also called an architectural wonder of the world).
More than $100 million was spent on construction, and the construction itself lasted more than 15 years! In addition to the opera hall itself, there is also a concert hall, drama and chamber theater halls, several restaurants and a reception hall. The theater can accommodate 1,507 people at the same time. Here is the world's largest mechanical organ with ten thousand pipes.
4. First computer

IN modern world It's hard to imagine life without computers. But just recently, some 50-60 years ago, the creation of such a machine as a computer seemed a pipe dream. After World War II, in 1946, the world learned about the creation of the first electronic computer ENIAC, which took more than half a million dollars and three years to develop.
The chief designer was Charles Babbage, who went down in history as the inventor of the first prototype of a computer. The machine was enormous: it weighed about 28 tons and absorbed about 140 kW of energy. The computers that were invented before him were a kind of prototype of ENIAC. Although he himself, whose power is equal to thousands of adding machines, was first called an “electronic calculator.”
5. Nuclear weapons

Sooner or later humanity would learn to create weapons mass destruction, which actually include nuclear. The United States was the first to achieve success in this area. The project to create an atomic bomb, which was called the Manhattan Project (led by Leslie Groves), was carried out on July 16, 1945.

First atomic bomb weighed 2722 kg, power reached 18 kt in TNT equivalent. The creation of such weapons led to tragic consequences: explosions in Hiroshima and Nagasaki. For a relatively short time, the United States had a monopoly in this matter. Already in 1949, on August 29, near the city of Semipalatinsk, the first Soviet nuclear device, codenamed “RDS-1,” was tested at a test site.

Availability nuclear weapons the USSR made it possible to maintain parity between the two states. Currently, the world community is trying to protect itself from this type of weapon and is trying to prevent its further spread, as well as try to destroy what has already been created.
The first tests of aircraft took place in the 18th century, but they were not very effective due to the lack of engines and the possibility of precise control.
With the invention of the steam locomotive in the 19th century, new stage in the development of transport. At the beginning of the 20th century main task was the creation of a controlled aircraft. And the inventors, the Wright brothers, succeeded in this - in 1903 they made the first flight in history for a vehicle with an engine. But that was only the beginning of the story. In 1907, the prototype of a helicopter was created - the first aircraft with rotating blades. In turn, the controlled one was first tested in Germany in 1936. At the end of the Second World War, the next speed limit was overcome - an aircraft with a jet engine was tested.
The fifties became the time. The first unmanned spacecraft was invented and designed in the USSR. And in 1961, the first person was caught - spacecraft became manned.
Means of communication
Not only the movement of people in space has accelerated, but also the transfer of information. In particular, important stage was the invention of television. The topic of transmitting images over a distance was of interest to scientists back in the 19th century, but the practical implementation of this project dates back to the twenties of the 20th century. In the thirties, the first regular television broadcasting began - in 1934, the first television viewers saw programs in Great Britain and Germany.
Historians of science usually do not name the inventor of the television, since both television broadcasting and the television apparatus itself were developed by several specialists, among whom was a native of Russia, Vladimir Zvorykin.
The breakthrough of the second half of the 20th century was the invention of the computer and the Internet. In the eighties, the World Wide Web began to spread more and more among private users, and in modern developed countries the number of Internet users is approaching 100%.
Medicine
The 20th century was a turning point for medical science. During World War II, penicillin was introduced into use, the first antibiotic that saved millions of lives. Were created revolutionary methods diagnostics - thanks to ultrasound and MRI machines, it has become possible to identify dangerous diseases in early stages. Although full-fledged artificial organs have not yet been created, many patients with heart failure are helped by the invention of the 20th century - the pacemaker. Thanks to these discoveries average duration life has increased significantly - a person born in developed countries has every chance of living more than 80 years.